A reliable and high throughput hybrid routing protocol for vehicular ad-hoc network
2012-08-13LeVanMinhGUOQingYANGMingchuan郭杨明川
Le Van Minh,GUO Qing,YANG Ming-chuan郭 庆, 杨明川
(Communication Research Center,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150001,China)
Vehicular communications have been considered to be an enabler for numerous vehicle safety and information applications.Many automobile manufacturers are in different stages of integrating communication devices in their vehicles for the purpose of safety,assisted driving,entertainment,and mobile commerce.As increasing number of vehicles start getting equipped with communication capability,large scale ad-hoc net-works can be envisioned in the foreseeable future.There are a lot of attractive applications emerged,which are unique for the vehicular setting.Vehicular-ad-hoc network(VANET)[1]applications include on-board active safety systems to assist drivers in avoiding collisions and to coordinate them at critical points such as intersections and highway entries.Safety systems may intelligently disseminate road information,such as incidents,real-time traffic congestion,high-speed tolling,or surface condition to vehicles in the vicinity of the subjected sites.This helps to avoid platoon vehicles and to improve the roads capacity accordingly.With such active safety systems,the number of car accidents and associated damage are expected to be largely decreased.In addition to the aforementioned safety applications,Inter-Vehicle Communications can be used to provide comfort applications as well.The services on the cars also may include weather information,gas station or restaurant locations,mobile e-commerce,entertaining applications,and interactive communications such as Internet access,music downloads,and content delivery.But now,there are a lot of the research challenges that need to be addressed until a wide deployment of VANET networks becomes possible.One of most important problems in VANET is routing protocol.It is main problem discussed in this paper.
A vehicle ad-hoc network is a set of mobile Cars(nodes),which communicate with each other and do not need any an existing infrastructure or central administration,illustrated in Fig.1.The topology of VANET is very flexible.Therefore,the routing protocols applied for this kind of network need be self-organizer.One of the very important communication problems in VANET is the stability of the link,which is able to transmit the packets according to the selected routing.This problem relates with speed and direction of moving cars,coverage of the propagation signal on cars.
There are a lot of routing protocol proposed for routing in VANET,each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages.For example,the Ad-hoc Ondemand Distance Vector(AODV)[2],or Ad-hoc Ondemand Multipath Distance Vector[3]all be on-demand protocol.It can save transmission system resources,but the delay in setting up the link for transmission will be large.Another example is Global State Routing(GSR)[4]protocol;it is the driven-table protocol.It takes more advantage on setting up link for transmission than on-demand routing protocol,but it requires system resources very large.Even,in some cases the system’s resources can not meet well.

Fig.1 Vehicular ad hoc network
In this paper,we propose a hybrid of two kind protocols mentioned above.The main contributions of this paper are threefold.Firstly,we adequately combine advantage characteristics of two categories routing protocols by using update neighbor instantaneously for each node and only performing route discovery process when receiving a communication requirements.This choice helps our proposed routing protocol restrict residual transactions between nodes better than tabledriven routing,and preparing information for route discovery process better than on-demand routing.Secondly,with building strong neighbor table of each node makes our proposed routing protocol have more reliable links in established routes.Furthermore,with the use of strong neighbors our proposed routing protocol reduces numerous route overheads in route discovery processes.Thirdly,by deeply recognizing of affections of the highly dynamic topology in VANET we choose proper parameters for construction route metric.Only parameters,which can withdraw from each node,aren’t involved performing many transactions between nodes or channel discovery.It makes our proposed routing protocol more suitable for VANET environment.
1 Related Works
1.1 VANET and Routing Protocol for VANET
In this part,we consider architecture and routing protocol for VANET.Each node in VANET can be seen as hosts and routers.As hosts,nodes need to provide user-oriented services;as routers,nodes need to run the routing protocols,in accordance with routing strategies,nodes involve packet forwarding and router maintenance.When the source nodes and destination nodes have the requirement of communication,and they are not within the scope of wireless transmission,and then they run the routing protocols by other nodes,and send data by wireless multi-hop approach.Therefore,ad hoc network can connect the isolate nodes and constitute a temporary group.With absence of network infrastructure,this feature can provide a new communication environment,and can broaden the mobile communications network applications.
According to the different driver models of route discovery,routing protocols for VANET can be divided into table-driven and on-demand routing protocol.Combined with the advantages of these two types of routing protocols,there is also a type of so-called"hybrid routing protocol."
1.1.1 Table-driven routing protocols
In table-driven routing protocols,because each node must retain the latest routing table in the local network,routing changes must be send to each node in order to obtain the consistent and up-to-date network routing when network topology changes.These kinds of routing protocol adapt to the requirements of VANET through the modification of existing routing protocols.
Table-driven routing protocols have the advantage that routes are available at the specific time they are needed.Because each node consistently maintains an up-to-date route to every other node in the network,a source can simply check its routing table when it has data packets to send to some destination and begin packet transmission.However,the primary disadvantage of these protocols is that the control overhead can be significant in large networks or in networks with rapidly moving nodes.Further,the amount of routing state maintained at each node scales as O(n),where n denotes the number of nodes in the network.Table-driven protocols tend to perform well in networks where there are a significant number of data sessions within the network.In these networks,the overhead of maintaining each of the paths is justified because many of these paths are utilized.
1.1.2 On-demand routing protocol
On-demand routing protocol is the flip-side of table-driven protocol.It initiates a routing request that is based on the specific needs of communications,instead of periodically broadcasting routing information packet.Therefore,it only performs routing operations when the node needs route,maintains the routing in the communication process,and deletes routing when there is no communication in long time.These mechanisms make on-demand routing save network resources effectively.Because of in on-demand routing protocol each node does not maintain a route to other nodes all time,so that from incurring of moving nodes,the route in each node maybe becomes stale.When a source node needs to send data packets to some destination,instead of the checking for its route table to determine whether it has a route,it uses RREQ message initiating route discovery process for destinations.If the RREQ message reaches either the destination or an intermediate node with a valid route entry to the destination,a Router Reply(RREP)message is sent back to the originator of the RREQ.A route is then set up between the source and the destination.If disruption link occurs when sending data process between source and destination nodes,the Route ERRor(RERR)message sends to source.
1.1.3 Hybrid routing protocols
The diverse applications of VANET pose a challenge for a single protocol that operates efficiently across a wide range of operational conditions and network configurations.Each of the purely table-driven or purely on-demand protocols described above performs well in a limited region of this range.For example,ondemand routing protocols are well suited for networks where the“call to mobility”ratio is relatively low.Table-driven routing protocols,on the other hand,are well suited for networks where this ratio is relatively high.The performance of either class of protocols degrades when the protocols are applied to regions of VANET space between the two extremes.
Hybrid routing protocol combines advantages of the table driven routing and the on-demand routing.It protects the more accurate routing information in the local scope by the use of table-driven routing.By the use of on-demand routing in further distance routing,it will reduce the overhead of overall routing protocol.Thus,it can play a better network performance;such agreements are more applicable to topology in special scenes,such as highly dynamic changes.
2 Some Related Routing Protocols
There are a lot of routing protocols proposed for VANET,each of which uses different assumption.In this paper we pay attention on the realistic VANET scenario.Firstly,we see some protocols applied for multirate propagation in VANET.The Medium Time Metric(MTM)with the consideration of multiple data rates was proposed[5].MTM can select optimal throughput paths,and tends to avoid long unreliable links.Another protocol Destination-Sequenced Distance-Vector(DSDV)was proposed[6],which is modified by using MTM as metric instead of hop-count.The simulation results of these protocols are good,but the disadvantage of the protocol based on MTM is designed for table-driven routing protocol,so that each node must maintain the whole network information of others.Therefore,MTM also have the disadvantage of tabledriven routing protocol,mentioned in part A.Also,MTM may be working not well at bottleneck link scenario.
Secondly,we see some routing protocols,which is improved of those protocols.The disadvantages of single rate routing protocols and MTM routing protocols were analyzed,and then a new protocol was proposed,which uses Routing Assessment Index(RAI)concept.It uses packet delivery,link reliability parameters to build RAI at rate rk.But if it would get packet delivery and link reliability values of propagation between node A and node B must implement a lot of time to propagate between node A and node B.It also requires a lot of network resources,special in case topology may change very fast in VANET.Chen et al.proposed an R-S-AOMDV routing protocol with routing metric combine hop-count,vehicle-motion and link-quality information[8],which is also on-demand routing protocol.
3 Proposed Routing Protocol
Lean on analysis network architecture and routing protocol of VANET above our proposed routing protocol came from an idea to build a routing protocol which can meet the requirement about minimum routing delay time,and uses minimum network resources and reliable in multi-rate network.From table-driven routing protocol properties,it can meet the requirement of minimum routing delay time,but it requires using a lot of network resources,special in VANET(because in VANET topology changes very fast caused by fast moving nodes,it requires updating routing information.It is a difficult problem).From on-demand routing protocol properties,it can meet the requirement of minimum used network resources,but it may take long routing time.
3.1.1 Routing matric and strong neighbors
From analyses above,we propose a routing protocol based on two kinds of routing protocols.It uses a neighbor table.The neighbor table is updated instantaneously when the topology of network is changed.Information of neighbor is built on the term load metric.The term load metric reflects how busy a node is engaged in receiving and forwarding packets over the wireless media.It also refers to processing,memory,bandwidth,and power load on the node.Consequently,the information in neighbor table of each node is updated from other node,including:
·Active path:this refers to the number of active routing paths supported by a node.Generally,the higher the number of active routing paths,the busier the node since it is responsible for forwarding data packets from an upstream node to a downstream node.
·Traffic size:this refers to the traffic load present at a node and its associated neighbors(measured in bytes).
·Packets in interface queue:this refers to the total number of packets buffered at both the incoming and outgoing wireless interfaces.
·Node delay:this refers to the delays incurred for packet queuing,processing,and successful transmission.
From those informations of neighbor node we build a list of Strong neighbors for routing process.At neighbor node j in the neighbor table of node i,let active path count at time t be n,and let traffic size be b,and let packets in interface queue count be p,and let node delay be d.Each of characteristic of route metric has its own measured unit,but in our works each is quantified into one number,respectively.We have a formula to estimate the routing metric:

Let X ={xj,xjis the routing metric value of neighbor jthin the routing table of node i}.We define the strong neighbors of node i as{neighbor xk,with xk(R-m)∈[L,R-mmax],L=E(X)}.
3.1.2 Route discovery strategy
Route discovery strategy is divided two phases.The first phase is the process to look for a destination node in the neighbor table.If Destination node is in neighbor table then the Source node sends RREQ to Destination node by using unicast,and Destination node replies RRER to Source node also by using unicast.After that the link between Source node and Destination node is setting up,the route discovery strategy process is finished.If Destination node is not in neighbor table then the route discovery process changes to second phase.In the second phase of route discovery,the Source node sends address of Destination node and weak node to strong node by using multicast.The Destination node address is for next node to continue discovery process to find Destination node.The weak node address is for restricting routing overhead in next step.In next step of route discovery process,each node in the set of strong neighbor node continues performing the route discovery process from the first phase.It will finish quick when find out the Destination node.
Parameters used in routing discovery process algorithm at one node are:
OVH-NBR:Number of overhead neighbor;
OVH-STR-NBR:Number of overhead strong neighbor;
RREQ-NUM:Number of allowable RREQ packets;
Nodei-address:IP address of node i.
Algorithm Discovery
IF nodeireceives a requirement to connect to nodej
THEN{
FOR(i=0;OVH-NBR-1;i++)
{IF neighbor-address==nodej-address THEN{
Send(Addr,RREQ);exit}
ELSE{
FOR(j=0;OVH-STR-NBR-1;j++)
{Send(Addr,RREQ);RREQ-Number++}
}}}
Where Send(Addr,RREQ)is a function to send RREQ message to next node,Addr is the address of Destination nodes.If Addr is only one address,it uses for unicast.If Addr includes all of strong neighbor,it uses for multicast.If Addr includes all of neighbor,it uses for broadcast.But in our proposed routing protocol does not use broadcast method.When Destination node receives the RREQ,it can use Reply(RRER)function.Reply(RRER)is a function to send RRER message back to prior node of current node.If prior node is intermediate node,itcontinuesto use Reply(RRER)to send RRER message to its prior node.
3.1.3 Protocol operation
For built the neighbor table,this protocol operation is the same as table-driven routing protocol.One node uses“Hello”packet to maintain the relationship with neighbor node.If there is any a new node in the propagative range,this node is using“Hello”packet to update information of the new node,as illustrated in Fig.2.Therefore,neighbor table of each node in network always is updated instantaneously.

Fig.2 One node uses“hello”packet for updating and maintaining information of neighbor nodes
The rest of the protocol is similar to on-demand routing protocol,but there is one modification.When Source node receives a requirement to send message to Destination node,the first step is to look for Destination node address in neighbor table.If Destination node is in neighbor table,it uses send(Addr,RREQ)send RREQ to Destination node,and Destination node uses reply(RRER)reply RRER to Source node and discovery process is finished.If Destination node is not in neighbor table,Source node sends RREQ to strong neighbor node.This operation restricts the routing overhead the same as OLSR[9].Also,it is a condition which will be sure that the setting up link will be reliable.
With neighbor of each node in network is updated on time,and the link between Source node to Destination node through strong neighbor make the proposed routing protocol meet the requirement of routing protocol for VANET.
4 Simulation Result and Analysis
We use the developed module in ns-2 with support of Monarch and Cygwin projects to simulate our proposed protocol,and compare with AODV and AOMDV[10]in the same condition of performance.The network was selected with the number of nodes varying from 50 to 200.Nodes are randomly distributed over 600 m ×600 m area.Send/receive data packets between Source node and Destination node use the IEEE 802.11g,uses IEEE 802.11 DCF for channel access,and data packet size is set to 1024 bytes.Each routing protocol is deployed in the same scenario for run simulation[11].
Fig.3 illustrates the result of the average route discovery time of proposed protocol(HAODV),AOMDV,and AODV routing protocol.

Fig.3 Average route discovery time
From the results in Fig.3,we can easily recognize that the average route discovery time is in direct ratio to the path length for all routing protocols.By neighbor nodes table is updated constantly,and restrict routing overheads by using strong neighbor make the HAODV routing process faster convergence than AOMDV and AODV.
Fig.4 illustrates the results of the average packet loss rate of three routing protocol HAODV,AOMDV,and AODV:The first result we can easily recognize is the effect of network density on broken links of all routing protocol.If the number of nodes increases,the number of broken links decreases.By using strong neighbor(including Link States of neighbor node,which is intermediate node in the transmission link)for routing process helps to restrict the drop link between Source node and Destination node when the topology of network changes.We can easily recognize it in Fig.4.And it also reflects to reliable link between Source node and Destination node.

Fig.4 Average packet loss rate
Fig.5 illustrates the results of the average network throughput of three routing protocols HAODV,AOMDV,and AODV:From Fig.5,we can also easily recognize the effect of network density on network throughput of all routing protocol.If the number of nodes increases,the network throughput also increases.In HAODV routing protocol by using strong neighbor node not only help reduce broken link between Source node and Destination node,but also increase the throughput of network.Because the use of capability of neighbor node when built the strong neighbor,intermediate node in link between Source node and Destination node is“strong”node.
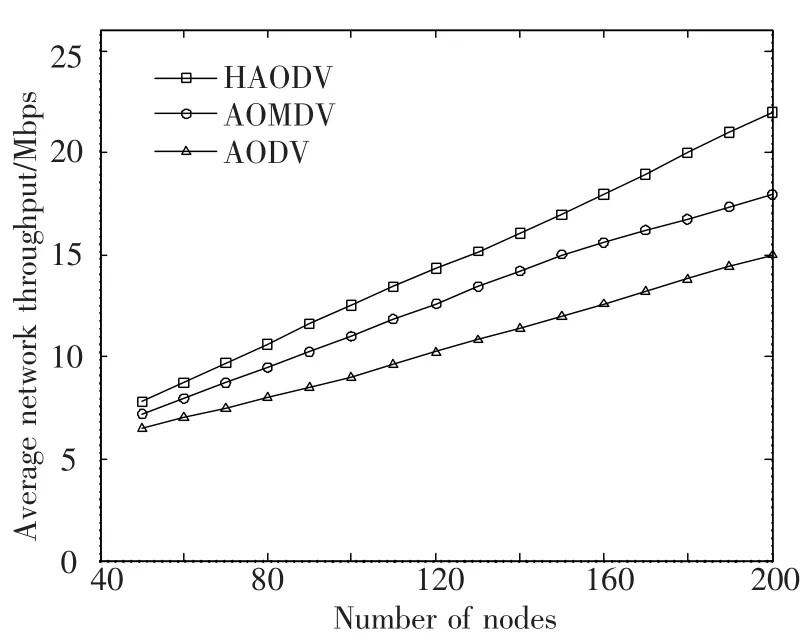
Fig.5 Average network throughput
Fig.6 shows average end-to-end data transfer time of three routing protocols AODV,AOMDV,and HAODV.As we argued above,AOMDV and HAODV on behalf of multipath routing protocols have transmitted data time lower than AODV.The HAODV routing protocol with maintaining neighbor table all time and route is built by strong neighbor characteristics,and its aver-age end-to-end data transfer time is always lower than AOMDV routing protocol.

Fig.6 Average end-to-end data transfer time
5 Conclusions
In this paper we propose a new routing protocol for VANET.It inherits the advanced properties of tabledriven routing protocol and on-demand routing protocol[12].Furthermore,by using unicast,multicast and broadcast mechanisms appropriately,it reduces significantly controloverhead and processing overhead.Therefore,it meets the communication requirements as setting up connection link and reliable link quickly,reducing broken link quickly,and increasing network throughput quickly.
[1]Yousefi S,Mousavi M S,Fathy M.Vehicular ad hoc networks(VANETs):challenges and perspectives.Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications.2006.761 -766.
[2]Perkins C E,Royer E M.Ad-hoc on-demand distance vector routing.Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications.Piscataway:IEEE Press,1999.90 -100.
[3]Marina M K,Das S R.On-demand multipath distance vector routing in Ad Hoc networks.Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Network Protocols.2001.14 -23.
[4]Chen Tsu-Wei,Gerla M.Global state routing:a new routing scheme for ad-hoc wireless networks.Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications.Piscataway:IEEE Press,1998.171-173.
[5]Awerbuch B,Holmer D,Rubens H.The medium time metric:High throughput route selection in multi-rate ad hoc wireless networks.MONET,2006,11(2):253 -266.
[6]Perkins C E,Bhagwat P.Highly dynamic destination-sequenced distance-vector routing(DSDV)for mobile computers.SIGCOMM.1994.234-244.
[7]Cao Trong Hieu,Hong Choong Seong.A reliable and high throughput multi-rate Ad Hoc routing protocol:cross layer approach.ICTC.2010.362-367.
[8]Chen Yufeng,Xiang Zhengtao,Jian Wei,et al.An adaptive cross-layer multi-path routing protocol for urban VANET.Proceedings of International Conference on Automation and Logistics.Hong Kong and Macau.2010.603 -608.
[9]Clausen T,Jacquet P.Optimized Link State Routing Protocol(OLSR).Rocquencourt:Hipercom,INRIA,2003.
[10]Chen Y F,Xiang Z T,Jian W,et al.A cross-layer AOMDV routing protocol for V2V communication in urban VANET.Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks.2009.353 -359.
[11]TohChai Keong,Le Anh-Ngoc,Cho You-Ze.Load balanced routing protocols for Ad Hoc mobile wireless networks.IEEE Communications Magazine,2009.78 -84.
[12]Yousefi S,Mousavi M S,Fathy M.Vehicular ad hoc networks(VANETs):challenges and perspectives.Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications.2006.761 -766.
杂志排行
Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology(New Series)的其它文章
- Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology(New Series)
- Design and realization of lamp life test instrument
- A modeling method of microburst based on multiple vortex ring
- Remediation of static lake water by intensified filter of dominant bacteria colony
- An innovative detection method of high frequency BPSK signal with low signal-to-noise ratio
- Research on the Seebeck effect in efficient turning process and improving tool life
