血清转化生长因子-β1在特发性血小板减少性紫癜患儿中的变化及临床意义
2012-11-30徐宝华季海娟康裕斌朱红英
徐宝华 束 进 季海娟 康裕斌 朱红英
江苏省镇江市第一人民医院儿科,江苏镇江 212002
血清转化生长因子-β1在特发性血小板减少性紫癜患儿中的变化及临床意义
徐宝华 束 进 季海娟 康裕斌 朱红英
江苏省镇江市第一人民医院儿科,江苏镇江 212002
目的 探讨血清中转化生长因子-β1(TGF-β1)在特发性血小板减少性紫癜患儿中的变化及临床意义。 方法采用双抗体夹心酶联免疫(ELISA)定量测定方法检测17例ITP患儿治疗前后TGF-β1水平、血小板计数的变化,并与16例正常健康儿童血清TGF-β1、血小板计数水平进行比较。 结果 ITP患儿血清TGF-β1水平均显著高于正常对照组(P<0.01),ITP患儿治疗前血清TGF-β1水平均高于治疗后(P<0.01);血清TGF-β1高者,治疗过程中血小板计数恢复较慢。相关分析显示:TGF-β1水平与患者血小板计数呈负相关,与骨髓内巨核细胞数呈正相关(均P<0.01)。 结论 TGF-β1参与ITP的发病过程,其水平与血小板变化密切相关,可能与机体免疫机制异常有关。
特发性血小板减少性紫癜;转化生长因子-β1;巨核细胞;儿童
特发性血小板减少性紫癜 (idiopathic thrombocytopeni purpura,ITP)是小儿时期常见的出血性疾病,目前认为自身免疫机制异常是其发病的主要因素,但在血小板生成调控方面有无异常改变目前报道较少,笔者对此进行相关研究,现报道如下:
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
17例血小板减少性紫癜患儿来自于江苏省镇江市第一人民医院儿科,为2010年1月~2012年5月门诊及住院患儿,男8例,女9例,年龄为18个月~12岁,中位年龄7岁。所有病例均符合WHO诊断标准。16例健康体检儿童作为正常对照,其中,男7例,女9例,年龄6个月~12岁,平均年龄7岁。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 标本采集 采集特发性血小板减少性紫癜患儿开始治疗前及治疗4周后空腹外周静脉血2 mL,以2 000 r/min的速度离心15 min,分离血清,-20℃冰箱保存,统一检测TGF-β1,抗凝外周血用于血小板计数。对照组检测血清TGF-β1、外周血血小板计数。治疗前常规骨髓穿刺涂片检查并进行巨核细胞计数。
1.2.2 人血清TGF-β1的定量测定 正常对照者于体检日早清晨空腹静脉血6 mL,形成血凝块后以2 000 r/min离心20 min,分离血清,于-80℃冰箱保存。血清TGF-β1水平采用酶联免疫吸附法 (ELISA)检测,检测试剂盒为美国Bender Medsystems公司产品,操作时严格按试剂盒说明进行。
1.2.3 血小板、骨髓涂片巨核细胞计数 血小板计数通过全血细胞分析仪计数。骨髓涂片进行伊红染色,显微镜下进行巨核细胞计数并分类。
1.3 临床治疗方案
血小板减少性紫癜患儿主要采用泼尼松进行治疗,部分辅以丙种球蛋白和 (或)浓缩血小板输注。泼尼松用量为1.5 mg/(kg·d),分2次口服。 治疗过程中,每周复查血小板计数2次,以了解患者血小板恢复所需时间。
1.4 统计方法
2 结果
2.1 血小板减少性紫癜患者治疗前、后各指标比较
采用配对资料t检验统计分析,各指标间均有显著差异,具体结果见表1。
表1 ITP患者治疗前、后各指标水平比较(±s)
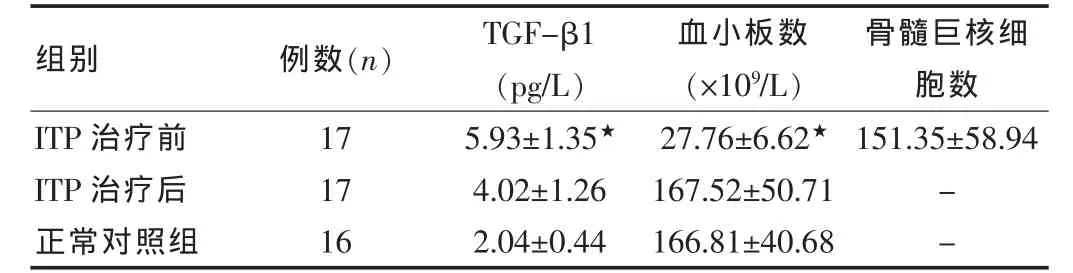
表1 ITP患者治疗前、后各指标水平比较(±s)
注:与ITP治疗后及正常对照组比较,★P<0.01
组别 例数(n) TGF-β1(pg/L)血小板数(×109/L)骨髓巨核细胞数ITP治疗前ITP治疗后正常对照组17 17 16 5.93±1.35★4.02±1.26 2.04±0.44 27.76±6.62★167.52±50.71 166.81±40.68 151.35±58.94--
ITP患儿治疗前及治疗后与正常对照组TGF-β1三指标间差异有统计学意义(均P<0.01)。
2.2 各指标间的相关性
ITP患者治疗前,TGF-β1水平与患者血小板数呈负相关,与骨髓内巨核细胞数(儿童骨髓巨核细胞数和分类正常值:总数为7~35)呈正相关(P<0.01)。血小板数和巨核细胞数呈负相关(P<0.01)。
2.3 ITP患者治疗前血清TGF-β1水平与血小板恢复关系
以血小板数恢复到100×109/L为标准统计患者恢复时所需时间,10例在2周内血小板数恢复正常,7例患者在治疗的第3、4周内恢复正常。对不同恢复时间患者TGF-β1水平比较分析,迟恢复组 TGF-β1分别为(5.22±1.02) pg/L,早恢复组 TGF-β1分别为(3.19±0.43)pg/L。 两组 TGF-β1水平差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
3 讨论
ITP患者以血小板减少为特征,多表现为巨核细胞生成血小板障碍。巨核细胞增殖、分化、成熟后生成血小板过程中受组织、细胞及细胞因子等多因素调控,细胞因子对巨核细胞和血小板的调节有重要作用[1]。其中TPO、IL-3、IL-6是正性调控因子,而 TGF-β1、PF4、TNF 等是负性调控因子[2]。 TGF-β1通过与巨核细胞表面TGF-β1Ⅲ型受体结合并抑制巨核细胞核内有丝分裂和CFU-MK的形成参与血小板生成调节[3-4],这种对血小板生成的负调控作用的发挥与TGF-β1相关的信号传导途径密切相关[5]。国内学者发现[6]:急性ITP组与慢性ITP组TGF-β1均明显高于健康对照组,且慢性ITP组明显高于急性ITP组。本结果中ITP患者血清TGF-β1水平明显升高,且与患者血小板计数呈负相关,反映了其负调控特征。但其与骨髓内巨核细胞数呈正相关,这可能是由于其作用致巨核细胞分化成熟障碍所致,说明TGF-β1与该类患者发病密切相关。
对 ITP患者 PBMCs相关因子表达研究发现[7]:IL-2、IFN-γ与IL-4、IL-5的mRNA表达水平的比率明显升高,且Th1/Th2比率与血小板计数呈负相关。在急性期患者,PBMCs中TGF-β1表达水平被明显抑制。对ITP患者外周单个核细胞TGF-β1低表达变化研究发现[8],血小板计数低时其TGF-β1低表达;血小板计数升高后TGF-β1表达增加。发现ITP患者血小板升高大于150×109/L患者Th3相关因子TGF-β1表达水平较血小板在 (50~150)×109/L者及健康对照组明显升高[9],说明ITP患者的转归与TGF-β1水平密切相关。本研究结果还显示:随着临床糖皮质激素治疗,血小板计数上升,患者的血清TGF-β1水平而下降。血小板迟恢复患者其血清TGF-β1水平较早恢复患者高,以上均说明ITP患者血清TGF-β1水平的变化与患者临床治疗的反应性密切相关。
综上所述,ITP患者存在TGF-β1表达异常,且TGF-β1表达水平与患者血小板恢复关系密切,与巨核细胞的分化、成熟有一定关系,可能在巨核细胞分化及血小板的生成中发挥调节作用,进一步的研究对阐明ITP的发病机制,尤其是难治性ITP的治疗有重要价值。
[1]Lu L,Wang LS,Cooper RJ,et al.Supp ressive effects of TNF-alha,TGF-beta 1,and chemokines on megakaryocytic colony formation in CD+34 cells derived from umbilical cord blood compared with mobilized peripheral blood and bone marrow[J].J Hematother Stem Cell,2000,9(2):195.
[2]Lu L,Wang LS,Cooper RJ,et al.Suppressive effects of TNF-alpha,TGF-beta 1,and chemokines on megakaryocyticn colony formation in CD+34 cells derived from umbilical cord blood compared with mobilized peripheral blood and bone marrow[J].J Hematother Stem Cell Res,2000,9(2):195.
[3]Akiyama T,Matsunaga T,Temi T,et al.Involvement of transforming growth factor2beta and thrombopoietin in the pathogenesis of mydlodysp tastic syndrome with myelofibrosis[J].Leukemia,2005,19(9):1558.
[4]AtabayB,Oren H,Irken G,et al.Role of transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene polymophisms in childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura[J].J Pediatr Hematol Oncol,2003,25(11):885.
[5]Fortunel N,Hatzfeld J,Kisselev S,et al.Release from quiescence of primitive human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells by blocking their cell-surface TGF-beta typeⅡreceptor in a short-term in vitro assay[J].Stem Cells,2000,18 (2):102.
[6]盛光耀,王璐,白松婷,等.骨髓TPO与 TGF-β1、TGF-βRⅢ的改变及其相关性在儿童ITP发病中的意义[J].中国小儿血液,2004,9(3):99.
[7]Panitsas FP,Theodoropoulou M,Kouraklis A,et al.Adult chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)is the manifestation of a type-1 polarized immune response[J].Blood,2004,103(7):2645.
[8] Andersson PO,Olsson A,Wadenvik H,et al.Reduced transforming growth factor-beta1 production by mononuclear cells from patients with active chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura[J].Br J Haematol,2002,116(4):862.
[9]Andersson PO,Stockelberg D,Jacobsson S,et al.A transforming growth factor-beta1-mediated bystander immune suppression could be associated with remission of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura[J].Ann Hematol,2000,79(9):507.
The change and clinical significance of serum transforming growth factorβ1 in young idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura patients
XU Baohua SHU Jin JI Haijuan KANG Yubin ZHU Hongying
Department of Pediatrics,Zhenjiang First People′s Hospital of Jiangsu Province,Zhenjiang 212002,China
Objective To discuss the change and clinical significance of serum transforming growth factor-beta1(TGF-β1)in young idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura patients.Methods The levels of TGF-β1 and the the counts of platelet were quantitative detected with double antibody sandwich enzyme linked immune(ELISA)for 17 cases with ITP before and after treatment,and compared with 16 cases of normal healthy children.Results In children with ITP,the levels of serum TGF-β1 were higher than the normal control group significantly (P<0.01).The levels of serum TGF-β1 were higher in cases before treatment than after treatment(P<0.01).The counts of platelet recovery is relative slowly through treatment process in those cases with higher levels of serum TGF-β1.Correlation analysis showed that there were negative correlation between the counts of platelet and the level of TGF-β1 (P<0.01)and there were positive correlation between the counts of megakaryocytes and the the levels of TGF-β1 (P<0.01).Conclusion TGF-β1 participated in the pathogenesis of ITP process,and there are closely relationship between its levels and the counts of platelet.The reason may be that the body′s immune mechanism is abnormal.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura;TGF-β1;Megakaryocyte;Children
R725.5
A
1674-4721(2012)11(c)-0054-02
2012-08-31 本文编辑:林利利)
