白内障超声乳化人工晶状体植入术后黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与最佳矫正视力的相关性研究
2014-07-25旷琳杨蕾蕾
旷琳 杨蕾蕾
【应用研究】
白内障超声乳化人工晶状体植入术后黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与最佳矫正视力的相关性研究
旷琳 杨蕾蕾
白内障;超声乳化吸出;人工晶状体植入术;黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度;最佳矫正视力
目的 探讨白内障超声乳化吸出联合人工晶状体植入术后黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与最佳矫正视力(best corrected visual acuity,BCVA)的相关性。方法 选取2013年1月至2014年3月于我院接受超声乳化吸出联合人工晶状体植入术治疗的67例(83眼)白内障患者的临床资料进行回顾性分析,根据患者术后黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度将患者分为低厚度组(≤330 μm)、中厚度组(330~350 μm)及高厚度组(≥350 μm),对比3组术后1周及术后1个月的BCVA差异,同时分析术后1周黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA的相关性。结果 3组术后1周及1个月BCVA均较术前显著提高,差异均有统计学意义(均为P>0.05);但术后1周及术后1个月BCVA比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后1周、1个月低厚度组BCVA均明显高于中厚度组及高厚度组,差异均有统计学意义(均为P<0.05),而中厚度组BCVA明显高于高厚度组,差异均有统计学意义(均为P<0.05)。术后1周低厚度组、中厚度组和高厚度组黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度分别为(322.67±36.61)μm、(341.72±37.36)μm、(352.61±29.59)μm,相关性分析显示,术后1周黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA存在显著的负相关(r=-0.724,P=0.000)。术后1周低厚度组、中厚度组和高厚度组BCVA与术前差值分别为-0.56±0.12、-0.41±0.41、-0.23±0.56,相关性分析显示,术后1周黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA差值也存在显著的负相关(r=-0.613,P=0.000)。结论 超声乳化吸出联合人工晶状体植入术后患者的黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA存在显著的负相关性。
[眼科新进展,2014,34(12):1167-1169]
白内障好发于老年人,可因眼部老化、外伤、营养障碍、中毒及辐射等原因而发病,晶状体蛋白质首先变性,进而发生晶状体混浊,阻扰光线到达视网膜,从而出现视物不清症状。本病可单眼发病,也可双眼同时发病。目前本病的治疗主要有药物及手术治疗,且每种治疗方法均有其特定的治疗指征,且各种治疗方法的治疗后视力也并不相同。本研究对我院应用白内障超声乳化吸出联合人工晶状体植入术后黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与最佳矫正视力(best corrected visual acuity,BCVA)的相关性进行分析,现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2013年1月至2014年3月于我院接受超声乳化吸出联合人工晶状体植入术治疗并行OCT检查的67例(83眼)白内障患者作为观察对象。所有入选患者均符合白内障诊断标准,同时均有完整的临床资料,均排除患有除白内障外其他眼科疾病者及既往行眼科手术治疗者。所有入选患者根据其术后黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度,分为低厚度组(≤330 μm)、中厚度组(330~350 μm)及高厚度组(≥350 μm)。低厚度组15例(23眼),其中男8例(16眼),女7例(7眼),年龄52~76(63.67±9.58)岁;病程1~6(3.78±1.15)个月;中厚度组23例(27眼),其中男17例(19眼),女6例(8眼),年龄53~77(63.91±9.28)岁,病程1~5(3.36±1.56)个月;高厚度组29例(33眼),其中男21例(23眼),女9例(10眼),年龄53~77(63.78±9.81)岁,病程1~7(3.88±1.65)个月;3组性别、年龄及病程比较差异均无统计学意义(均为P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.2 手术方法 术前根据SRK-II公式计算需植入的人工晶状体度数,均植入非球面折叠人工晶状体。术前常规散瞳,球后麻醉。开睑后,以上穹隆部基底做结膜瓣,巩膜电凝止血。在角膜缘后1.5 mm处作3.0 mm左右直线巩膜隧道切口,将巩膜隧道分离至角膜内。角膜刀在距角膜缘前约1.0 mm处进入前房,并选取3点或9点钟方位在透明角膜处做辅助侧切口,将黏弹剂注入前房内,然后用撕囊镊连续撕囊,水分离囊与皮质,水分层核与皮质,超声乳化晶状体核并吸出,将皮质用注吸手柄吸尽,后囊膜抛光,并将黏弹剂注入囊袋及前房内,适当扩大切口,植入人工晶状体至囊袋内,吸除囊袋及前房内黏弹剂,灌注恢复眼压,密闭切口。术后妥布霉素地塞米松眼膏涂眼并包扎,全部手术均由同一经验丰富医师完成。
1.3 观察指标 利用SPECTRALIS-OCT 检测记录患者术后黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度,同时检测患者术前、术后1周及术后1个月的BCVA,并对患者黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与术后1周BCVA及手术前后BCVA差值相关性进行分析。
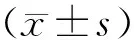
2 结果
2.1 BCVA 3组手术前后BCVA比较见表1。从表1可知,3组术前BCVA比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);3组术后1周及1个月BCVA均较术前显著提高,差异均有统计学意义(均为P>0.05);但术后1周及术后1个月BCVA比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后1周、1个月低厚度组BCVA均明显高于中厚度组及高厚度组,差异均有统计学意义(均为P<0.05),而中厚度组BCVA明显高于高厚度组,差异均有统计学意义(均为P<0.05)。

表1 3组手术前后BCVA比较Table 1 Comparison of preoperative and postoperative BCVA among three groups
2.2 黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA的相关性 术后1周低厚度组、中厚度组和高厚度组黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度分别为(322.67±36.61)μm、(341.72±37.36)μm、(352.61±29.59)μm,相关性分析显示,术后1周黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA存在显著的负相关(r=-0.724,P=0.000)。术后1周低厚度组、中厚度组和高厚度组BCVA与术前差值分别为-0.56±0.12、-0.41±0.41、-0.23±0.56,相关性分析显示,术后1周黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA差值也存在显著的负相关(r=-0.613,P=0.000)。
3 讨论
目前有研究认为白内障患者视力下降主要与患者的像差相关[1-2]。生理情况下,人眼也可产生一定的像差,人体角膜虽可消除一定的像差,但无法完全将其抵消[3-4]。随着年龄的增加,角膜抵消像差的作用也逐渐减低[5]。同时老年人晶状体折射率增大,也可使老年人视力显著下降[6]。超声乳化吸出联合人工晶状体植入手术治疗,可取出白内障患者晶状体并置入人工晶状体,可使光线通过晶状体,但手术治疗后视力改善程度并不理想[7],其与患者自身眼部状况有关[8-9]。
本研究对我院接受超声乳化吸出联合人工晶状体植入手术治疗并行OCT检查的白内障患者的临床资料进行回顾性分析,以分析患者术后黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA的相关性。本观察中所应用的OCT检查,是近年来应用于眼科检查的常用方法,有着分辨率高、检查速度快及器械体积更小等优点,故应用其进行检查,可有效地提高检查准确性,国外相关研究证明OCT检查可以为外科手术提供更多有价值的信息[10]。结果显示:3组患者术后1周及1个月BCVA均较术前显著提高,但术后1周与术后1个月BCVA比较差异无统计学意义。同时低厚度组BCVA均明显高于中厚度组及高厚度组,而中厚度组BCVA明显高于高厚度组。本观察中所有患者均接受人工晶状体植入手术,其植入的人工晶状体均为同一厂家、同一批次生产,但患者术后根据不同黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度分组后的视力均存在显著差异,可见其不同黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度患者其BCVA存在显著的差异。同时经相关性分析显示,黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA存在显著的负向直线相关性,研究表明其为BCVA的唯一独立决定因素[11]。本观察中,在除外人工晶状体对患者术后视力的影响后,对黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA的相关性进行分析,结果显示,白内障接受超声乳化吸出联合人工晶状体植入术治疗后随着黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度的增加,患者BVCA却随之降低,与国内相关研究结论一致[12]。分析其原因可能与黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度对射入眼部的光线敏感度不同所致。
综上所述,白内障患者行超声乳化吸出联合人工晶状体植入术治疗后患者的黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与BCVA存在显著的负向相关性。
1 Liang JZ,Williams DR.Aberration and retinal image quality of the normal human eye[J].JOptSocAmAOptImageSciVis,1997,14(11):2873-2883.
2 贾丁,瞿佳.高度近视的病因学研究进展[J].眼视光学杂志,2003,5(2):123-125.
3 Moreno-Barriuso E,Marcos J,Navarro R,Burns SA.Comparing laser ray tracing,the spatially resolved refractometer,and Hartmann-shack sensor to measure the ocular wave aberration[J].OptomVisSci,2001,78(3):152-156.
4 Holladay JT,Piers PA,Koranyi G,van der Mooren M,Norrby NE.A new intraocular lens design to reduce spherical aberration of pseudophakic eyes[J].JRefractSurg,2002,18(6):683-691.
5 Artal P,Berrio E,Guirao A,Piers P.Contribution of the cornea and internal surface to the change of ocular aberration with age[J].JOptSocAmAOptImageSciVis,2002,19(1):137-143.
6 Artal P,Guirao A,Berrio E,Willimas DR.Compensation of corneal aberrations by the internal optics in the human eye[J].JVis,2011,1(1):1-8.
7 汤萍,潘永称.高度近视白内障患者人工晶状体屈光度数计算公式的选择[J].中华眼科杂志,2003,39(5):290-293.
8 Tsang CS,Chong GS,Yiu Ep,Ho CK.Intraocular lens power calculation formulas in Chinese eyes with high axial myopia[J].JCataractRefractSurg,2003,29(7):1358-1364.
9 Packer M,Fine IH,Hoffman RS,Piers PA.Improved functional vision with a modified prolate intraocular lens[J]?JCataractRefractSurg,2004,30(5):986-992.
10 Tanner V,Chauhan DS,Jackson TL,Williamson TH.Optical coherence tomography of the vitreoretinal interface in macular hole formation[J].BrJOphthalmol,2011,85(9):1092-1099.
11 Noma H,Funatsu H,Harino S,Nagaoka T,Mimura T,Hori S.Influence of macular microcirculation and retinal thickness on visual acuity in patients with branch retinal vein occlusion and macular edema[J].JpnJOphthalmol,2010,54(5):430-434.
12 金淑萍.黄斑病变治疗后黄斑区结构和功能的改变[D].昆明医科大学,2013.
date:Jul 27,2014
Accepted date:Sep 30,2014
From theDepartmentofOphthalmology,PuaiHospitalAffiliatedtoTongjiMedicalCollege,HuazhongSci-techUniversity,Wuhan430000,HubeiProvince,China
Relationship between macular foveal retinal thickness and BCVA after phacoemulsification and IOL implantation
KUANG Lin,YANG Lei-Lei
cataract;phacoemulsification;intraocular lens implantation;macular foveal retinal thickness;best corrected visual acuity
Objective To discuss the relationship between macular foveal retinal thickness and best corrected visual acuity (BCVA)after phacoemulsification and intraocular lens (IOL)implantation.Methods Sixty-seven cataract patients (83 eyes)underwent phacoemulsification and IOL implantation in our hospital from January 2013 to March 2014 were retrospectively analyzed.According to the postoperative macular foveal retinal thickness,the patients were divided into low thickness group(≤330 μm),moderate thickness group (330-350 μm)and high thickness group (≥350 μm),the differences of BCVA at postoperative 1 week and 1 month between three groups were compared,and the relationship between macular foveal retinal thickness and BCVA at postoperative 1 week was analyzed.Results The BCVA at postoperative 1 week and 1 month in three groups were all increased,there were statistical differences (allP<0.05),but no difference was found between postoperative 1 week and 1 month (P>0.05).BCVA at postoperative 1 week and 1 month in low thickness group were obviously higher than those in moderate and high group,there were statistical differences (allP<0.05),and the moderate group was higher than the high thickness group,there were statistical differences (allP<0.05).The macular foveal retinal thickness at postoperative 1 week in low,moderate and high thickness group were (322.67±36.61)μm,(341.72±37.36)μm and (352.61±29.59)μm,respectively.The macular foveal retinal thickness at postoperative 1 week was negative correlated with BCVA (r=-0.724,P=0.000).BCVA values different from pre-operation at postoperative 1 week in low,moderate and high thickness group were-0.56±0.12,-0.41±0.41 and -0.23±0.56,respectively.The macular foveal retinal thickness at postoperative 1 week was negative correlated with BCVA differences (r=-0.613,P=0.000).Conclusion The macular foveal retinal thickness in cataract patients after phacoemulsification and IOL implantation is obviously negative correlated with BCVA.
旷琳,杨蕾蕾.白内障超声乳化人工晶状体植入术后黄斑中心凹视网膜厚度与最佳矫正视力的相关性研究[J].眼科新进展,2014,34(12):1167-1169.
10.13389/j.cnki.rao.2014.0324
旷琳,女,1971年7月出生,湖北人,副主任医师。研究方向:白内障。联系电话:18672319315;E-mail:kl1971@163.com
About KUANG Lin:Female,born in July,1971.Associate chief physician.Tel:18672319315;E-mail:kl1971@163.com
2014-07-27
修回日期:2014-09-30
本文编辑:周志新
430000 湖北省武汉市,华中科技大学同济医学院附属普爱医院眼科
[Rec Adv Ophthalmol,2014,34(12):1167-1169]
