长链非编码RNA在青少年特发性脊柱侧凸中的表达研究
2014-04-07刘晓阳邱贵兴翁习生吴志宏于斌王以朋
刘晓阳 邱贵兴 翁习生 吴志宏 于斌 王以朋
(中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院骨科,北京 100730)
长链非编码RNA在青少年特发性脊柱侧凸中的表达研究
刘晓阳 邱贵兴 翁习生 吴志宏 于斌 王以朋*
(中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院骨科,北京 100730)
背景:长链非编码 RNA(lncRNAs)是真核细胞中 一类长度 超过 200 核苷酸的非编码 RNA 分子,与人类众多疾病的发生有密切的关系。然而,lncRNAs在青少年特发性脊柱侧凸(AIS)的表达情况尚不清楚。
目的:利用基因芯片筛选AIS患者外周血中差异表达的lncRNAs和mRNAs,分析lncRNAs在 AIS发病中的可能作用。
方法:选取 2013 年北京协和医院就诊的 20 例 AIS 患者和 20 例正常对照。利用 Agilent human lncRNA+mRNAArray V3.0 微阵列芯片检测 4 例 AIS 患 者和 4 例年龄匹配的正常对照的 lncRNAs和 mRNAs表达,对差异表达的 mRNAs进行GO、Pathway 分析,构建 lncRNAs和 mRNAs的共表达网络,预测 lncRNAs的可能调控靶点。
结果:AIS 患者中差异表达的 lncRNAs有 139 条,差异表达的 mRNAs有 546 条。GO 分析发现,差异表达的 mRNAs产物主要参与蛋白结合、金属离子结合、核苷酸结合、调节转录、RNA剪切等。差异表达的mRNAs主要参与细胞黏附分子、Wnt通路、Toll样受体通路、MAPK 通路等。靶基因预测,7 条 lncRNAs可能通过调节 mRNAs的表达参与了 AIS的发病。结论 :本研 究发 现了 AIS 患 者外 周 血 中 差 异 表 达 的 lncRNAs 和 mRNAs。lncRNAs可能 通过 调控 mRNA 的 表 达 参 与AIS的发病或发展。
特发性脊柱侧凸;青少年;长链非编码RNA
Background:Long noncoding RNAs(lncRNAs)are broadly classified as transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides,which function in a wide range of diseases.Expression profile of lncRNAs inAIS was still unclear.
Objective:To detect differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs in peripheral blood samples from AIS patients using microarray and explore the role of lncRNAin the pathogenesis ofAIS.
Methods:A total of 20 AIS patients from Peking Union Medical College Hospital were recruited as cases together with 20 healthy controls.Peripheral blood was collected from 4 patients with AIS and 4 age-matched normal children and tested with Agilent human lncRNA+mRNA Array V3.0.GO and Pathway analysis was performed.The coding-non-coding gene co-expression network was constructed based on the correlation analysis.Target regulated by lncRNAs was predicted with bioinformatic prediction.
Results:A total of 139 deregulated lncRNAs and 546 deregulated mRNAs were detected in AIS patients.GO Term enrichment in the differentially expressed mRNA list included protein binding,metal ion binding,nucleotide binding,regulation of transcription,RNA splicing et al.Differentially expressed mRNAs may involve in Cell adhesion molecules,Wnt signaling pathway,Toll-like receptor signaling pathway,MAPK signaling pathway and so on.Seven lncRNAs may regulate mRNAs expression in pathogenesis ofAIS.
Conclusions:This is the first time to find lncRNAs and mRNAs expression in AIS patients using microarray.Differentially expressed lncRNAs may play a role in the pathogenesis ofAIS.
青 少 年 特 发 性 脊 柱 侧 凸(adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,AIS)占特发性脊柱侧凸总数的 80%左右,累及脊柱、胸廓、肋骨、骨盆,不但影响外观,还严重影响生命质量及预期寿命。大规模流行病学调查发现,AIS 患者的子女患病率高达 27%,远高于人群发病率[1],单卵双生的 AIS 发病一致性远高于异卵双生子,提示 AIS 具有遗传倾向[2]。目前连锁分析定位了一些 AIS 病因相关区域[3,4],关联分析也发现了一些基因多态性与 AIS 的临床特征相关[5,6]。然 而 ,不同研究的结论并不一致[7]。无论是连锁分析的阳性连锁区域还是关联分析的阳性基因,均不能很好解释AIS的遗传方式和发病机制。
长 链 非 编 码 RNA(long non-coding RNAs,lncRNAs)是一类在真核细胞内被普遍转录的长度超过200个核苷酸的功能性RNA分子,不具有或很少具有蛋 白 编码 功 能,但可通 过 RNA-蛋白、RNA-DNA 或RNA-RNA 等 多 种 相 互 作 用 方 式 发 挥 调 控 功 能[8-10]。现有研究已证实,lncRNAs在疾病的发生和发展中发挥了重要作用,许多疾病与lncRNAs的调控有密切的关系[11,12]。到目前为止,国内外尚未开展 AIS 发病机制中 lncRNAs的相关研究,发现 AIS 的 lncRNAs表达谱系对于进一步研究AIS的发病机制具有重要的意义。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
采用病例-对照研究方法,病例组为 2013年4 月至2013年10月在北京协和医院就诊的20例中国汉族 人 群 青 少 年 女 性 AIS 患 者 ,年 龄(14.0± 2.0)岁 ,Cobb 角范围为 47.4°±12.4°。所有患者的体格检查和阅片均由同一名医师完成,根据以下诊断标准确诊:全脊柱侧位片显示Cobb角>15°伴椎体旋转,无椎体的先天性畸形,无椎旁肌萎缩,并排除马凡综合征、神经纤维瘤病、神经系统疾病、骨骺发育不良等疾病。对照组为年龄匹配的正常对照20例,排除脊柱畸形疾病及家族史、内分泌疾病等。采集所有受试者的临床资料、影像学资料,清晨空腹安静状态下抽静 脉 血 6 ml,采 血 后 立 即 与 3 倍 体 积 的 Trizol LS 混匀,分装至EP管中,置于-80℃冰箱保存备用。
1.2 主要试剂及仪器
1.2.1 主 要 试 剂 :Trizol LS(美 国 Ambion 公 司 );异 丙醇、氯仿、无水乙醇(上海化学试剂有限公司);RNA纯 化 试 剂 盒(德 国 QIGEN 公 司 ),PrimeScript RT reagent kit反转录试剂盒(宝生物工程有限公司);定量PCR检测试剂盒(宝生物工程有限公司)。基因芯片检测使用 Agilent human lncRNA+mRNAArray V3.0,委托北京博奥生物技术有限公司进行。
1.2.2 主要 仪器 :ND-1000 超微 量分 光光 度计(美 国NanoDrop 公司);普通 PCR 仪(美国 ABI公司);Realtime PCR 仪(宝 生 物 工 程 有 限 公 司);-80℃ 冰 箱 、高速冷冻离心机等设备以及其他常规仪器。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 基因芯片检测:年龄匹配的 4 例 AIS 患者和 4 例正常对照进行基因芯片分析。外周血和 Trizol LS 冻存混合液室温融化后剧烈摇匀;使用化学试剂发提取 全 血 总 RNA,并 使 用 QIAGEN Rneasy Kit纯 化RNA,所 得总 RNA OD260/OD280≥1.8,电 泳 检 测 有清晰的 18S 和 28S rRNA 条带,同时28S/18S 的比例接近1∶1。反转录合成双链cDNA,进一步合成Cy3荧光标记cRNA,测定浓度和纯度后上芯片进行杂交。使用 Agilent芯片扫描仪(G2565CA)对清洗后的芯片进行扫描,得到杂交图片。
1.3.2 基因芯片数据分析:提取杂交图片数据并进行归一化处理获得各区域荧光强度,经过折叠倍率(fold change,FC)筛选 ,筛 选 出 所 有 差 异 表 达 的 lncRNAs和 mRNAs,参数选择标准为 P<0.05,FC>2。
基 因 本 体 论(gene ontology,GO)分 析 描 述 差 异表达的 mRNAs的功能属性。基于最新的 Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes(KEGG)数据库,对差异表达的mRNAs数据进行生物学途径分析,明确差异表达的mRNAs数据主要富集分布于哪些生物学途径。构建编码基因和非编码基因的共表达网络(the coding-non-coding gene co-expression network),直观显示 lncRNAs和 mRNAs之间的相关性。在 lncRNAs和 mRNAs共表 达基础 上预 测 lncRNAs的 可能调控靶点。Cis-预测寻找基因组位置在 10 kb 之内的 lncRNA-mRNA 对,Trans-预测对lncRNA 和mRNA序列进行比对,筛选序列相似的 lncRNA-mRNA 对。1.3.3 定量 PCR:以年龄匹配的 20 例 AIS 患者和 20 例正常女性为研究对象,选取差异表达较明显的、靶基因预测显示可能参与 AIS 发病的 lncRNAs进行实时定量PCR验证。
2 μg 总 RNA 去除 DNA,反转录成 cDNA。实时定 量 PCR 采 用 20 μl反 应 体 系 ,包 括 SYBR Premix(10 μl)、正向引物(0.4 μl)、反向引物(0.4 μl)、cDNA模板(1 μl)、双蒸水(8.2 μl)。定量 PCR 所用引物由北 京 Inventrogen 生 物 工 程 有 限 公 司 合 成( 表 1)。94℃反应 5 min;变性和扩增和延伸,94℃反应 30 s,58℃反应 30 s,72℃反 应 40 s,共 40 个循 环 ;72℃反应7 min。采用△△cycle threshold(△ △ Ct)方 法 进 行定量分析[13]。每样本重复 3 次,基因平均拷贝数经管家基 因 3-磷 酸 甘 油 醛 脱 氢 酶(Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase,GAPDH)的 拷 贝 数 校 正 。 计 算2-△△Ct值,即为实验组的目的基因表达量是对照组表达量的百分数,大于200%为表达上调,小于50%为表达下调。

表1 实时定量PCR引物
2 结果
2.1 芯片实验结果
2.1.1 差异表达 lncRNAs 和 mRNAs:采用 Agilent human lncRNA+mRNAArray V3.0 检测,AIS 患者有 139条 lncRNAs差异表达。其中上调的 lncRNAs 120 条,下 调 的 lncRNAs 19 条 。 差 异 表 达 的 mRNAs 共 546条,上调表达 mRNAs 512 条,下调表达的 lncRNA 34条 。 上 调 、下 调 倍 数 最 明 显 的 10 条 lncRNAs 和mRNAs分别见表2和表3。通过分层群聚图可直观的看到 AIS 组与 NC 组 lncRNAs与 mRNAs的差异表达(图1A和图1B)。从红色到绿色,颜色越深差异表达越明显。
2.1.2 GO、Pathway 分析:GO 功能分类注释得出 ,差 异表达的mRNAs参与转录调节、免疫反应、信号转导、RNA剪切、凋亡、细胞周期过程、生物学周期过程等过程。Pathway 分 析 显示,差异表达 mRNAs在 细 胞黏附分子、造血细胞、T细胞受体信号通路、结直肠癌、Wnt信号通路等方面功能的基因有显著地变化。
2.1.3 CNC 网 络 图 :相 关 性 分 析 发 现 ,共 64 对 lncRNAs-lncRNAs相关性 、280 对 lncRNAs-mRNAs相关性根据基因之间的相关性,构建CNC网络图。图2显 示 的 AIS 患 者 降 低 表 达 最 多 的 lncRNA p1842 的CNC 网 络 图 。 p1842 同 时 与 8 条 lncRNAs 和 13 条mRNAs具有相关性。
2.1.4 lncRNAs的作用靶点预测:经过Cis-和Trans-预测发现 ,7 条 lncRNAs(uc002ddj.1,uc021tnw.,uc021zdc.1, HIT000067310,ENST00000577528.1,ENST0000060-2322.1,TCONS_00001429)可 能调 控 5 条 mRNAs的表达(表4)。
2.2 定量PCR
选取靶基因可能参与运动系统发育的lncRNAs(ENST00000602322.1 和 HIT000067310)以及差异表达 最 多 的 lncRNAs(ENST00000440778.1、TCONS_ 00028768 和 ENST00000414894.1)用 定 量 PCR 对 基因芯片的结果进行验证。结果显示,4条lncRNAs在扩大样本中得到较好的验证,qPCR的结果与芯片数据趋势基本一致(图3),1条lncRNA的基因芯片结果未能在扩大样本中得到验证。
3 讨论
人类基因组中只有不到2%的序列编码蛋白质,除去大约7%的非转录区,其余91%的基因组序列转录产生非编码 RNA[14]。随着科学技术的发展和相关研究的不断深入,现在越来越多的长链非编码RNA(1ncRNAs)被鉴定出来,并成为病因学研究和分子生物学研究领域中一个全新的热点。现有研究表明,lncRNAs的表达紊乱与多种人类重大疾病的发生发展密切相关[11,15-17],对 lncRNAs 的 深 入 研 究 对 于推动人们对生命现象的重新阐释具有重大意义。本研究揭示了 AIS 疾病中的 lncRNAs表达轮廓,对于进一步研究和探讨AIS的发病机制具有重要的作用和意义。
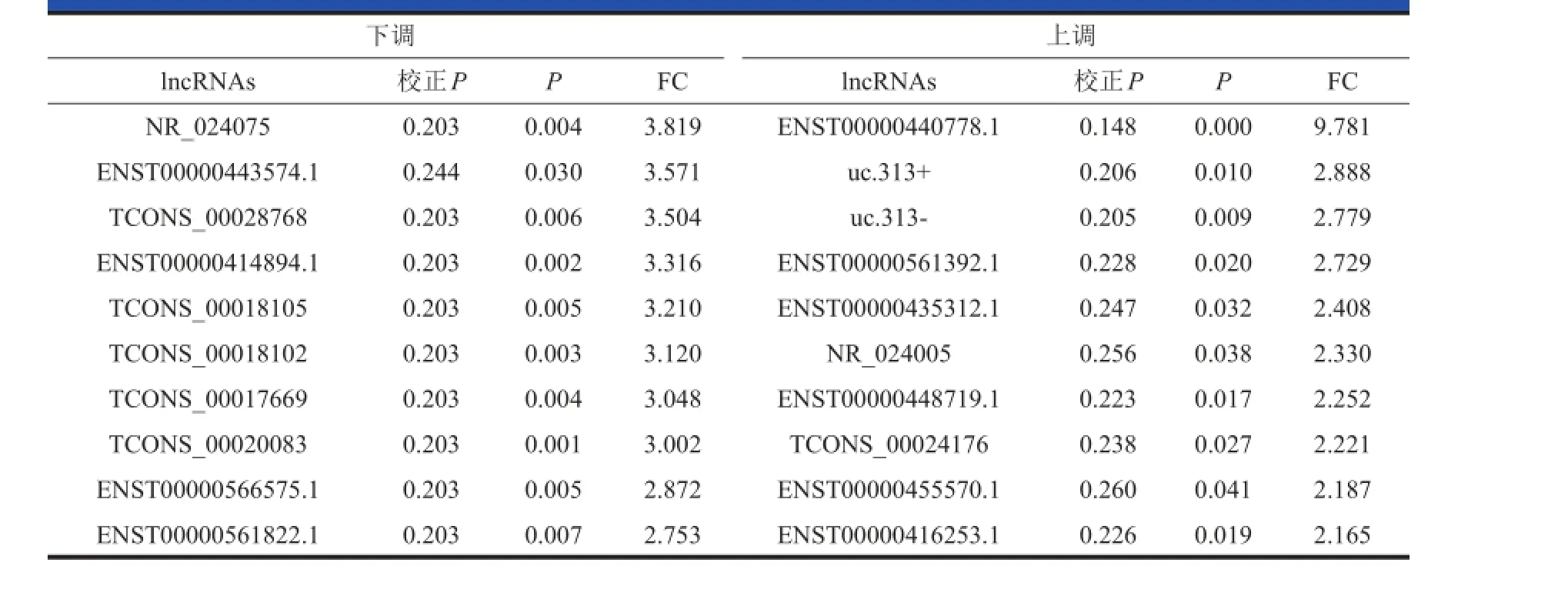
表2 与正常对照组比较,AIS组差异表达前 10 位 lncRNAs
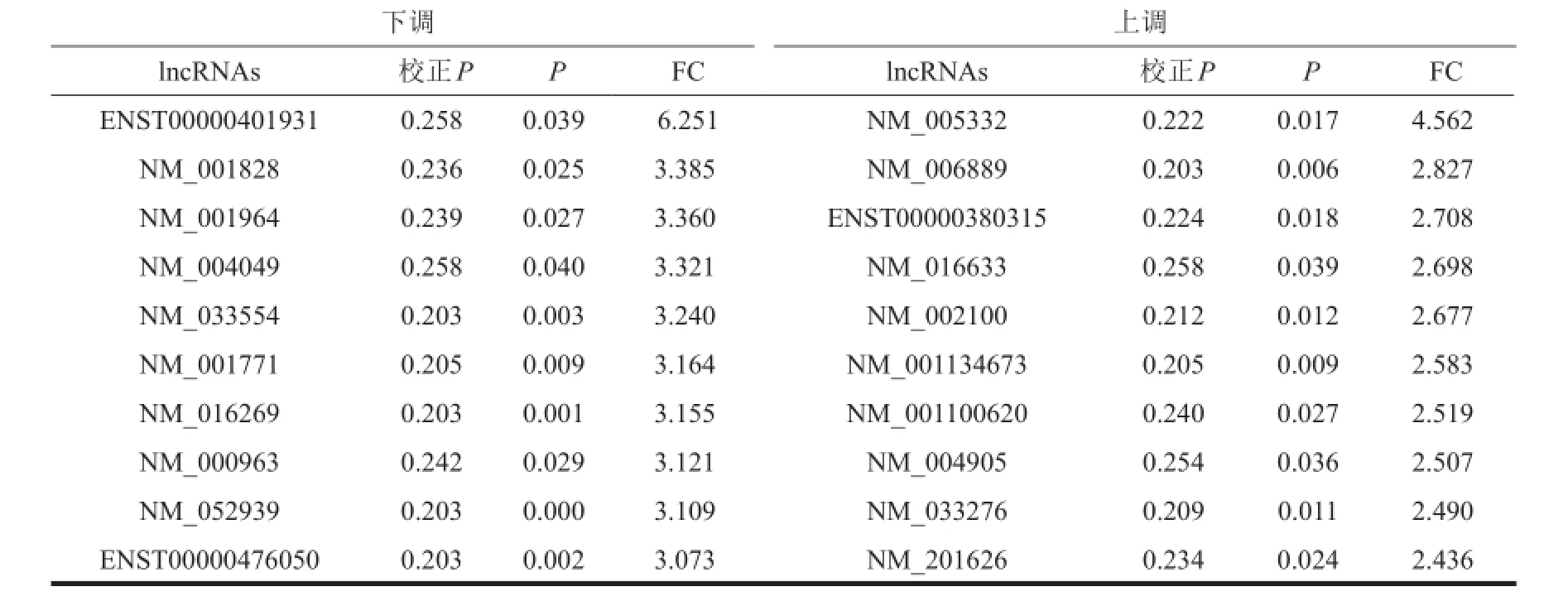
表3 与正常对照组比较,AIS 组差异表达前10位的mRNAs
基因转录是一个受到严格调控的生物学过程。lncRNAs作为细胞中的重要调控因子,也参与了基因的转录调控。此研究中的ENST00000602322.1位于11 号 染 色 体 长 臂 上 ,紧 邻 Pcf11(Protein 1/Cleavage Factor 1)。Pcf11 的编码蛋白参与 pre-mRNA 剪切[18],在调控转录起始、延长以及mRNA的从核内向胞浆转运过程中发挥重要的调节作用[19-21]。Pcf11 在转录和 pre-mRNA 剪切中的作用主要是通过与 RNA 聚合酶 II的 C 端 结 构域(RNA polymerase Ⅱ C-terminal domain(Poly Ⅱ CTD)和多聚腺苷酸因子结合来实现的[22,23]。Poly Ⅱ CTD 的磷酸化状态直接影响 Pcf11 与RNA 聚合酶Ⅱ的结合,lncRNAs作为顺式调控因子间接影响 Pcf11 和 pre-mRNA 的结合[24,25]。鉴于 Pcf11在调控转录和mRNA剪切过程中的重要作用,差异表 达 的 Pcf11 可 能 参 与 了 AIS 发 病 及 发 展 。ENST00000602322.1对 Pcf11 转录和翻译的调控机制也需要在将来研究中进一步确认。
定量 PCR 结果与芯片结果基本一致,4 条 lncRNAs的表达趋势完全一致,只是qPCR结果较芯片数据的差异倍数有所减小。1条 lncRNAs的芯片数据未能在大样本中得到验证,原因可能是芯片检测的偶然误差,也可能是由于样本的个体特征差异引起。部分lncRNAs的群体表达特征还需要大样本人群来验证。ENST00000440778.1 在 AIS 组和 NC 组间的差异仅为 FC=2.17,芯片数据与 qPCR 结果有一定的差距,原因可能是用于芯片检测的样本不能很好的代表人群中lncRNAs的表达轮廓。
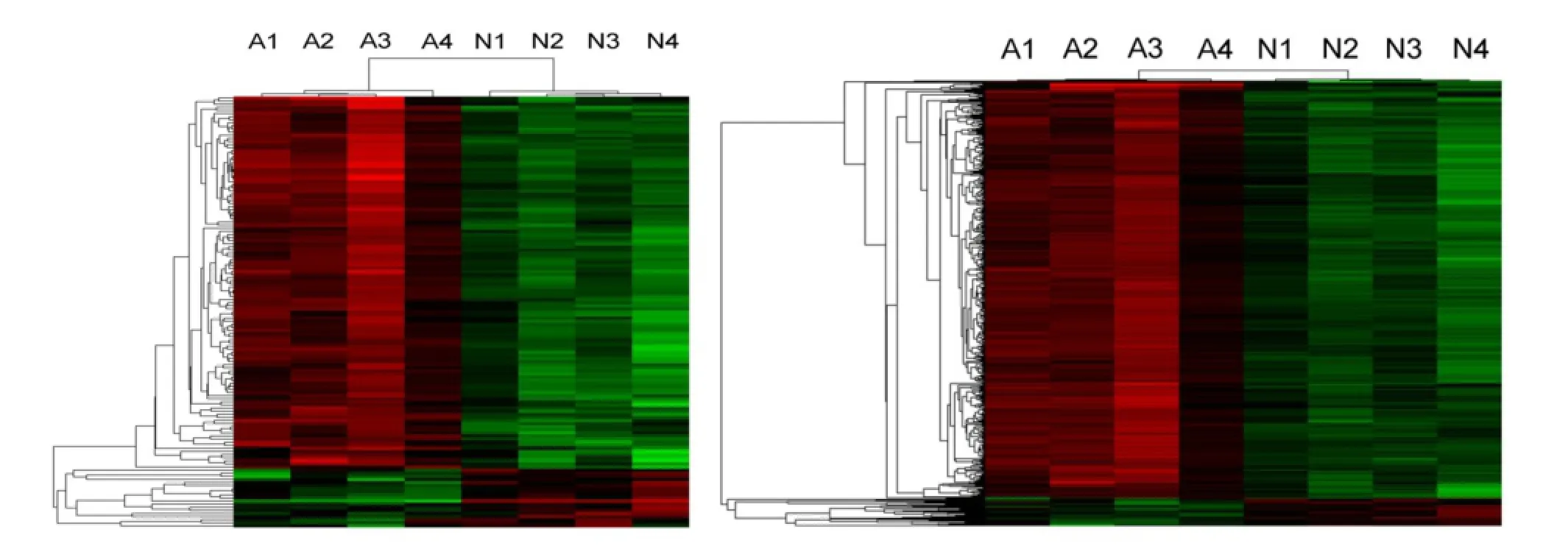
图 1 差异表达的 lncRNAs(左图)和 mRNAs(右图)分层群聚图

图 2 p1842的 CNC网络图三角形代表lncRNA,圆形代表mRNA
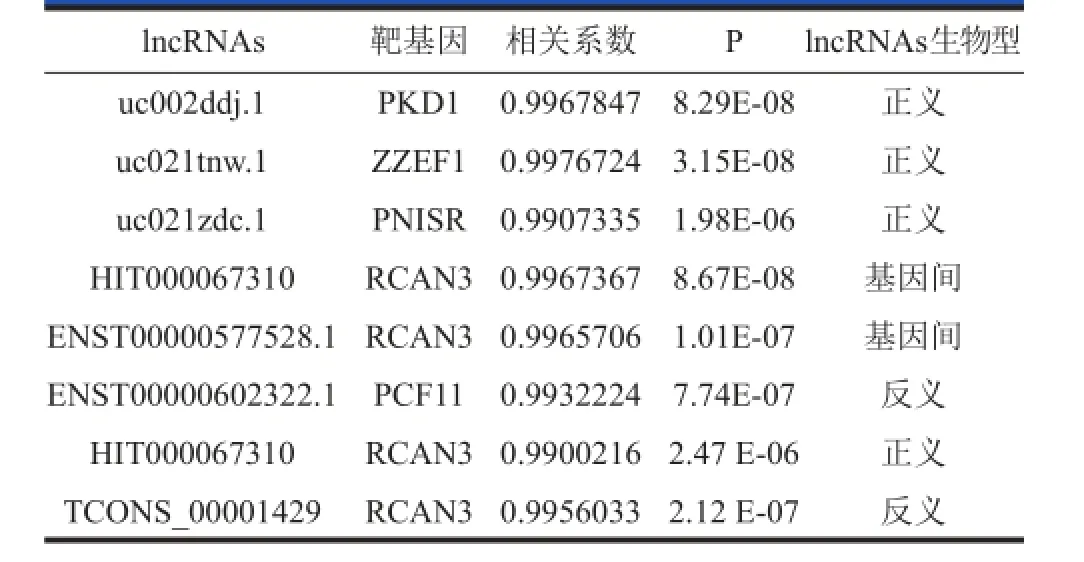
表 4 lncRNAs及其 mRNAs预测靶点信息
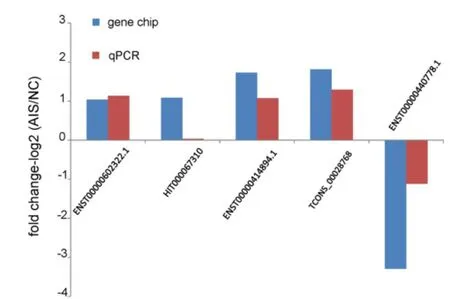
图3 定量PCR验证基因芯片结果
在组织分化和发育过程中,lncRNAs的表达具有时间特异性和空间特异性[26]。lncRNAs较 mRNAs具有更高的特异性,还具有易于检测的特性,采用普通PCR 即可完成[27,28]。因此,该研究发现的 AIS 患者特异性表达的 lncRNAs对于将来发掘 AIS 患者的特异性诊断和预后标记具有重要的指导意义。
我们的研究也具有局限性:①研究发现了大量AIS 患者 差 异表 达的 lncRNAs,这些 差 异表 达的 lncRNAs 可 能 参 与 了 AIS 的 发 病 。 但 是 ,缺 乏 lncRNAs的更详细信息以及它们在 AIS发病中的确切机制。②用于芯片检测的样本每组仅有4对,可能会遗漏一些信息,降低了筛选生物标记的准确性。③此 研 究 标本取自外周血,差 异 表 达的 lncRNAs还需要在骨骼肌肉系统中进一步验证。但是,获取正常青少年的骨骼肌肉具有相当大的难度。因此,将经外周血筛查发现的差异表达的 lncRNAs与 AIS 患者骨骼肌肉系统中的表达状况进行比对,可能进一步 缩小 AIS 发 病相 关 lncRNAs的筛 选范围 ,该 研 究为进一步探讨 lncRNAs在 AIS 发病机制中的作用打下了基础。
[1]Harrington PR.The etiology of idiopathic scoliosis.Clin Orthop Relat Res,1977,(126):17-25.
[2]Kesling KL,Reinker KA.Scoliosis in twins.A meta-analysis of the literature and report of six cases.Spine(Phila Pa 1976),1997,22(17):2009-2015.
[3]Miller NH,Justice CM,Marosy B,et al.Identification of candidate regions for familial idiopathic scoliosis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976),2005,30(10):1181-1187.
[4]Raggio CL,Giampietro PF,Dobrin S,et al.A novel locus for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis on chromosome 12p.J Orthop Res,2009,27(10):1366-1372.
[5]Bae JW,Cho CH,Min WK,et al.Associations between matrilin-1 gene polymorphisms and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis curve patterns in a Korean population.Mol Biol Rep,2012,39(5):5561-5567.
[6]Jiang H,Qiu X,Dai J,et al.Association of rs11190870 near LBX1 with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis susceptibility in a Han Chinese population.Eur Spine J,2012,22(2):282-286.
[7]Ogura Y,Takahashi Y,Kou I,et al.Areplication study for association of 53 single nucleotide polymorphisms in a scoliosis prognostic test with progression of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Japanese.Spine(Phila Pa 1976),2013,38(16): 1375-1379.
[8]Ponting CP,Oliver PL,Reik W.Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs.Cell,2009,136(4):629-641.
[9]Mercer TR,Dinger ME,Mattick JS.Long non-coding RNAs:insights into functions.Nat Rev Genet,2009,10(3):155-159.
[10]Wang KC,Chang HY.Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs.Mol Cell,2011,43(6):904-914.
[11]Qiu MT,Hu JW,Yin R,et al.Long noncoding RNA:an emerging paradigm of cancer research.Tumour Biol,2013, 34(2):613-620.
[12]Klattenhoff CA,Scheuermann JC,Surface LE,et al.Braveheart,a long noncoding RNA required for cardiovascular lineage commitment.Cell,2013,152(3):570-583.
[13]Jovanova-Nesic K,Shoenfeld Y.MMP-2,VCAM-1 and NCAM-1 expression in the brain of rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis as a trigger mechanism for synaptic plasticity and pathology.J Neuroimmunol,2006, 181(1-2):112-121.
[14]Birney E,Stamatoyannopoulos JA,Dutta A,et al.Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1%of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project.Nature,2007, 447(7146):799-816.
[15]Spizzo R,Almeida MI,Colombatti A,et al.Long non-coding RNAs and cancer:a new frontier of translational research?Oncogene,2012,31(43):4577-4587.
[16]Zhang Q,Chen CY,Yedavalli VS,et al.NEAT1 long noncoding RNA and paraspeckle bodies modulate HIV-1 posttranscriptional expression.MBio,2013,4(1):e00596-12.
[17]Tsai MC,Spitale RC,Chang HY.Long intergenic noncoding RNAs:new links in cancer progression.Cancer Res, 2011,71(1):3-7.
[18]Zhang Z,Gilmour DS.Pcf11 is a termination factor in Drosophila that dismantles the elongation complex by bridging the CTD of RNA polymerase II to the nascent transcript. Mol Cell,2006,21(1):65-74.
[19]Loya TJ,O'Rourke TW,Reines D.A genetic screen for terminator function in yeast identifies a role for a new functional domain in termination factor Nab3.Nucleic Acids Res,2012,40(15):7476-7491.
[20]Rougemaille M,Dieppois G,Kisseleva-Romanova E,et al. THO/Sub2p functions to coordinate 3'-end processing with gene-nuclear pore association.Cell,2008,135(2):308-321.
[21]Zhang Z,Klatt A,Henderson AJ,et al.Transcription termination factor Pcf11 limits the processivity of Pol II on an HIV provirus to repress gene expression.Genes Dev,2007, 21(13):1609-1614.
[22]Ghazy MA,Gordon JM,Lee SD,et al.The interaction of Pcf11 and Clp1 is needed for mRNA 3'-end formation and is modulated by amino acids in the ATP-binding site.NucleicAcids Res,2012,40(3):1214-1225.
[23]Haddad R,Maurice F,Viphakone N,et al.An essential role for Clp1 in assembly of polyadenylation complex CF IA and Pol II transcription termination.Nucleic Acids Res, 2012,40(3):1226-1239.
[24]Mayer A,Heidemann M,Lidschreiber M,et al.CTD tyrosine phosphorylation impairs termination factor recruitment to RNA polymerase II.Science,2012,336(6089):1723-1725.
[25]Lunde BM,Reichow SL,Kim M,et al.Cooperative interaction of transcription termination factors with the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain.Nat Struct Mol Biol,2010,17 (10):1195-1201.
[26]陈龙,李俐俐.非编码RNA及其功用.生物学教学,2007, 32(7):4-6.
[27]Li D,Chen G,Yang J,et al.Transcriptome analysis reveals distinct patterns of long noncoding RNAs in heart and plasma of mice with heart failure.PLoS One,2013,8(10): e77938.
[28]Weber DG,Johnen G,Casjens S,et al.Evaluation of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 as a candidate blood-based biomarker for the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Res Notes,2013,6:518.
Study on expression of long non-coding RNAin adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
LIU Xiaoyang,QIU Guixing,WENG Xisheng,WU Zhihong,YU Bin,WANG Yipeng*
(Department of Orthopedic Surgery,Peking Union Medical College Hospital,ChineseAcademy of Medical Sciences& Peking Union Medical College,Beijing 100730,China)
idiopathic scoliosis;adolescent;long non-coding RNA
*通信作者:王以朋,E-mail:ypwang133@163.com
