MMI-166对人胰腺癌细胞株SW1990体外增殖及凋亡的影响
2012-11-06巩本刚徐怀勇成丕光高崇崇吴俊本
巩本刚 徐怀勇 成丕光 高崇崇 吴俊本
·论著·
MMI-166对人胰腺癌细胞株SW1990体外增殖及凋亡的影响
巩本刚 徐怀勇 成丕光 高崇崇 吴俊本
目的探讨基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂MMI-166对人胰腺癌SW1990细胞增殖和凋亡的影响。方法应用不同浓度(25、50、100 μg/ml)的MMI-166处理人胰腺癌SW1990细胞24、48 h。用四甲基偶氮唑蓝(MTT)法检测细胞增殖抑制率;采用Annexin Ⅴ-PI法检测细胞凋亡,流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率。结果25、50、100 μg/ml MMI-166处理细胞24 h后,细胞生长抑制率分别为(34.23±3.87)%、(44.81±2.01)%、(53.91±1.74)%;48 h的抑制率为(39.95±1.83)%、(52.26±3.46)%、(63.20±2.48)%,呈浓度及时间依赖性。24 h的细胞凋亡率分别为(4.17±0.55)%、(8.22±0.70)%、(14.10±0.44)%;48 h的细胞凋亡率为(11.19±0.47)%、(23.01±0.53)%、(28.10±0.52)%,均显著高于对照组的(0.09±0.12)%(P<0.05)。结论MMI-166以浓度和时间依赖性抑制胰腺癌SW1990细胞增殖,诱导细胞凋亡。
胰腺肿瘤; 细胞系,肿瘤; 金属蛋白酶类组织抑制剂; 细胞增殖; 细胞凋亡
基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂通过抑制基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)的活性在胰腺癌治疗中发挥重要作用。研究证实,一代、二代MMPs抑制剂具有明显副作用,因此寻找一种高效低毒的MMPs抑制剂是目前研究方向之一。MMI-166是第三代新型选择性MMPs抑制剂,可特异性抑制MMP-2、MMP-9活性,从而抑制肿瘤侵袭和转移[1]。目前国外已有报道,MMI-166在肺癌、直肠癌和胰腺癌等动物实验中具有抗肿瘤浸润、转移作用[2-4]。本研究观察MMI-166对人胰腺癌细胞SW1990增殖和凋亡的影响,探讨其量效关系。
材料与方法
一、细胞增殖抑制率检测
人胰腺癌细胞株SW1990购于上海细胞库,在含有10%胎牛血清的L-15型培养液中培养、传代。取对数生长期细胞,以每孔1000个细胞接种于96孔板。细胞贴壁后,每孔分别加入终浓度为25、50、100 μg/ml的MMI-166,以不加MMI-166作为对照,继续培养24、48 h,分别加入5 mg/ml的MTT 20 μl继续孵育4 h,去培养液,每孔加入DMSO 150 μl,振荡混匀10 min,上酶标仪测各孔560 nm波长的吸光值(A560值),以单纯培养液调零。每一浓度设6个复孔,实验重复3次。抑制率=(1-实验组A560值/对照组A560值)×100%。
二、细胞形态观察
按每孔1.0×105个SW1990细胞接种于24孔板,细胞贴壁后按上述分为对照组和MMI-166各组继续培养24、48 h,于倒置相差显微镜下观察细胞形态变化。
三、细胞凋亡检测
收集上述各组细胞,用反应缓冲液制成单细胞悬液,密度≥1×105个/ml。取200 μl细胞悬液,加Annexin V 10 μl和PI 2 μl,混匀后室温避光孵育15 min,取100 μl置荧光显微镜下观察细胞染色。另一半加入400 μl反应缓冲液轻轻振荡,混匀,上流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡率。
四、统计学分析
结 果
一、MMI-166对SW1990细胞的增殖抑制作用
MMI-166呈浓度及时间依赖性抑制SW1990细胞的增殖(P<0.05,表1)。
二、SW1990细胞形态的变化
MMI-166处理后,SW1990细胞数明显减少,细胞皱缩,遮光性差,细胞膜破碎,随后贴壁细胞脱落漂浮在培养液中;对照组细胞生长良好(图1)。

表1 MMI-166对SW1990细胞的增殖抑制率
注:同时间点组间比较,aP<0.05;同浓度组间比较,bP<0.05
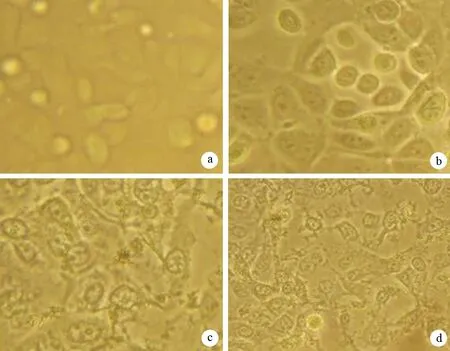
图1对照组(a)及MMI-166 25(b)、50(c)、100 μg/ml(d)组细胞形态(×100)
三、细胞凋亡
正常活细胞Annexin V、PI均低染;凋亡早期细胞Annexin V高染、PI低染,呈绿色荧光;凋亡晚期细胞和坏死细胞Annexin V、PI均高染,呈红、绿双色荧光(图2)。
MMI-166处理后,细胞凋亡率较对照组明显升高(P<0.05,表2、图3)。

图2MMI-166 25(a)、50(b)、100(c)μg/ml组细胞凋亡染色(×100)

表2 各组SW1990细胞的凋亡率
注:与对照组比较,aP<0.05;同浓度组内比较,bP<0.05
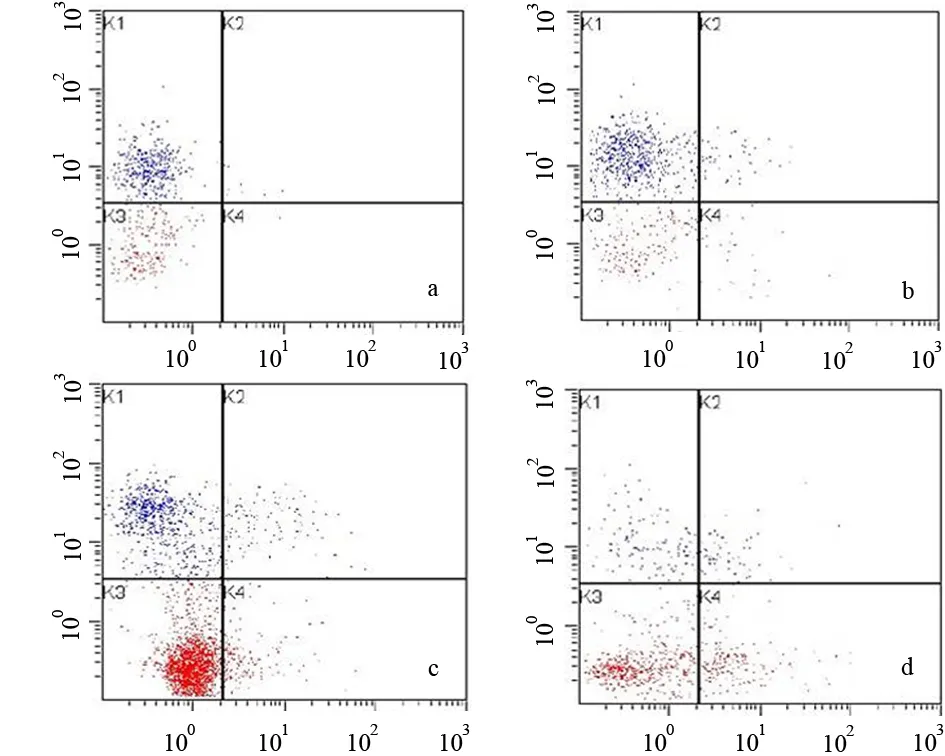
图3对照组(a)及MMI-166 25(b)、50(c)、100μg/ml(d)组细胞凋亡图(流式细胞仪)
讨 论
MMPs是一组锌离子依赖的分泌蛋白酶,它通过降解细胞外基质(ECM)和基底膜调节细胞间的黏附,促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和转移以及肿瘤组织中新生血管的形成,MMP抑制剂通过抑制MMPs的活性,抑制肿瘤侵袭、转移及肿瘤生长。在Ⅲ期临床研究中发现第一代MMPs抑制剂marimastat联合吉西他滨治疗晚期胰腺癌疗效并不优于单药吉西他滨[5],并可导致炎症性关节炎等不良反应。第二代MMPs抑制剂BAY12-9566在体外实验和Ⅰ期临床实验中显示出较好的抑制肿瘤的效果和更少的不良反应,但Ⅱ期临床试验中期分析结果后,因吉西他滨单药组无进展生存期和中位生存期较联合治疗组显著延长而被终止[6]。
MMI-166是第三代新型MMPs抑制剂,可选择性抑制MMP-2、MMP-9的活性。国外研究显示,MMI-166对多种恶性肿瘤细胞如胃癌、肺癌、结肠癌、头颈鳞状细胞癌及胶质瘤等[7-9]具有抗肿瘤侵袭、转移及抑制肿瘤生长的作用。Wang等[10]报道,MMP-9可酶解E-cad,稳定β-连环蛋白从而激活Wnt信号通路,促进细胞增殖。Meyer等[11]应用MMP siRNA导入结肠腺癌细胞SW480,使细胞免于PKC/p53诱导的凋亡。Chetty等[12]应用MMP-2 siRNA导入A549肺腺癌细胞,可诱导caspase-3、8、9以及PARP-1分裂体形成,诱导Fas/FasL的活化,从而发挥抗凋亡作用。本实验结果亦证实,MMI-166呈浓度及时间依赖性抑制人胰腺癌SWl990细胞的增殖,并促进细胞凋亡,有望成为一种新的治疗胰腺癌的化疗药物。
[1] Tamura Y, Watanabe H, Nakatani T, et al. Highly selective and orally active inhibitors of type IV collagenase (MMP-9 and MMP-2): Nsulfonylamino acid derivatives. J Med Chem, 1998, 41: 640-649.
[2] Fujino H, Kondo K, Ishikura H, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor MMI-166 inhibits lymphogenous metastasis in an orthotopically implanted model of lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther, 2005, 4: 1409-1416.
[3] Ohta M, Konno H, Tanaka T, et al. Effect of combination therapy with matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor MMI-166 and mitomycin C on the growth and liver metastasis of human colon cancer. Jpn J Can Res,2001, 92:688-695.
[4] Matsushita A, Onda M, Uchida E, et al. Antitumor effect of a new selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, MMI-166, on experimental pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer, 2001, 92:434-440.
[5] Bramhall SR, Rosemurgy A, Brown PD, et al. Marimastat as first-line therapy for patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer: a randomized trial.J Clin Oncol,2001,19:3447-3455.
[6] Moore MJ,Hamm J,Dancey J, et al. Comparison of gemcitabine versus the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor BAY 12-9566 in patients with advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol,2003,21:3296-3302.
[7] Maki H, Hojo K, Tanaka H, et al. Augmented anti-metastatic efficacy of a selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, MMI-166,in combination with CPT-11. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2002,19: 519-526.
[8] Katori H, Baba Y, Imagawa Y, et al. Reduction of in vivo tumor growth by MMI-166, a selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, through inhibition of tumor angiogenesis in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines of head and neck. Cancer Lett, 2002, 178:151-159.
[9] Nakabayashi H, Yawata T, Shimizu K.Anti-invasive and antiangiogenic effects of MMI-166 on malignant glioma cells. BMC Cancer, 2010, 10:339.
[10] Wang XQ,Li H,van Putten V,et al.Oncogenic K-Ras regulates proliferation and cell junctions in lung epithelial cells through induction of cyclooxygenase-2 and activation of metalloproteinase-9.Mol Biol Cell,2009,20:791-800.
[11] Meyer E,Vollmer JY,Bovey R,et al.Matrix metalloproteinases 9 and 10 inhibit protein kinase C-potentiated,p53-mediated apoptosis.Cancer Res,2005,65:4261-4272.
[12] Chetty C,Bhoopathi P,Lakka SS,et al.MMP-2 siRNA induced Fas/CD95 mediated extrinsic Ⅱ apoptotic pathway in the A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell line.Oncogene.2007,26:7675-7683.
EffectsofMMI-166onproliferationandapoptosisinhumanpancreaticcancerSW1990cell
GONGBen-gang,XUHuai-yong,CHENGPi-guang,GAOChong-chong,WUJun-ben.
DepartmentofHepatobiliarySurgery,BinzhouPeople′sHospital,BinzhouMedicalCollege,Shandong256600,China
XUHuai-yong,Email:xhy314552445@163.com
ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of MMI-166 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human pancreatic cancer SW1990 cells.MethodsMMI-166 of different concentrations (25, 50, 100 μg/ml) were used to treat human pancreatic cancer SW1990 cell for 24, 48 h. Effect of MMI-166 on cell proliferation was detected by 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazole)-2-5-biphenly-tetrazole bromide (MTT) method and effect on cell apoptosis was tested by Annexin V-PI method and flow cytometry (FCM).ResultsTwenty-four hours after MMI-166 treatment of different concentrations (25, 50, 100 μg/ml), the inhibitory rates of the cells were (34.23±3.87)%, (44.81±2.01)%, (53.91±1.74)%, and the corresponding values were (39.95±1.83)%, (52.26±3.46)%, (63.20±2.48)% at 48 h, which suggested a time-and concentration-dependent manner. The cell′s apoptosis rates were (11.19±0.47)%, (23.01±0.53)%, (28.10±0.52)% at 24 h, and the corresponding values were (11.19±0.47)%, (23.01±0.53)%, (28.10±0.52)% at 48 h, which were significantly higher than those in control group [(0.09±0.12)%,P<0.05].ConclusionsMMI-166 can inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of human pancreatic SW1990 cell in a time- and concentration-dependent manner.
Pancreatic neoplasms; Cell line, tumor; Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; Cell proliferation; Apoptosis
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2012.02.008
山东省科技发展计划项目(2009GG20002096)
256600 滨州,滨州医学院附属滨州市人民医院肝胆外科
徐怀勇,Email:xhy314552445@163.com
2011-09-26)
(本文编辑:屠振兴)
