Efficacy Observation on Acupuncture Combined with Auricular Point Sticking Treatment for Primary Dysmenorrhea
2013-07-18LiuXiaoxiaWangXi
Liu Xiao-xia, Wang Xi
Acupuncture Department of Kunshan Bacheng People’s Hospital, Jiangsu 215311, China
Efficacy Observation on Acupuncture Combined with Auricular Point Sticking Treatment for Primary Dysmenorrhea
Liu Xiao-xia, Wang Xi
Acupuncture Department of Kunshan Bacheng People’s Hospital, Jiangsu 215311, China
Objective: To observe the clinical efficacy of acupuncture combined with auricular point sticking treatment for primary dysmenorrhea.
Methods: Sixty-eight patients with primary dysmenorrhea were randomly divided into two groups, and 35 cases in the treatment group were treated by acupuncture combined with auricular point sticking, while 33 cases in the control group were only treated by acupuncture. The treatments for the patients in both groups began from one week before their menstruation and continued till the menstruation came. And the efficacy was observed after treatments of three consecutive menstrual cycles.
Results: The total effective rate was 94.2% in the treatment group, versus 84.8% in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Acupuncture combined with auricular point sticking treatment for primary dysmenorrhea is more effective than simple acupuncture.
Acupuncture Therapy; Auricular Point Sticking; Primary Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea refers to various pain symptoms of women before, during or after menstruation, such as lower abdominal pain, pain radiating to the lumbosacral region, down-bearing lower abdominal pain, or excruciating pain that may cause faint. Primary dysmenorrhea is defined as cramping pain in the absence of any identifiable pelvic disease. I have treated 35 patients with primary dysmenorrhea from February 2008 to August 2012 by combined use of acupuncture and auricular point sticking, compared with acupuncture alone. And the report is given as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
It refers to diagnostic criteria of primary dysmenorrhea in theObstetrics and Gynecology[1]. If the patient is mainly present with down-bearing lower abdominal pain during menstruation without positive signs of gynecological examination.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Meeting the diagnostic criteria; aged between 14 and 35 years old, and symptoms occuring at 1 or 2 years after menarche; without any othertreatments during this study; and willing to sign the informed consent form.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Secondary dysmenorrhea caused by endometriosis, adenomyosis and other diseases; long-term use of Western medicine or herbs treatment; failure to follow the treatment regulations, or quitting or receiving other treatment.
1.4 General data
Sixty-eight patients who met the inclusion criteria were outpatients in our hospital, and they were randomly divided into two groups according to visiting sequence. There were 35 patients in the treatment group, aged from 15 to 35 years old, with the duration between six months and 20 years. There were 33 patients in the control group, aged from 18 to 33 years old, with the duration between one year and 18 years. Two sets of data were analyzed statistically and the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable.
2 Therapeutic Methods
2.1 Treatment group
2.1.1 Acupuncture
Major acupoints: Guanyuan (CV 4), Sanyinjiao (SP 6).
Adjunct acupoints: For syndrome of qi stagnation and blood stasis and syndrome of coagulated cold in uterus, add Geshu (BL 17), Tanzhong (CV 17), Qihai (CV 6) and Xuehai (SP 10); for syndrome of qi and blood deficiency, add Pishu (BL 20), Guilai (ST 29) and Zusanli (ST 36).
Operation: After routine disinfection in acupoint areas, filiform needles of 0.30 mm in diameter and 40 mm in length were used for acupuncture. Patients were firstly in a sitting position and then turned to a supine position after punctured at bilateral Geshu (BL 17) and Pishu (BL 20). Even reinforcing and reducing manipulation was used at Guanyuan (CV 4), Sanyinjiao (SP 6), Danzhong (CV 17), Geshu (BL 17), Qihai (CV 6) and Xuehai (SP 10) after arrival of qi. However, reinforcing method was used in Pishu (BL 20), Guilai (ST 29) and Zusanli (ST 36). Needles were retained for 20 min with TDP abdominal irradiation. The treatment began from one week before menstruation, once a day, and stopped when menstruation came.
2.1.2 Auricular point sticking
Major acupoints: The Uterus (TF2), Endocrine (CO18), Sympathetic (AH6a), and Subcortex (AT4)[2].
Adjunct acupoints: Shenmen (TF4), Abdomen (AH8), Liver (CO12), Kidney (CO10)[2]and Pelvic (TF5).
Operation: The major acupoints were selected every time, and the adjunct acupoints were selected according to syndromes of traditional Chinese medicine. After disinfection with 75% alcohol swab for ear skin, disposable granular needle was placed by hemostatic forceps at the sensitive points and pressed until heat, pain, soreness and distention feeling in the points areas. And the above treatment was given alternately to the ear every other day. The patient was asked to push and press them 4-6 times daily, and press 10 times for each acupoint. If the patient suffered from severe pain, asked her to simultaneously press both ears; if the patient still had abdominal pain after menstruation, asked her to have auricular point sticking therapy till relieved. And they were totally treated for three menstrual cycles.
2.2 Control group
Patients in the control group were only treated with TDP radiation and acupuncture in abdomen, and the methods of acupoints selection, operation and treatment duration were the same as the treatment group.
Patients in both groups were told to avoid from cold, fresh and stimulation food, cold and overwork during treatment.
3 Efficacy Observation
3.1 Clinical efficacy criteria
The criteria were accorded to dysmenorrhea efficacy criteria in theCriteria of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Effect of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine[3].
Cure: Pain disappears and there is no recurrence in three menstrual cycles after stopping treatment.
Markedly effective: Significant relief of pain, intermittent episodes after stopping treatment.
Improvement: Relief of pain after 3 consecutive menstrual cycles’ treatments.
Invalid: After treatment, the pain does not relieve.
3.2 Therapeutic results
The difference of the total effective rates between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05), suggesting that the efficacy of the treatment group was better than that of the control group (table 1).
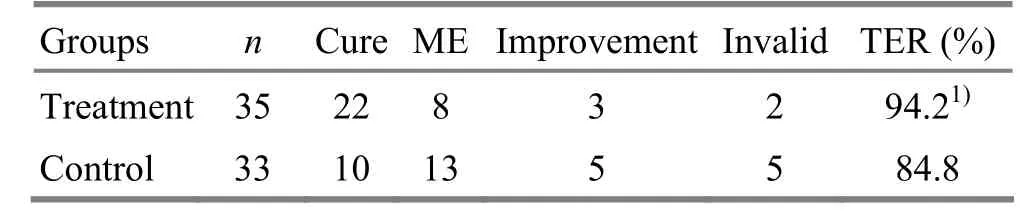
Table 1. Efficacy comparison of the two groups (case)
4 Discussion
Primary dysmenorrhea belongs to the category of abdominal pain during menstruation in traditionalChinese medicine. Its occurrence has close relation with the cyclical physiological changes of the Thoroughfare Vessel, the Conception Vessel and the uterus. And its main pathogenesis is that pathogenic qi lies within the body or constitutional essence-blood deficiency. Because there are abrupt physiological changes of qi and blood of the Thoroughfare and Conception Vessels around the menstruation period, qi and blood are easy to form stagnation and stasis, that is that ‘the obstruction causes the pain’; or uterus lacks nourishment, that is ‘the malnourishment causes the pain’.
The former belongs to excess syndrome, which is mainly caused by qi stagnation and blood stasis as well as coagulated cold in uterus, thus the treatment needs to expel evil qi, stimulate qi and blood circulation and warm and dredge meridians and vessels. Guanyuan (CV 4) is closely related to uterus and has interference with Three Yin Meridians of Foot, it has an effect of stimulating qi and blood circulation as well as resolving blood stasis to relieve pain. Adding TDP irradiation can warm uterus and warm meridian to expel cold; Sanyinjiao (SP 6) is the intersection acupoint of foot yin meridians, it can strengthen the spleen and stomach, benefit the liver and kidney and regulate the Thoroughfare Vessel and th eConception Vessel. The two acupoints together can balance the Thoroughfare Vessel and Conception Vessel, stimulate qi and blood movement as well as dredge meridians to kill pain. Meanwhile, adding Danzhong (CV 17), Qihai (CV 6), Xuehai (SP 10) and Geshu (BL 17) can enhance the function of activating qi and promoting blood circulation as well as removing stasis to ease pain. The latter one belongs to deficiency syndrome, which is mostly caused by qi and blood deficiency, deficiency of blood sea, failure of nourishment of uterus. Therefore, Guanyuan (CV 4) and Sanyinjiao (SP 6), accompanied with Pishu (BL 20), Guilai (ST 29) and Zusanli (ST 36) are selected together to tonify qi and blood and warm meridians to kill pain.
Meanwhile, according to the bio-holographic theory, the body's internal organs, limbs and bones respectively have the corresponding point on the ear (auricular point). Therefore, pathologic changes in certain parts of the body can be indicated in corresponding auricular point through meridians conduction. Modern research shows that auricular point sticking has a lot of functions such as dredging the meridians, regulating qi and blood, regulating nerve function, balancing endocrine system and so on[4]. It also has a strong effect of killing pain because it can improve the function of the brain antinociception structure as well as release endorphins and enkephalins[5-6]. Endocrine (CO18) and Subcortex (AT4) are selected to regulate endocrine and ovarian function, while the Subcortex (AT4) can enhance endorphin to achieve the purpose of killing pain[2]; Kidney (CO10) is selected to tonify kidney qi and regulate the Thoroughfare Vessel and Conception Vessel; because the Liver Meridian goes through the genital organs and the lower abdomen, Liver (CO12) is selected to relieve liver qi stagnation and depression to relieve abdominal pain; dysmenorrhea commonly dues to vascular cramps in primary menstruation period, thus choosing Sympathetic (AH6a) can dilate blood vessels and relieve smooth muscle spasm of the uterine to relieve the pain and make menstruation come smoothly; Uterus (TF2), Abdomen (AH8) and Pelvic (TF5) are the corresponding points and can regulate qi and blood as well as stimulate qi movement to kill pain; Subcortex (AT4) can recuperate subcortical brain function and relieve mental tension; Shenmen (TF4) is used during menstruation to keep calm and kill pain[7-8]. Various acupoints achieve a function of dredge meridians, stop spasm and kill pain, keep calm and tranquilization. Therefore, acupuncture combining with auricular point sticking can complement each other and have a significant effect, that’s why the therapy is worthy of wide use in clinic.
[1] Le J. Obstetrics and Gynecology. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. 2005: 347.
[2] Huang LC. Auricular Point Therapeutics. Beijing: Scientific and Technological Literature Publishing House, 2005: 21, 23, 32, 237.
[3] State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 1994: 62.
[4] Li L, Wang ZY. Clinical therapeutic effects of body acupuncture on juvenile simple obesity and effects on metabolism of blood lipids. Zhongguo Zhenjiu, 2006, 26(3): 175-178.
[5] Xing QX. Observation on the therapeutic effect of pricking bloodletting at ear points on primary dysmenorrhea. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2011, 30(4): 235-236.
[6] Chang Y, Liu YB, He JJ. Clinical observation on auricular point sticking for treatment of 25 children of semiluxation of circoaxis vertebrae. Zhongguo Zhenjiu, 2006, 26(10): 710-712.
[7] Xing QX. Observations on the therapeutic effect of pricking bloodletting at ear points on primary dysmenorrhea. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2011, 30(4): 235-236.
[8] Cai ZJ, Li F, Lu M. Treatment of dysmenorrheal by acupuncture plus auricular acupuncture. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2004, 2(6): 45-46.
Translator: Deng Ying
R246.3
A
Date: March 25, 2013
Author: Liu Xiao-xia, bachelor, attending physician.
E-mail: jingyue8698@126.com
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Clinical Study on Acupoint Injection for Primary Osteoporosis
- Treatment of Post-stroke Spastic Hemiplegia by Acupuncture plus Rehabilitation Training
- Clinical Observation on Electroacupuncture for Post-stroke Flaccid Paralysis
- Effect of Electroacupuncture on Anxiety and Craving in Heroin Addicts During Detoxification
- Clinical Observation on Acupuncture Treatment for Post-stroke Spastic Hemiplegia
- Clinical Observation on Acupoint Sticking Therapy for Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Hernination
