5-(3-吡啶基)间苯二甲酸构筑的镉ギ配位聚合物的合成、晶体结构及荧光性质
2013-06-27崔运成齐长利赵艳辉刘春波王家军
崔运成 齐长利 赵艳辉 刘春波 王家军
(吉林师范大学化学学院,环境友好材料制备与应用教育部重点实验室,四平 136000)
0 Introduction
Nowadays,the currently densely interests for the design and fabrication of novel metal-organic coordination polymers is rooted not only in their fascinating structures but also from their promising properties and great potential applications in the fields of gas storage[1],ion-exchange[2],catalysis[3]and nonlinear optics[4]. Hydrothermal synthesis is an efficiency strategy to constructthe coordination polymers through the direct coordination interaction of metal ions and suitable organic nitrogen-donor or oxygen-donor ligands[5-8].
As we allknown,in constructing desired coordination polymers,the selection of organic ligands leads a crucial role.Conventionally,one usually selected dicarboxylate linker,tricarboxylate linker(e.g.1,3-benzenebicarboxylic acid and 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid),or pyridine-multicarboxylic acid[9].In this article,we report a longated pyridylcarboxylic acid ligand with one pyridyl donor and two carboxylic groups,i.e.,5-(pyridin-3-yl)isophthalic acid(H2pyip)[10].On the basis of this T-shaped rigid ligand and the Cadmium nitrate tetrahydrate,a new coordination polymer have been synthesized,which is [Cd(pyip)(H2O)2]n(1)with 3D framework structure.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and instruments
All reagents were commercially available and were used without further purification.Elemental analysis(C,H,N)were performed on a Perkin-Elmer 2400 CHN elemental analyzer.Infrared (IR)spectra were recorded on a Perkin-Elmer FTTR instrument as KBr pellets (4 000~400 cm-1).The TG analysis is conducted on a Diamond TG/DTA 6300 thermal analyzer(P.E.Company,USA).
1.2 Synthesis of[Cd(pyip)(H2O)2]n
A mixture of Cd(NO3)2·4H2O(0.31 g,1 mmol),5-(pyridin-3-yl)isophthalic acid (H2pyip) (0.36 g,1.5 mmol),terephthalic acid (0.10 g,0.5 mmol)and H2O(16 mL)were sealed in a 25 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and heated at 160℃for 4 d,and then slowly cooled to room temperature.Colorless crystals of 1 (yield 45%based on Cd)suitable for X-ray crystallographic analysis was obtained.IR data(KBr,cm-1):3 408s,3 001m,1 682vs,1 611vs,1 580s 1 509m,1486m,1417vs,1282s,1 164m,1 098w,1 077m,1 019 w,1001w,937m,881m,831w,782w,730s,690s,656 w,568m,538m.Anal.calcd.for C13H11CdNO6(%):C 40.04,H 2.82,N 3.59;Found(%):C 39.98,H 2.85,N 4.63.
1.3 X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallographic data of 1 was collected at room temperature using epoxy coated crystals mounted on glass fiber.All measurements were made on a Bruker Smart Apex CCD diffractometer using graphite-monochromated Mo Kα radiation (λ=0.071 073 nm)with φ-ω scans mode.The structure was solved by direct methods and refined with the full-matrix least Squares technique using the SHELXS-97 and SHELXL-97 programs[11].Anisotropic thermal parameters were assigned to all non-hydrogen atoms.The hydrogen atom positions on the aryl rings were fixed geometrically at calculated distances and allowed to ride on the parent atoms,while the hydrogen atom positions on coordinate water were assigned by the Fourier electron density map.The crystallographic data are listed in Table 1.
CCDC:854164.
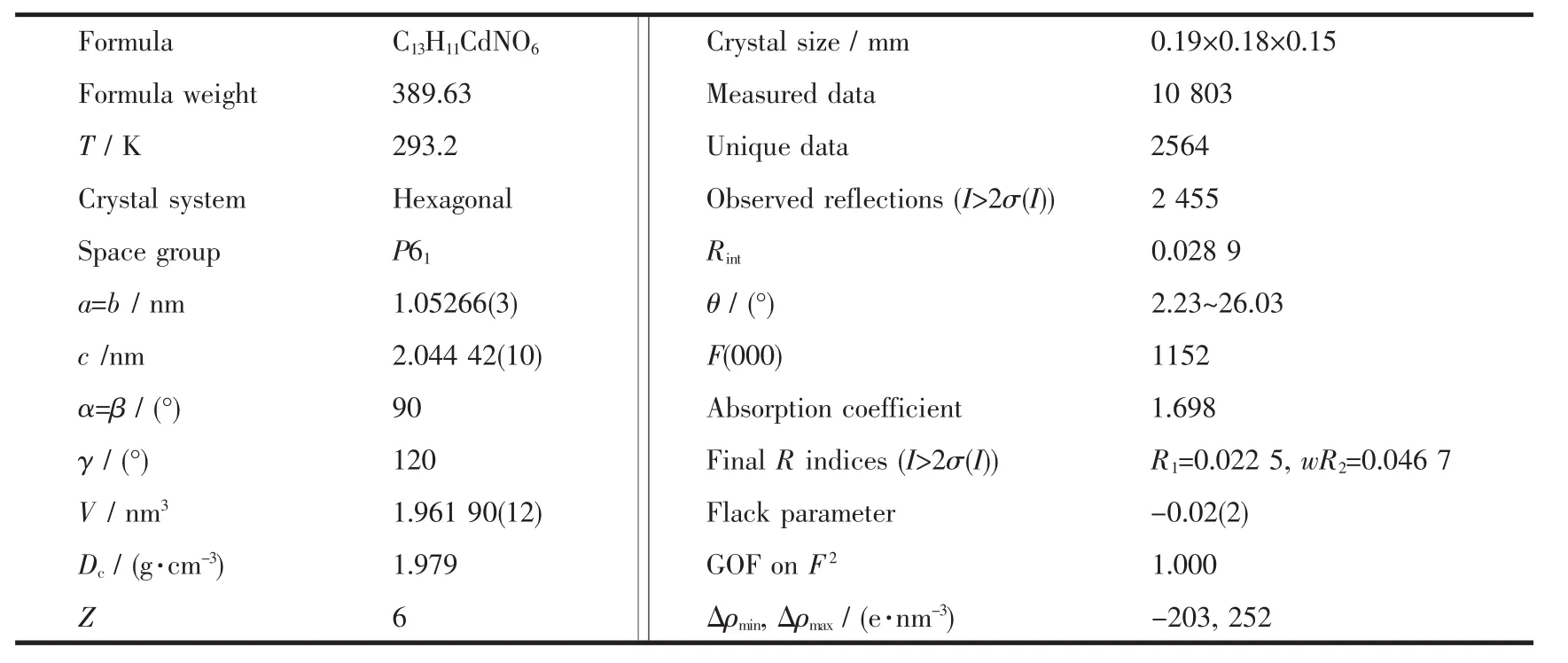
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for coordination polymer 1
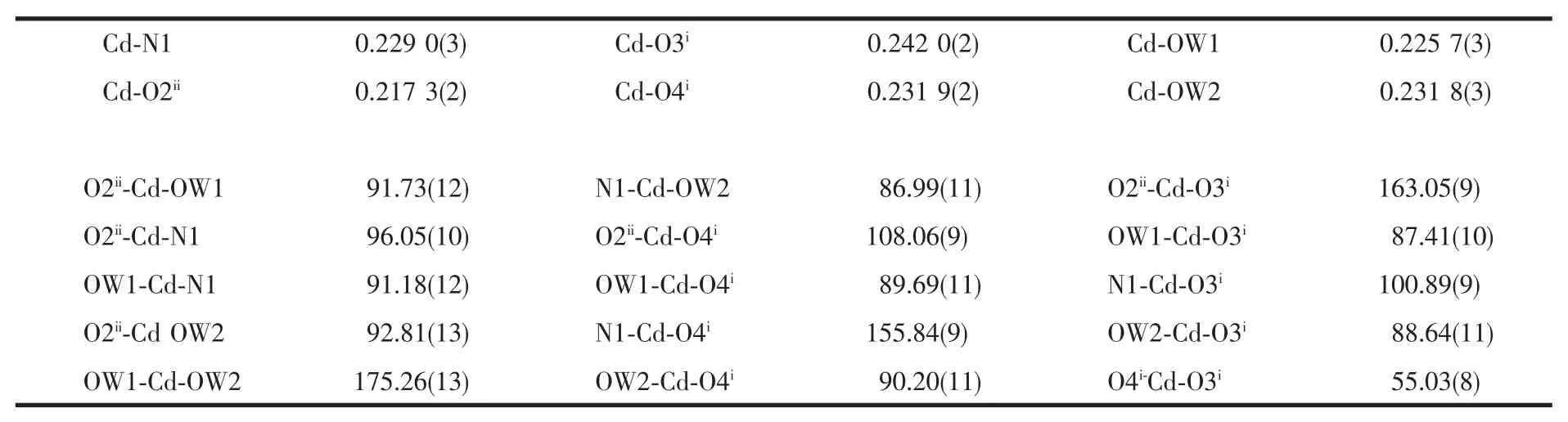
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)for coordination polymer 1
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that 1 is crystallized in the hexagonal,P61space group.As shown in Fig.1,in coordination polymer 1,each Cd ion adopts a six coordinate with three oxygen atoms coming from two different pyip ligands and the other two oxygen atoms coming from two coordinated water molecules,another coordinated site is occupied by a nitrogen atom which from the third pyip ligand.The two coordinated water molecules occupied the axial positions,while the other four atoms are situated on the equatorial position and basically in a plane.In this coordinated manner,center Cd formed a slightly distorted octahedron coordinate geometry.
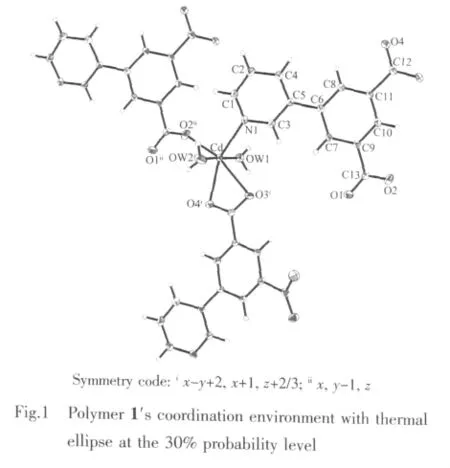
As indicated in Fig.1,for each pyip ligand,two of the three coordinated carboxylate oxygen atoms(O3i,O4i,ix-y+2,x+1,z+2/3)adoptbidentate chelate coordination mode and another coordinated carboxylate oxygen atom adopts the single dentate bridging mode,while the fourth carboxylate oxygen atom is a noncoordinated atom,and it is deprotonized for keeping the charge balance.In 1,the average Cd-Ocarboxyldistance is 0.229 7(6)nm,this distance is shorterthan the typicalaverage Cd-O distance 0.236 0(0)nm[12].The Cd-N1 distance(0.229 0(3)nm)is also shorter than the normal Cd-Npyridinedistance 2.32(2)[12].Each pyip joins three Cd centers together and each Cd center connected three pyip ligands to resultin an infinitethree-dimensionalpolymeric frameworks of[Cd(pyip)(H2O)2]n(Fig.2).
2.2 IR spectrum
The IR Spectrum shows that the strong peak at 3 408 cm-1(KBr pellet),which can be attribute to the coordination water molecules′O-H stretching vibration.We can regard the moderate strength band at 3 001 cm-1as the stretching vibration of the aromatic rings′C-H,and deem the bands at 1 611(vs),1 580(s)and 1 509(m)cm-1as the stretching vibration of the aromatic rings′C=C and C=N.While the COO-is coordinated with its asymmetric and symmetric stretching appearing at 1 682(vs,(OCO)assym),1 486(vs,(OCO)sym)and 1 417(vs,(OCO)sym)cm-1.The Δν(ν(OCO)assymν(OCO)sym)are 196(<200)and 255 cm-1(> 200),respectively.These two values indicate the presence of chelate and monodentate linkages of carboxylates in the pyip dianions.Thus,according to literature[13-14],the carboxylates coordinate to the metal cadmium center as the chelate and monodentate ligands via the carboxylate groups.In addition,X-raydiffraction analysis further reveals the existence of the chelate and monodentate coordination manners of the carboxylate groups.
2.3 Luminescent properties
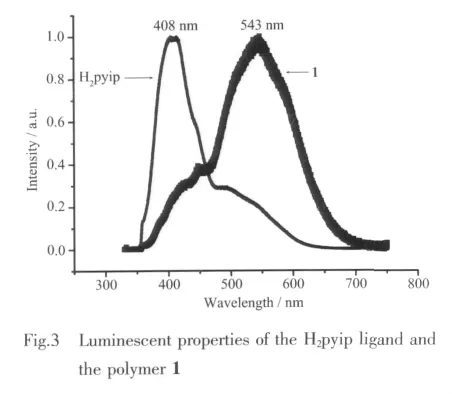
The luminescent properties of free ligand(H2pyip)and its metal coordination polymer 1 were investigated in solid state at room temperature.From Fig.3 we can see that the free ligand exhibits an emission band with the maximum intensity at 408 nm,and the Cd compound exhibits a broad emission band with the maximum intensity at543 nm,upon excitation at 325 nm and is red-shifted 135 nm compared to the emission wavelength of the free ligand.The band at 543 nm for 1 might neither LMCT(ligand-to-metal charge transfer)nor MLCT(metal-toligand charge transfer)in nature,and tentatively can be assigned to the intraligand fluorescent emission of coordinated pyip ligands due to the planar configuration of excimeric pyip molecules maintained by the cadmium ion[15-16].Generally,the intraligand fluorescence emission wavelength is determined by the energy gap between π and π*molecular orbitals of the free ligand,which is simply related to the extent of π conjugation in the system[17].This large red shift reveals stronger interactions than that of the ligandsbetween moleculesand istheresultof significant π-π stacking of the aromatic rings[18].
2.4 Thermogravimetric analysis
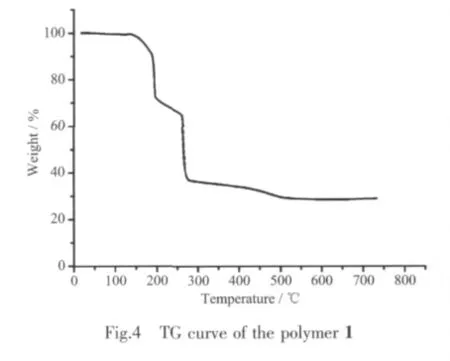
To determine the amount of the thermal stability of the polymer 1,thermogravimetry of the polymer 1 was examined in the range of 18~750 ℃ (Fig.4).The TG analysis of polymer 1 exhibits that it is stability before 130℃.However,from 130 to 155℃,the weight loss of 8.50%,we can corresponding to the loss of all the two coordinated water molecules(calcd.9.24%).From 210 to 500 ℃ ,the weight loss of 60.20%may corresponding to the loss of the pyip ligand (calcd.61.85%).After 500 ℃,there is no weight loss.The residues (28.50%)may be CdO(calcd.32.95%).
[1]Abrahams B F,Jackson P A,Robson R.Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.,1998,37:2656-2659
[2]Yaghi O M,Li H.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,1996,118:295-296
[3]Sawaki T,Dewa T,Aoyama Y.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,1998,120:8539-8540
[4]Evans O R,Lin W B.Acc.Chem.Res.,2002,35:511-522
[5]REN Yan-Ping(任艳平),KONG Xiang-Jian(孔祥建),LONG La-Sheng(龙 腊 生 ),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2011,27(6):1015-1020
[6]SU Zhi(苏志),LÜ Gao-Chao(吕高超),OKAMURA Taki-aki(岗村高明),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2011,27(5):971-976
[7]HOU Ke-ling(侯克玲),WANG Jian-ling(王建玲),DENG Chao-Yan(邓 朝 艳),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2011,27(7):1314-1318
[8]Zhou Y F,Jiang F L,Yuan D Q,et al.Angew.Chem.,2004,116:5783-5786
[9]Xiong R G,Wilson S R,Lin W B.J.Chem.Soc.,Dalton Trans.,1998:4089-4090
[10]Xiang S L,Huang J,Li L,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2011,50:1743-1748
[11]Sheldrick G M.Acta Cryst.,2008,A64:112-122
[12]Orpen A G,Brammer L,Allen F H,et al.J.Chem.Soc.Dalton Trans.,1989:S1-S83
[13]Kazuo N.Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds:Part B,6thEd.Hoboken,New Jersey(USA):John Wiley&Sons,Inc.,2009:64-67
[14]Deacon G B,Phillips R J.Coord.Chem.Rev.,1980,33:227-250
[15]Xu Y Q,Yuan D Q,Wu B L,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2006,6:1168-1174
[16]Shi X,Zhu G S,Fang Q R,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2004:185-191
[17]Perkovic M W.Inorg.Chem.,2000,39:4962-4968
[18]Zhang X J,Wu J Y,Zhang M L,et al.Trans.Metal Chem.,2003,28:707-711