丹参酮ⅡA的药理作用及疾病治疗的最新进展
2015-02-23闫俊,冯娟,杨雪,黄磊
闫 俊,冯 娟,杨 雪,黄 磊
丹参酮ⅡA的药理作用及疾病治疗的最新进展
闫 俊,冯 娟*,杨 雪,黄 磊
丹参酮ⅡA是中药丹参的主要成分,具有抗炎、抗氧化、调节细胞凋亡等药理作用,目前广泛用于临床心脑血管疾病的治疗。近年研究发现,丹参酮ⅡA还有具有抗肿瘤、免疫调节、抗多种脏器纤维化等作用。本文在介绍丹参酮ⅡA治疗心血管疾病和神经保护作用的基础上,对近年来国内外丹参酮ⅡA其他方面的药理学作用及疾病治疗方面的进展进行总结。
丹参酮ⅡA;心血管保护;神经保护;抗肿瘤;免疫调节
0 引言
丹参酮ⅡA是我国传统中药丹参的主要成分之一。丹参酮ⅡA不溶或微溶于水,易溶于二甲基亚砜、乙醇等有机溶剂。由于含有醌型结构,易被氧化还原,具有多种生理活性。丹参酮ⅡA主要用于心脑血管疾病。由于其水溶性低,丹参酮ⅡA的水溶性衍生物丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠也已被用于治疗心绞痛和心肌梗死。近年来,国内外学者对丹参酮 ⅡA的药理作用和临床应用进行了更为深入的研究,发现了一些新的药理作用,也使得其在防治疾病方面的广泛应用成为可能。本文对丹参酮ⅡA的药理作用和应用研究近况进行总结。
1 丹参酮ⅡA在治疗心血管方面的研究应用
1.1 抗动脉粥样硬化 动脉粥样硬化的发病机制复杂多样,与炎症反应、氧化应激、脂类代谢的异常以及血管内皮损伤等多种因素密切相关。动脉粥样硬化最基本的病理变化是动脉粥样硬化性斑块的形成。近年来,国内外大量临床研究及基础实验研究证实,丹参酮ⅡA通过抗炎、抗氧化、调节脂类代谢、保护血管内皮等多种途径抗动脉粥样硬化[1]。见图1。
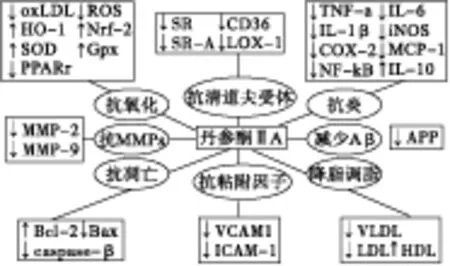
图1 丹参酮ⅡA抗动脉粥样硬化药理机制的简图
炎症反应在动脉粥样硬化的进展中起重要作用,粘附因子、趋化因子、细胞因子等促炎性的物质促使循环中单核细胞聚集,在血管内皮下增多的单核细胞分化为巨噬细胞,在清道夫受体介导下巨噬细胞吞噬氧化的脂类物质成为泡沫细胞。泡沫细胞聚集形成动脉粥样硬化病灶的中心部分,释放促炎性的细胞因子,进一步使T细胞、树突细胞、肥大细胞聚集在病灶处,加速动脉粥样硬化斑块形成。基质金属蛋白酶MMPs(MMP-9、MMP-2等)可以使动脉粥样硬化斑块的破裂的风险增加[2]。Xu等[3]发现,在ApoE敲除的高胆固醇饮食的小鼠模型里,丹参酮ⅡA 可以减少主动脉窦和前主动脉中动脉粥样硬化病变的面积,减少病变部位巨噬细胞的浸润以及IL-6(白介素-6)、TNF-α(肿瘤坏死因子-α)、MCP-1(单核细胞趋化蛋白-1)的分泌,增加平滑肌细胞和胶原蛋白的含量,同时下调主动脉中NF-κB(核转录因子)和MMP-9的表达,增加了斑块的稳定性,通过抗炎机制抗动脉粥样硬化。
氧化应激的加剧促进脂类物质被氧化,使体内氧化脂类增加,人体内最主要的氧化脂类是氧化的低密度脂蛋白(oxLDL)。丹参酮ⅡA可以一方面显著抑制LDL的氧化,减少血浆中oxLDL,另一方面抑制凝集素样氧化的低密度脂蛋白受体(LOX-1)、清道夫受体(SR-A、CD36)的表达,通过这两方面减少巨噬细胞吞噬oxLDL,也就减少了泡沫细胞的形成,进一步减少动脉粥样块的形成[4]。丹参酮ⅡA还能提高Nrf2等多种抗氧化酶的转录因子的活性,增加超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GPx)等抗氧化酶的表达,减轻由抗氧化酶引起的氧化应激,从而通过抗氧化机制来治疗动脉粥样硬化[5]。
研究表明,丹参酮ⅡA抑制脂质在动脉中的沉积,减少血清中总胆固醇、三酰甘油、LDL、极低密度脂蛋白(VLDL),增加血清中的高密度脂蛋白(HDL),发挥调脂、降脂作用,从而抑制动脉粥样硬化的形成[6]。
血管内皮的损伤曾被认为是动脉粥样硬化形成的第一步,内皮细胞的凋亡增加以及功能失调是动脉粥样硬化的发病的重要危险因素。丹参酮ⅡA能够抵抗氧化应激引起的人血管内皮细胞的损伤,通过增加抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2、减少促凋亡蛋白Bax 和caspase-3、下调 Bax/Bcl-2的比例和减少血管内皮细胞的凋亡,从而缓解动脉粥样硬化[7]。 血中的淀粉样β蛋白(Aβ)可以通过促进炎症反应、影响细胞内的脂质代谢等途径引起动脉粥样硬化。丹参酮ⅡA可以干扰血小板淀粉前蛋白(APP)的代谢,减少淀粉样β蛋白,从而达到治疗动脉粥样硬化的效果[8]。
1.2 心脏保护 大量的随机对照的临床试验已经证明,与单用常规西药相比,加用丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠可以明显减轻急性心肌梗死以及心绞痛患者的临床症状,改善患者的心律失常,减少死亡病例数且不良反应少[9-10]。丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠已经被列为一种改善心绞痛和心肌梗死的药物在临床上应用。
在2015年,研究发现,丹参酮ⅡA作为植物雌激素有望通过激素代替疗法治疗心血管疾病。丹参酮ⅡA与17β-雌二醇的化学结构相似,可以与雌激素受体结合,通过细胞外信号调节激酶通路,抑制体内的炎性反应和氧化应激,改善绝经后女性心血管疾病的病情[6]。
近年来发现,骨髓间充质干细胞转移疗法可以有效缩小心肌梗死的面积,并且有助于心功能的改善。但是由于只有少部分的细胞可以转移进入病变部位的心肌,并且转移的细胞不易存活,因此,影响了此疗法的治疗效果[11-12]。在大鼠心肌梗死的动物模型中发现,丹参酮ⅡA联合骨髓间充质干细胞转移疗法治疗心肌梗死,可以显著减少心肌梗死的面积,提高转移的骨髓间充质干细胞的存活率,并通过上调基质细胞衍生因子-1 :趋化因子受体-4轴促使骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌缺血部位迁移,从而治疗心肌缺血,达到心脏保护的作用[13]。
肺动脉高血压是一种由慢性阻塞性肺疾病、阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停等多病因导致的,慢性进展性疾病,最终将会导致右心室肥厚和右心衰竭。肺动脉平滑肌细胞的电压门控钾离子通道在肺动脉高血压发病中起到了重要作用。急性缺氧可以抑制电压门控钾离子通道的活性,甚至可以导致通道的关闭。慢性缺氧可以下调通道的数量。两者都使肺动脉平滑肌细胞凋亡减少、增殖增加,从而加重肺动脉高血压病情[14]。最新研究表明,丹参酮ⅡA可以对肺动脉平滑肌细胞内电压门控钾离子通道的数量及功能有明显的恢复作用,进而减轻肺动脉壁的重塑,从而缓解肺动脉高血压带来的心脏损害[15]。
2 丹参酮ⅡA在神经系统保护方面的应用
2.1 治疗中枢神经系统缺血缺氧性损伤 丹参酮ⅡA具有调节细胞凋亡、抗炎、抗氧化的性质,不仅在循环系统疾病中广泛应用,神经系统疾病中也有着显著的治疗作用。临床试验已经证实,丹参酮ⅡA能够治疗短暂性脑缺血发作、脑血栓形成、缺血性脑卒中、脑梗死且治疗效果显著,并在临床上已经应用。
在抗凋亡方面,丹参酮ⅡA可以通过激活细胞凋亡的相关通路,保护神经元抵抗淀粉样β蛋白引起的细胞毒性[16]。丹参酮ⅡA还可以增加缺血的脊髓中Bcl-2 的表达,通过抗凋亡机制来降低缺血再灌注导致的损伤[17]。在抗炎方面,丹参酮ⅡA可以通过减弱白细胞的激活,保护血脑屏障抵抗白细胞有关的缺氧复氧损伤[18]。在抗氧化和调节代谢方面,丹参酮ⅡA可以提高脑缺氧病灶中谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶的活性,减少丙二醛的含量,有效缓解氧化应激[19]。丹参酮ⅡA还可以增强神经元的三磷酸腺苷酶和蛋白质二硫键异构酶活性,改善能量代谢的平衡,同时保持细胞内的稳态,从而保护和修复神经元[20]。
谷氨酸是人脑内最重要的神经递质之一,参与神经元的兴奋作用,但是过高浓度的谷氨酸可以引起许多病理改变,如钙超载,线粒体功能失调,氧化应激,引起并加重脑的缺血缺氧性损伤。丹参酮ⅡA可以有效调节缺血的大脑皮层和海马中谷氨酸浓度,使谷氨酸和抑制性神经递质γ-氨基丁酸保持平衡,从而减轻神经兴奋毒性引起的神经元的损伤[21]。
在脑缺血情况下,星形胶质细胞经过增殖、激活等变化,最终导致坏死组织周围胶质瘢痕的形成,而胶质瘢痕可以破坏神经元轴突的正常生长。Zhou等[22]研究发现,丹参酮ⅡA能够抑制由于脑缺血引起的星形胶质细胞激活,减少胶质瘢痕的形成,从而起到神经保护的作用。
2.2 治疗阿尔茨海默病 近年来,大量的在体、离体实验表明,丹参酮ⅡA对阿尔茨海默病有治疗作用。在2014年,Jiang等[23]在阿尔茨海默病的大鼠的模型中发现,50 mg/kg丹参酮ⅡA可以减少阿尔茨海默病引起的一氧化氮、过氧亚硝基阴离子的释放,同时减少大鼠海马的诱导型一氧化氮合酶、MMP-2、NF-κB的表达,改善学习和记忆能力,通过抗氧化机制来治疗阿尔茨海默病。
Aβ多肽的错误折叠和聚集形成淀粉样纤维是阿尔茨海默病的主要发病机制之一,用Aβ刺激大鼠的嗜铬细胞瘤细胞系PC-12已经作为研究阿尔茨海默病的模型而广泛应用。Dong等[24]在用Aβ(25-35)刺激PC-12细胞后引起了细胞的凋亡,而用丹参酮ⅡA治疗24 h后,凋亡细胞的数量减少,细胞的生存力明显增强,丹参酮ⅡA通过激活PI3K/Akt通路对神经细胞起到保护作用,从而治疗阿尔茨海默病。
2.3 治疗其他神经系统疾病 近年研究发现,丹参酮ⅡA可以通过抑制胶质细胞的激活,减少炎性细胞因子表达,下调氧化应激等途径改善神经性疼痛[25-26]。此外,丹参酮ⅡA可以在体外促进神经元的再生和增殖[27]。在动物模型中,丹参酮ⅡA对糖尿病神经功能受损、脊髓外伤后的运动功能受损、惊厥等疾病也有一定的治疗作用[28-30]。
3 丹参酮ⅡA在抗肿瘤方面的应用
近年来大量科学研究聚焦于丹参酮ⅡA对肿瘤的治疗,包括结肠癌、乳腺癌、肝癌、肾癌、胃癌等。丹参酮ⅡA可以通过多种途径来治疗肿瘤。丹参酮ⅡA可以抑制肿瘤细胞的生长、增殖、侵袭转移,同时促进肿瘤细胞的分化、凋亡以及自噬性的死亡,还能调节肿瘤细胞对化疗药物的敏感性。是一种很有前途的防治肿瘤的药物。
Munagala等[31]研究证明,丹参酮ⅡA可以抑制人类宫颈癌细胞系癌基因中人乳头状瘤病毒 E6 和人乳头状瘤病毒E7的表达,并且增加p53 等抑癌基因的表达,抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖。通过调节Bcl-2、Bax等与凋亡密切相关的蛋白的表达,诱导肿瘤细胞的凋亡,从而防治宫颈癌及其他人乳头状瘤病毒感染有关的癌症。
Yun等[32]在2014年的丹参酮ⅡA治疗白血病的研究中发现,丹参酮ⅡA可以激活 KBM-5白血病细胞腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶和细胞外信号调节激酶,抑制mTOR和p70S6K,引起肿瘤细胞的自噬性细胞死亡,从而治疗白血病。
丹参酮ⅡA还可以促进肿瘤细胞的分化。骨髓祖细胞分化形成成熟的粒细胞需要在一些必要的转录因子的激活下进行,如C/EBPβ。CHOP可抑制C/EBPβ调节的骨髓细胞的分化。全反式维甲酸就是通过调节二者的平衡来治疗白血病。而近年研究发现,丹参酮ⅡA可以通过上调C/EBPβ的活性,下调CHOP的活性,促进急性早幼粒细胞性白血病细胞的分化,因此有望成为治疗全反式维甲酸耐药的急性早幼粒细胞性白血病的有效药物[33]。
P-糖蛋白与多种药物的耐药有关,可以导致乳腺癌、宫颈癌等肿瘤对化疗药物紫杉醇产生耐药性[34]。丹参酮ⅡA能够下调P-糖蛋白的表达,同时激活线粒体有关的凋亡和内质网的应激反应,抵抗紫杉醇的耐药性,治疗肿瘤[35]。
脱氧核酸嘧啶内切酶在多种肿瘤中呈高表达,并且与DNA修复、氧化还原反应密切相关,影响p53等与肿瘤细胞生长代谢、耐药、血管生成有关因子的表达,与肿瘤患者复发增加、生存期缩短、预后不良有密切联系[36-37]。丹参酮ⅡA可以通过破坏脱氧核酸嘧啶内切酶的功能,抑制肿瘤细胞的生长,增强电离辐射和化疗药物对肿瘤细胞产生的细胞毒性,促进肿瘤细胞死亡[38]。
丹参酮ⅡA可以通过下调前列腺癌细胞中雄激素受体抗前列腺癌[39];通过调节NF-κB通路抑制MMP-2、MMP-9的活性,有效抑制肝癌细胞的侵袭和转移[40]。
4 丹参酮ⅡA在炎症相关疾病和免疫调节方面的应用
丹参酮ⅡA能够抑制病理生理异常的免疫炎症反应,通过调节多种免疫细胞的功能和数量,以及相关的细胞因子分泌,减少组织损伤。
Zhang等[41]研究显示,在脂多糖诱发的急性肺炎小鼠模型中,丹参酮ⅡA可以抑制呼吸道上皮细胞黏蛋白1的表达,减少支气管肺泡灌洗液中角质细胞趋化因子、TNF-α的水平以及中性粒细胞的浸润,通过对呼吸道的抗炎作用来预防急性肺炎。Yu等[42]在同种异体皮肤移植的大鼠模型中发现,5 mg/kg的丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠可以显著提高移植皮肤的生存时间,减少同种移植物内炎性细胞的浸润,下调促炎性细胞因子的表达,以及受体大鼠外周血CD4+T细胞与CD8+T细胞的比例。丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠有望成为一种改善同种异体移植排斥的新药,甚至可能用于治疗Th1细胞有关的免疫性疾病。树突细胞作为一种抗原呈递细胞,可以促进T细胞的增殖和激活,在适应性免疫中至关重要。
丹参酮ⅡA可以抑制树突细胞的成熟,减弱树突细胞刺激T细胞增殖和分泌IL-12、IL-1等促炎性细胞因子的能力[43]。自然杀伤细胞在先天性和适应性免疫中发挥重要作用。在IL-15的刺激下,丹参酮ⅡA可以促进自然杀伤细胞的成熟和分化[44]。
类风湿性关节炎是一种慢性的炎症性疾病,以滑膜增生和进展性的关节损害为主要表现。丹参用于治疗类风湿关节炎已有很长的历史[45]。近年研究发现,丹参酮ⅡA可以通过促进类风湿性关节炎患者的成纤维样滑膜细胞的凋亡,来缓解类风湿关节炎[46]。
5 丹参酮ⅡA对脏器纤维化方面的应用
近年研究发现,丹参酮ⅡA对肺、肾、肝、心等脏器的纤维化有显著的改善作用。特发性肺纤维化是一种慢性进展性的纤维性肺病,致死率高且病因尚不明确。最新研究发现,丹参酮ⅡA可以显著改善大鼠肺纤维化的程度,同时减少TNF-α、前列腺素 E2等炎性物质的表达[47]。丹参酮ⅡA可以减慢结构性肾脏疾病的进展,改善慢性肾脏疾病的肾功能不全[48]。其通过显著下调纤连蛋白的表达,同时减少促炎性细胞因子的表达以及NF-κB 等炎性通路的激活,减轻肾脏炎症和肾小球硬化[49]。
6 结语
综上所述,丹参酮ⅡA具有抗动脉粥样硬化、心脏保护、神经保护、抗肿瘤等多种药理学活性,已经广泛用于在临床心脑血管等疾病的治疗,长期使用不良反应小。近年来大量的科学研究证实,丹参酮ⅡA还有很多其他药理作用,但是此类研究大多限于动物实验或体外细胞实验,因此进一步的研究有待完善。总之,丹参酮ⅡA在很多领域具有潜在的应用开发前景,有待研究者的进一步了解和广泛应用。
[1] Wang W,Ma B,Hu X,et al.The Effect of Tanshinone ⅡA and simvastatin treating the legs atheromatosis [J].Chinese Journal of Arteriosclerosis,2010,18(11): 897-899.
[2] Dabek J,Glogowska-Ligus J,Szadorska B.Transcription activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 metalloproteinase genes and their tissue inhibitor (TIMP-2) in acute coronary syndrome patients [J].Journal of Postgraduate Medicine,2013,59(2): 115-120.
[3] Xu S,Little PJ,Lan T,et al.Tanshinone II-A attenuates and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques in Apolipoprotein-E knockout mice fed a high cholesterol diet [J].Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,2011,515(1-2): 72-79.
[4] Tang FT,Cao Y,Wang TQ,et al.Tanshinone IIA attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) mice through down-regulation of scavenger receptor expression [J].European Journal of Pharmacology,2011,650(1): 275-284.
[5] Zhu H,Itoh K,Yamamoto M,et al.Role of Nrf2 signaling in regulation of antioxidants and phase 2 enzymes in cardiac fibroblasts: Protection against reactive oxygen and nitrogen species-induced cell injury [J].Febs Letters,2005,579(14): 3029-3036.
[6] Liu X,Guo CY,Ma XJ,et al.Anti-inflammatory effects of tanshinone lla on atherosclerostic vessels of ovariectomized apoe mice are mediated by estrogen receptor activation and through the erk signaling pathway [J].Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology,biochemistry,and pharmacology,2015,35(5): 1744-1755.
[7] Jia LQ,Yang G,Ren L,et al.Tanshinone IIA reduces apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide in the human endothelium-derived EA.hy926 cells [J].Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2012,143(1): 100-108.
[8] Kokjohn TA,Van Vickle GD,Maarouf CL,et al.Chemical characterization of pro-inflammatory amyloid-beta peptides in human atherosclerotic lesions and platelets [J].Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Basis of Disease,2011,1812(11): 1508-1514.
[9] Liu D,Mao J.Protective effect of sodium tanshinone ⅡA sulfonate on myocardial oxidative stress injury after thrombolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction patients [J].China Journal of Modern Medicine,2014,24(19): 96-99.
[10]Zhang H,Long M,Wu Z,et al.Sodium tanshinone IIA silate as an add-on therapy in patients with unstable angina pectoris [J].Journal of Thoracic Disease,2014,6(12): 1794-1799.
[11]Nagaya N,Fujii T,Iwase T,et al.Intravenous administration of mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in rats with acute myocardial infarction through angiogenesis and myogenesis [J].American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology,2004,287(6): H2670-H2676.
[12]Barbash I M,Chouraqui P,Baron J,et al.Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the infarcted myocardium - Feasibility,cell migration,and body distribution [J].Circulation,2003,108(7): 863-868.
[13]Tong Y,Xu W,Han H,et al.Tanshinone IIA increases recruitment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to infarct region via up-regulating stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXC chemokine receptor 4 axis in a myocardial ischemia model [J].Phytomedicine,2011,18(6): 443-450.
[14]Wang J,Juhaszova M,Rubin LJ,et al.Hypoxia inhibits gene expression of voltage-gated K+channel alpha subunits in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells [J].The Journal of clinical investigation,1997,100(9): 2347-2353.
[15]Zheng L,Liu M,Wei M,et al.Tanshinone IIA attenuates hypoxic pulmonary hypertension via modulating K-v currents [J].Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology,2015,205(1): 120-128.
[16]Qian Y-H,Xiao Q,Xu J.The protective effects of tanshinone IIA on beta-amyloid protein (1-42)-induced cytotoxicity via activation of the Bcl-xL pathway in neuron [J].Brain Research Bulletin,2012,88(4): 354-358.
[17]Chen Y,Wu X,Yu S,et al.Neuroprotective Capabilities of Tanshinone IIA against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Anti-apoptotic Pathway in Rats [J].Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2012,35(2): 164-170.
[18]Zhang W-j,Feng J,Zhou R,et al.Tanshinone IIA protects the human blood-brain barrier model from leukocyte-associated hypoxia-reoxygenation injury [J].European Journal of Pharmacology,2010,648(1-3): 146-152.
[19]Tang Q,Han R,Xiao H,et al.Neuroprotective effects of tanshinone IIA and/or tetramethylpyrazine in cerebral ischemic injury in vivo and in vitro [J].Brain Research,2012,1488(7): 81-91.
[20]Wen PY,Yang FZ,Wang F,et al.Study on regulation of tanshinone II(A) on GFAP and ATPase and PDI of cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats [J].Journal of Chinese medicinal materials,2012,35(10): 1628-1632.
[21]He Z,Pan Z,Lu W.Neuroprotective effects of tanshinone II A on vascular dementia in rats [J].China journal of Chinese materia medica,2010,35(14): 1883-1886.
[22]Zhou L,Bondy S C,Jian L,et al.Tanshinone iia attenuates the cerebral ischemic injury-induced increase in levels of gfap and of caspases-3 and-8 [J].Neuroscience,2015,288(12): 105-111.
[23]Jiang P,Li C,Xiang Z,et al.Tanshinone IIA reduces the risk of Alzheimer's disease by inhibiting iNOS,MMP-2 and NF-kappa Bp65 transcription and translation in the temporal lobes of rat models of Alzheimer's disease [J].Molecular Medicine Reports,2014,10(2): 689-694.
[24]Dong H,Mao S,Wei J,et al.Tanshinone IIA protects PC12 cells from beta-amyloid(25-35)-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J].Molecular Biology Reports,2012,39(6): 6495-6503.
[25]Cao F-L,Xu M,Wang Y,et al.Tanshinone IIA attenuates neuropathic pain via inhibiting glial activation and immune response [J].Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior,2015,128(1): 1-7.
[26]Tang J,Zhu C,Li ZH,et al.Inhibition of the spinal astrocytic JNK/MCP-1 pathway activation correlates with the analgesic effects of tanshinone IIA sulfonate in neuropathic pain [J].Journal of Neuroinflammation,2015,12(25):
[27]Shen JL,Chen YS,Lin JY,et al.Neuron regeneration and proliferation effects of danshen and tanshinone lla [J].Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2011:378907.
[28]Liu Y,Wang L,Li X,et al.Tanshinone IIA improves impaired nerve functions in experimental diabetic rats [J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2010,399(1): 49-54.
[29]Yin X,Yin Y,Cao FL,et al.Tanshinone IIA attenuates the inflammatory response and apoptosis after traumatic injury of the spinal cord in adult rats [J].Plos One,2012,7(6): 1-11.
[30]Buenafe O E,Orellana-Paucar A,maes J,et al.tanshinone IIA exhibits anticonvulsant activity in zebrafish and mouse seizure models [J].Acs Chemical Neuroscience,2013,4(11): 1479-1487.
[31]Munagala R,Aqil F,Jeyabalan J,et al.Tanshinone IIA inhibits viral oncogene expression leading to apoptosis and inhibition of cervical cancer [J].Cancer Letters,2015,356(2): 536-546.
[32]Yun SM,Jung JH,Jeong SJ,et al.Tanshinone IIA induces autophagic cell death via activation of AMPK and ERK and inhibition of mTOR and p70 S6K in KBM-5 leukemia cells [J].Phytotherapy Research,2014,28(3): 458-464.
[33]Zhang K,Li J,Meng W,et al.C/EBP beta and CHOP participate in Tanshinone IIA-induced differentiation and apoptosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells in vitro [J].International Journal of Hematology,2010,92(4): 571-578.
[34]Murray S,Briasoulis E,Linardou H,et al.Taxane resistance in breast cancer: Mechanisms,predictive biomarkers and circumvention strategies [J].Cancer Treatment Reviews,2012,38(7): 890-903.
[35]Pan TL,Wang PW,Hung YC,et al.Proteomic analysis reveals tanshinone IIA enhances apoptosis of advanced cervix carcinoma CaSki cells through mitochondria intrinsic and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways [J].Proteomics,2013,13(23-24): 3411-3423.
[36]Tell G,Fantini D,Quadrifoglio F.Understanding different functions of mammalian AP endonuclease (APE1) as a promising tool for cancer treatment [J].Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences,2010,67(21): 3589-3608.
[37]Luo M,He H,Kelley MR,et al.Redox Regulation of DNA Repair: Implications for Human Health and Cancer Therapeutic Development [J].Antioxidants & Redox Signaling,2010,12(11): 1247-1269.
[38]Sui J,Li M,Qian C,et al.Functional analysis of tanshinone IIA that blocks the redox function of human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease I/redox factor-I [J].Drug Design Development and Therapy,2014,8(21):47-60.
[39]Won SH,Lee HJ,Jeong SJ,et al.Activation of p53 signaling and inhibition of androgen receptor mediate tanshinone IIA induced G1 arrest in LNCaP prostate cancer cells [J].Phytotherapy Research,2012,26(5): 669-674.
[40]Xu Y,Tian F,Li R,et al.Tanshinone II-A inhibits invasion and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo [J].Tumori,2009,95(6): 789-795.
[41]Zhang K,Wang J,Jiang H,et al.Tanshinone IIA inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced MUC1 overexpression in alveolar epithelial cells [J].American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology,2014,306(1): C59-C65.
[42]Yu Q,Chen H,Sheng L,et al.Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate prolongs the survival of skin allografts by inhibiting inflammatory cell infiltration and T cell proliferation [J].International Immunopharmacology,2014,22(1): 277-284.
[43]Li HZ,Lu YH,Huang GS,et al.Tanshinone II A inhibits dendritic cell-mediated adaptive immunity: Potential role in anti-atherosclerotic activity [J].Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine,2014,20(10): 764-769.
[44]Kim WS,Kim DO,Yoon SJ,et al.Cryptotanshinone and tanshinone IIA enhance IL-15-induced natural killer cell differentiation [J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2012,425(2): 340-347.
[45]Zhou LM,Zuo Z,Chow MSS.Danshen: An overview of its chemistry,pharmacology,pharmacokinetics,and clinical use [J].Journal of Clinical Pharmacology,2005,45(12): 1345-1359.
[46]Jie L,Du H,Huang Q,et al.Tanshinone IIA induces apoptosis in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via blockade of the cell cycle in the G2/M phase and a mitochondrial pathway[J].Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2014,37(8): 1366-1372.
[47]He H,Tang H,Gao L,et al.Tanshinone IIA attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats [J].Molecular medicine reports,2015,11(6): 4190-4196.
[48]Ahn YM,Kim SK,Lee SH,et al.Renoprotective Effect of Tanshinone IIA,An Active Component of Salvia miltiorrhiza,on Rats with Chronic Kidney Disease [J].Phytotherapy Research,2010,24(12): 1886-1892.
[49]Wang DT,Huang RH,Cheng X,et al.Tanshinone IIA attenuates renal fibrosis and inflammation via altering expression of TGF-beta/Smad and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in 5/6 nephrectomized rats [J].International Immunopharmacology,2015,26(1): 4-12.
Recent progress on pharmacological effects and therapeutic use of tanshinoneⅡA
YAN Jun,FENG Juan*,YANG Xue,HUANG Lei
(Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University,Shenyang 110004,China)
TanshinoneⅡA,the main ingredient of Chinese medicine salvia miltiorrhiza,has anti-inflammatory,antioxidant,apoptosis regulation and many other pharmacological effects,it is now widely used in clinical treatment of diseases of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. In recent years,a large number of studies have found that tanshinoneⅡA has anti-tumor,anti-fibrosis and immune regulation effects. In this review,we summarize its new progress in pharmacological effects and therapeutic use of tanshinoneⅡA on the basis of its function in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and neural protection.
TanshinoneⅡA; Cardiovascular protection;Neural protection;Anti-tumor;Immunoregulation
2015-02-05
中国医科大学附属盛京医院,沈阳 110004
辽宁省科学计划重大疾病动物实验研究及临床应用(2012225021);辽宁“百千万人才工程”入选项目(2010921072)
10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.201508027
*通信作者
