Observation on Clinical Effect of Acupuncture for Allergic Rhinitis
2013-07-18SongHaiyunZhangDongyun
Song Hai-yun, Zhang Dong-yun
Taihe Hospital Affiliated to Hubei Medical College, Shiyan 442000, China
Observation on Clinical Effect of Acupuncture for Allergic Rhinitis
Song Hai-yun, Zhang Dong-yun
Taihe Hospital Affiliated to Hubei Medical College, Shiyan 442000, China
Objective: To observe the clinical effect of acupuncture plus acupoint injection and laser radiation on the nasal cavity for allergic rhinitis.
Methods: Ninety patients with allergic rhinitis were randomly divided into a treatment group and a control group, 45 cases in each group. The treatment group was treated by acupuncture, acupoint injection method and He-Ne laser radiation on the nasal cavity. The control group was treated by Triamcinolone Acetonide nasal spray. The clinical effects were assessed after two courses of treatment.
Results: The clinical curative rate was 88.9% and the total effective rate was 100.0% in the treatment group, versus 57.8% and 80.0% in the control group. The clinical curative rate and total effective rate were remarkably higher in the treatment group than those in the control group (P<0.05). In comparison of the therapeutic effects in the different courses between the two groups, the curative rates in the one course and two courses were higher in the treatment group than those in the control group (P<0.05). In the follow-up visit of the cured patients of the two groups for half a year, the recurrence rate was 2.5% in the treatment group versus 34.6% in the control group, with a statistical difference between the two groups (P<0.01).
Conclusion: Acupuncture plus acupoint injection and laser radiation on the nasal cavity for allergic rhinitis has better clinical effect and long-term effect, and can obviously shorten the course, enhance the clinical effect and reduce the recurrence rate.
Acupuncture-moxibustion Therapy; Acupoint Therapy; Hydroacupuncture; Laser Therapy; Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis is an allergic disease mainly manifested by congestion and edema of the nasal mucosa and hyperactive gland secretion, and mainly characterized by sudden and repeated nasal obstruction, nasal itching and sneezing. The incidence rate is 10%-25%[1], and the incidence rate increases annually. It can affect all age groups and occur at anytime of the year. When the organism is encountered with some external specific allergens (such as cold air, pollen, dust, pest mite, oil, smoking, fur and hair, chemicals), the sensitivity will be elevated and the symptoms will be aggravated. Allergic rhinitis is not a severe disease itself, but it is easy to attack and linger, and to induce occurrence of bronchial asthma, nasal polyps, sinusitis, otitis media or allergic conjunctivitis[2], which severely influence the patient’s quality of life. In recent years, it has been reported in many clinical articles that certain therapeutic effects have been achieved in the treatment of allergic rhinitis
by acupuncture, acupoint injection and He-Ne laser radiation[3-5]. Since 2008, we treated allergic rhinitis patients with acupuncture, acupoint injection and He-Ne laser radiation on nasal cavity. Now, the report is given as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
In reference to the diagnostic criteria of allergic rhinitis in theCriteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine[6]promulgated by the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine andDiagnostic Criteria of Allergic Rhinitis[7]recommended by China Society of Otolaryngology. Paroxysmal nasal itching, continuous sneezing, excessive nasal discharge, purulent in infection; sudden onset; stuffy obstruction in the nasal cavity, stuffy sensation in the ear, breathing through the mouth, decreased or inability to perceive odor (anosmia), headache, dizziness; induced by frequent contact with pollen, smoking, cold air, chemical gas, or induced by changes in environment and temperature; pale nasal mucosa, anemic edema, congestion worse in the inferior nasal concha in some cases, full of watery or mucous secretion in the common nasal meatus and base of the nasal cavity; positive eosinophilic smear of nasal secretions; excluding accompanied fever, total account of white blood cell over the normal range in routine blood test; excluding chronic rhinitis, sinusitis and nasal polyps; excluding administration of other drugs or therapeutic methods before the visit.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
In conformity with the above diagnostic criteria; male or female; aged 16-70 years old; duration ≥6 months.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those not in conformity with the above diagnostic criteria and inclusion criteria; those have to take Aspirin or Steroids; those in pregnancy; those not in cooperation or not willing to accept the research measures or with mental disorders; those complicated with chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps or with obvious deviation of the nasal spectrum[7-8].
1.4 General data
Ninety cases from the Acupuncture Department and Inpatient Department of the hospital were divided randomly into a treatment group and a control group by their visit order, 45 cases in each group. Of 45 cases in the treatment group, their age ranged from 17 to 66 years old, and the duration ranged from 8 months to 24 years, including 32 cases with seasonal attack, 13 cases with perennial attack, 6 cases with the problem on the unilateral side, 39 cases with the problem on the bilateral sides, and 6 cases with a family history. Of 45 cases in the control group, their age ranged from 19 to 67 years old, and the duration ranged from 10 months to 22 years, including 30 cases with seasonal attack, 15 cases with perennial attack, 7 cases with the problem on the unilateral side, 38 cases with the problem on the bilateral sides, and 6 cases with a family history. There were no statistical differences in gender, age, condition and duration (P>0.05), and indicating the two groups were comparable.

Table 1. Comparison of general data between the two groups
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Treatment group
The treatment group was treated with acupuncture, acupoint injection and He-Ne laser radiation on the nasal cavity.
2.1.1 Acupuncture
Acupoints: Yingxiang (LI 20), Yintang (GV 29), Hegu (LI 4) and Zusanli (ST 36).
Operation: The patient took a sitting or supine position. After routine disinfection, the disposable needles of 0.3 mm in diameter and 25-40 mm in length were quickly inserted into the acupoints and retained for 30 min after the arrival of the needling sensation. The treatment was given once every day and 7 d made one course, with a 3-day interval between two courses. The therapeutic effects were assessed after two courses.
2.1.2 Acupoint injection
Acupoints: Quchi (LI 11) and Zusanli (ST 36).
Operation: The patient took a sitting or supine position. After routine disinfection, No. 5 needle and 5 mL syringe were used to draw 2 mL (40 mg) of Triamcinolone Acetonide, 1 mL of Lidocaine injection, and 2 mL (55 ug) of Vitamin B12. The syringe was inserted into the acupoints by routine technique. After the patients had the sour, distending and numb sensation and without withdrawal blood, 2.5 mL mixed injection was pushed into each acupoint. After the second time and afterward, the mixed injection of 2 mL (500 ug) of Vitamin B12, 2 mL (100 mg) of Vitamin B1and 2% of Lidocaine injection was given. Each time, Quchi (LI 11), Zusanli (ST 36) on one side were injected. The two sides were used alternatively. Seven sessions in continuous six days was one course, with a 3-day interval between the courses. The therapeutic effects were assessed after two courses.
2.1.3 He-Ne laser treatment
After the patient took a sitting position and fluid or secretions in the nasal cavity was rinsed clean, He-Ne laser apparatus manufactured by Changchun Optics and Fine Mechanics Institute was used and the disinfected laser fiber output head was aimed at the anterior of the inferior nasal concha and middle nasal concha and mucous of the nasal septum, by the intermittent output frequency, 8-15 mw of output power and 2 mm of spot diameter. The nasal cavity of each side was radiated for 8 min every day. Seven days made one course, with a 3-day interval between the courses. The therapeutic effects were assessed after two-course treatment.
2.2 Control group
Triamcinolone Acetonide nasal spray was given for both sides of the nasal cavity, 400 mg, 2 times every day, seven-day treatments constitute a course, and the therapeutic effects were assessed after two-course treatment.
3 Therapeutic Effects
3.1 Criteria of therapeutic effects
Clinical cure: The subjective symptoms disappeared, without nasal discharge and obstruction, without secretions in the nasal cavity, without congestion in the mucosa and tumefaction.
Effect: The subjective symptoms were improved, the nasal secretions were reduced and nasal obstruction was relieved, with little secretions in the inspection of the nasal cavity, congestion in the mucosa and relief of tumefaction.
Failure: There was no obvious improvement in the subjective symptoms, in the nasal obstruction and nasal discharge, and there was no difference in the inspection of the nasal cavity.
3.2 Statistical methods
All data were processed by the SPSS 17.0 version statistical software. The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (). The self-comparison of measurement data were analyzed byt-test. The analysis of variance was used for comparison between the groups.P<0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.
3.3 Therapeutic results
3.3.1 Comparison of short-term effect between the two groups
The clinical curative rate was 88.9% and the total effective rate was 100.0% in the treatment group, versus 57.8% and 80.0% in the control group. The differences between the two groups were statistically significant (P<0.05), indicating that the therapeutic effect was better in the treatment group than that in the control group (table 2).
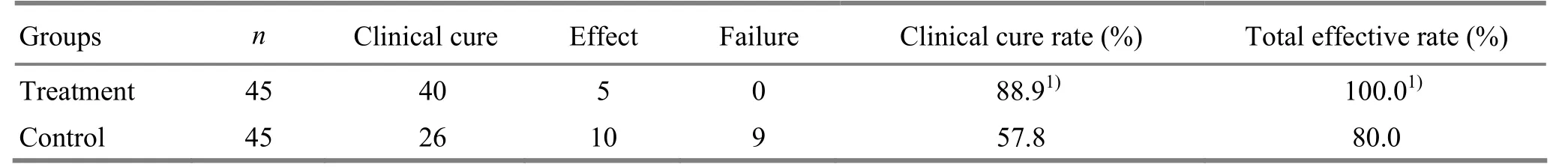
Table 2. Comparison of clinical effects between the two groups (case)
3.3.2 Comparison of clinical effects at different courses between the two groups
Of the 40 cured cases in the treatment group, 28 cases were cured by one course, accounting for 70.0%, and 12 cases were cured by two courses, accounting for 30.0%. Of the 26 cured cases in the control group, 6 cases were cured by one course, accounting for 23.1%, and 20 cases were cured by two courses, accounting for 76.9%. By Chi-square test, the differences between the two groups were statistically significant (P<0.05), indicating that the combination of three therapies can obviously shorten the treatment course for allergic rhinitis (table 3).
3.3.3 Comparison of long-term effects between the two groups
The follow-up of the cured patients after six months showed that 1 case had a relapse in 40 cured patients in the treatment group, with the recurrence rate at 2.5%, versus 9 cases in 26 cured cases in the control group, with the recurrence rate at 34.6%. In comparison of the recurrence rate, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.01), indicating that the therapeutic effect was more stable in the treatment of allergic rhinitis by the combination of the three therapies (table 4).
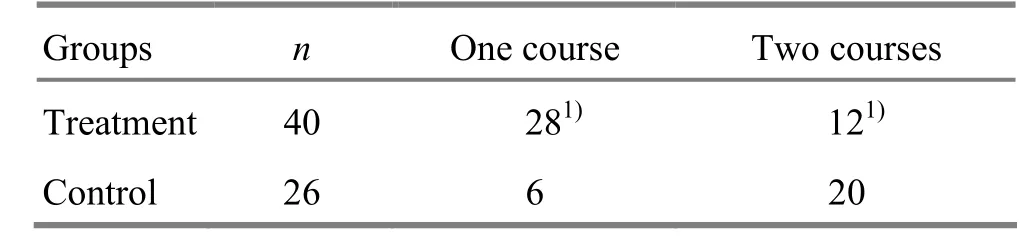
Table 3. Comparison of clinical effects at the different courses between the two groups (case)
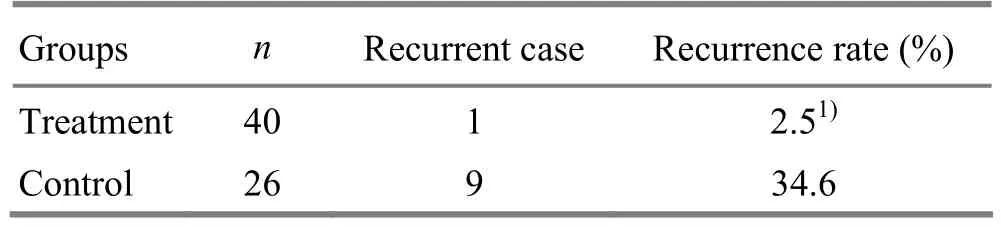
Table 4. Comparison of recurrence rates between the two groups after 6 months (case)
4 Discussion
It is believed in Western medicine that allergic rhinitis belongs to type I of allergic reaction, referring to chronic allergic disease of the nasal mucosa, involved by the release of IgE-mediated neurotransmitter and a variety of immune cells and cytokines, after the atopic individuals expose to allergen[9]. It is believed in Chinese medicine that this disease is induced by insecurity of Wei-Defensive qi due to qi deficiency in the lung and kidney plus invasion of pathogenic wind and cold or irritation of different gas and smell, leading to failure of the lung in spreading and descending[10], belonging to the scope of ‘nasal disorders’ in traditional Chinese medicine.
He-Ne laser is a kind of weak laser, also termed low-energy laser[11], a visible red light, with the penetrating depth of the tissues at 5-6 cm, and has the biological irritating and regulatory effect, and the proper amount can strengthen leukocyte phagocytosis and also inhibit the bacterial growth[11-13]. He-Ne laser radiation on the nasal mucosa can produce a series of biological effect, mainly thermal effects, photochemical effects, pressure effects, electromagnetic effects and strong laser biostimulation[12]. It can promote local blood circulation, accelerate metabolism, strengthen the intracellular enzyme activity of the local tissues, speed up the phagocytosis of the reticular cells, and promote the absorption and dissipation of inflammation[13]. At the same time, He-Ne laser can regulate the immune function of the body, increase the concentration of immunoglobulins, reduce the parasympathetic excitability inside the nasal cavity, reduce the sensitivity of the nasal mucosa, so as to reduce the release of inflammatory mediators and accelerate tissue repair[14].
Yingxiang (LI 20), a crossing acupoint of the Large Intestine Meridian of Hand Yangming and Lung Meridian of Hand Taiyin, can be used to treat the problems of the two meridians and is an important acupoint for nasal diseases and can clear away the lung heat, disperse pathogenic wind, and open the nasal aperture. Zusanli (ST 36), an acupoint of the Stomach Meridian of Foot Yangming, with its meridian running to the nose, is a commonly used acupoint to strengthen the spleen and stomach and can strengthen the spleen to remove dampness, enhance the immunity of the organism, and support body resistance and consolidate the constitution. The Governor Vessel is the sea of yang meridians and has the effects to regulate the meridian qi of the whole body. Yintang (GV 29) is supposed to excite yang qi and strengthen the anti-pathogenic ability of the organism. Hegu (LI 4) is a Yuan-Primary acupoint of the Large Intestine Meridian of Hand Yangming and is very extensive in the therapeutic scope and has the better effects to clear away heat from Yangming Meridians, dredge collaterals and open the orifices[15].
In this clinical study, Quchi (LI 11) was selected from the Large Intestine Meridian of Hand Yangming and Zusanli (ST 36) from the Stomach Meridian of Foot Yangming are composed as ‘a pair of acupoints’for acupoint injection, based upon the theory of‘communication of meridian qi’ in meridians sharing same name. Acupoint injection is a comprehensive therapy combining medications, acupuncture and meridian regulation. In this method, the stimulating effect of the acupoint by acupuncture and the anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects are integrated, so as to realize advantage of the quick pharmacological effects and long-term effects, and also to avoid the disadvantage of the adverse reactions of glucocorticoid in the whole body. This method needs to be popularized in the clinical treatment.

[1] Liu LM. Progress of Chinese medical therapy for allergic rhinitis. Zhongyi Erbihou Kexue Yanjiu Zazhi, 2008, 7(2): 34-36.
[2] Gu RQ. Clinical Allergic Diseases. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Publishing House, 1991: 21.
[3] Zhao YH. Observation on therapeutic effect in the treatment of 61 cases of allergic rhinitis by acupuncture, cupping method plus medications. Jilin Zhongyiyao, 2005, 25(1): 36-37.
[4] Zhou J. Effective observation on treating allergic rhinitis by point injection. Zhongyi Linchuang Yanjiu, 2011, 3(4): 46.
[5] Lin L, Xu LF, Yang DD, Zhang W. Clinical observation on He-Ne laser treatment of acute rhinitis. Dangdai Yixue, 2008, (5): 49-50.
[6] State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Nanjing:Nanjing University Press, 1994: 107-108.
[7] Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Rhinology Group of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Society of Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of allergic rhinitis. Zhongguo Linchuang Yisheng, 2010, 38(6): 67-68.
[8] Zhang CH, Hong J, Ma XP. Therapeutic observation on acupuncture-moxibustion plus moving cupping in treating allergic rhinitis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2012, 31(11): 835-837.
[9] Li BS. Chinese Medical Encyclopedia: Otolaryngology. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House, 1980: 74.
[10] Tian JQ, Yan DN, Wang DF. Preliminary study on allergic rhinitis in deficient and cold pattern. Jilin Zhongyiyao, 2004, 24(10): 57-59.
[11] Yin ZC, Dong YH, Zhu J. Influence of low-energy He-Ne laser intravascular radiation on blood circulation. Yingyong Jiguang, 2004, 24(6): 413-414, 420.
[12] Wang SH, Liu HQ, Zhang GY. Laser treatment of chronic otitis media with effusion in children. Jiguang Zazhi, 2002, 23(6): 76-77.
[13] Yang ZF, Yang JG, Gao GH. Research progress of immunomodulatory effect of lower-energy laser. Zhonghua Liliao Zazhi, 2001, 24(4): 244-247.
[14] Jiang X, Cai CS, Cai P, Gu MY. Mechanism study on He-Ne Laser treatment of chronic simple rhinitis. Zhonghua Yixue Yanjiu Zazhi, 2004, 4(7): 583-585.
[15] Zheng MF, He FR, Wu MX, Zheng LP. Effects of acupuncture at different groups of Yangming Meridian points on allergic rhinitis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2011, 30(1): 35-37.
Translator: Huang Guo-qi
R246.7
A
Date: July 24, 2013
Author: Song Hai-yun, associate chief nurse
Zhang Dongyun, associate chief nurse.
E-mail:1508666523@qq.com
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Clinical Study on Electroacupuncture for Cervical Intervertebral Disc Herniation
- Observation on Clinical Effects of Electroacupuncture Therapy for Apoplexy with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome
- Clinical Observation on Acupuncture Therapy for Depression at Perimenopause
- Therapeutic Efficacy Observation on Combining Herbal Cake-partitioned Moxibustion with Plumblossom Needle Therapy for Cervical Radiculopathy
- Therapeutic Observation on Swift Needling with Fire Needle plus Medication for Herpes Zoster
- Shu-Stream Points for Two Cases with Time-related Disease
