The Development of Sustained Release Antimicrobial Silk Sutures
2014-11-16PethileSibandaChenXiaojieWangLu
Pethile Sibanda,Chen Xiaojie,Wang Lu
Key Laboratory of Textile Science and Technology of Ministry of Education,College of Textiles,Donghua University(Shanghai,201620)
0 INTRODUCTION
The development of infection at the incision site following suturing is among the main concerns that surgeons,physicians and patients have in the medical field[1].The role of suture material in the development of wound surgical site infections has been the subject of speculation among surgeons since the 1960s[2]. A numerous number of bacteria may contaminate not only the tissue material but also the suture material.Once the sutures become contaminated it is difficult for local tissue defense or antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria and prevent infection[3-4]. Therefore it is very important to take note of the antimicrobial properties of a suture before using it in the wound litigation.
Silk fibers in the form of sutures have been used for centuries due to its ability to offer a wide range of properties.They are well known for their impressive mechanical properties,biocompatibility,environmental morphologic flexibility and stability[5].
Poly Epsilon-Caprolactone(PCL)is a widely used polymer in the field of medical research due to its appealing properties as linear aliphatic polyester that is biodegradable whose biocompatibility,low melting and elastomeric properties[6].
A numberofstudiesshowed a considerable decrease in the bacterial adherence to triclosan and chitosan coated sutures in vitro[7-9].Therefore the main aim of this study is to try to explore the use of Sulfamethoxazole Trimethoprim as a suitable antibacterial coating agent on braided silk sutures in order to produce antimicrobial coated silk sutures which can posses the properties that match the current ones used in the medical field today.
1 MATERIALS AND METHODS
1.1 Suture material
The silk suture that was used was procured from,Jiangsu Medical Supplies Ltd Co.in China.It was a size 2 -0 silk suture of 0.320 -0.331 mm diameter.
1.2 Preparation of the antimicrobial coating agent
Compound Sulfamethoxazole(SMZ)tablets a synergic drug made from a combination of Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim where used as the antibacterial agent. A biodegradable polymer,Polycaprolactone(PCL)of 80 000 molecular weight was chosen to act as the drug carrier polymer add on for the suture.
2500 μg/mL of antibacterial agentwasfirst suspended in acetic acid and homogenized at high speed(250 rev/min)for 10 minutes to reduce the gathering of particles.Then the coating agent,PCL was added into the resulting suspension and stirred for 1 hr at high speed(350 rev/min)to build up the drug concentration of 10%under sterile conditions using the same method[10].
1.3 Test organisms
Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC25923)and Escherichia coli(ATCC25922)were used for in vitro tests.All the strains were cultured to late logarithmic growth phase on agar plates at 37℃for 18 hrs before conducting tests under aseptic conditions in a laminar airflow.The colonies where touched with a loop and then transferred to a tryptone soy broth(TSB)and incubated at 37℃until the growth reached turbidity equal to or greater than that of 0.5 McFarland standard.The culture was then diluted using broth to give a turbidity of 1×10^8(CFU)/mL bacterium concentration.
1.4 Coating process
The sterile sutures were first coated with SMZ solution only and then another set of sutures were coated with SMZ+PCL in solution using a dip coating method[11].A uniform distribution of the polymer coating along the length of the suture was done through the use of a roller drying system as shown in the following figure(Fig.1 ).

图1 涂装设备示意图Fig.1 The schematic diagram of the coating equipment
1.5 Evaluation of antibacterial suture
After coating the silk suture with antibacterial agent,then an in vitro performance evaluation on antimicrobial properties of suture was done.This included the zone of inhibition assay,sustained efficacy assay,scanning electron microscopy tests,and drug release evaluation whereby the suture without coating acted as the control
1.5.1 Zone of inhibition Assay
A qualitative agar diffusion test was carried out on the coated silk sutures of 5 cm in length.It was done according to the antimicrobial performance evaluation(Zone of inhibition assay)standard(ISO 20645:2004)Determination of antibacterial properties-Part 1:agar diffusion method[12].The zone of inhibition diameter was measured using an electronic Venire Calipers measuring instrument.Pieces of braided silk sutures(5 cm each)with and without antibacterial agent were challenged in vitro with indicator strains of selected test organisms and incubated at 37°C for 24 h and examined for zones of inhibition.
1.5.2 Sustained efficacy Assay
Five-centimeter sections of braided silk sutures with antibacterial agent were evaluated by zone of inhibition assays,as described above.After 24 hrs of incubation at 37°C,suture samples were transferred daily onto new Petri plates growing a similar number of bacteria[13]. The assay wasterminated when the sutures ceased to inhibit bacterial growth.
The inhibition zone diameterwas calculated according to the following formula[14]:
H=(D-d)/2
Where H is inhibition zone(mm)
D is the total diameter of specimen and inhibition zone(mm)
d is the total diameter of specimen(mm)
1.5.3 Drug release study under static conditions
The study of drug release was done using a UV VIS Spectrophotometer(TU -1901,Beijing,China)to compare the drug release of sutures coated with SMZ only and those coated with SMZ+PCL.The sutures where divided into two sets whereby each set had four 5 cm samples of coated sutures.They where immersed in 4 mL PBS Solution(pH 7.4)and left under static conditions for 1 day[15].The supernatant was replaced with fresh PBS Solution every day until it showed no traces of SMZ in the UV VIS spectrophotometer.The amount ofdrug released in the supernatantwas determined by observing the absorbance ofthe supernatant solution at 259 nm using the UV VIS Spectrophotometer.The value of absorbance was then used in the equation y=mx(standard absorbance curve)to calculate the concentration of compound SMZ in the solution.

图2 SMZ标准吸收曲线Fig.2 The standard absorbance curve for SMZ
1.6 Surface morphological analysis
The scanning electron microscope (SEM,HITACHI/SU8010, JEOL, Japan)wasusedto observe the effect of antimicrobial coating on the suture.SEM images of sutures coated with SMZ only where obtained and then compared with SEM images of sutures coated with both PCL and SMZ.
2 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
2.1 Zone of inhibition assay
The sutures coated with SMZ demonstrated antibacterial efficacy against both test strains.The antibacterial treated sutures prevented both the test strains from colonizing and growing on the suture surface and inhibited both gram positive and gram negative bacteria.However the zone of inhibition results for sutures first coated with SMZ only showed larger zone diameters compared to the ones coated with both PCL and SMZ.As shown in figure 3 it is seen that picture(b)has a larger zone diameter than(a)against both test strains.This shows that the introduction of PCL into the antibacterial coating solution helped enhance the viscosity of the coating agent solution,thus improving the better binding of coating agent onto the silk fibres.The larger zone diameters of sutures coated with SMZ only,show that there was an outburst of drug release from the surface of the sutures.The polymetric structure of PCL helps retain the antibacterial particles on the braided structure so that they are not released at once but are released at slow controlled rate.This is good for the production of longlasting antibacterial sutures.

图3 抑菌试验区Fig.3 Zone of inhibition assay,

表1 抑菌试验区Tab.1 Zone of inhibition assay
2.2 Sustained efficacy assay
Sustained efficacy against S.aureus and E.coli was observed for the sutures coated with SMZ+PCL coating agent. As shown in Table 2, a zone of inhibition that is greater 1mm was observed for up to 4 days compared to only 2 days for sutures coated with SMZ only.SMZ was continually released from the SMZ+PCL coated suture and therefore antibacterial efficacy continued for up to 4 days.The sutures coated with SMZ alone,show that the antibacterial agent was released at once and therefore antibacterial efficacy stopped after 2 days.
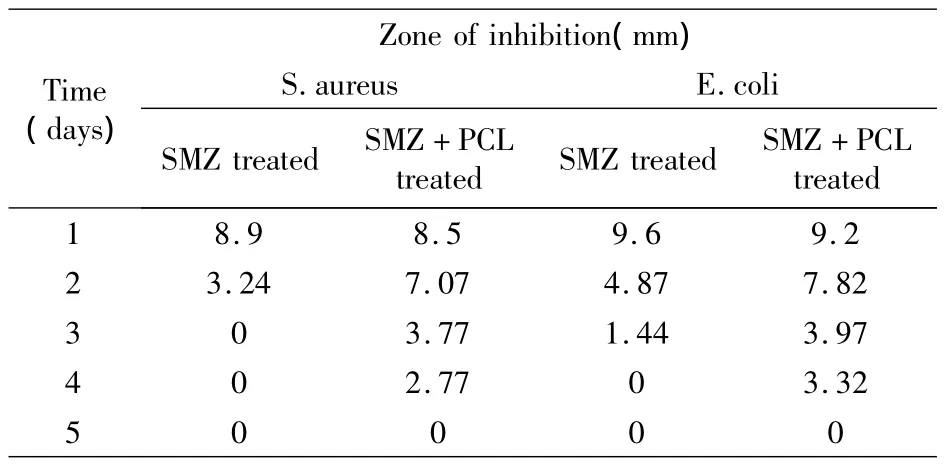
表2 抑菌效果Tab.2 Sustained efficacy assay
2.3 Drug release study
The SMZ+PCL combination on the silk suture showed bestresults.TraitsofSMZ drug where observed for up to 4 days as compared to only 2 days for sutures coated with SMZ only.The graph in figure 4 below show that,the drug embedded on the surface of the suture is released faster initially and the remaining residual drug inside the structure of the suture is released slowly when the suture is coated with PCL+SMZ.This indicates that there is a possibility of drug release from suture even after a day or so when the suture is used on the patients'wound litigation.
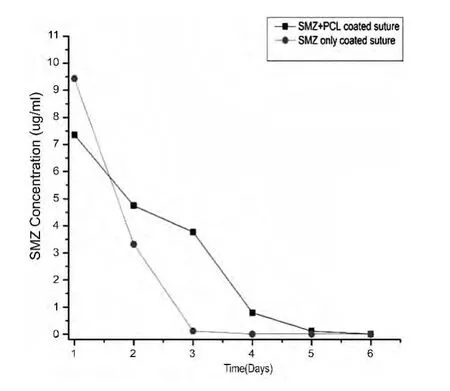
图4 药物释放动力学Fig.4 Drug release kinetics
2.4 Surface morphological analysis
Figure 5 shows a smoother surface on the suture treated with PCL+SMZ as compared to suture only treated with SMZ only.The SEM images show that a stable and regular coating was applied on the surface of the suture after the addition of PCL into the coating agent.This shows relatively good properties for sutures as it prevents friction during suturing process.

图5 SEM纤维纺织显微图Fig.5 SEM micrographs of braided silk suture
3 CONCLUSION
Sulfamethoxazole Trimethoprim is a suitable anti- bacterial agent for braided silk sutures.However a biodegradable polymer like PCL has to be applied with it for it to provide stable and sustainable antibacterial efficacy.Therefore it can be concluded that PCL+SMZ can be used as a coating agent for silk sutures in order for them to provide sustained antibacterial efficacy.
[1]F.Saleh,B.Palmieri,D.Lodi,et al.An innovative method to evaluate the suture compliance in sealing the surgical wound lips[J].International Journal of Medical Sciences,2008,5(6):354-360.
[2]J.W.Alexander,J.Z.Kaplan,W.A.Altemeier.Role of suture materials in the development of wound infection[J].Annals of Surgery,1967,165(2):192-199.
[3]G.T.Rodeheaver,L.D.Kurtz,W.T.Bellamy,et al.Biocidal braided sutures[J].Archives of Surgery,1983,118(3):322-327.
[4]C.R.Uff,A.D.Scott,A.G.Pockley,et al.Influence of soluble suture factors on in-vitro macrophage function[J].Biomaterials,1995,16(5):355-360.
[5]C.Vepari,D.L.Kaplan.Silk as a biomaterial[J].Progress in Polymer Science,2007,32(8-9):991-1007.
[6]J.P.Borges,C.R.Gomes,C.R.Henriques,et al.Electrospinning poly(e-caprolactone)dissolved in acetic acid[C].TERMIS EU Conference.NUI Galway,Ireland,13th-17th June 2010.
[7]C.E.Edmiston,G.R.Seabrook,C.J.Crepel,et al.Bacterial adherence to surgical sutures:Can antibacterialcoated sutures reduce the risk of microbial contamination[J].Journal of the American College of Surgeons,2006,203(4):481-489.
[8]S.Katz,M.Izhar,D.Mirelman.Bacterial adherence to surgical sutures.A possible factor in suture induced infection[J].Annals of Surgery,1981,194(1):35 -41.
[9]F.D.Matl,A.B.Obermeier,S.Repmann,et al.New anti- infective coatings of medical implants[J].Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy,2008,52(6):1957-1963.
[10]S.Viju,G.Thilagavathi.Effect of chitosan coating on the characteristics of silk - braided sutures[J].Journal of Industrial Textiles,2012,42(3):256 -268.
[11]Elayarajah,R.Rajendran,Venkatrajah.,et al.Biodegradable tocopherol acetate as a drug carrier to prevent ureteral stent -associate infection[J].Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences,2011,14(5):336 -343.
[12]E.Pinho,L.Magalhaes,M.Henriques.,et al.Antimicrobial activity assessment of textiles:standard methods comparison[J].Annals of Microbiology,2010,61(3):493-498.
[13]X.Ming,S.Rothenburger,D.Yang.In vitro antibacterial efficacy of monocryl plus antibacterialSuture(oliglecaprone 25 with Triclosan)[J].Surgical Infections,2007,8(2):201-208.
[14]E.Kimiran,A.S.Yurudu,N.O.Sanli.The evaluation of antibacterial activity of fabrics impregnated with dimethyltetradecyl 3(Trimethoxysilyl)Propyl)mmonium chloride[J].IUFS Journal of Biology,2008,67(2):115-122.
[15]O.L.Shanmugasundaram,R.V.M.Gowda,D.Saravanan.Drug release and antimicrobial studies on polylactic acid suture[J].International Journal for Biotechnology and Molecular Biology Research,2011,2(5):80-89.
