生氰糖苷类物质的结构和代谢途径研究进展
2014-01-09柳春梅吕鹤书
柳春梅,吕鹤书
北京农学院 农业部都市农业(北方)重点实验室,北京 102206
生氰糖苷(Cyanogentic glycosides)亦称氰苷,作为具有防御功能的次生代谢产物已在包括蕨类,裸子植物和被子植物在内的2500 多种植物中被发现,它们储存于液泡中,当植物组织遭到破坏,如食草动物侵袭或病原体入侵,生氰糖苷与降解酶相接触,释放有毒物质HCN 和酮(或醛)类物质,提供植物一个立即的防御对抗。在对橡胶产胶量的研究中,发现植物中的生氰糖苷还具有转运、存储氮元素的作用。在4 亿多年植物和动物共同进化的过程中,动物可以从外界获取或是自身合成该类化合物为己所用[1],因此在动物界,主要在一些节肢动物和昆虫中存在生氰糖苷,这类物质既可作为化学防御物质,也可作为性信息素,在择偶和交配期起到重要作用[2-4]。本文对该类物质的结构类型、合成和降解途径等方面进行综述,为深入研究该类化合物在植物和动物中的作用提供资料。
1 生氰糖苷的结构
生氰糖苷是氰醇衍生物的羟基和D-葡萄糖缩合形成的糖苷(图1),根据取代基不同主要分为脂肪族生氰苷和芳香族生氰苷。该类化合物主要由三种脂肪族蛋白质氨基酸(L-valine,L-isoleucine,Lleucine),两种芳香族氨基酸(L-phenylalanine,Ltyrosine)以及一种脂肪族非蛋白质氨基酸(2-(2'-Cyclopentenyl)-glycine)衍生而来[5],结构综述如下(图2,3)

图1 生氰糖苷的基本结构式Fig.1 Basic chemical structure of cyanogentic glycosides
2 生氰糖苷的生物合成
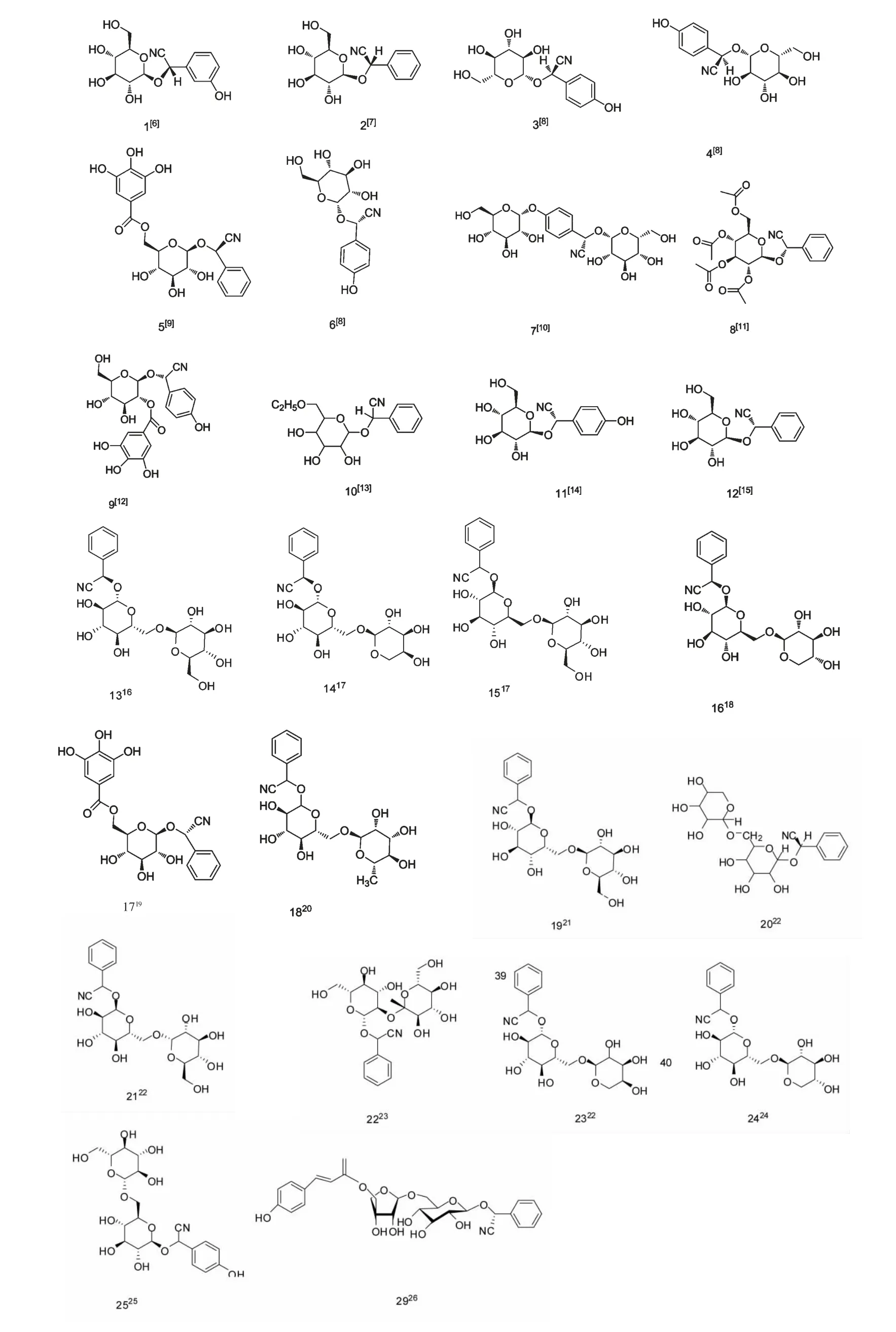
图2 芳香族生氰糖苷的结构式Fig.2 Chemical structures of aromatic cyanogenic glycoside
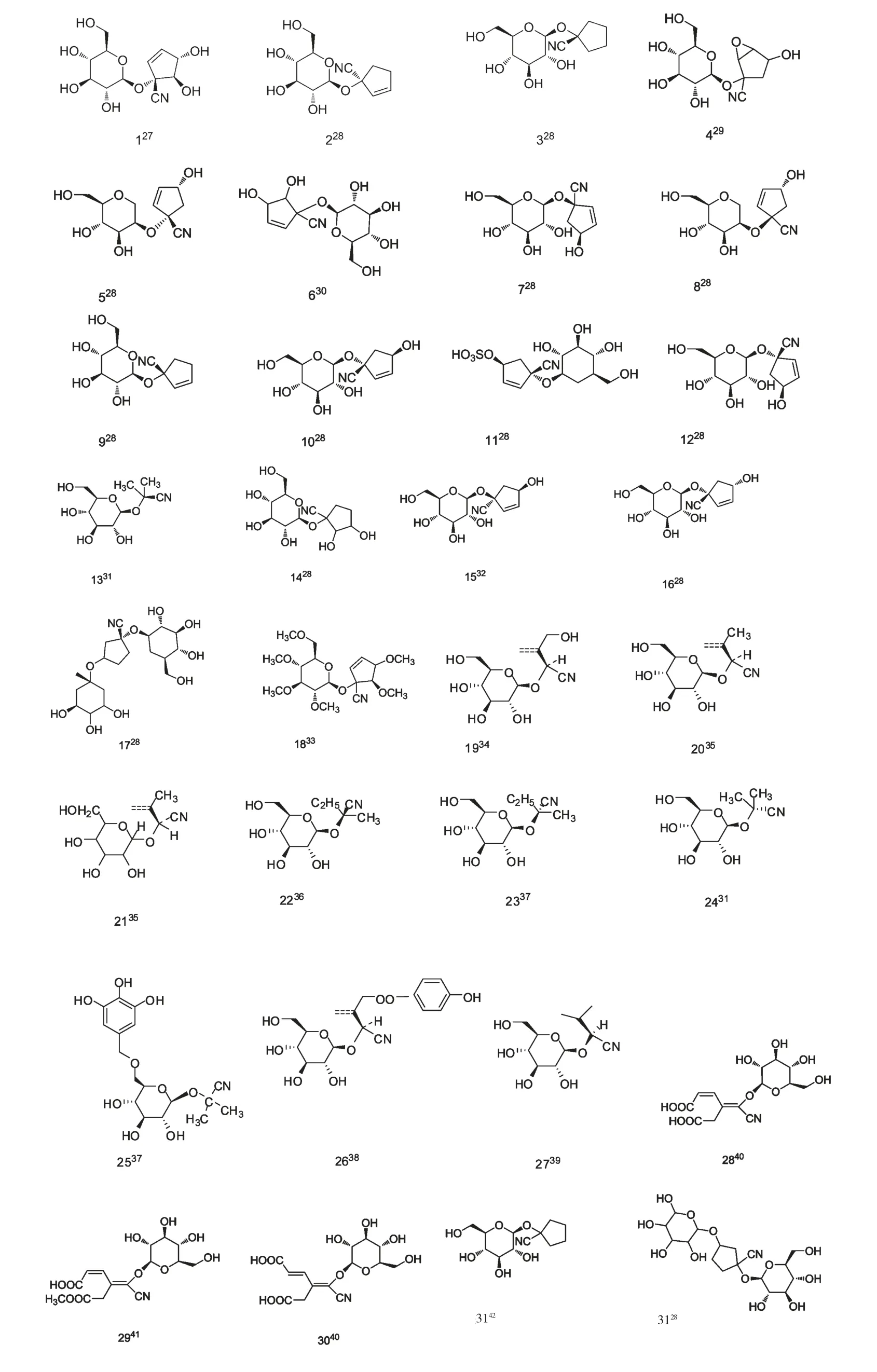
图3 脂肪族生氰糖苷的结构式Fig.3 Chemical structures of aliphatic cyanogenic glycoside
生氰糖苷生物合成过程中涉及3 大类酶,分别属于CYP79、CYP71 家族的两种细胞色素CYP450(也称P450)及葡萄糖转移酶UGT8581。CYP450 是一类以还原态与CO 结合后在波长450 nm 处有吸收峰的含血红素的单链蛋白质[43](图4)。不同植物中合成生氰糖苷的部位有所差异,例如高粱CYP79A1 主要表达于幼苗;日本百脉根CYP79D3主要表达在叶子,而CYP79D4 在根组织上表达相对低,表明生氰糖苷的积累发生在顶端组织;在木薯中,生氰糖苷先在地上部分合成,随后运送到根部贮存,第一片展开的叶子和叶柄具有最高的生氰苷生物合成活性。高粱、利马豆、葡萄、苦杏仁、亚麻籽中的生氰苷类物质研究较多。在生氰苷中作用的第一个酶是细胞色素P450,其生物合成途径是α-氨基酸羟基化形成N-羟基氨基酸,然后形成醛肟,进一步形成腈。生氰糖苷生物合成的最后一步是由糖基转移酶催化的半氰醇的糖基化反应。
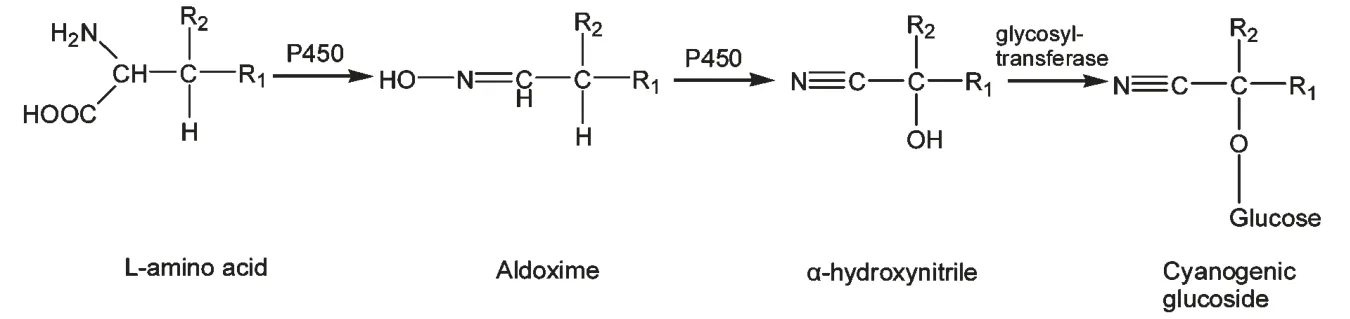
图4 生氰糖苷生物合成途径Fig.4 Biosynthetic pathway of cyanogenic glycoside
3 生氰糖苷的降解
生氰糖苷本身不呈现毒性,在正常植物体内生氰糖苷和(-葡萄糖苷酶并不会相遇,当草食动物或病原体损伤生氰植物组织时,组织内的β-葡萄糖苷酶(β-Glucosidase)与生氰糖苷相遇,对其进行降解,随后α-羟腈酶(α-Hydroxynitrile lyase)降解细胞内的生氰类化合物,生成并释放出有毒的氰化氢以及葡萄糖和醛或酮,即产生化学防御反应(图5)。正常情况下,植物体内产生的极少量HCN 可通过体内不同的途径进行脱毒反应,转化为无毒化合物(图6)。
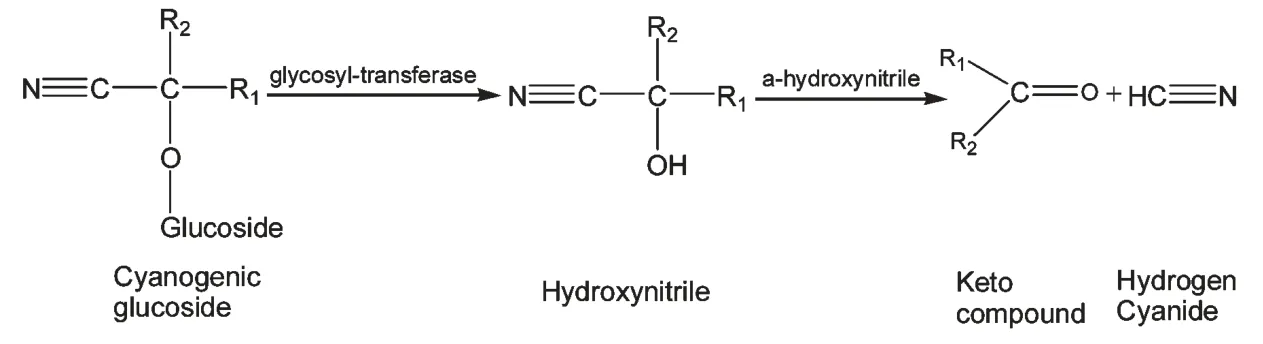
图5 生氰苷降解途径Fig.5 degradation pathway of cyanogenic glycoside
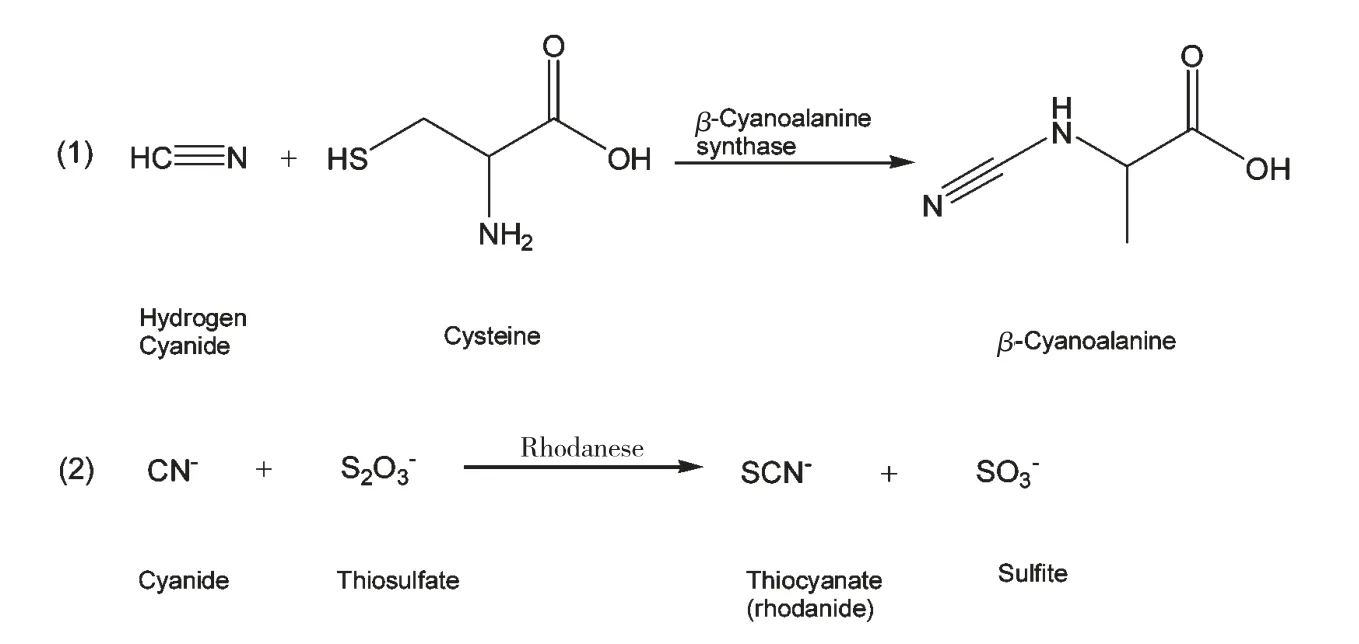
图6 HCN 在体内不同的脱毒反应途径Fig.6 Detoxification pathway of HCN in vivo
4 结语
目前已发现2000 多种植物,多种细菌、真菌以及鳞翅目昆虫体内含有生氰糖苷类物质,这类物质的结构类型变化较少,主要是脂肪族、芳香族取代的单糖或二糖类的生氰糖苷。迄今为止,国内外对生氰糖苷类物质的研究,多限于该类物质的分离和鉴定方面,对生氰糖苷的代谢途径的研究仅限于木薯、高粱、百脉根等少数植物。因此,对含氰植物体内生氰糖苷的生物合成途径以及抗虫抗病机理的深入研究,将为其作为基因资源增强农作物抗病虫害能力具有重要意义,同时有助于人为地调控生成途径中的基因,从而干扰其毒性物质的产生,对提高含氰植物的食用安全性,同样具有重要意义。
1 Mika Z,et al.Cyanogenic glucosides in the biological warfare between plants and insects:The Burnet moth-Birdsfoot trefoil model system.Phytochemistry,2011,72:1585-1592.
2 Bak S,et al.Cyanogenic glycosides;a case study for evolution and application of cytochromes P450.Phytochem Rev,2006,5:309-329.
3 Mφller BL,et al.Biosynthesis of cyanogenic glucosides,cyanolipids and related compounds.In:Singh,B.K.(Ed.),Plant Amino Acids.M.Dekker,New York,1999.563-609.
4 Zagrobelny M,et al.Cyanogenic glucosides and plant-insect interactions.Phytochemistry,2004,65:293-306.
5 Zhang Y(张岩),et al.Research progress of cyanogentic glycosides in plant.Biotechnology Bulletin(生物技术通报),2009,4:12-15.
6 Yang CJ,et al.Two new cyanogenic glucosides from the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla.Molecules,2012,17:5396-5403.
7 Jin QH,et al.Chemical constituents from the fruits of Prunus mume.Nat Prod Sci.2012,18:200-203.
8 Miller RE,et al.Reports on the distribution of aromatic cyanogenic glycosides in Australian tropical rainforest tree species of the Lauraceae and Sapindaceae.Phytochemistry,2013,92:146-152.
9 Tan HP,et al.Characterisation of galloylated cyanogenic glucosides and hydrolysable tannins from leaves of phyllagathis rotundifolia by LC-ESI-MS/MS.Phytochemical Analysis,2011,22:516-525.
10 Swenson WK,et al.Cyanogenesis in the Proteaceae.Phytochemistry,1989,28:821-823.
11 Schwarzmaier U,et al.The cyanogenesis of Bambusa vulgaris and B.guadua.Chemische Berichte,1976,109:379-389.
12 Otsuka H,et al.Glochidiolide,isoglochidiolide,acuminaminoside,and glochidacuminosides A-D from the leaves of Glochidion acuminatum Muell.Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2004,52:591-596.
13 Fu P,et al.New flavonoid glycosides and cyanogenic glycosides from Dracocephalum peregrinum.Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2009,57:207-210.
14 Miller R,et al.The rare cyanogen proteacin,and dhurrin,from foliage of Polyscias australiana,a tropical Araliaceae.Phytochemistry,2013,93:210-215.
15 Franks TK,et al.Cyanogenic glucosides in grapevine:polymorphism,identification and developmental patterns.Phytochemistry,2005,66:165-173.
16 Zhou WJ,et al.Chemical comparison of two dosage forms of hemp seed pills by UHPLC-Q-ToF-MS/MS and multivariate statistical techniques.J Pharm Biomed Anal,2013,84:59-68.
17 Lee JY,et al.Quantification of amygdalin in nonbitter,semibitter,and bitter almonds(Prunus dulcis)by UHPLC-(ESI)QqQ MS/MS.J Agric Food Chem,2013,61:7754-7759.
18 Turczan JW,et al.Cyanogenetic glycosides.The 220 MHz nuclear magnetic resonance studies of amygdalin and some related compounds.J-Association of Official Analytical Chemists,1978,61:192-207.
19 Miller RE,et al.A galloylated cyanogenic glycoside from the Australian endemic rainforest tree Elaeocarpus sericopetalus(Elaeocarpaceae).Phytochemistry,2006,67:1365-1371.
20 Chassagne D,et al.A cyanogenic glycoside from Passiflora edulis fruits.Phytochemistry,1998,49:757-759.
21 Nagumo S,et al.Cyanogenic glycosides and 4-hydroxycoumarin glycosides from Gerbera jamesonii hybrid.Chemical &Pharmaceutical Bulletin,1985,33:4803-4806.
22 Derbre S,et al.Automating a 96-well microtiter plate assay for identification of AGEs inhibitors or inducers:application to the screening of a small natural compounds library.Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2010,398:1747-1758.
23 Aritomi M,et al.Chemical studies on the constituents of edible plants.Part 4.Cyanogenic glycosides in leaves of Perilla frutescens var.acuta.Phytochemistry,1985,24:2438-2439.
24 Miller RE,et al.Cyanogenic glycosides from the rare Australian endemic rainforest tree Clerodendrum grayi(xLamiaceae).Phytochemistry,2006,67:43-51.
25 Selmar D,et al.Dhurrin-6'-glucoside,a cyanogenic diglucoside from Sorghum bicolor.Phytochemistry,1996,43:569-572.
26 Wang GC,et al.Five new phenolic glycosides from Hedyotis scandens.Bioorgan & Med Chem Lett,2013,23:1379-1382.
27 Webber BL,et al.Constitutive polymorphic cyanogenesis in the Australian rainforest tree,Ryparosa kurrangii(Achariaceae).Phytochemistry,2007,68:2068-2074.
28 Jaroszewski JW,et al.Cyanohydrin glycosides of Passiflora:distribution pattern,a saturated cyclopentane derivative from P.guatemalensis,and formation of pseudocyanogenic αhydroxyamides as isolation.Phytochemistry,2002,59:501-512.
29 Olafsdottir ES,et al.Structure determination of natural epoxycyclopentanes by x-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy.J Org Chemistry,1991,56:2650-2655.
30 Jensen SR,et al.Gynocardin in Ceratiosicyos laevis(achariaceae).Phytochemistry,1986,25:2349-2350.
31 Bayoumi SAL,et al.Constituents and secondary metabolite natural products in fresh and deteriorated cassava roots.Phytochemistry,2010,71:598-604.
32 Webber BL,et al.Constitutive polymorphic cyanogenesis in the Australian rainforest tree,Ryparosa kurrangii(Achariaceae).Phytochemistry,2007,68:2068-2074.
33 Alberte RS,et al.Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergy extracts from nettle.Dan.US 20100009927 A1 20100114,2010.
34 Seigler DS,et al.New cyanogenic glycoside from Cardiospermum hirsutum.Phytochemistry,1974,13:2330-2332.
35 Maslin BR,et al.Cyanogenesis in Australian species of Acacia.Phytochemistry,1988,27:421-428.
36 Bjarnholt N,et al.Diversification of an ancient theme:Hydroxynitrile glucosides.Phytochemistry,2008,69:1507-1516.
37 Cai WH,et al.Supinaionosides A and B:megastigmane glucosides and supinanitrilosides A-F:hydroxynitrile glucosides from the whole plants of Euphorbia supina RAFINESQUE.Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2009,57:840-845.
38 Kim DK,et al.A new cyanogenic glycoside from Sorbaria sorbifolia var.stellipila.Chem Pharm Bull,2000,48:1766-1767.
39 Nakamura S,et al.Bioactive constituents from Chinese natural medicines.XXVI.Chemical structures and hepatoprotective effects of constituents from roots of Rhodiola sachalinensis.Chem Pharm Bull,2007,55:1505-1511.
40 Nahrstedt A,et al.Characterization of cyanogenic glucoside and b-glucosidases in Triglochin maritima seedlings.Phytochemistry,1979,18:1137-1141.
41 Sharples D,et al.Major cyanogenic glycoside in Thalictrum aquilegifolium.Phytochemistry,1972,11:3069-3071.
42 Jaroszewski JW,et al.Biosynthesis of cyanohydrin glucosides from unnatural nitriles in intact tissue of Passiflora morifolia and Turnera tifolia.Phytochemistry,1996,42:649-654.
43 Mika Z,et al.Cyanogenesis in plants and arthropods.Phyto-chemistry,2008,69:1457-1468.
