Analysis of Internal Stress and Fracture Morphology for 20 Steel Under Ultrasonic Vibration Uniaxial Tensile
2013-12-07CHENGXueliZHAOMingliQINJunLIUChuanshao
CHENG Xueli, ZHAO Mingli, QIN Jun, LIU Chuanshao
1.Department of Mechanical Engineering, Henan Mechanical and Electrical Engineering College,Xinxiang 453000, China;2.School of Mechanical and Power Engineering, Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo 454000, China;3.Siping City Haige Crane Manufacting Limited Liability Company, Siping 136000, China
AnalysisofInternalStressandFractureMorphologyfor20SteelUnderUltrasonicVibrationUniaxialTensile
CHENG Xueli1*, ZHAO Mingli2, QIN Jun3, LIU Chuanshao2
1.DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering,HenanMechanicalandElectricalEngineeringCollege,Xinxiang453000,China;2.SchoolofMechanicalandPowerEngineering,HenanPolytechnicUniversity,Jiaozuo454000,China;3.SipingCityHaigeCraneManufactingLimitedLiabilityCompany,Siping136000,China
Inthispaper,theultrasonicvibrationuniaxialtensiletestofthe#20steelwasconductedandtheinternalstresswasanalyzedbyfiniteelementmethod.Itisconcludedthatthestressofworkpieceonbothendsoftheminimumdiameterplaceisthebiggestandthatofthemiddleisbigger,whichisconsistentwiththepositionofthefracture.Sincetheplasticstrainandstresscurvearechangedwithtime,itisprovedthattheinternalworkpieceissubjecttoanalternativestressloadunderultrasonicvibrationuniaxialtensile.Basedonthecomparisonbetweenthetensilefractureoftheultrasonicandthatofthecommoncondition,itisfoundthatallthefractureisacupofconefracturetypeandthefracturehasmoreapparentcupedges,moresmoothandbrightatultrasoundstretch.Furthermore,itisfoundthatthefracturebecomescoarseandunevenwiththedecreaseoffrequency.Therefore,thegreaterthepoweris,themoreobviousthetypicalfatiguestripeis.
ultrasonicvibration,uniaxialtensile,stressanalysis,fracturemorphology
1.Introduction
In aerospace, marine and bearing industries, a number of high-speed parts often occur high-energy, high-frequency vibration, the alternative stress generated by the vibration will seriously affect the carrying capacity of these parts, and common materials would appear “soften” behavior. Therefore, the conventional thinking of these parts can not be adopted in the process of designing and checking these parts, and the stress distribution of these parts should be considered. In addition, in the ultrasonic vibration cutting industry, material under the ultrasonic load will appear “soften” phenomenon, which will benefit the machinability of this material [1]. In order to study the stress distribution and fracture morphology of the metal material in the ultrasound, the authors take the #20 steel for example, apply ultrasonic vibration for the uniaxial tensile test and expect to provide some theoretical basis for the application of the material and to predict the changing trend of other metal material’s mechanical properties in the ultrasonic vibration tension.
2.The finite element simulation of the stress distribution under the ultrasonic vibration tension
In order to understand the internal stress distribution of the workpiece under the maximum external load and the relationship between the center stress of workpiece and time, the nonlinear structural analysis was adopted in the finite element method. Nonlinear means the structural rigidity of material is changeable with time and state. For the nonlinear analysis, in order to reflect the different loading, the load was gradually divided into different load-step and each analysis is still a discrete analysis process. Therefore, the analysis result at any time of the process could be obtained[2]. The analysis model is shown in Fig.1, the model is a combination of the workpiece and the horn; the boundary conditions are as follows: workpiece bottom surface’s longitudinal displacement ofy=1.2 × 10-5sin2πft(fis the ultrasonic vibration frequency), the other two displacementsx、z=0; external load imposed by the upper and lower surfacesσb. The analysis result is shown in Fig.2.

Fig.1 Three dimensional model

Fig.2 Compound stress distribution at maximum load
As can be seen from Fig.2, the internal stress of the workpiece in the minimum diameter is the maximum, and that of the middle diameter has the second value, which is consistent with the position of fracture . In order to display the changes of internal stress in the workpiece, the authors made the curves of plastic strain-time and stress-time of the workpiece at the center point, and they are shown in Fig.3 and Fig.4.
From the Fig.3 and 4, we can see the strain and stress at the center of the workpiece are wave curves, stress is the sine curve, the starting point is stress without ultrasound, and the peak is the maximum. From the Fig.4, we could obtain the internal part of workpiece has an alternative stress load and this is mainly due to the ultrasonic vibration signal.
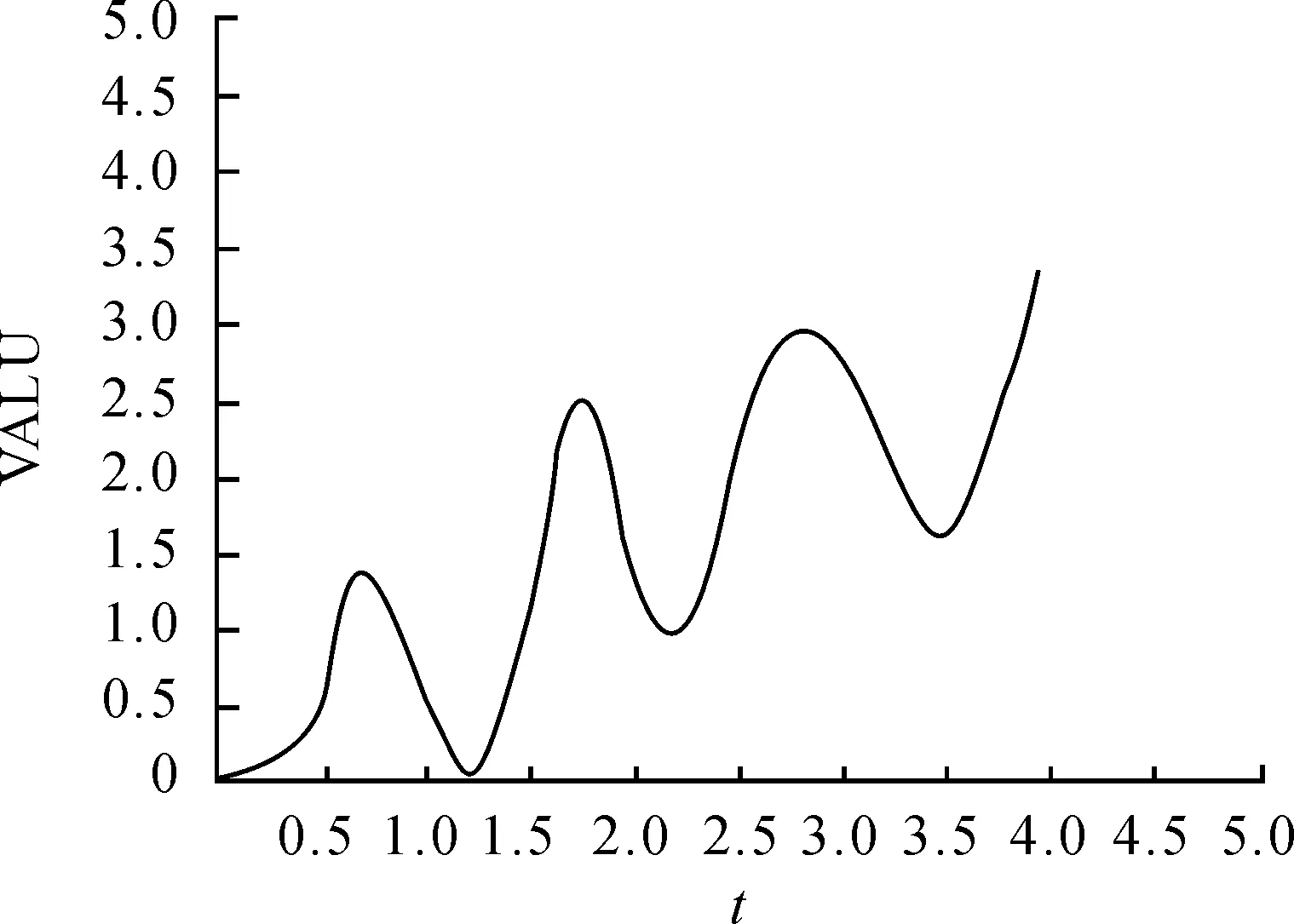
Fig.3 The curve of plastic strain in workpiece center

Fig.4 The curve of stress in workpiece center
3.The fracture morphology analysis under ultrasonic vibration uniaxial tensile
3.1.Thetestpreparationandthetestmethod
The fracture specimen preparation methods: make film-replica-carbon with vacuum coating machine-cut 2 mm×2 mm boxex-put them into the acetone solution-and expand them with the water-observe with electron microscope[3].
3.2.Thefracturemorphologyanalysisenlarged3times
The fractography enlarged three times as shown in Fig.5, through this Figure the followings could be obtained: ① The entire fracture is irregular and has slight uneven geometry[3]; ② All the fractures are cup cone fracture, the sizes are almost the same, the fracture edge with ultrasound tensile is more obvious, and the fracture internal is more smooth; ③ The internal fracture with ultrasound is brighter than that of conventional fracture.
3.3.Thefracturemorphologyanalysisenlarged300times
3.3.1.The influence of frequency on the fracture morphology
The fixed ultrasonic vibration power is 80W, and the frequencies are 20.845 kHz and 21.5 kHz (resonant frequency). The obtained tensile fracture is shown in Fig.6.
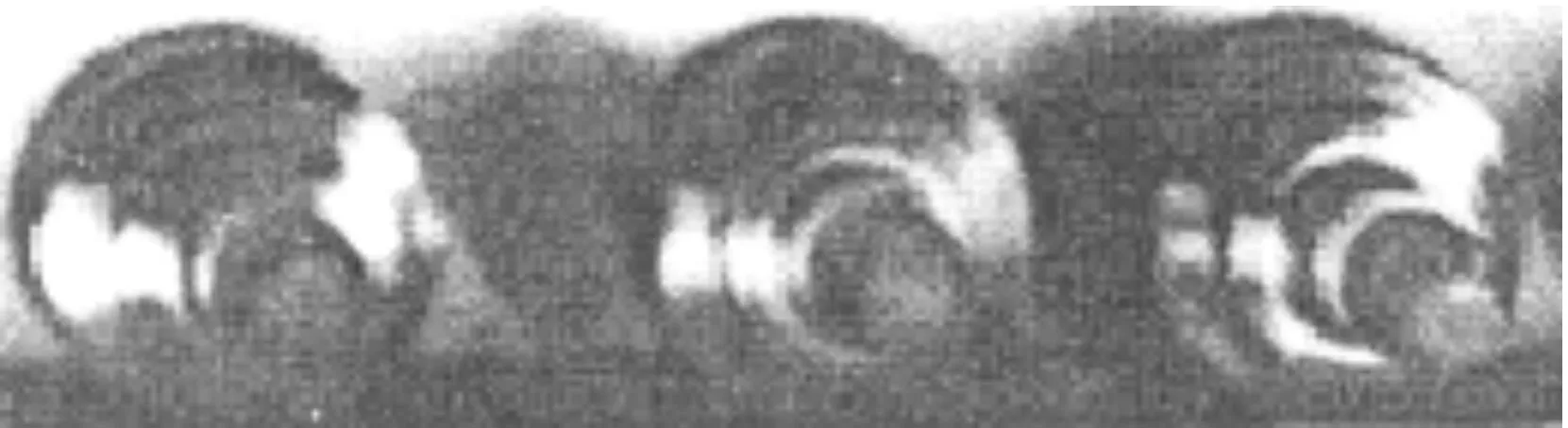

Fig.5 The tensile fracture morphology observed under the low powe

Fig.6 The tensile fracture morphology of 20# steel in fracture center when p equals 80 W and f equals 20.845 kHz (left) and 21.5 kHz (right) separately
From the Fig.6, we can see the grain boundary is elongated with different loading frequency. With the decrease of frequency, the fracture surface becomes rough and uneven. Whenf=20.845 kHz, the fracture surface showes the obvious fatigue striped. These stripes have a better continuity which means this material has good plasticity and toughness properties[4]. Whenf=21.5 kHz, we still can obviously observe the fatigue stripes, however the continuity of the stripes get worse, a little long-shaped shadow appears on the photo. In the fracture without ultrasonic tensile (normal tensile fracture), stripes are not obvious or continuous, the material is toughness and shows the brittle characteristics. Whenf=21.5 kHz, #20 steel fracture morphology is like “sugar candy” characteristics, which is typical intergranular fracture characteristics, but sugar candy morphology is not very clear. From the fracture morphology, we can see the Ultrasonic vibration tensile test is similar to the high-cycle fatigue test, but it has high-frequency characteristic. The effect of the high-frequency vibration is the inner material that has the energy effect in a short time and this load might cause phase change. From the lower magnification, we can see that the fracture with ultrasound is brighter and it is shown that the bond between atoms has been destroyed.
3.3.2.The influence of power on the fracture morphology
If keep the ultrasonic vibration frequency as 20.845 kHz and change the power as 80 W and 70 W, the tensile fractures are obtained as shown in Fig.7.
As can be seen from Fig.7, there are typical fatigue stripes or wavy stripes with different tension power. The greater the power is, the more obvious the phenomenon is, i.e., the crack extension is still similar to the general fatigue damage which is primarily extended by fatigue fracture. When the power is 80 W, the intercrystalline fracture appears on the fracture, this is because the three-dimensional stress generated at the leading edge for high-power ultrasonic vibration stretching is larger, the general high ductility fracture morphology will appear in the crack propagation process[5-6]. When the power is 70 W, there is the tiny pit in the cross section, with the traces of tear in local. When the effect of ultrasonic vibration with small power is not obvious, static tensile mechanical factors play a very important role for fracture mechanisms[4], and it is could be observed that the static fracture characteristics appear on the part of the fracture. Based on the above analysis, we can conclude the power of the ultrasonic vibration will influence the micro-cracks of the material.
4.Conclusions
In this paper, the ultrasonic vibration uniaxial tensile test of the #20 steel was conducted, the internal stress distribution and fracture morphology were analyzed, the following conclusions could be drawn:
1) The stress of workpiece on both ends of the minimum diameter place is the biggest and that of the middle is bigger, which is consistent with the position of the fracture. Since the plastic strain and stress curve are changed with time, it is proved that the internal workpiece is subject to an alternative stress load under ultrasonic vibration uniaxial tensile.
2) Based on the analysis of fracture morphology, ultrasound tensile fracture has similar points with normal tensile fracture, although it has some differences. The entire fracture is irregular and has slight uneven geometry. All the fractures are cup cone fracture, the size has no obvious distinction and the fracture edge with ultrasound tensile is more obvious. The more smooth the internal fracture is, the brighter the internal fracture with ultrasound is; Under the condition of different frequencies, the grain boundary gets elongated with the decrease of frequency and the fracture surface becomes rough and uneven; With different power, the typical fatigue stripes or wavy stripes can be obtained in the case of stretching, and the greater the power is,the more obvious the phenomenon is.
[1] QIN Jun.Study on mechanical property of 20# steel under ultrasonic vibration simple tension[D].Henan Jiaozuo:Henan Polytechnic University,2005:69-72.
[2] LI Xianren.Finite element method based[M].Beijing:Defense industry press, 2002:1-6.
[3] PENG Wei,KANG Qingyun. The Tensile Sample Fracture of 45 Steel Studied[J].Physical test,2002(3):16-18.
[4] LIZifeng,LI Jingyuan,ZHAO Ping.Mechanic Analysis of Expansion Screen Pipe[J].Petroleum machinery, 2003(12):6-8.
[5] Henry G, Smedt D H.Macroscopic and Microscopic Fractography [M].Beijing:Machinery Industry Press,1990.
[6] SUN Maocai.Mechanical property of metal [M].Harbin:Harbin industrial university press,2003:102-123.
超声振动单向拉伸20号钢内部应力及断口形貌分析
程雪利1*,赵明利2,秦 军3,刘传绍2
1.河南机电高等专科学校 机械工程系,河南 新乡 453000;2.河南理工大学 机械与动力工程学院,河南 焦作 454000;3.四平市海格起重机器制造有限公司,吉林 四平 136000
对20号钢进行了超声振动单向拉伸试验,对其内部应力进行了有限元分析,得出了工件在直径最小处两端的应力最大,中间次之,这和断口断裂的位置是一致的。研究了工件中心点处塑性应变及应力随时间变化的曲线,证明了在超声振动单向拉伸下工件内部受到的是一个交变的应力载荷。通过对超声与常态拉伸断口的比较,发现了所有断口都是杯锥型断口,而超声拉伸的断口杯状边缘更明显,断口内部更平整,断口更明亮;还发现了随着频率的降低,断口变得粗糙且不均匀,功率越大,典型疲劳条纹也越明显。
超声振动;单向拉伸;应力分析;断口形貌
TG115.5
The Education Department of Henan Province Natural
Science Research Project(12A460004)
*CHENG Xueli.E-mail:chenguxeli2005@126.com
10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2013.06.021
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
机床与液压的其它文章
- Research and Realization of the Control System for Cement Screw Packing Machine Based on MCGS and S7-200PLC
- Modeling and Simulation about Sinusoidal Non-circular Gear Pitch Curve of the High Order and Denatured Feature
- The Study of Stability Control Based on the Yawing Moment of Electric Vehicle
- Structure Optimization Design of Time-Grating with Variable Coupling Coefficient Based on ANSOFT Electromagnetic Analysis
- Prediction Chatter Stability and Bifurcation in Milling Machine
- Design of Structure Optimization for Engine Exhaust Manifold
