海洋稀有放线菌 Salinispora arenicola CNP193 基因组新颖PKS 和NRPS基因簇的发掘
2014-12-15房耀维王淑军吕明生焦豫良陈国强潘建梅
房耀维, 刘 姝, 王淑军, 吕明生, 焦豫良, 陈国强, 潘建梅, 牛 军
(淮海工学院 海洋学院, 江苏 连云港 222005)
天然产物是开发新药或重要先导化合物的主要源泉之一[1-2]。聚酮 (Polyketide) 化合物是功能和结构最多样化的天然产物之一, 具有包括抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤、抗病原生物、抗结核和免疫抑制等生物活性[3]。迄今, 通过活性追踪指导从微生物发酵液中纯化聚酮化合物, 然后进行化学分析仍是发现新型聚酮化合物的主要策略, 随着研究的进行, 尽管筛选微生物的范围从陆地拓展到了海洋, 重复发现率仍越来越高, 越来越难发现新的聚酮化合物, 因此, 亟待开发更为快速有效的新型聚酮化合物筛选策略[4-5]。
基因组发掘(Genome mining)是利用现代生物信息学手段从基因组序列中寻找和识别特定功能基因或基因簇的技术[6]。基因组发掘表明, 即使是对天然被广泛研究的细菌而言, 发现的次级代谢产物种类也远远低于基因组发掘获得的次级代谢产物基因簇[7-8]。随着基因测序技术的飞速发展, 基因组序列测定速度提高, 成本降低, 海量的微生物基因组序列和宏基因组序列被测定[9]。通过基因组发掘技术发掘天然产物基因簇技术发展迅速, 促使基因组发掘成为更加准确高效的新型聚酮化合物筛选策略[10]。通过基因组发掘技术, 越来越多的新颖基因簇被发掘, 从而引导大量的新型聚酮化合物被发现和研究[11-12]。新颖基因簇既为异源表达提高次级代谢产物生产效率奠定基础, 也为阐明活性物质代谢途径, 从而通过代谢工程为提高生产效率奠定基础, 同时又为通过组合生物合成技术对化合物结构进行改造提供了基因序列信息[13]。
目前, 已知的具有生物活性的聚酮类化合物的2/3是放线菌产生的[3]。海洋放线菌代谢产物的结构和活性多样更加丰富多样[14]。2005年, 首个专性海洋放线菌属盐孢菌属 (Salinosporasp.) 报道, 该属放线菌可以产生丰富的聚酮化合物[8]。2007年, 菌株S.tropicaCNB440 和菌株S.arenicolaCNS-205基因组序列被测定, 是专性海洋放线菌的首次全基因组测序, 打开了海洋放线菌基因组发掘之门。对两个菌株的基因组序列进行发掘, 共发现了包括PKS、NPRS、siderophore、melanin、terpenoid 和 aminocyclitol 等 49 个次生代谢产物基因簇 (Orphan gene cluster), 其中, 只有9个基因簇发现了代谢产物[15]。根据获得基因簇信息, Moore 研究组从盐孢菌属放线菌发现了Salinosporamide K[16], Lomaiviticin[17]和 Cyanosporasides C-F[18]。菌株S.arenicolaCNP-193 具有良好的抗菌活性, 利用 molecular networking技术对 35株盐孢菌属菌株进行测定, 发现菌株CNP193能产生不同于其他菌株的新颖代谢产物。因此, 作者以S.arenicolaCNS 205 基因组中含有的基因簇为参照, 发掘菌株S.arenicolaCNP193 基因组中新颖的 PKS 和 NRPS 基因簇, 并对基因簇进行比较分析, 为基因簇的异源表达, 基因簇的功能鉴定及新型聚酮化合物的发现提供信息。
1 材料与方法
1.1 新颖PKS 和NRPS 基因簇发掘
将S.arenicolaCNS 205基因组序列和S.arenicolaCNP193 基因组序列提交 antiSmash 在线网站(http: //www.secondarymetabolites.org/)预测和分析次级代谢产物基因簇, 通过 NRPS-PKS knowledgebase (http: //www.nii.ac.in/~pksdb/sbspks/master.html)对预测结果进行验证后, 初步筛选出二者不同的PKS及NRPS基因簇[10]。进一步利用NCBI BLAST对初筛新颖基因簇的基因序列进行比对分析, 获取没有较高基因序列相似性的基因簇[12]。利用 NapDos(http: //napdos.ucsd.edu/) 对基因簇中的 KS domain和 C domain 的进化进行分析[9]。
1.2 新颖PKS 和NRPS 基因簇的功能预测
根据 antiSmash搜索已知功能的同源基因簇,并预测基因簇中生合成基因对应产物的核心结构,初步判断基因簇代谢产物, 利用NCBI BLAST对基因簇所有同源序列进行搜索, 最后利用NapDos对基因簇中的 KS domain 和 C domain 的进化进行分析, 获悉 KS domain 和 C domain 的催化功能, 综合确定产物的类型及结构信息。
2 结果
2.1 S.arenicola CNP193 基因组中PKS 和NRPS 基因簇预测与分析
通过 antiSmash 预测, 并经过 NRPS-PKS knowledgebase 进一步验证的S.arenicolaCNP193 基因组中次级代谢产物基因簇如表1。在菌株S.arenicolaCNP193 基因组序列中共发现次级代谢产物基因簇23个, 其中t1PKS 基因簇4个, t2PKS 基因簇和 t3PKS 基因簇各 1 个, NRPS 基因簇3个, NRPSPKS基因簇2个。
2.2 S.arenicola CNP193 基因组中新颖PKS和NRPS 基因簇的筛选
菌株S.arenicolaCNS 205基因组序列中共有次级代谢产物基因簇 25 个, 其中 t1PKS 基因簇7 个, t2pks 基因簇和 t3PKS 基因簇各1个, NRPS基因簇 4 个, NRPS-PKS 基因簇2个。Nett等[15]报道菌株S.arenicolaCNS 205中已经明确功能的基因簇有5个, 对应产物分别为 利福霉素、星孢菌素、去铁敏、Lymphostin 和Cyclomarin。根据Nett等[15]报道基因簇信息和 antiSmash 推测的S.arenicolaCNS 205基因组中的次级代谢产物基因簇, 找到S.arenicolaCNS 205中5个明确基因簇功能的包括编号, 产物类型和大小等基因簇信息, 并了解基因簇的结构组成 (图1) 。根据这些信息从菌株S.arenicolaCNP193基因组中寻找产物类型相同, 大小和结构组成相似度较高的基因簇。中和S.arenicolaCNS 205中5个明确功能的基因簇均能在菌株S.arenicolaCNP193中找到对应的基因簇 (表2)。除Rifamycin 基因簇外, 两菌株中星孢菌素、去铁敏、Cyclomarin 和 Lymphostin的基因簇大小相同, 结构组成基本相同, 序列相似度高于 99%。虽然菌株S.arenicolaCNS 205 中利福霉素 基因簇较菌株S.arenicolaCNP193中对应的基因簇大20 kb, 但是S.arenicolaCNP193与对应大小S.arenicolaCNS 205中的基因簇相似性高达 99%。且二者 antiSmash 在线预测两个基因簇的核心结构只是在中间位置有 3个组成单位不同(图2), 因此推测S.arenicolaCNP193的基因簇产物属于Rifamycin同系物。
根据基因簇产物类型, 大小和结构组成, 以及antiSmash 在线预测的基因簇产物核心结构, 判断菌株S.arenicolaCNP 193基因组中基因簇是否在S.arenicolaCNS 205 中有相同的基因簇, 发现S.arenicolaCNP193 基因组中具有四个与S.arenicolaCNS 205 不同的基因簇, 分别为基因簇7, 基因簇 8, 基因簇 10和基因簇 20(表1)。利用 NCBI BLAST 对初筛新颖基因簇的基因序列进行比对分析(图3)。基因簇8中98%的序列和S.arenicolaCNS205 中包含基因簇 8的部分序列的相似性高达达到99%; 基因簇 7同Micromonospora echinospora的卡里奇霉素基因簇相似性最高, 基因簇 7 中 67%的序列同该序列的相似性为到 81%; 62% 的基因簇10 同S.arenicolaCNS 205 基因组中序列相似性为98%; 基因簇 20 中有 26% 的序列同S.arenicolaCNS 205 基因组中序列相似性为 99%。表明S.arenicolaCNP193基因组中所具有的新颖 PKS和NRPS 基因簇为基因簇7, 基因簇10和基因簇20。

表1 菌株S.arenicola CNP193和菌株S.arenicola CNB 440 基因组序列中的次级代谢产物基因簇Tab.1 The secondary metabolite gene clusters mined from S.arenicola CNP193 and S.arenicola CNB 440

图1 菌株 S.arenicola CNP193和菌株 S.arenicola CNS 205 基因组序列中已知功能次级代谢产物基因簇结构组成Fig.1 Modular organization of the gene clusters from S.arenicola CNP193 and S.arenicola CNS 205
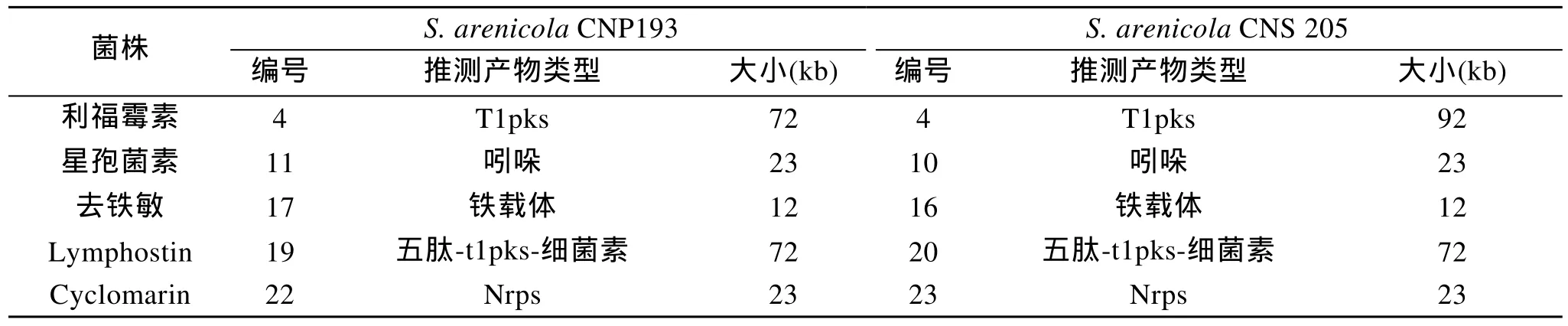
表2 菌株 S.arenicola CNP193和菌株 S.arenicola CNS 205 基因组序列中已知功能次级代谢产物基因簇信息比较Tab.2 Information comparison of the gene clusters from S.arenicola CNP193 and S.arenicola CNS 205

图2 antiSmash 在线预测菌株 S.arenicola CNP193和菌株 S.arenicola CNS 205 基因组序列中利福霉素基因簇核心结构Fig.2 The core structure of Rifamycin predicting with antiSmash based on gene cluster of S.arenicola CNP193 and S.arenicola CNS 205
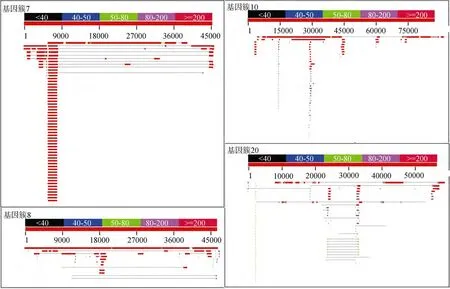
图3 Blast搜索基因簇同源序列Fig.3 Homologous gene clusters searching with Blast
2.3 基因簇7
基因簇 7 属于 t1PKS, 位于基因组的 2036897–2082794, 长度约为 46 kb。基因簇的构成见图4。antiSmash 预测已知功能同源关系最近的基因簇序列为卡里奇霉素, maduropeptin和新制癌菌素, 都属于烯二炔化合物(图5)。NCBI BLAST对基因组序列进行比对分析, 表明基因簇 7 同M.echinospora的 卡里奇霉素 基因簇相似性最高, 基因簇 7 中67% 的序列同该序列的相似性达到 81%。而只是同S.arenicolaCNS 205 和S.tropicaCNB 440 只是在基因簇的两端有较高的重复序列(图3)。利用 Nap-Dos 对图3 所示的基因簇中的 KS domain 蛋白序列进行同源性分析, 结果见表3。该 KS domain 和M.echinospora菌株的 卡里奇霉素基因簇中的 CALEAM_AAM94794_ene10 (KS domain)蛋白质序列相似性为89%, 属于烯二炔家族, 由 Ahlert 等 2002 年报道[19]。初步表明基因簇7为烯二炔类化合物基因簇。
2.4 基因簇10
基因簇10 属于寡糖-t1pks-nrps-五肽, 位于基因组的 2254459–2343659, 长度为 89.2 kb。基因簇的构成见图6, 基因簇中含有 ER domain, KS domain,AT domain 和 DH domain 各一个; A结构域和C结构域各两个。antiSmash 预测没有发现已知功能同源基因簇序列。NCBI BLAST对基因组序列进行比对分析结果见表4, 62% 的基因簇 10 同S.arenicolaCNS 205 基因组中序列相似性为 98%, 30% 的基因簇 10 同M.echinospora基因组中序列相似性为98%。对基因簇中KS domain和C domain的蛋白序列利用NapDos分析, 结果见表5。和基因簇7中的KS domain 类似, 该 KS domain和M.echinospora菌株的 卡里奇霉素 基因簇中的 KS domain 蛋白质相似性为 88%。两个C domain均属于LCL家族, 同S.tropica合成 sporolide A 的基因簇中的C domain 的相似性分别为 34%和43%。
2.5 基因簇20
基因簇 20 属于 NRPS-t1PKS, 位于基因组的3923744–3981049, 长度约为57.3 kb。基因簇的构成见图7, 基因簇中含有C domain 4个, A domain 3个。虽然 antiSmash 预测没有发现已知功能同源基因簇序列, 但是成功的预测了基因簇对应产物的核心结构为三个半胱氨酸缩合物(图8)。NCBI BLAST对基因组序列进行比对分析, 26% 的基因簇序列同S.arenicolaCNS 205 基因组中序列相似性为 99%,5% 的基因簇序列 同Verrucosispora marisAB-18-032 基因组中序列相似性为 80%。对基因簇中KS 结构域和C结构域的蛋白序列利用在线工具NapDos分析, 结果见表6。KS1 domain 属于杂和KS domain, 同菌株Sorangium cellulosumSo ce90产 epothilone 基因簇中的编号为 EpoC_Q9L8C8_H的 KS domain[20]的相似度达58%。C1 domain 和Bacillus licheniformisATCC 10716产bleomycin的bacit1_C1_cyc domain[21]相似度为 36%; C2, C3,C4均和Streptomyces verticillusATCC15003 的bleom9_C2_cyc domain[22]相似度分别为45%, 44%和 46%。
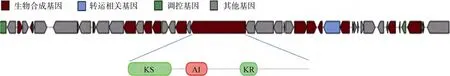
图4 基因簇7的结构组成Fig.4 Modular organization the gene cluster 7
图5 antiSmash比对获得的基因簇7同源基因簇Fig.5 The Homologous gene clusters searching with antiSmash
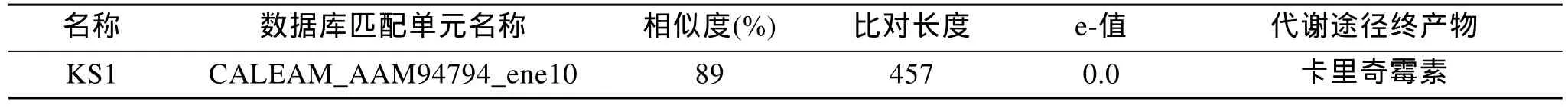
表3 NapDos分析基因簇7中KS domain 的同源蛋白序列Tab.3 Homologous protein sequences of KS domain from gene cluster 7 searching with NapDos
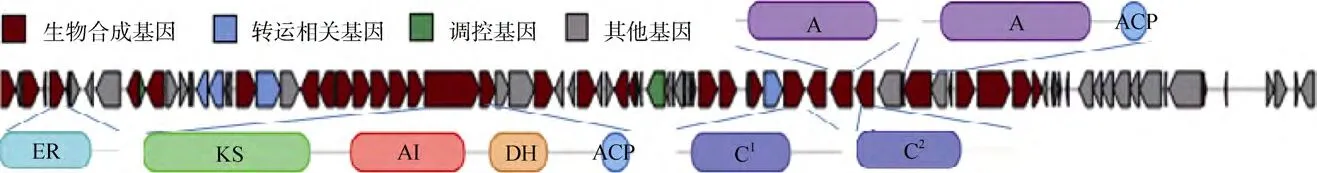
图6 基因簇10结构组成Fig.6 Modular organization of the gene cluster 10

表4 NCBI blast 基因簇10同源序列Tab.4 Homologous sequences of gene cluster 10 with NCBI blast
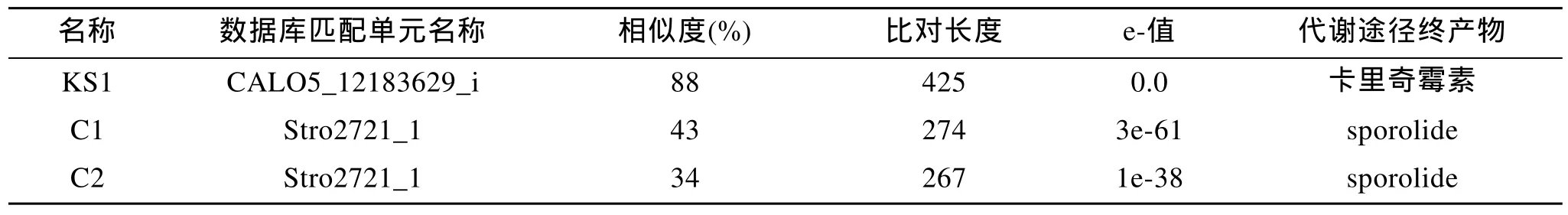
表5 NapDos分析基因簇10中KS domain h和C domain 的同源蛋白序列Tab.5 Homologous protein sequences of KS domain and C domain from gene cluster 10 searching with NapDos
3 讨论
3.1 PKS及NRPS 基因簇的挖掘
基因组挖掘技术在搜寻新颖微生物次级代谢产物方面优势明显, 聚酮 (Polyketide) 化合物具有多种生物活性, 是新药开发的最重要前体化合物之一,因此通过基因组发掘技术发掘新颖PKS及NRPS基因簇成为研究热点。有关PKS及NRPS基因的数据库, 发掘新颖PKS及NRPS的软件和在线网站逐年增多, 即可以对基因框架, 宏基因组序列, 以及整个基因组范围内的PKS及NRPS基因簇进行筛选, 对基因簇的进化及来源进行探索, 又可以对基因簇的组成结构进行分析, 对代谢产物结构初步预测[23-24]。
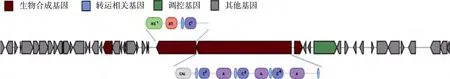
图7 基因簇20结构组成Fig.7 Modular organization of the gene cluster 20
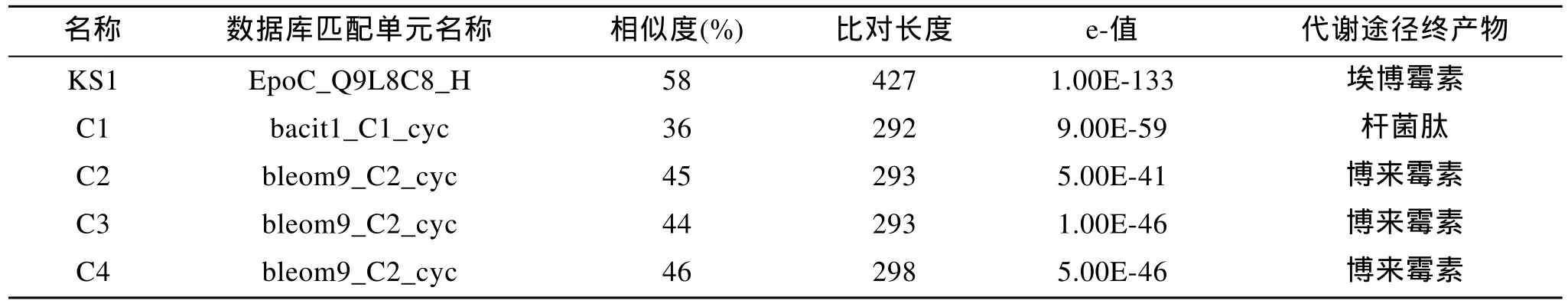
表6 NapDos分析基因簇20中KS domain h和C domain 的同源蛋白序列Tab.6 Homologous protein sequences of KS domain and C domain from gene cluster 20 searching with NapDos

图8 antiSmash 在线预测基因簇20对应产物的核心结构Fig.8 The core structure of gene cluster 20 predicting with antiSmash
发掘的技术核心是在收集尽量多的 PKS及NRPS基因簇序列信息, 在分析不同基因簇的结构组成, 催化单元, 相关酶及底物高级结构的基础上, 利用对基因或蛋白序列的多重比对, 以及不同的运算法则对功能结构域进行检索分析, 从而识别待测基因组中PKS及NRPS基因簇, 并对其功能进行推测[25]。Antismash 是美国, 德国, 英国及和荷兰等研究者开发的微生物次级代谢代谢产物预测及分析网站, 几经升级, 可以对包括PKS及NRPS在内的次级代谢产物基因簇进行识别和分析[10]。NRPS-PKS knowledgebase是专门的 NRPS, PKS数据库, 用于分析NRPS, PKS和NRPS/PKS杂合基因簇及其结构等。因此, 本研究在利用 antiSmash 识别筛选基因簇的基础上, 利用NRPS-PKS knowledgebase验证, 提高基因簇预测的准确性。
3.2 基因簇的新颖性确定
基因簇的新颖性是指基因簇生物合成基因, 调控基因等基因本身或排布不同, 从而更趋向于合成新颖的代谢产物。以S.arenicolaCNS 205为对照, 利用同一网站对S.arenicolaCNP-193基因簇的发掘,比较基因簇的结构结合基因簇的大小, 可以最大限度的去除相同基因簇。S.arenicolaCNS 205的基因簇8比S.arenicolaCNP-193基因簇9大接近20 kb,但是大部分组成结构相近, 认为是相同基因簇。S.arenicolaCNP-193中, 基因簇 8(2128462-2175754)和基因簇 9(2159970-2225471)有约 16Kb的重合区域。这是由于antiSmash最大程度的预测可能次级代谢产物基因簇, 部分基因序列和其前后的基因序列都能形成基因簇, 因此会有预测基因簇重合现象。
通过NCBI Blast 比对获得基因簇基因序列, 发现S.arenicolaCNP-193基因簇8中98%的序列和S.arenicolaCNS 205中包含部分基因簇8的序列相似性高达达到99%。说明S.arenicolaCNP-193基因簇8不具新颖性, 同时也表明S.arenicolaCNP-193基因簇8没有在S.arenicolaCNS 205预测为次级代谢产物基因簇, 是由于其部分序列包含在了S.arenicolaCNS 205中基因簇9中。基因簇10和基因簇20和其他基因序列的同源性较低。通过NapDos比对基因簇中KS domain和C domain的蛋白序列, KS domain与其他KS domain蛋白质序列相似性低于80%,C domain 与其他C domain 蛋白质序列相似性低于50%, 进一步证明基因簇的新颖性。
3.3 新颖基因簇的对应产物预测
基因簇对应产物可以通过搜索基因或蛋白同源序列进行预测, 也可以根据基因簇中生物合成基因的构成及其编码酶的催化功能进行预测。antiSmash,NCBI Blast以及NapDos对基因簇中的KS domain的比对分析都表明基因簇7和M.echinospora菌株的卡里奇霉素有最高同源性。卡里奇霉素结构见图9, 属于烯二炔类抗肿瘤抗生素。烯二炔类抗生素对肿瘤细胞有强烈的杀伤作用。一般比阿霉素、丝裂霉丝等强1000倍以上。作为新型抗肿瘤物质, 烯二炔类抗生素受到广泛重视[26]。Scripps海洋研究所生物技术与生物医药研究中心从于2006年从S.pacifica发酵产物中分离了烯二炔类化合物 cyanosporasides A-B, 2013年, 分离获得了 cyanosporasides C-F, 并对产生该类化合物的基因簇基因簇进行了比较和结构分析[18]。除此以外, 尚未从Salinispora属发现新的烯二炔类化合物。基因簇 7 的发现, 表明S.arenicolaCNP193有可能产生新颖的烯二炔类抗肿瘤抗生素。
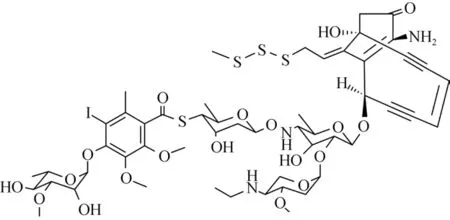
图9 卡里奇霉素结构Fig.9 The structure of calicheamicin
antiSmash, NCBI Blast没有发现已知功能的同源基因簇。NapDos对基因簇10中的KS domain和C domain的比对分析都表明, KS domain 和M.echinospora菌株的卡里奇霉素基因簇中的 KS domain有最高同源性, 两个C domain 均属于LCL家族, 同S.tropica合成sporolide A的基因簇中的C domain 同源。但是根据这些信息, 尚不能预测相应产物结构。
antiSmash预测了基因簇 20不考虑是否发生环化反应是的核心结构, 由半胱氨酸缩合而成。KS domain和C domain和EpoC_Q9L8C8_H, bacit1_C1_cyc, bleom9_C2_cyc相似度最高, 分别在合成埃博霉素 A, 杆菌肽 A以及博来霉素的中催化半胱氨酸之间及半胱氨酸与其他氨基酸之间的缩合成噻唑环。埃博霉素 A为大环内酯类抗癌药物[24], 杆菌肽 A为抗菌脂肽[25], 博来霉素为糖肽抗癌药物[26]。三者结构见图10, 均具有噻唑环, 因此可初步摧测基因簇20对应产物为含有噻唑环, 有半胱氨酸及其他氨基酸参与合成的肽类化合物。
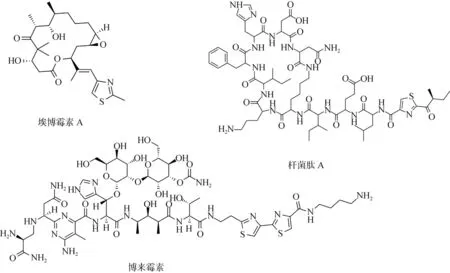
图10 埃博霉素A, 博来霉素和杆菌肽A的结构Fig.10 The structure of epothilone A, bleomycin, and bacitracin
致谢:
感谢加州大学圣地亚哥分院Scripps海洋研究所生物技术与生物医药研究中心 Jensen R Paul 教授提供菌株Salinispora arenicolaCNP193基因组信息。
[1]Winter J M, Tang Y.Synthetic biological approaches to natural product biosynthesis[J].Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2012, 23: 736-743.
[2]杨建, 洪葵.宏基因组文库技术获得聚酮化合物[J].遗传, 2006, 28(10): 1330-1336.
[3]Manivasagan P, Venkatesan J, Sivakumar K, et al.Marine actinobacterial metabolites: current status and future perspectives[J].Microbiological Research, 2013,168: 311-332.
[4]Oman T J, van der Donk W A.Follow the leader: the use of leader peptides to guide natural product biosynthesis[J].Nature Chemical Biology, 2010, 6: 9-18.
[5]Lane A L, Moore B S.A sea of biosynthesis: marine natural products meet the molecular age[J].Natural Product Reports, 2011, 28: 411-428.
[6]Kersten R D, Yang Y L, Xu Y, et al.A mass spectrometry-guided genome mining approach for natural product peptidogenomics[J].Nature Chemical Biology,2012, 7: 794-802.
[7]Bentley S D, Chater K F, Cerdeno-Tarraga A M, et al.Complete genome sequence of the model actinomyceteStreptomyces coelicolorA3(2) [J].Nature, 2002, 417:141-147.
[8]Udwary D W, Zeigler L, Asolkar R N, et al.Genome sequencing reveals complex secondary metabolome in the marine actinomyceteSalinispora tropica[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2007, 104:10376-10381.
[9]Ziemert, N, Podell S, Penn K, et al.The natural product domain seeker NaPDoS: a phylogeny based bioinformatic tool to classify secondary metabolite gene diversity[J].PloS One, 2012, 7: e34064.
[10]Blin K, Medema M H, Kazempour D, et al.antiSMASH 2.0—a versatile platform for genome mining of secondary metabolite producers[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2013, 21: 204-212.
[11]Wu J, Li L, Deng Z, et al.Analysis of the mildiomycin biosynthesis gene cluster in Streptoverticillum remofaciens ZJU5119 and characterization of MilC, a hydroxymethyl cytosyl-glucuronic acid synthase[J].Chem Bio Chem, 2012, 13(11): 1613-1621.
[12]Velasquez J E , van der Donk W A.Genome mining for ribosomally synthesized natural product[J].Curr Opin Chem Biol, 2011, 15: 11-21.
[13]McGlinchey R P, Nett M, Eustaquio A S, et al.Engineered biosynthesis of antiprotealide and other unnatural salinosporamide proteasome inhibitors[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130: 7822-7824.
[14]Lane A L, Moore B S.A sea of biosynthesis: marine natural products meet the molecular age [J].Natural Product Reports, 2011, 28: 411-428.
[15]Nett M, Ikeda H, Moore B S.Genomic basis for natural product biosynthetic diversity in the actinomycetes[J].Natural Product Reports, 2009, 26: 1362-1384.
[16]Kersten R D, Lane A L, Nett M, et al.Bioactivityguided genome mining reveals the lomaiviticin biosynthetic gene cluster inSalinispora tropica[J].Chem Bio Chem, 2013, 14: 955-962.
[17]Eustaquio A S, Nam S, Penn K, et al.The Discovery of Salinosporamide K from the marine bacterium “Salinispora pacifica” by genome mining gives insight into pathway evolution[J].Chem Bio Chem 2011, 12: 61-64.
[18]Lane A L, Nam S J, Fukuda T, et al.Structures and comparative characterization of biosynthetic gene clusters for cyanosporasides, enediyne-derived natural products from marine actinomycetes[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135: 4171-4174.
[19]Ahlert J, Shepard E, Lomovskaya N, et al.The calicheamicin gene cluster and its iterative Type I enediyne PKS[J].Science, 2002, 297: 1173-1176.
[20]Konzl D, Klensl A, Schbrgendorfer K, et al.The bacitracin biosynthesis operon ofBacillus licheniformisATCC 10716: molecular characterization of three multi-modular peptide synthetases[J].Chemistry Biology, 1997, 4: 927-937.
[21]Du L, Sanchez C, Chen M, et al.The biosynthetic gene cluster for the antitumor drug bleomycin from Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003 supporting functional interactions between nonribosomal peptide synthetases and a polyketide synthase[J].Chemistry Biology, 2000, 7: 623-642.
[22]Molnár I, Schupp T, Ono M, et al.The biosynthetic gene cluster for the microtubule-stabilizing agents epothilones A and B from Sorangium cellulosum So ce90[J].Chemistry Biology, 2000, 7: 97-109.
[23]Jensen P R, Williams P G, Oh D C, et al.Speciesspecific secondary metabolite production in marine actinomycetes of the genusSalinispora[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73: 1146-1152.
[24]姚琳, 郭东林.PKS-NRPS数据库的研究进展[J].中国农学通报, 2009, 25(16): 280-283.
[25]Nikolouli K, Mossialos D.Bioactive compounds synthesized by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases and type-I polyketide synthases discovered through genome-mining and metagenomics[J].Biotechnology Letters, 2012, 34: 1393-1403.
[26]李丽, 顾觉奋, 吴梧桐.烯二炔类抗肿瘤抗生素单克隆抗体导向药物研究进展[J].药物生物技术, 2006,12(4): 275-277.
