MiR-1在肿瘤中的研究进展
2012-12-25蒋森赵亚萍杜云翔
蒋森,赵亚萍,杜云翔
(1.蚌埠医学院,安徽 蚌埠 233000;2.解放军第八二医院肿瘤中心,江苏淮安 223001;3.解放军第八二医院检验科,江苏 淮安 223001)
微小RNA(microRNA,miRNA)是一类高度保守的、具有调控功能的非编码小分子RNA[1]。目前发现的miRNA有15 000多种,其中人类有2 000多种[2]。据研究,miRNA参与调节人类大约30%蛋白质的翻译[3],几乎与细胞分化、代谢、生长、增殖和凋亡等所有分子过程的调节有关。越来越多的研究表明,miRNA多定位于肿瘤相关的脆性位点,与肿瘤的发生密切相关[4]。近年来,miRNA-1(miR-1)在肿瘤发生、发展过程中的作用受到关注,本文就此作一综述。
1 miR-1的基本特征
miR-1 家族包括 miR-1-1、miR-1-2 和 miR206[5]。Hsa-miR-1家族由2个miRNAs组成:hsa-miR-1-1和hsa-miR-1-2。miR-1-1位于人的第20号染色体上C20orf166基因初级转录本的第2个内含子区,miR-1-2位于人的18号染色体上蛋白质编码基因MIB1的第12个内含子区。miR-1的生物合成与其他miRNA一样,首先由细胞核内编码miRNA的基因转录产生初始miRNA(primary miRNA,pri-miRNA)[6],pri-miRNA 被RNaseⅢ内切酶进一步切割成前体miRNA(precursor miRNA,pre-miRNA)[7-9]。该前体在 Exprotin-5 的作用下转运到细胞质内[10]。在细胞质内,被RNA内切酶ⅢDicer酶剪切成成熟 miRNA[7,11]。在基因沉默复合物(RISC)的引导下,成熟的miRNA与特定靶基因mRNA的3'端非翻译区完全或不完全碱基互补配对引导RISC与目的mRNA结合,从而降解靶基因mRNA或阻遏其翻译[2],在转录后水平沉默基因的表达。通过在线数据库miRanda(http://www.microrna.org/)分析发现miR-1在心脏、甲状腺、子宫、前列腺、卵巢等组织中均有表达,参与细胞生长、分化、凋亡以及心脏、内耳发育等生理过程,与肿瘤、代谢类疾病、精神类疾病有关[12]。
2 miR-1在肿瘤中的表达
已有研究表明,miR-1在多种肿瘤细胞中表达异常,并参与了肿瘤的增殖、侵袭、迁移和凋亡(表1)。miR-1在绝大部分肿瘤中表达下调,发挥了抑癌基因的角色,然而,Liu等[13]分析胃癌患者和正常人血清标本miRNA表达谱,发现miR-1在胃癌患者血清中含量明显上调,具体机制尚不十分清楚。
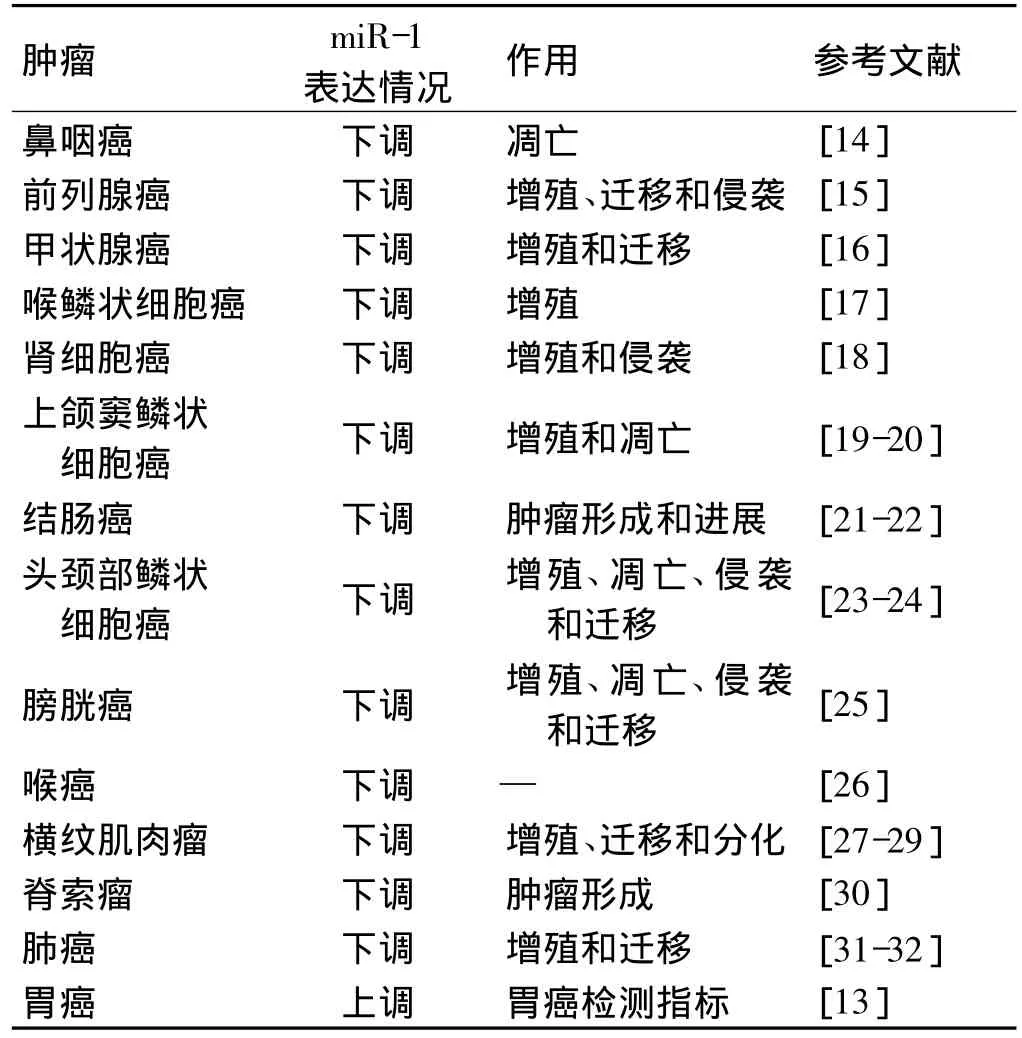
表1 miR-1在肿瘤中的表达情况
3 miR-1的靶基因
分析与鉴定miR-1的靶基因对于研究miR-1的功能具有重要意义。然而,由于miR-1与靶mRNA3'端非翻译区并非完全匹配,导致鉴定其靶基因有一定的困难,但是,目前对其靶基因的研究也取得了一定的进展,首先通过Targetscan、miRbase、Pictar等在线软件进行靶标预测,进一步采用荧光素酶报告实验、蛋白质印迹实验、实时荧光定量PCR技术进行验证,发现miR-1作用靶标基因多参与细胞增殖、侵袭、凋亡等(表2),提示miR-1可能通过下调这些基因表达参与肿瘤的发生发展的机制。
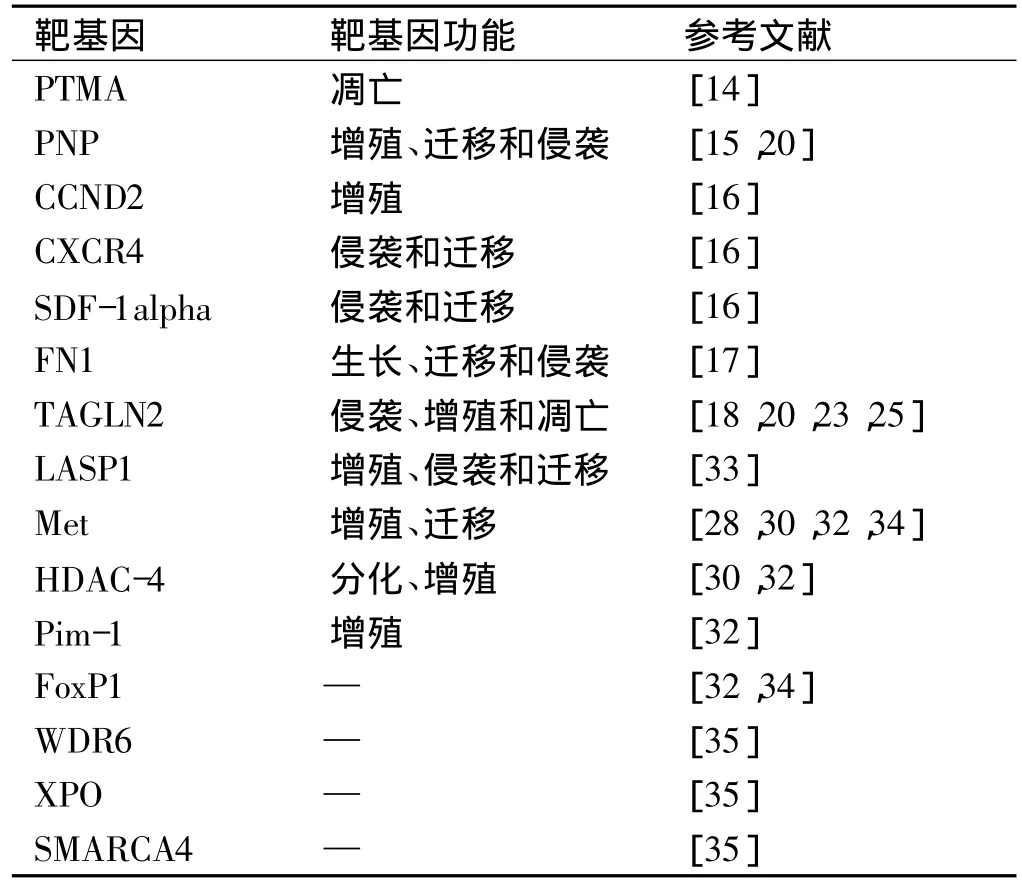
表2 miR-1的靶基因
4 miR-1与肿瘤的形成与发展
4.1 miR-1与肿瘤增殖和凋亡
肿瘤的发生是一个复杂的过程,与细胞的异常增殖和凋亡密切相关[36-37]。miR-1可通过抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和促进细胞凋亡而抑制肿瘤的发生。Taulli等[38]证实了miR-1在人类横纹肌肉瘤中的作用。过表达miR-1可以促进横纹肌肉瘤细胞的肌源性分化,同时抑制细胞的增殖。Wu等[14]研究发现miR-1转染的鼻咽癌细胞呈现出典型的凋亡代谢过程,其机制可能与下调PTMA(靶基因胸腺素a)表达有关。另外,Nohata等[19-20]利用 qRT-PCR技术发现,与正常组织相比,miR-1在上颌窦鳞状细胞癌组织中表达明显减少,而TAGLN2和PNP mRNA表达明显上升。过表达miR-1可以抑制癌细胞增殖、诱导其凋亡,生物信息学分析提示TAGLN2和PNP是受miR-1调节的靶基因。进一步研究证明这两种靶基因沉默后都能抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,从而间接提示miR-1可以通过抑制TAGLN2和PNP表达产生抑制肿瘤增殖的作用。
4.2 miR-1与肿瘤侵袭和迁移
miR-1不仅参与了肿瘤的增殖和凋亡,而且也同时参与了肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移。miR-1表达失调在肿瘤侵袭迁移过程中起着关键作用。Leone等[16]研究提示miR-1在甲状腺癌中表达下调,并参与了甲状腺肿瘤细胞的迁移。有趣的是,miR-1表达下调也出现在甲状腺非肿瘤性病变例如甲状腺肿。利用生物信息学方法找到趋化因子CXCR4和基质细胞衍生因子SDF-1a为miR-1的靶基因。在乳突状和未分化甲状腺癌中,miR-1表达水平和CXCR4、SDF-1a蛋白表达水平呈负相关。miR-1可能通过调控CXCR4和SDF-1a基因表达对甲状腺癌细胞侵袭和迁移产生影响。Yip等[39]也发现与非侵袭性乳头状甲状腺癌相比,侵袭性甲状腺癌miR-1表达明显下调,提示miR-1与肿瘤侵袭性行为密切相关。另外,Kojima等[15]检测了miR-1在前列腺癌细胞中的功能和意义,发现与正常前列腺组织相比,前列腺癌组织中miR-1表达明显下调。miR-1可以抑制前列腺癌细胞PC3和DU145侵袭和迁移。进一步采用全基因组基因表达分析和荧光素酶报告试验提示,前列腺癌组织标本表达显著增高的基因PNP受miR-1直接调节,miR-1通过沉默PNP基因抑制了PC3和DU145迁移和侵袭。该发现为揭示前列腺癌肿瘤形成机制提供了新的思路。Nasser等[32]将稳定转染miR-1的肺癌细胞A549和H1299细胞接种裸鼠,发现A549和H1299细胞的成瘤性、肿瘤生长和转移性均受到了明显的抑制。另有研究表明miR-1与肾细胞癌、膀胱癌、头颈部鳞状细胞癌等肿瘤的侵袭和迁移能力也密切相关[18,24-25]。
4.3 DNA甲基化对miR-1表达的调节
表观遗传学改变对miR-1的表达具有调控作用。miR-1编码启动子序列的CpG岛可以发生DNA的甲基化,从而调节miR-1的表达。而miR-1可通过调节甲基化的相关酶,改变肿瘤细胞的DNA甲基化状态,从而调控肿瘤的生长和转移。Datta等[34]利用DNA去甲基化试剂和组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂处理肝癌细胞,使肝癌细胞发生表观遗传学改变,检测发现miR-1表达水平升高。肝癌细胞系和组织中甲基化是普遍存在的,DNA去甲基化试剂作用于肝癌细胞可以重新激活miR-1的表达,从而抑制下游靶蛋白MET和FOXP1的表达,抑制了肝癌细胞的生长、诱导细胞凋亡。Suzuki等[40]以结肠癌细胞为研究对象,同样发现miR-1的表达受DNA甲基化的调节。
5 展 望
miR-1在绝大部分肿瘤中表达下调,且与肿瘤细胞增殖、侵袭、迁移和凋亡密切相关,提示这是一条在肿瘤诊断、病情监测以及预后判断中具有重要价值的miRNA。然而,目前有关miR-1的研究还处于初步阶段,对其作用靶基因需要进一步证实,许多靶基因尚有待进一步研究,有关其在肿瘤发生、发展机制中的研究多停留在体外实验,体内研究报道很少。由于组织特异性miR-1具有调节转录产物的能力,过表达miR-1可以抑制癌基因表达、阻止肿瘤生长,比起单个靶基因药物治疗肿瘤,作为一种无毒分化因子,miR-1可能具有更好的治疗潜能,在肿瘤诊治中发挥重要作用。
[1]AMBROS V.The functions of animal microRNAs[J].Nature,2004,431(7006):350-355.
[2]KOZOMARA A,GRIFFITHS-JONES S.miRBase:integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2011,39(Database issue):152-157.
[3]FILIPOWICZ W,BHATTACHARYYA S N,SONENBERG N.Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRN-As:are the answers in sight?[J].Nat Rev Genet,2008,9(2):102-114.
[4]CALIN G A,SEVIGNANI C,DUMITRU C D,et al.Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2004,101(9):2999-3004.
[5]LU L,ZHOU L,CHEN E Z,et al.A Novel YY1-miR-1 regulatory circuit in skeletal myogenesis revealed by genome-wide prediction of YY1-miRNA network[J].PLoS One,2012,7(2):e27596.
[6]van ROOIJ E,OLSON E N.MicroRNAs:powerful new regulators of heart disease and provocative therapeutic targets[J].J Clin Invest,2007,117(9):2369-2376.
[7]LEE Y,AHN C,HAN J,et al.The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing[J].Nature,2003,425(6956):415-419.
[8]DENLI A M,TOPS B B,PlASTERK R H,et al.Processing of primary microRNAs by the microprocessor complex[J].Nature,2004,432(7014):231-235.
[9]GREGORY R I,YAN K P,AMUTHAN G,et al.The microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs[J].Nature,2004,432(7014):235-240.
[10]LUND E,GUTTINGER S,CALADO A,et al.Nuclear export of microRNA precursors[J].Science,2004,303(5654):95-98.
[11] HUTVAGNER G,MCLACHLAN J,PASQUINELLI A E,et al.A cellular function for the RNA-interference enzyme Dicer in the maturation of the let-7 small temporal RNA[J].Science,2001,293(5531):834-838.
[12]ZHAO Y,SAMAL E,SRIVASTAVA D.Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis[J].Nature,2005,436(7048):214-220.
[13]LIU R,ZHANG C,HU Z,et al.A five-microRNA signature identified from genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling serves as a fingerprint for gastric cancer diagnosis[J].Eur J Cancer,2011,47(5):784-791.
[14]WU C D,KUO Y S,WU H C,et al.MicroRNA-1 induces apoptosis by targeting prothymosin alpha in nasopharyngeal carc-inoma cells[J].J Biomed Sci,2011,18:80.
[15]KOJIMA S,CHIYOMARU T,KAWAKAMI K,et al.Tumour suppressors miR-1 and miR-133a target the oncogenic function of purine nucleoside phosphorylase(PNP)in prostate cancer[J].Br J Cancer,2012,106(2):405-413.
[16]LEONE V,D'ANGELO D,RUBIO I,et al.MiR-1 is a tumor suppressor in thyroid carcinogenesis targeting CCND2,CXCR4,and SDF-1alpha[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2011,96(9):E1388-E1398.
[17]WANG F,SONG G,LIU M,et al.miRNA-1 targets fibronectin1 and suppresses the migration and invasion of the HEp2 la-ryngeal squamous carcinoma cell line[J].FEBS Lett,2011,585(20):3263-3269.
[18]KAWAKAMI K,ENOKIDA H,CHIYOMARU T,et al.The functional significance of miR-1 and miR-133a in renal cell ca-rcinoma[J].Eur J Cancer,2012,48(6):827-836.
[19]NOHATA N,HANAZAWA T,KIKKAWA N,et al.Tumour suppressive microRNA-874 regulates novel cancer networks in maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma[J].Br J Cancer,2011,105(6):833-841.
[20]NOHATA N,HANAZAWA T,KIKKAWA N,et al.Identification of novel molecular targets regulated by tumor supperssive miR-1/miR-133a in maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma[J].Int J Oncol,2011,39(5):1099-1107.
[21]OBERG A L,FRENCH A J,SARVER A L,et al.miRNA expression in colon polyps provides evidence for a multihit model of colon cancer[J].PLoS One,2011,6(6):e20465.
[22]SARVER A L,FRENCH A J,BORRALHO P M,et al.Human colon cancer profiles show differential microRNA expression depending on mismatch repair status and are characteristic of undifferentiated proliferative states[J].BMC Cancer,2009,9:401.
[23]NOHATA N,SONE Y,HANAZAWA T,et al.miR-1 as a tumor suppressive microRNA targeting TAGLN2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J].Oncotarget,2011,2(1-2):29-42.
[24]CHIDS G,FAZZARI M,KUNG G,et al.Low-level expression of microRNAs let-7d and miR-205 are prognostic markers of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J].Am J Pathol,2009,174(3):736-745.
[25] YOSHINO H,ChIYOMARU T,ENOKIDA H,et al.The tumour-suppressive function of miR-1 and miR-133a targeting T-AGLN2 in bladder cancer[J].Br J Cancer,2011,104(5):808-818.
[26]WANG P,FU T,WANG X.Primary,study of miRNA expression patterns in laryngeal carcinoma by microbarr-ay[J].Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi,2010,24(12):535-538.
[27]RAO P K,MISSIAGLIA E,SHIELDS L,et al.Distinct roles for miR-1 and miR-133a in the proliferation and differentiation of rhabdomyosarcoma cells[J].FASEB J,2010,24(9):3427-3437.
[28]YAN D,DONG XDA E,et al.MicroRNA-1/206 targets c-Met and inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma development[J].J Biol C-hem,2009,284(43):29596-29604.
[29]MIYACHI M,TSUCHIYA K,YOSHIDA H,et al.Circulating muscle-specific microRNA,miR-206,as a potential diagnostic marker for rhabdomyosarcoma[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2010,400(1):89-93.
[30]DUAN Z,CHOY E,NIELSEN G P,et al.Differential expression of microRNA(miRNA)in chordoma reveals a role for miRNA-1 in Met expression[J].J Orthop Res,2010,28(6):746-752.
[31]MELKAMU T,ZHANG X,TAN J,et al.Alteration of microRNA expression in vinyl carbamate-induced mouse lung tumors and modulation by the chemopreventive agent indole-3-carbinol[J].Carcinogenesis,2010,31(2):252-258.
[32]NASSER M W,DATTA J,NUOVO G,et al.Down-regulation of microRNA-1(miR-1)in lung cancer.Suppression of tumorigenic property of lung cancer cells and their sensitization to doxorubicin induced apoptosis by miR-1[J].J Biol Chem,2008,283(48):33394-33405.
[33]CHIYOMARU T,ENOKIDA H,KAWAKAMI K,et al.Functional role of LASP1 in cell viability and its regulation by mic-roRNAs in bladder cancer[J].Urol Oncol,2012,30(4):434-443.
[34]DATTA J,KUTAY H,NASSER M W,et al.Methylation mediated silencing of microRNA-1 gene and its role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis[J].Cancer Res,2008,68(13):5049-5058.
[35]AMBS S,PRUEITT R L,YI M,et al.Genomic profiling of microRNA and messenger RNA reveals deregulated microRNA expression in prostate cancer[J].Cancer Res,2008,68(15):6162-6170.
[36]石明,仇雪梅,樊红.血浆miRNA检测在肿瘤临床应用的研究进展[J].东南大学学报:医学版,2012,31(1):122-125.
[37]徐效峰,周怀君.miRNA-30c的研究进展[J].东南大学学报:医学版,2011,30(3):514-518.
[38]TAULLI R,BERSANI F,FOGLIZZO V,et al.The musclespecific microRNA miR-206 blocks human rhabdomyosarcoma growth in xenotransplanted mice by promoting myogenic differentiation[J].J Clin Invest,2009,119(8):2366-2378.
[39]YIP L,KELLY L,SHUAI Y,et al.MicroRNA signature distinguishes the degree of aggressiveness of papillary thyroid carc-inoma[J].Ann Surg Oncol,2011,18(7):2035-2041.
[40]SUZUKI H,TAKATSUKA S,AKASHI H,et al.Genome-wide profiling of chromatin signatures reveals epigenetic regulation of microRNA genes in colorectal cancer[J].Cancer Res,2011,71(17):5646-5658.
