胃癌SGC7901/DDP细胞microRNA的表达谱分析及其在耐药逆转中的作用
2012-06-05左静,陈勇,刘颖,高鸿,刘巍*
左 静,陈 勇,刘 颖,高 鸿,刘 巍*
(1.河北医科大学第四医院肿瘤内科,河北石家庄 050011;2.江苏省苏北人民医院肿瘤内科,江苏扬州 225001)
胃癌SGC7901/DDP细胞microRNA的表达谱分析及其在耐药逆转中的作用
左 静1,陈 勇2#,刘 颖1,高 鸿1,刘 巍1*
(1.河北医科大学第四医院肿瘤内科,河北石家庄 050011;2.江苏省苏北人民医院肿瘤内科,江苏扬州 225001)
目的 分析胃癌SGC7901/DDP细胞 microRNA表达谱及其耐药特性,研究筛选出的 microRNA-200c对SGC7901/DDP细胞耐药的影响。方法 采用MTT法检测细胞的药物敏感性;应用microRNA芯片进行表达谱分析;运用生物信息学对筛选出的microRNA进行靶点预测和生物学进程分析。采用实时荧光定量RT-PCR检测microRNA-200c的表达;采用细胞转染分析microRNA-200c对SGC7901/DDP细胞药物敏感性的影响。结果 SGC7901/DDP细胞对顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇的IC50均显著高于SGC7901细胞(P<0.05)。与SGC7901细胞相比,SGC7901/DDP细胞中表达上调和下调超过2倍的microRNA分别有5和14个。microRNA高低表达组预测的靶点均广泛参与信号传导、细胞周期、分化、凋亡及增殖等生物学进程。实时荧光定量PCR分析证实microRNA-200c在SGC7901/DDP细胞中的表达显著降低(P<0.05),microRNA-200c能够显著降低SGC7901/DDP细胞对顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇的IC50(P<0.05)。结论 SGC7901/DDP细胞的多药耐药特性可能与microRNA表达谱的改变有关,其耐药表型的逆转可能与microRNA-200c的表达有关。
microRNA;胃癌;耐药;表达谱
*通信作者(corresponding author):hebeiliuwei@yahoo.com.cn#与第1作者相同贡献
microRNA是一类短链非编码RNA。microRNA与肿瘤的诊断、增殖、侵袭转移、临床分期及预后等生物学行为密切相关,同时越来越多的证据表明肿瘤细胞对抗肿瘤药物的敏感性受microRNA的影响。随着胃癌顺铂耐药细胞系 (SGC7901/DDP)的建立,对于SGC7901/DDP细胞的研究也逐步开始。虽然已有一些关于其耐药机制的报道,但是目前对该细胞的microRNA表达谱特征的研究尚未开展,同时microRNA在胃癌顺铂耐药过程中的作用也没有进一步的研究。本研究将采用microRNA芯片对SGC7901/DDP进行microRNA表达谱进行分析,对异常表达的microRNA进行高通量筛选,并通过细胞转染技术观察芯片筛选出的microRNA-200c对SGC7901/DDP细胞体外药物敏感性的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料及细胞培养
胎牛血清,RPMI1640培养液(Gibco公司);Trizol(Invitrogen公司);miRCURYTMArray Labelling kit及miRCURYTMArray microarray kit(Exiqon公司);siPORTMNeoFXTMTransfection Agent、miRNA-200c前体及Negative Control序列(Ambion公司)。人胃癌顺铂耐药SGC7901/DDP细胞及其亲代SGC7901细胞由本室保存。以含10%胎牛血清的RPMI1640培养液于37℃、5%CO2的培养箱中常规培养。耐药细胞培养液中含1 mg/L的顺铂,实验前1周开始使用常规培养基进行培养。
1.2 MTT法检测细胞体外的药物敏感性
贴壁细胞以0.25%胰蛋白酶消化,用含10%胎牛血清的RPMI1640培养液制备成单细胞悬液,以每孔7×103个细胞接种于96孔培养板中,每孔加入100 μL培养液,细胞贴壁后,加入100 μL不同浓度梯度的顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇。以不加药物干预作为对照组,以不接种细胞而仅加培养基作为调零孔,每种药物每个浓度设3个复孔。常规培养48 h后,每孔加新鲜配制的 MTT溶液(5 μg/μL)20 μL,37 ℃、5%CO2下继续培养4 h后,终止培养,小心吸弃孔内培养上清。每孔加入150 μL DMSO,振荡10 min,在酶联免疫检测仪上测定490 nm波长处各孔的吸光度(A)值,取3个重复孔的平均A值。按以下公式计算细胞的生长抑制率:细胞生长抑制率=(A对照组-A实验组)/A对照组×100%。根据不同药物浓度的细胞生长抑制率曲线,计算药物对细胞的半数抑制浓度(half inhibition concentration,IC50)。
1.3 RNA提取及鉴定
采用Trizol一步法分别提取对数生长期SGC7901/CDDP及SGC7901细胞的总RNA。采用微量分光光度计测定RNA的浓度和纯度。取1 μg总RNA进行1.5%甲醛变性琼脂糖凝胶电泳(100 V,30 min),检查18 S和28 S条带的存在。
1.4 microRNA芯片检测两株细胞的microRNA表达谱
应用丹麦Exiqon公司生产的microRNA芯片miRCURYTMLNA Array(v11.0)进行检测,由上海康成生物工程有限公司代理检测和分析。分别取1 μg上述两种细胞样本的总RNA,采用miRCURYTTMArray labeling kit标记Hy3荧光后应用 miRCURYTMArray microarray kit进行芯片杂交。杂交后芯片进行图像扫描,所得数据通过原始值减去背景值来做修正,并用中值做标准化,分别计算出两种样本中microRNA的标准值及比值。以两种细胞Hy3荧光标记信号强度的比值≤0.5或≥2为标准判定差异表达microRNA。
1.5 差异表达microRNA的生物信息学分析
应用 TargetScan(http://www.targetscan.org/)及 MicroCosm Targets Version 5(http://www.ebi.ac.uk/enright-srv/microcosm/htdocs/targets/v5/)分别进行在线生物信息学分析,筛选出两种方法预测到的共同的靶点。将所有预测到的靶点按其对应的microRNA表达改变情况分为两组,分别采用Blast2GO对两组预测的靶点在线批量GO分析(http://www.blast2go.org/start_blast2go),对不同 microRNA 表达组的靶基因的生物学进程进行注释,预测其生物学功能。
1.6 实时荧光定量PCR检测细胞的microRNA-200c表达
提取细胞总RNA,cDNA合成过程中采用microRNA-200c特异茎环引物构建反转录体系,反应条件为16℃ 30 min、42℃ 42 min、85℃ 5 min。构建PCR体系进行实时荧光定量PCR扩增,反转录及PCR引物序列见表1。反应条件为:95℃,5 min之后进行40个PCR循环,每个循环包括:95℃,10 s;60℃,20 s;72℃,20 s;78℃,20 s(收集荧光强度),内参照为U6。数据分析采用2-△△Ct法进行分析。△Ct=(microRNA-200c)Ct-U6Ct,比较microRNA-200c在两株细胞间表达的差异时△△Ct=(SGC7901/DDP)△Ct-(SGC7901)△Ct。
1.7 细胞转染
SGC7901/DDP细胞转染 microRNA-200c前体(pre-200c)过程,参照 siPORTTMNeoFXTMTransfection Agent使用说明进行。转染24 h后,提取细胞总RNA;采用实时荧光定量RT-PCR检测转染效果;比较转染后microRNA-200c表达改变时的△△Ct=(pre-200c)△Ct-(Control)△Ct;转染后24 h收集细胞进行体外药物敏感性实验。同时以转染Negative Control序列作为阴性对照。
1.8 统计学分析
2 结果
2.1 两株细胞对顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇的敏感性
SGC7901/DDP细胞对顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇的IC50均显著高于SGC7901细胞(P<0.05)(表2)。

表1 microRNA-200c和U6实时荧光定量PCR所使用的引物序列Table 1 Primers of microRNA-200c and U6 for real-time fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR
表2 SGC7901/DDP及SGC7901细胞的顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇IC50值Table 2 IC50values of the two cell lines to DDP,doxorubicin,5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel respectively( ± s,n=3)
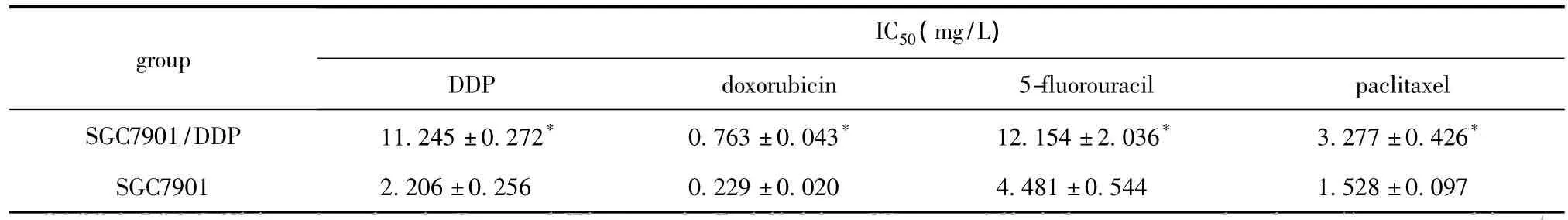
表2 SGC7901/DDP及SGC7901细胞的顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇IC50值Table 2 IC50values of the two cell lines to DDP,doxorubicin,5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel respectively( ± s,n=3)
*P<0.05 compared with SGC7901.
group IC50(mg/L)DDP doxorubicin 5-fluorouracil paclitaxel SGC7901/DDP 11.245±0.272* 0.763±0.043* 12.154±2.036* 3.277±0.426*1.528±0.097 SGC7901 2.206±0.256 0.229±0.020 4.481±0.544
2.2 RNA的质量检测
从SGC7901/DDP及SGC7901细胞提取出RNA的浓度分别为:1 145.77 mg/L和1 853.74 mg/L,A260/A280值均在1.9~2.0之间。其18 S和28 S条带清晰,亮度比约为1∶2,总RNA纯度达到实验要求且无明显降解(图1)。
图1 两株细胞的RNA甲醛变性琼脂糖凝胶电泳图Fig 1 RNA agarose gel electrophoresis of the two cell lines
2.3 microRNA芯片检测结果
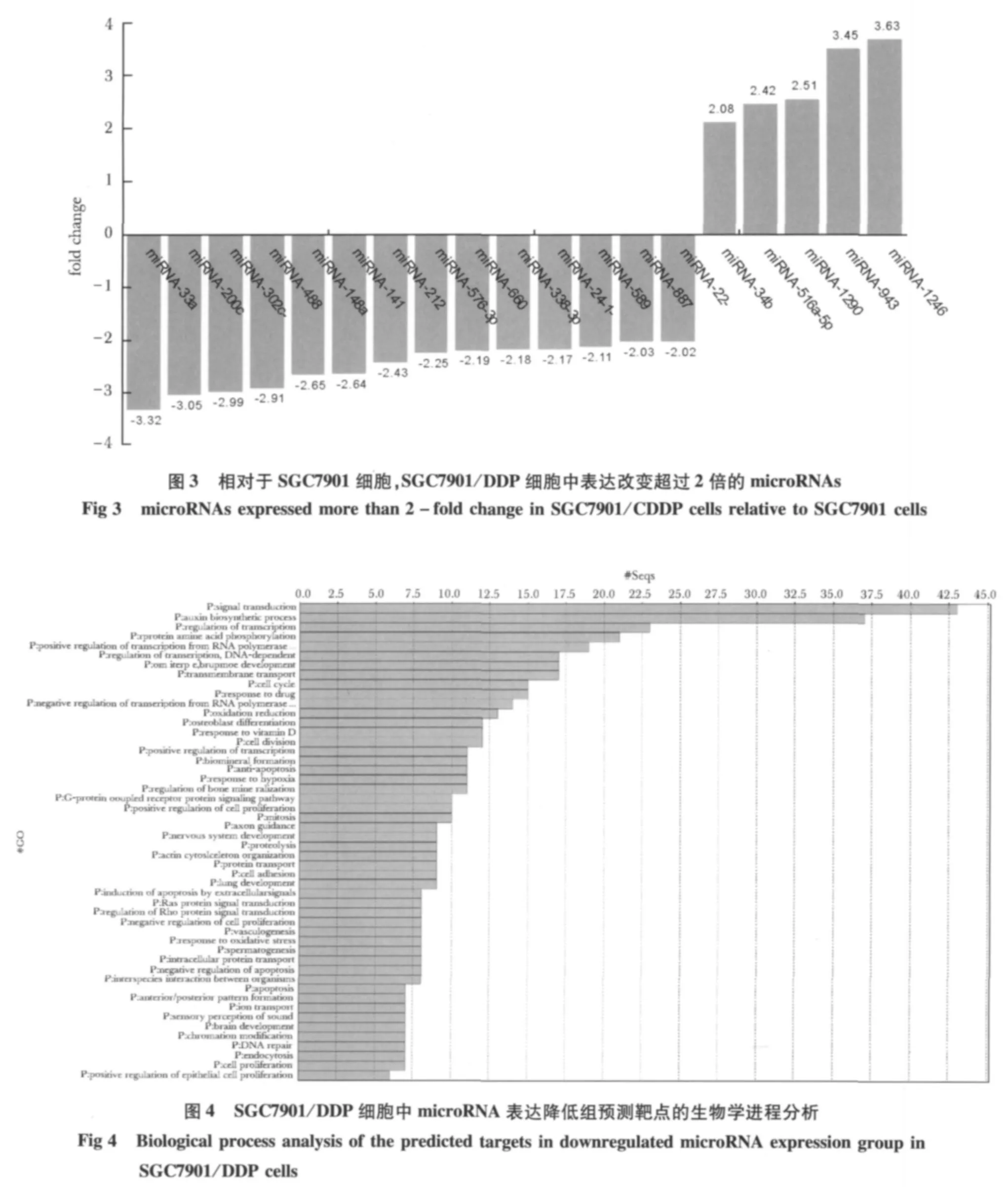
与SGC7901细胞相比,SGC7901/DDP细胞中表达下调超过2倍的microRNA有14个,分别为microRNA-33a,microRNA-200c,microRNA-302c*,microRNA-488,microRNA-148a,microRNA-141,microRNA-212,microRNA-576-3p,microRNA-660,mi croRNA-338-3p,microRNA-24-1*,microRNA-589,microRNA-887,microRNA-22*;表达上调超过2倍的 microRNA有5个,分别为:microRNA-1246,microRNA-943,microRNA-1290,microRNA-516a-5p,microRNA-34b(图2,3)。
2.4 生物信息学分析结果
TargetScan未能成功预测靶点的microRNA有:microRNA-302c*、microRNA-24-1*和microRNA-22*;MicroCosm未能成功预测靶点的microRNA有:microRNA-1290和microRNA-1246。microRNA表达降低组共有451个预测靶点,Blast2GO分析显示这些靶点参与信号传导、转录调控、蛋白质磷酸化、跨膜转运、细胞周期、药物敏感性、细胞分化、凋亡、增殖、细胞黏附及DNA修复等生物学进程(图4)。microRNA表达增高组共有98个预测靶点,Blast2GO分析显示这些靶点参与信号传导、转录调控、跨膜转运、细胞周期、凋亡、增殖、分化及组织发生等生物学进程(图5)。
2.5 实时荧光定量PCR分析microRNA-200c在两株细胞中的表达
SGC7901/DDP细胞 microRNA-200c的△Ct为15.470±0.036,SGC7901细胞的△Ct为14.657±0.229。SGC7901/DDP细胞microRNA-200c的相对表达量是SGC7901细胞的0.573±0.084倍,显著低于敏感株细胞的表达(P<0.05),与microRNA芯片结果一致。

图2 SGC7901细胞及SGC7901/DDP细胞的microRNA芯片杂交图Fig 2 microRNA microarray maps of SGC7901and SGC7901/DDP cells
2.6 microRNA-200c对SGC7901/DDP体外药物敏感性的影响
SGC7901/DDP细胞转染 microRNA-200c前体24 h后 microRNA-200c的△Ct为12.660 ±0.079,阴性对照组为15.493±0.080;microRNA-200c表达水平较对照组提高7.128±0.159倍(P<0.05)。转染microRNA-200c前体组细胞对顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇的IC50显著低于阴性对照组 (P<0.05)(表3)。

图5 SGC7901/DDP细胞中microRNA表达增高组预测靶点的生物学进程分析Fig 5 Biological process analysis of the predicted targets in upregulated microRNA expression group in SGC7901/DDP cells
表3 SGC7901/DDP细胞转染microRNA-200c前体后对顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇IC50值Table 3 IC50values of SGC7901/DDP cells to DDP,doxorubicin,5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel after transfection of microRNA-200c precursor or negative control( ± s,n=3)
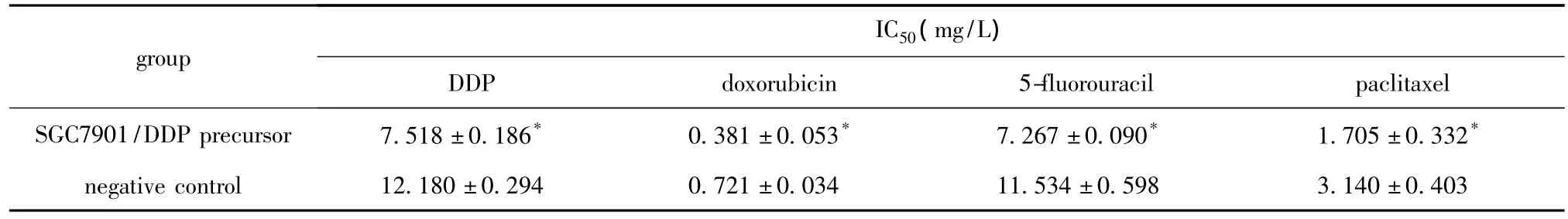
表3 SGC7901/DDP细胞转染microRNA-200c前体后对顺铂、阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇IC50值Table 3 IC50values of SGC7901/DDP cells to DDP,doxorubicin,5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel after transfection of microRNA-200c precursor or negative control( ± s,n=3)
*P <0.05 compared with negative control.
group IC50(mg/L)DDP doxorubicin 5-fluorouracil paclitaxel SGC7901/DDP precursor 7.518±0.186* 0.381±0.053* 7.267±0.090* 1.705±0.332*1.534±0.598 3.140±0.403 negative control 12.180±0.294 0.721±0.034 1
3 讨论
microRNA是一类主要以调控mRNA表达和翻译方式发挥作用的短链非编码RNA。microRNA不仅广泛参与肿瘤的发生发展过程,它还影响着肿瘤细胞对抗肿瘤药物的敏感性。
SGC7901/DDP细胞是胃癌细胞的耐药株,本研究发现SGC7901/DDP细胞除对顺铂耐药外,还对阿霉素、5-氟脲嘧啶及紫杉醇存在交叉耐药,呈现出多药耐药特点。目前在乳腺癌、胃癌、卵巢癌耐药细胞中陆续建立了microRNA表达谱特征[1-3],但还没有对SGC7901/DDP细胞microRNA表达谱进行研究,本研究通过microRNA芯片分析共筛选出19个异常表达的microRNA。随后通过目前常用的靶点预测软件,进行靶点功能预测及GO分析,结果显示这些靶点广泛参与多种生物学进程,表明胃癌细胞顺铂耐药是多个microRNA综合作用的结果。
在筛选出的microRNA中,只有少部分的microRNA与肿瘤耐药的联系得到研究。其中microRNA-148a不仅能够增加前列腺癌耐药细胞对紫杉醇的敏感性[4],还能够增加食管腺癌及鳞癌细胞对顺铂和5-氟脲嘧啶的细胞毒作用[5]。对 microRNA-200c的研究显示其在多种肿瘤耐药细胞(顺铂耐药的乳腺癌细胞、吉西他滨耐药的胰腺癌细胞)中表达下降[6-7],它可直接调控 TUBB3 和 ERRFI-1 蛋白的表达增加肿瘤细胞对紫杉醇和表皮生长因子抑制剂的敏感性[8-9],同时还能够增加阿霉素的抗肿瘤作用[10]。目前,尚没有证据显示其他microRNA直接参与肿瘤耐药,但是它们的一些靶点如HMGB1(microRNA-141的靶点)和ABCA1(microRNA-33a的靶点)均与肿瘤的耐药密切相关。因此这些异常表达的microRNA在胃癌细胞耐药中的作用有待于广泛的研究。
本研究对表达异常的microRNA-200c进行了进一步的研究。实时荧光定量PCR分析结果与microRNA芯片结果一致,microRNA-200c在SGC7901/DDP细胞中的表达水平显著下调。进一步研究发现上调microRNA-200c表达后,SGC7901/DDP细胞对4种化疗药的药物敏感性均显著增加,然而其中的作用机制还未得到阐述。由于与microRNA-200c密切相关的一些蛋白(如E-钙黏蛋白)及细胞表型(如上皮间质转变)均与肿瘤耐药密切相关[11-12],因此microRNA-200c的作用机制还需要进一步的研究。
随着研究的深入,microRNA在肿瘤耐药中作用也将逐渐阐明。本研究筛选出了SGC7901/DDP细胞中多条表达改变的microRNA,并发现microRNA-200c的化疗增敏作用,为下一步研究microRNA的调控机制奠定了基础。
[1]Kovalchuk O,Filkowski J,Meservy J,et al.Involvement of microRNA-451 in resistance of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin[J].Mol Cancer Ther,2008,7:2152 -2159.
[2]Xia L,Zhang D,Du R,et al.miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells[J].Int J Cancer,2008,123:372 -379.
[3]Sorrentino A,Liu CG,Addario A,et al.Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells[J].Gynecol Oncol,2008,111:478-486.
[4]Fujita Y,Kojima K,Ohhashi R,et al.MiR-148a attenuates paclitaxel resistance of hormone-refractory,drug-resistant prostate cancer PC3 cells by regulating MSK1 expression[J].J Biol Chem,2010,285:19076-19084.
[5]Hummel R,Watson DI,Smith C,et al.Mir-148a improves response to chemotherapy in sensitive and resistant oesophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma cells[J].J Gastrointest Surg,2011,15:429-438.
[6]Pogribny IP,Filkowski JN,Tryndyak VP,et al.Alterations of microRNAs and their targets are associated with acquired resistance of MCF-7 breast cancer cells to cisplatin[J].Int J Cancer,2010,127:1785 -1794.
[7]LI Y,VandenBoom TG,KONG D,et al.Up-regulation of miR-200 and let-7 by natural agents leads to the reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells[J].Cancer Res,2009,69:6704-6712.
[8]Cochrane DR,Spoelstra NS,Howe EN,et al.MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic agents[J].Mol Cancer Ther,2009,8:1055 -1066.
[9]Adam L,Zhong M,Choi W,et al.miR-200 expression regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer cells and reverses resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor therapy[J].Clin Cancer Res,2009,15:5060-5072.
[10]Tryndyak VP,Beland FA,Pogribny IP.E-cadherin transcriptional down-regulation by epigenetic and microRNA-200 family alterations is related to mesenchymal and drugresistant phenotypes in human breast cancer cells[J].Int J Cancer,2010,126:2575 -2583.
[11]Ferreira P,Oliveira MJ,Beraldi E,et al.Loss of functional E-cadherin renders cells more resistant to the apoptotic agent taxolin vitro[J].Exp Cell Res,2005,310:99-104.
[12]Arumugam T,Ramachandran V,Fournier KF,et al.Epithelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to drug resistance in pancreatic cancer[J].Cancer Res,2009,69:5820-5828.
Microarray analysis of microRNA expression profile and its role in reversing drug resistance in gastric cancer cell line SGC7901/DDP
ZUO Jing,CHEN Yong#,LIU Ying,GAO Hong,LIU Wei*
(1.Dept.of Medical Oncology Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050011;2.Dept.of Medical Oncology Subei Hospital,Yangzhou 225001,China)
ObjectiveTo analyze the microRNA expression profile and drug resistance characteristic and explore the roles of microRNA-200c on drug resistance in gastric cancer cell line SGC7901/DDP.MethodsDrug sensitivity of SGC7901/DDP and SGC7901 cells were tested by means of MTT assay.microRNA array was used to analyze microRNA expression profile,and bioinformatics analysis was used to predict potential targets and biological functions of differentially expressed microRNAs.Real-time fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR was used to validate the result of microRNA-200c expression change from microRNA array analysis.And the effects of microRNA-200c on drug resistance were also analyzed in SGC7901/DDP cells by means of cell transfection.ResultsThe IC50of cisplatin,doxorubicin,5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel were significantly higher in SGC 7 9 0 1/DDP cells than that in SGC7901 cells(P<0.05).Compared with SGC7901 cells,5 microRNAs were upregulated more than 2-fold,and 14 microRNAs were downregulated more than 2-fold in SGC7901/DDP cells.The predicted targets in both downregulated and upregulated microRNA expression group were involved in the biological processes of signal transduction,cell cycle,cell differentiation,apoptosis,proliferation and etc.microRNA-200c was confirmed down expressed in SGC7901/DDP cells by real-time fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR.And SGC7901/DDP cells transfected with microRNA-200c precursor displayed significantly decreased IC50of cisplatin,doxorubicin,5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel(P<0.05).ConclusionsChanges of microRNA expression may be related to the multidrug-resistant in SGC7901/DDP cells,and its reversed drug resistance phenotype may be correlate with the microRNA-200c expression.
microRNA;gastric cancer;drug resistance;expression profile
R 735.2
A
1001-6325(2012)01-0042-07
2011-02-24
2011-06-13
河北省医学科学研究重点课题(20090169)
