多通道混沌调制模拟-信息转换
2014-05-22陈胜垚
陈胜垚 席 峰 刘 中
多通道混沌调制模拟-信息转换
陈胜垚*席 峰 刘 中
(南京理工大学电子工程系 南京 210094)
为了降低混沌调制中采样通道的采样速率,该文提出一种多通道混沌调制模拟-信息转换结构。该结构通过采样参数调制混沌系统的多个状态输出作为压缩测量,可实现在总采样速率不变的情况下降低每个采样通道的采样速率。与混沌调制相比,多通道混沌调制增加了低速采样单元的个数,但显著提高了高稀疏度信号的重构性能。基于混沌脉冲同步理论,该文给出了多通道混沌调制结构的信号可重构条件与被采样状态变量选择方法。以Lorenz系统为例,仿真验证了多通道混沌调制结构的有效性。
混沌压缩感知;混沌调制;多通道混沌调制;模拟-信息转换;可重构性
1 引言
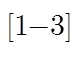
混沌调制压缩采样系统由测量系统和重构系统两部分组成[12]。在测量系统中,模拟稀疏信号被调制到混沌系统参数上,以外加激励的方式作用于驱动混沌系统;通过对驱动系统输出(或状态)的采样实现压缩采样。重构系统根据混沌脉冲同步理论和基于同步的混沌参数估计技术恢复原激励信号。将压缩采样作为同步脉冲驱动响应混沌系统,然后利用混沌同步误差来估计激励信号的参数,当响应系统与驱动系统实现脉冲同步时,通过信号合成输出重构激励信号。
值得注意的是,混沌调制重构系统建立在混沌脉冲同步基础之上。因此,混沌调制的降采样速率受到混沌系统最大可同步采样间隔的限制。为了降低混沌调制中采样通道的采样速率,本文提出一种多通道混沌调制结构。该结构通过采样参数调制混沌系统的多个状态变量,可获得了更大的可同步采样间隔,从而能够在总采样速率不变的前提下有效降低每个采样通道的采样速率。在相同的低速采样通道数下,多通道混沌调制实现复杂度远小于随机调制预积分模拟-信息转换[13]结构,且具有更高的信号重构性能。另外,基于混沌脉冲同步理论[14],本文还给出了多通道混沌调制的信号可重构条件和被采样状态变量选择方法。为了验证多通道混沌调制的有效性,本文以Lorenz系统为例进行了仿真实验,验证了多通道混沌调制结构的可实现性和有效性。
2 多通道混沌调制基本框架
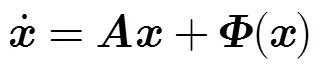
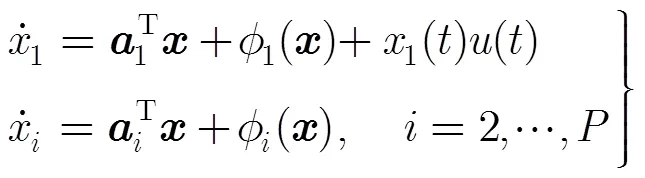
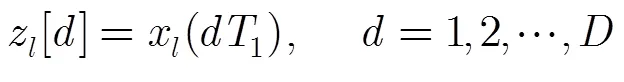
多通道混沌调制重构系统如图1(b)所示。在多通道混沌调制重构系统中,响应混沌系统的系统结构与系统式(2)相同,其演化过程可由如下的脉冲微分方程描述:
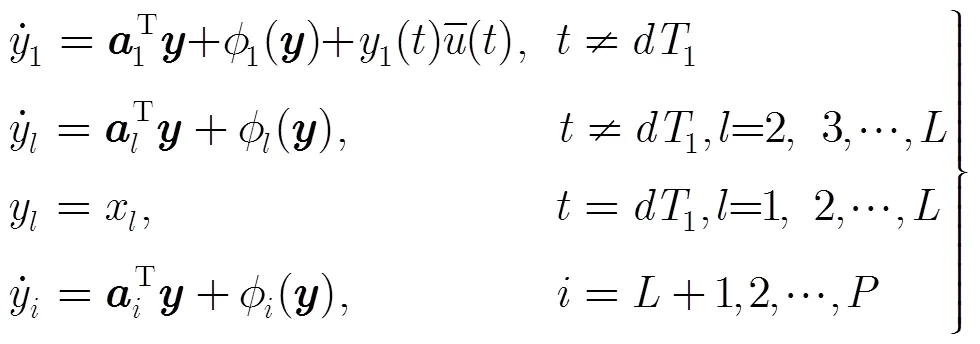
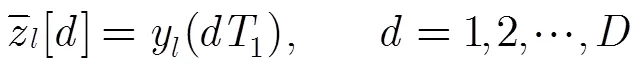
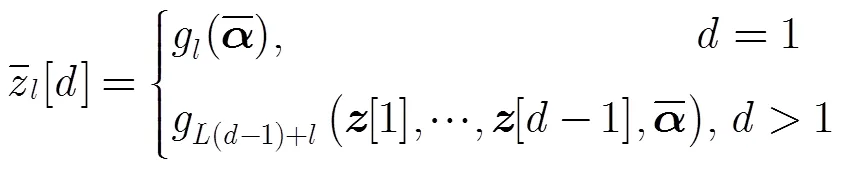
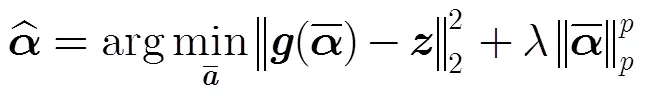
3 信号可重构性分析与被采样状态变量选择
3.1 信号可重构性分析
信号可重构性分析是CS理论的核心问题之一,是判断模拟-信息转换结构能否有效感知信号的理论工具。在线性CS中,存在多种方法来衡量测量矩阵的信号可重构性,其中约束等距特性(Restricted Isometry Property, RIP)是最常用的一种方法。通过分析线性模拟-信息转换结构等效测量矩阵的RIP,可定性获得该结构的信号重构性能和适用范围,例如随机采样和随机解调适合用于感知频域稀疏信号[6,8],随机卷积适合由于感知任意稀疏信号[16]。对于ChaCS,由于混沌系统的高度非线性,传统基于线性CS推广而来的非线性CS信号可重构性分析方法[17]不再适用。为了有效分析多通道混沌调制的信号可重构性,本文从混沌同步的观点出发,给出一种适用于ChaCS的新型信号可重构条件。
命题1从混沌脉冲同步角度给出了信号的可重构条件。理论上,只要响应系统同驱动系统可同步,稀疏信号即可被重构。通过计算误差系统的最大SLLE,就可以确定可同步的脉冲采样间隔和被采样状态变量组合。信号重构通过估计重构系统的激励信号参数实现,当误差系统的最大SLLE为负数时,稀疏信号系数可根据同步误差估计出来。然而,在信号重构实际实现时,重构系统中控制算法求解的问题式(7)是一个非凸优化问题,信号重构质量受到控制算法性能的影响,当信号稀疏度增加时,控制算法更容易收敛到局部最优解。
3.2 被采样状态变量选择
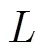
下面,以Lorenz混沌系统为例展示如何选择被采样状态变量组合。Lorenz系统的系统方程为
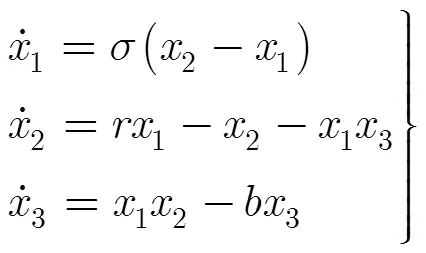
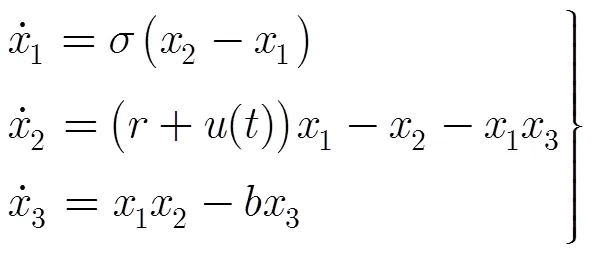
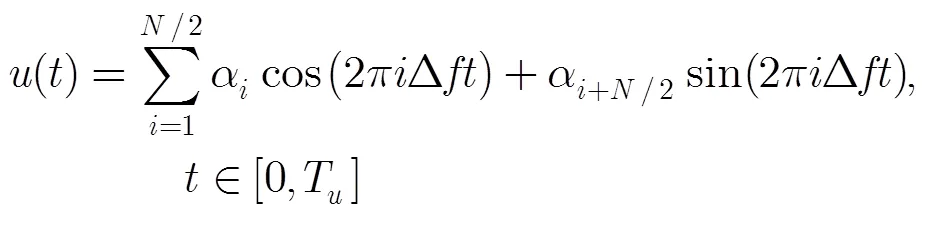
4 仿真分析

图2 采样不同状态变量组合时Lorenz误差系统的最大SLLE
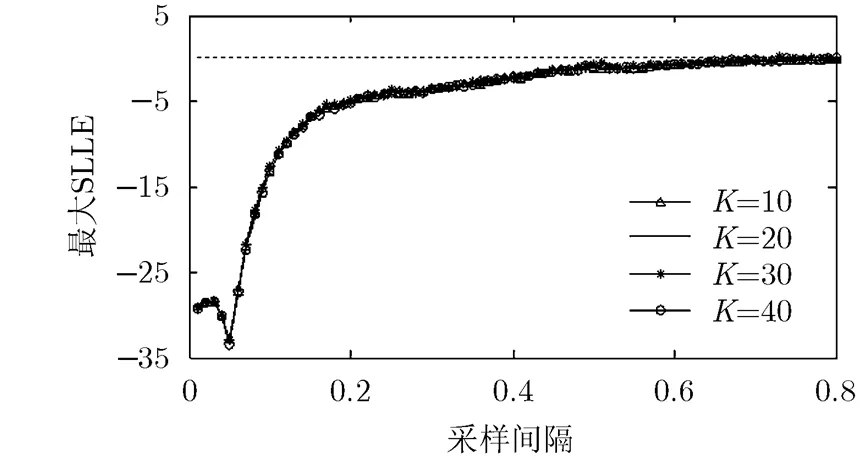
图3不同稀疏度信号调制时参数调制Lorenz误差系统的最大SLLE
可以看出,在两种概率分布信号情况下,多通道混沌调制的信号重构性能均优于混沌调制,尤其是在信号稀疏度较高的情况下。该现象产生的原因是多通道采样包含了多个混沌状态变量的信息,得到的测量值随机化程度更强,从而得到了更好的信号重构性能。
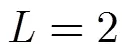
5 结论
混沌调制是由混沌压缩感知理论发展而来的非线性模拟-信息转换结构,该结构比基于线性压缩感知的随机解调结构具有更好的信号可重构性能。本文将混沌调制拓展到多通道采样情况,提出一种多通道混沌调制模拟-信息转换结构,以降低混沌调制中采样通道的采样速率。该结构可实现在总采样速率不变的情况下降低每个采样通道的采样速率,且增加的硬件开销较小。另外,本文基于混沌脉冲同步理论,给出了多通道混沌调制的采样状态变量选择方法和信号可重构条件,为该结构的工程实现提供了一定的理论指导。最后,本文以Lorenz系统为例仿真分析了多通道混沌调制的信号重构性能,验证了该结构的可实现性和有效性。
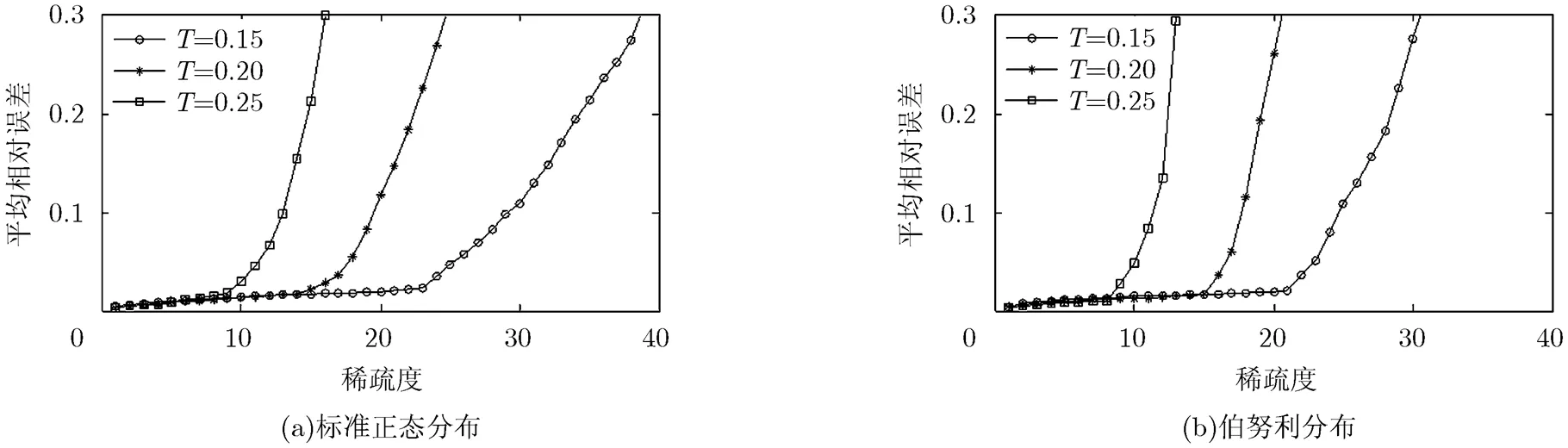
图4 不同采样间隔和稀疏度下单通道混沌调制的信号重构性能
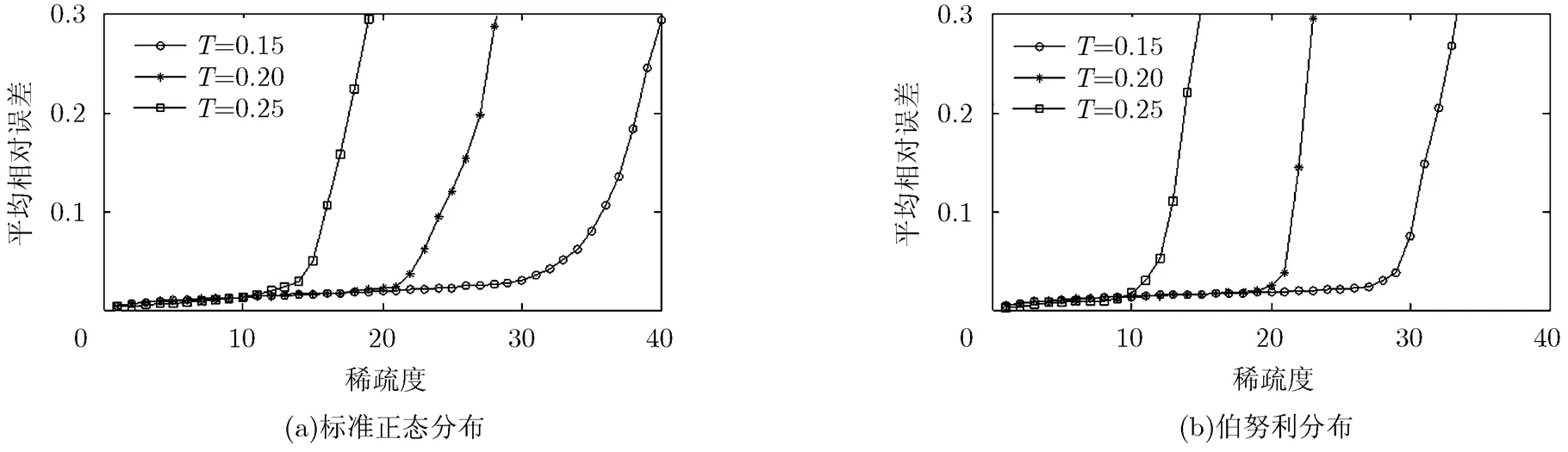
图5 不同采样间隔和稀疏度下多通道混沌调制的信号重构性能
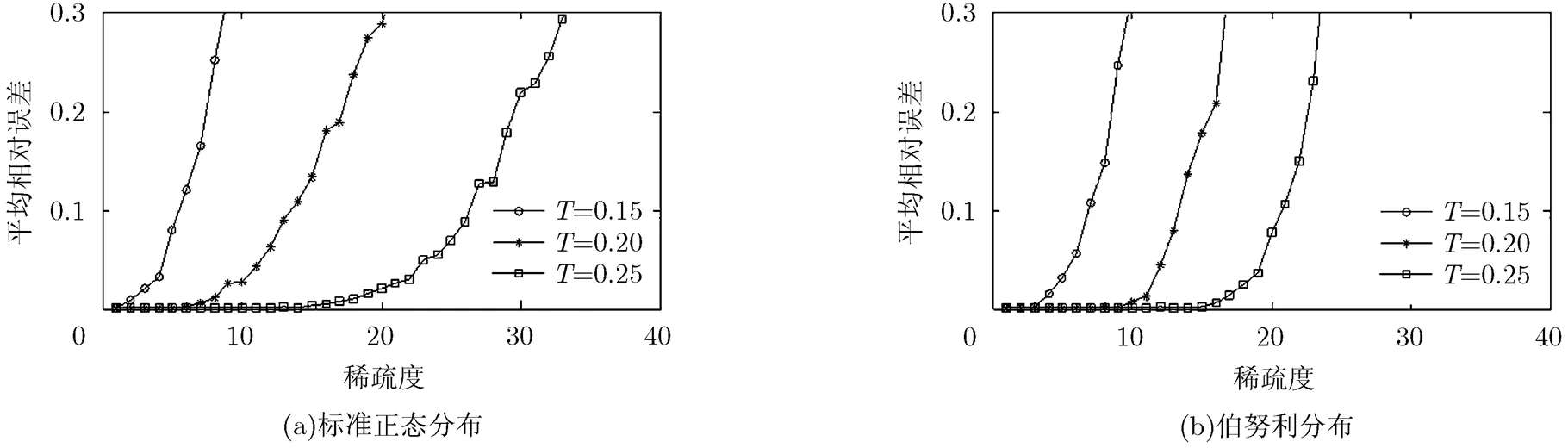
图6 不同采样间隔和稀疏度下RMPI的信号重构性能
[1] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]., 2006, 52(4): 1289-1306.
[2] Candès E J, Romberg J, and Tao T. Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information[J]., 2006, 52(2): 489-509.
[3] Candès E J and Tao T. Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies?[J]., 2006, 52(12): 5406-5425.
[4] Liu Z, Chen S Y, and Xi F. A compressed sensing framework of frequency-sparse signals through chaotic systems[J]., 2012, 22(6): 1250151.1-1250151.9.
[5] 陈胜垚, 席峰, 刘中. 基于混沌压缩感知的稀疏时变信号在线估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(4): 838-843.
Chen Sheng-yao, Xi Feng, and Liu Zhong. Online estimation of sparse time-varying signals with chaotic compressive sensing[J].&, 2012, 34(4): 838-843.
[6] Laska J N, Kirolos S, Massoud Y,. Random sampling for analog-to-information conversion of wideband signals[C]. IEEE Dallas/CAS Workshop on Design, Applications, Integration and Software, Dallas, USA, 2006: 119-122.
[7] Tropp J A, Wakin M B, Duarte M F,. Random filters for compressive sampling and reconstruction[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toulouse, France, 2006: 872-875.
[8] Tropp J A, Laska J N, Duarte M F,. Beyond Nyquist: efficient sampling of sparse bandlimited signals[J]., 2010, 56(1): 520-544.
[9] Taheri O and Vorobyov S A. Segmented compressed sampling for analog-to-information conversion: method and performance analysis[J]., 2011, 59(2): 554-572.
[10] Xi F, Chen S Y, and Liu Z. Chaotic analog-to-information conversion: principle and reconstructability with parameter identifiability[OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1212.2725, 2012, Dec.

Xi Feng, Chen Sheng-yao, and Liu Zhong. Chaotic analog-to-information conversion: sparse signal reconstruction with multiple shooting method[J].&, 2013, 35(3): 608-613.
[12] Chen S Y, Xi F, and Liu Z. Chaotic modulation for analog-to-information conversion[OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/ 1301.0387, 2013, Jan.
[13] Becker S. Practical compressed sensing: modern data acquisition and signal processing[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], California Institute of Technology, 2011.
[14] Chen S Y, Xi F, and Liu Z. Supreme local Lyppunov exponents and chaotic impulsive synchronization[OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1212.5770, 2013, April.
[15] 陈胜垚, 席峰, 刘中.范数正则化的混沌压缩感知信号重构性能[J]. 系统仿真学报, 已录用.
Chen Sheng-yao, Xi Feng, and Liu Zhong. Reconstruction performance of chaotic compressive sensing with-norm regularization[J]..
[16] Romberg J. Compressive sensing by random convolution[J]., 2009, 2(4): 1098-1128.
[17] Blumensath T. Compressed sensing with nonlinear observations and related nonlinear optimisation problems[J]., 2013, 59(6): 3466-3474.
[18] Willsey M S Cuomo K M, and Oppenheim A V. Quasi-orthogonal wideband radar waveforms based on chaotic systems[J]., 2011, 47(3): 1974-1984.
[19] Chartrand R and Yin W. Iteratively reweighted algorithms for compressive sensing[C]. Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Las Vegas, USA, 2008: 3869-3872.
陈胜垚: 男,1985 年生,博士后,主要研究方向为压缩采样、混沌同步和参数估计.
席 峰: 男,1980 年生,副教授,主要研究方向为压缩采样、雷达信号处理、传感器网络.
刘 中: 男,1963 年生,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为混沌与信息动力学、现代信号处理等.
Multi-channel Chaotic Modulation for Analog-to-information Conversion
Chen Sheng-yao Xi Feng Liu Zhong
(,,210094,)
To reduce the sampling rate in chaotic modulation, this paper proposes a multi-channel chaotic modulation Analog-to-Information Conversion (AIC) structure. The proposed structure samples multiple-channel state outputs of parameter-modulation chaotic system to obtain compressed measurements and reduces the sampling rate of each sampling channel with total sampling rate unchanged. In comparison with chaotic modulation, the new structure increases the number of sampling units, but greatly enhances the reconstruction performance of the high-sparsity signals. According to chaotic impulsive synchronization theory, the reconstruction condition is developed and the method to select the sampled system states is supplied. The Lorenz system is taken an example to study the reconstruction performance of frequency-sparse signals. Numerical simulations illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed AIC structure.
Chaotic compressive sensing; Chaotic modulation; Multi-channel chaotic modulation; Analog-to-Information Conversion (AIC); Reconstructability
TN911.7
A
1009-5896(2014)01-0152-06
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00476
2013-04-11收到,2013-07-18改回
国家自然科学基金(60971090, 61101193)资助课题
陈胜垚 chen_shengyao@163.com
