中国三代虫科名录及已知种检索表
2012-05-25贺怀亚史妍茹尤平
贺怀亚,史妍茹,尤平
(陕西师范大学生命科学学院,陕西 西安 710062)
中国三代虫科名录及已知种检索表
贺怀亚,史妍茹,尤平*
(陕西师范大学生命科学学院,陕西 西安 710062)
列出了中国已知三代虫科3属54种的名录,纪录了各种的已知分布区和寄主。编制了分属种检索表,简要总结了各省区的研究状况和已知的寄主多样性等数据。为进一步开展此科的研究准备必要的资料。
单殖吸虫;三代虫科;三代虫属;薄片吸虫属;拟三代虫属
Introduction
There are four subfamilies in the family Gyrodactylidae:Isancistrinae,Gyrdicotylinae,Macrogyrodactylinae and Gyrodactylinae[1].Of these,only members of Gyrodactylinae are known to be present in Eurasia.In China,the first reported taxonomic work on these parasites was Yin and Sproston(1948)in which described of Gyrodactylus elegans sinicus subsp.n.and reported G.rarus in China[2].Subsequently there have been numerous studies on the Gyrodactylidae in China,but these are mostly in Chinese journals and books.Examples include“Notes on seven new parasitic species of monogenetic trematodes-Gyrodactylus from freshwater fishes of China”[3],“Fish Diseases and Sausa.Pathogenic Fauna Hupei Province”[4],“Fauna of Zhejiang,Trematoda”[5],“Fauna Sinica,Platyhelminthes:Monogenea”[1]and so on.And there are a lot of species from Amur river in Gusev’s work[6]were found in China.In the“Fauna Sinica,Platyhelminthes:Monogenea”,there are 38 species of Gyrodactylidae were listed from freshwater and marine fishes of China[1].After examinaton of the literature that referred to the Chinese Gyrodactylidae and the studies in these years,we confirmed that there are now 54 species of Gyrodactylus Nordmann,1832,Paragyrodactylus Gvosdev et Martechov,1953,and Laminiscus Palsson and Beverly-Burton,1983 in China.In this study,we catalogue the information on these species and provide an updated diagnostic key.
Gyrodactylidae Van Beneden et Hesse,1863
Small,elongated Monogenea;anterior end bilobed;each lobe with head organ.Haptor well-developed,bearing one pair of large hamuli with dorsal and ventral bars and 16 marginal hooks.Intestine bifurcate,the tow limbs not uniting posteriorly.Eye spots absent.Male copulatory organs(MCO)armed with row of minute spines and usually with trianglular cuticular plaque.Ovary V-shaped or lobed,posterior or ventral to testis;vitellaria absent or united with ovary;vagina absent.Viviparous.
Gyrodactylinae Van Beneden et Hesse,1863
Small,haptor bearing one pair of large hamuli,pointed to ventral,with dorsal and ventral bars and 16 marginal hooks.Other characters of subfamily correspond to familial features.
Ⅰ Gyrodactylus Nordmann,1832
Viviparous;larva,including humuli and marginal hooks,usually present in parent in utero.Hamuli with single superficial root.Ventral bar with membrane.Host -specific.About 50 species occur in freshwater,brackish water and marine from China.
Ⅱ Paragyrodactylus Gvosdev et Martechov,1953
Small-bodied Gyrodactylidae;anterior end bilobed;each lobe with head organ.Haptor well-developed,bearing one pair of hamuli with single superficial,ventrally-irected root;with dorsal and ventral bars,and 16 marginal hooks evenly distributed on haptor.Ventral bar with posterior membrane.Supplementary haptoral hard part in shape of helmit,with a medial and narrow portion lying against ventral bar and a dorsal portion folding back over roots of hamuli.Intestinal crura bifurcate,ending blindly.Male copulatory organ(MCO)armed with large and small spines in single terminal row.Marginal hooks relatively small,with variable shapes of sickles.
Ⅲ Laminiscus Palsson et Beverley-Burton,1983
Marginal hooks distributed on periphery of haptor in three groups:two anterolateral groups of four hooks each,and one posterior group of eight more widely distributed hooks.Humuli with short,deep root and elongated superficial root.Ventral bar without membrane. On gill of marine and brackish water teleosts[7].
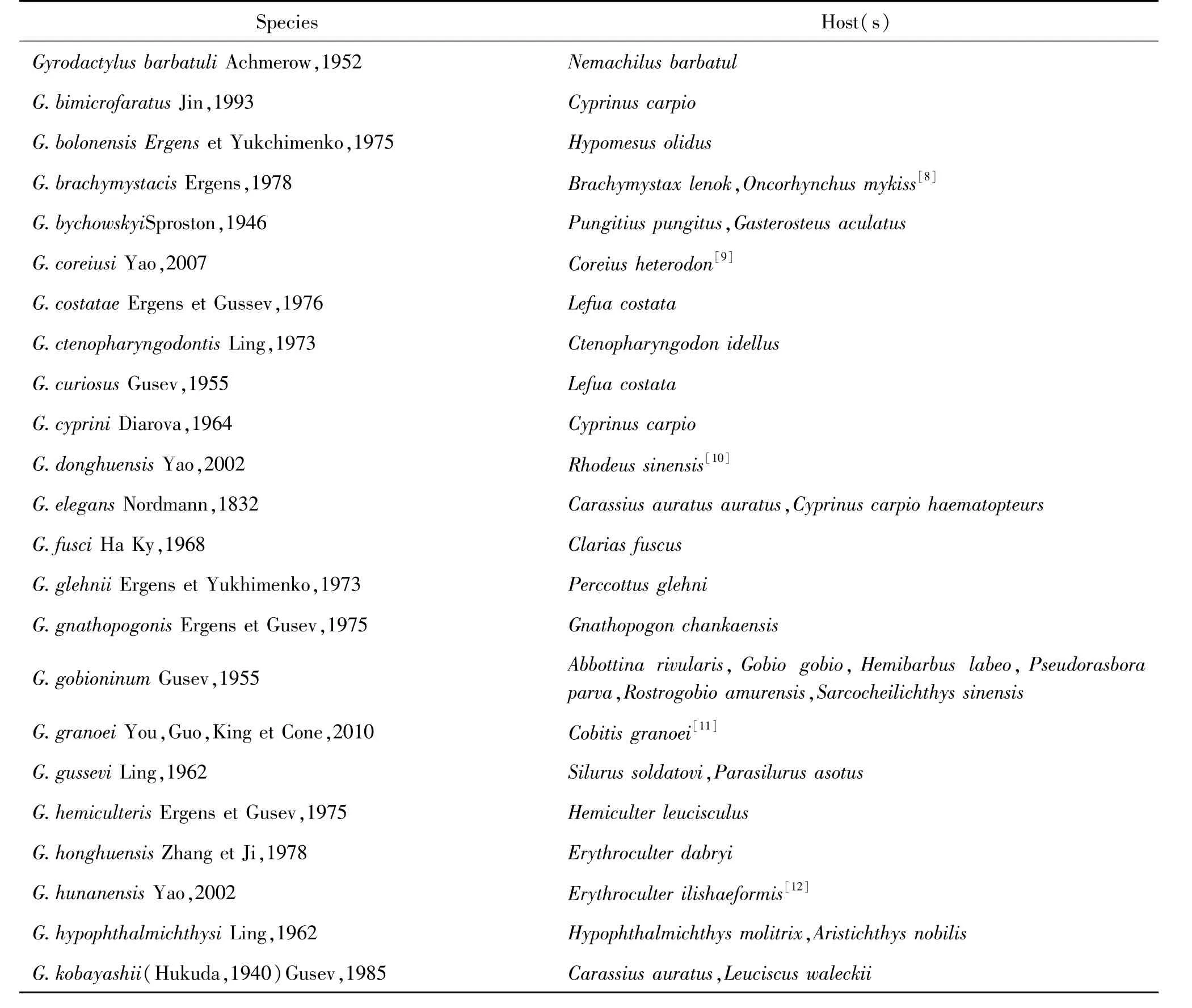
Table 1 Catalogue of the Chinese Gyrodactylidae

Key to the Chinese species of Gyrodactylidae
1.Marginal hooks in three groups,two anterolateral with four hooks each,one posterior with eight hooks;hamuli with two roots,deep and superficial;one transverse bar ventral(Laminiscus)……………Laminiscus strelkowi Marginal hooks evenly distributed on haptor;hamuli with single superficial root;two transverse bars present,dorsal and ventral…………………………………………………………………………………………………2
2.With a supplementary chitinoid armament consisting of chitinoid arch and two extending processes(Paragyrodactylus)…………………………………………………………………………Paragyrodactylus sp. Without a supplementary chitinoid armament(Gyrodactylus)……………………………………………………3
3.Parasitic in marine fish …………………………………………………………………………………………4
Parasitic in brackish or freshwater fish …………………………………………………………………………5
4.Hamuli with root longer,ratio of length of root to shaft is more than 0.45;dorsal bar straight,ventral bar membrane less than 10 μm;male copulatory organs(MCO)with 1 large and 8-9 small terminal spines……………………………………………………………………………………Gyrodactylus lateolabrax Hamuli with root shorter,ratio of length of root to shaft is less than 0.45;dorsal bar curving in middle,ventral bar membrane more than 10μm;MCO only with 7 small terminal spines………………………G.xiamenensis
5.Ventral bar with prominent anterolateral processes ……………………………………………………………6
Ventral bar with small anterolateral processes…………………………………………………………………29
6.Ventral bar with anterolateral processes not shorter than the length of“U”shaped ventral bar………………7
Ventral bar with anterolateral processes shorter than the length of ventral bar………………………………10
7.The width of ventral bar and the membrane almost equal ………………………………………………………8
The width of the membrane less than the ventral bar …………………………………………………………9
8.Hamuli with point longer,ratio of length of point to hamuli more than 0.35;root with a spine distally…………………………………………………………………………………………………G.parabotia
Hamuli with point shorter,ratio of length of point to hamuli less than 0.35;root without a spine distally……………………………………………………………………………………………………G.zhukovi
9.Ventral bar with membrane without a notch;MCO with 1 large,8 middle and small terminal spines………………………………………………………………………………………………G.ophiocephali
Ventral bar membrane with a notch distally …………………………………………………………G.elegans
10.Dorsal bar with a deep middle notch in the posterior margin ………………………………………………11
Dorsal bar without a distinctly middle notch in the posterior margin………………………………………12
11.Ventral bar membrane pectinate;MCO with 1 large,7 middle and small terminal spines……………G.latus
Ventral bar membrane linguiform;MCO with 1 large and 4 small terminal spines……………………G.rarus
12.Dorsal bar with 2 spurs in the anterior margin;Ventral bar membrane linguiform,with a small notch distally……………………………………………………………………………………………G.ctenopharyngodontis
Dorsal bar without distinct spurs in the anterior margin ……………………………………………………13
13.Hamuli with relatively short root,no more than 1/4 length of the hamulus…………………………………14
Hamuli with relatively long root,more than 1/4 length of the hamulus……………………………………15
14.Hamuli with root about 1/4 length of the hamulus;MCO with 1 large and 5 small terminal spines………………………………………………………………………………………………………G.lotae Hamuli with root about 1/7 length of the hamulus;MCO with 2 large and 4 small terminal spines……………………………………………………………………………………………………G.gussevi
15.Length of marginal hooks more than 30 μm …………………………………………………………………16
Length of marginal hooks less than 30 μm …………………………………………………………………21
16.The ratio of length to width of ventral bar about 1∶3.5;MCO with 1 large and 4 small terminal spines………………………………………………………………………………………………………G.mantschuricus
The ratio of length to width of ventral bar more than 1∶3……………………………………………………17
17.Hamuli with root very expanded proximally,with a distinct inner bend after there;ventral bar with membrane narrow,about 1/2 width of the bar………………………………………………………………G.bychowskyi
Hamuli with root light expanded proximally …………………………………………………………………18
18.Length of marginal hooks more than 35 μm …………………………………………………………………19
Length of marginal hooks less than 35 μm …………………………………………………………………20
19.Marginal hooks with sickle less than 10 μm;MCO with 1 large,7 middle and small terminal spines……………………………………………………………………………………………G.brachymystacis
Marginal hooks with sickle more than 10 μm;MCO with 1 large and 6 small terminal spines………G.lenoki
20.Length of hamuli more than 75 μm;MCO with 1 large and 7 small spines………………………G.perccotti
Length of hamuli less than 55 μm;MCO with 1 large,7 middle and small terminal spines………G.parvae
21.Dorsal bar with middle of the anterior margin expanded,slender each lateral;MCO with 1 large and 5 small spines……………………………………………………………………………………………G.gobioninum
Dorsal bar with each margin straightly ………………………………………………………………………22
22.Ventral bar with a cupped posterior margin …………………………………………………………………23
Ventral bar with a comparatively straight posterior margin …………………………………………………25
23.Marginal hooks with sickle wider distally than proximally;MCO with 1 large,2 middle and 4 small spines………………………………………………………………………………………………G.kobayashii
Marginal hooks with sickle shorter distally than proximally …………………………………………………24
24.Ventral bar with comparatively straight anterior margin;hamuli with root equal in middle…………G.rhodei Ventral bar dumbbell in shape;hamuli with root slender in middle;MCO with 1 large and 7 small spines…………………………………………………………………………………………………G.coreiusi
25.The ratio of length to width of ventral bar about 1:2;MCO with 1 large,4 middle and 4 small spines…………………………………………………………………………………………………G.costatae
The ratio of length to width of ventral bar is 1:3~1:4;MCO with 1 large and 6~8 small spines……26
26.The ratio of length to width of ventral bar about 1:4;MCO with 1 large and 7 small spines…………G.lefua
The ratio of length to width of ventral bar about 1:3;MCO with 1 large and 6 or 8 small spines…………27
27.MCO with 1 large and 8 small spines………………………………………………………………G.rivularae
MCO with 1 large and 6 small spines ………………………………………………………………………28
28.Ventral bar with membrane small,no more than 10 μm;length of hamuli less than 35 μm……G.bolonensis Ventral bar with membrane long,more than 10 μm;length of hamuli more than 45 μm…………G.medius
29.Ventral bar with expanded lateral end in every margin,dumbbell in shape…………………………………30
Ventral bar without expanded lateral end in every margin,subrectangular in shape………………………43
30.Hamuli with root shorter,less than 1/3 length of the hamulus ………………………………………………31
Hamuli with root longer,not less than 1/3 length of the hamulus…………………………………………36
31.The ratio of length to width of ventral bar no more than 1∶5………………………………………………32
The ratio of length to width of ventral bar more than 1∶5……………………………………………………33
32.Ventral bar membrane with a notch distally;dorsal bar with 2 spurs in the anterior margin…G.lichuanensis
Ventral bar with membrane smoothly distally;dorsal bar with each margin smoothly…………G.rhinogobius
33.Length of hamili about 60~70 μm;marginal hooks with sickle wider distally than proximally………………………………………………………………………………………………G.macrorhodei
Length of hamili less than 60 μm;marginal hooks with sickle wider proximally than distally……………34
34.Ventral bar with membrane indistinctly;MCO with 1 large and 5~6 small spines……………G.misgurni
Ventral bar with membrane distinctly;MCO with small spines no more than 4……………………………35
35.Ventral bar with membrane small,about 10 μm in length;MCO with 1 large and 3 small spines…………………………………………………………………………………………………G.shulmani
Ventral bar with membrane about 14 μm in length;MCO with 1 large,1 middle and 4 small spines…………………………………………………………………………………………………G.parasiluri
36.Ventral bar with posterolateral processes distinctly;hamili large,more than 170 μm…………G.donghuensis
Ventral bar without posterolateral processes;hamili no more than 80 μm…………………………………37
37.Hamuli with root more than 1/2 of shaft in length …………………………………………………………38
Hamuli with root no more than 1/2 of shaft in length ………………………………………………………39
38.Hamuli with root expanded proximally distinctly;length of marginal hooks more than 40 μm;MCO with 3 large
9 middle and small spines………………………………………………………………………………G.fusci Hamuli without root expanded proximally distinctly;length of marginal hooks less than 20 μm;MCO with 1
large 10~11 middle and small spines…………………………………………………………G.monstruosus
39.Length of hamili about 60~80 μm;hamulus shaft with a small process distally;MCO with 1 large and 4 small
spines…………………………………………………………………………………………………G.curiosus
Length of hamili less than 50 μm;hamulus shaft without a small process distally…………………………40
40.Ventral bar with anterior margin wider than the posterior,membrane pectinate;MCO with 1 large and 8 small spines………………………………………………………………………………………………G.sprostonae
Ventral bar with anterior margin not wider than the posterior,membrane linguiform………………………41
41.Ventral bar with membrane more than 20 μm in length,with a light dent distally;marginal hooks with sickle wider distally than proximally;MCO with 5 large and 2 small spines……………………………G.honghuensis Ventral bar with membrane less than 20μm in length,without a light dent distally;marginal hooks with sickle not wider distally than proximally……………………………………………………………………………42
42.Ventral bar with membrane small,less than 10 μm in length;marginal hooks with sickle shorter,about 1/9 of
the total length,about equal distally and proximally…………………………………………G.wuchangensis Ventral bar with membrane longer,more than 10 μm in length;marginal hooks with sickle longer,about 1/4 of the total length,shorter distally than proximally;MCO with 1 large and 3 small spines………G.squaliobarbi
43.Hamuli with a oval hole in the root……………………………………………………………G.bimicrofaratus
Hamuli without a hole in the root ……………………………………………………………………………42
44.Dorsal bar with a deep middle notch in the posterior margin ………………………………………………45
Dorsal bar without distinctly middle notch in the posterior margin…………………………………………46
45.Hamuli with root short,about 1/4 of the total length;ventral bar with membrane linguiform;MCO with 1 large,4 middle and 4 small spines…………………………………………………………………G.macracanthus
Hamuli with root long,about 1/2 of the total length;ventral bar with membrane necktieform;MCO with 1 large,2 middle and 3 small spines…………………………………………………………………………G.cyprini
46.Ventral bar with a distinct spur in the middle of posterior margin…………………………………………47
Ventral bar without a spur in the middle of posterior margin ………………………………………………48
47.Hamuli large,more than 50μm,with root about 1/3 of the total length;MCO with 1 large 9-19 middle and small spines…………………………………………………………………………………………G.barbatuli
Hamuli small,less than 45μm,with root about 1/4 of the total length;MCO with 1 large and 35 small spines…………………………………………………………………………………………………G.sedelnikowi
48.Hamuli with root longer,about 1/2 of the total length ………………………………………………………49
Hamuli with root shorter,about 1/3 of the total length ………………………………………………………50
49.The ratio of length to width of ventral bar about 1∶5,length of the membrane less than 10 μm;MCO with 1 large and 6 small spines…………………………………………………………………………G.hunanensis
The ratio of length to width of ventral bar about 1∶2,length of the membrane more than 15 μm;MCO with 1 large and 8 small spines…………………………………………………………………G.hypophthalmichthysi
50.Length of hamuli more than 40 μm …………………………………………………………………………51
Length of hamuli no more than 30 μm ………………………………………………………………………53
51.Hamuli with point more than 20 μm,MCO with 7 medium and 3 minute spines in multiple rows near pore edge………………………………………………………………………………………………………G.granoei
Hamuli with point no more than 20 μm ……………………………………………………………………52
52.Hamuli with ratio of root to shaft about 1∶3 in length;width of ventral bar more than 10 μm;marginal hooks with sickle almost equal distally to proximally;MCO with 1 large 10 middle and small spines……G.glehnii Hamuli with ratio of root to shaft about 1∶2.5 in length;width of ventral bar less than 10 μm;marginal hooks with sickle wider proximally than distally…………………………………………………………G.oxycephali
53.Hamuli with root expanded proximally distinctly;marginal hooks with sickle less than 5 μm,about 1/5 of the total length………………………………………………………………………………………G.gnathopogonis Hamuli with root expanded proximally lightly;marginal hooks with sickle not less than 5 μm,about 1/3 of the total length………………………………………………………………………………………G.hemiculteris
Remarks
There are 1052 species freshwater fish in China(including Cyclostomata,Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes)[16].Of them 56 species of these fish had been found parasiting 54 species belong 3 genus of Gyrodactylidae(Table 1-2).About 5%of freshwater fish in China had been found parasiting Gyrodactylidae.But a lots of these Gyrodactylidae species parasite Cypriniformes(40),particularly in Cyprinidae(27).And some freshwater fish parasite more than one Gyrodactylidae species.Example that,Lefua costata had been found five these parasites.Carassius auratus and Cyprinus carpio haematopteurs had four,Cobitis taenia,Misgurnus anguilicaudatus,Cyprinus carpio,Rhodeus sinensis and Parasilurus asotus had three,Erythroculter ilishaeformis,Gobio gobio,Phoxinus lagowskii variegatus,Pseudorasbora parva,Brachymystax lenok,Oncorhynchus mykiss and Perccottus glehni had been found two of these parasites.
The parasitic species show very host-specific.Of these 54 parasitic species,about 37(68%)were found in one host,more than the monogeneans(60%)[17];16 were found in two or three hosts,and most of them are same family,only two species are found in two(G.monstruosus)or three(G.latus)families,but they are in same order;and only two were found five(G.sprostonae,two families belongn two orders)or six(G.gobioninum,same family)hosts.
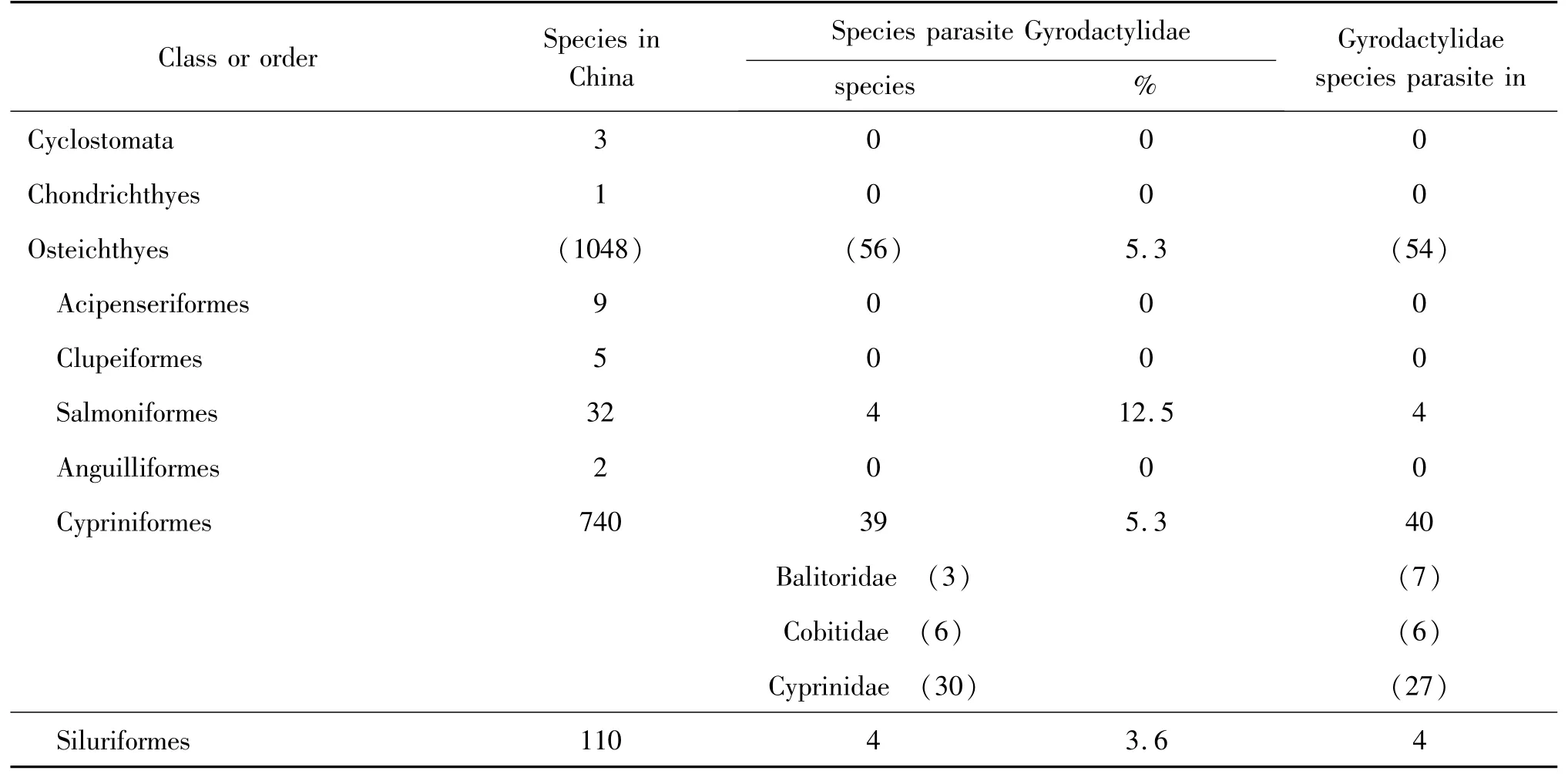
Table 2 The summary of freshwater fish in China parasite Gyrodactylidae
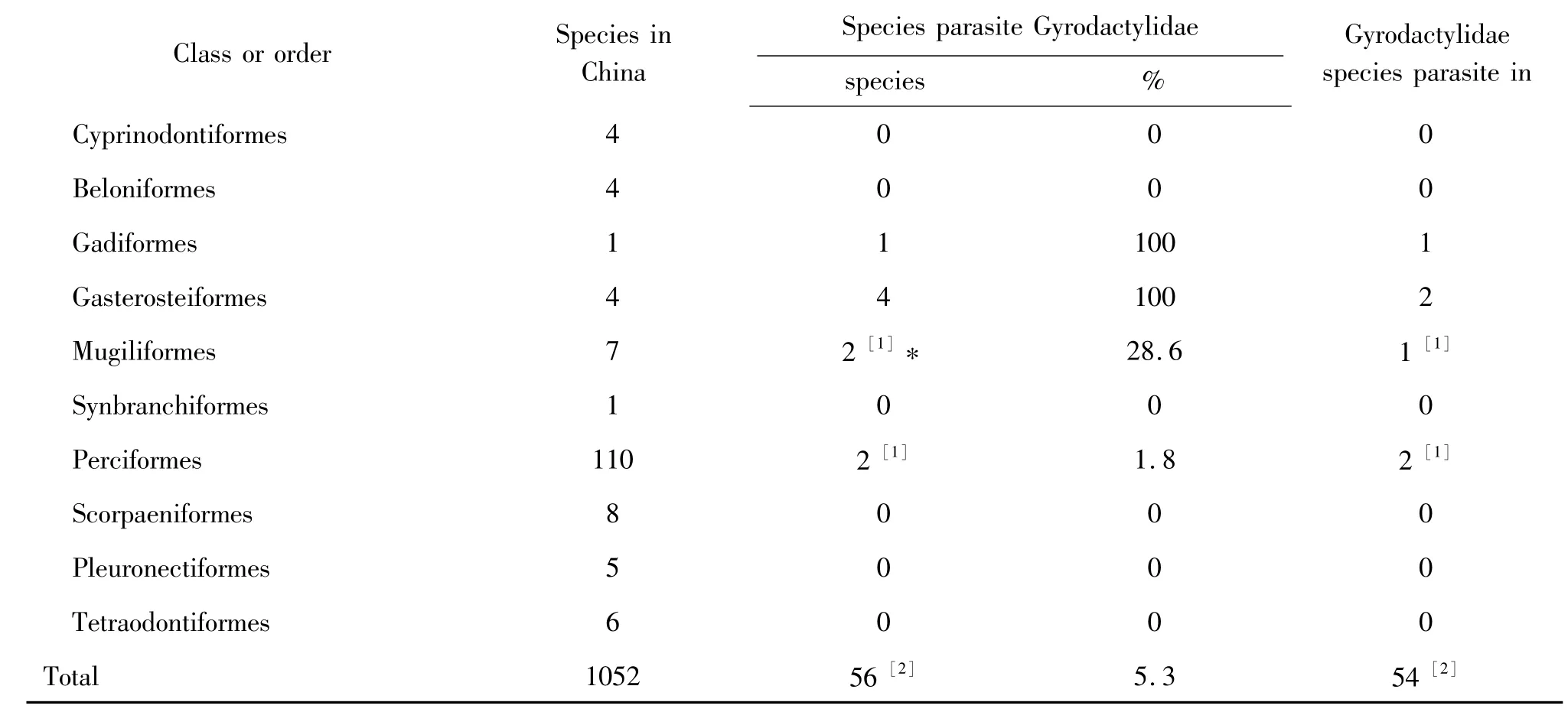
*the number in[]is marine fish.
These parasitic species are distributed about 19 provinces in China(Figure 1).They are located northeast,central,south and east of China.There are few species found in northern,northwestern,western and southwestern China.It is not that there are few species in these areas.We considered that there was less investigation in these provinces.
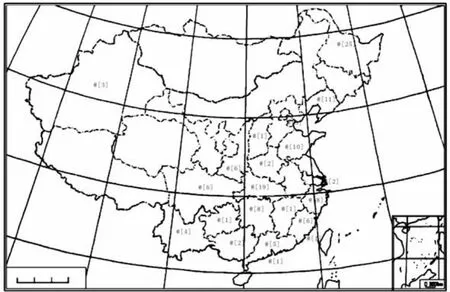
Figure 1 The distribution of the Gyrodactylidae species in China(the number in[]is the species found the area)
Reference:
[1]Wang W,J,Yao W-J.Gyrodactylidea Bychowsky,1937.In:Wu B-H,Lang S,Wang W-J et al.(eds.),Fauna Sinica,Platyhelminthes:Monogenea[M].Beijing:Science Press,2000,583-616.[王伟俊,姚卫建.三代虫科.见:吴宝华,郎所,王伟俊等编著.中国动物志,扁形动物门:单殖吸虫纲.北京:科学出版社,2000,583-616].
[2]Yin WY.Sproston NG.Studies on the monogentic trematodes of China:Parts 1-5[J].Sinensia,1948,19(1-6):57-85.
[3]Ling ME.Notes on seven new parasitic species of monogenetic trematodes-Gyrodactylus from freshwater fishes of China[J].Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,1962,2(4):67-78.[林慕恩.淡水鱼类寄生单殖吸虫三代虫属的7新种.水生生物集刊,1962,2(4):67-78].
[4]Ling ME.Gyrodactylidea.In:Institute of Hydrobiology in Hubei Province(ed.),Fish Diseases and Sausa.Pathogenic Fauna Hupei Province[M].Beijing:Science Press,,1973,151-153,384-385.[林慕恩.三代虫科.见:湖北省水生生物研究所主编.湖北省鱼病病原区系图志.北京:科学出版社,1973,151-153,384-385].
[5]Wang SX.Gyrodactylinae.In:Wu,B-H,Sun,X-D&Song C-C(eds.),Fauna of Zhejiang,Trematoda[M]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang Science and Technology Publishing House,1991,174-178.[王淑霞.三代虫科.见:吴宝华,孙希达,宋昌存主编.浙江动物志,吸虫类.杭州:浙江科学技术出版社,1991,174-178].
[6]Gusev AV.No.2.Parasitic Metazoa(Coelenterata and Monogenea).In:Bauer,O.N.(ed.),Key to parasites of freshwater fishes of USSR[M].Leningrad:Izdatel'stvo"Nuka",1985,1-424.
[7]Palsson J,Beverly-B M.Laminiscus n.g.(Monogenea:Gyrodactylidae)from capelin,Mallotus villosus(Müller)(Pisces:Osmeridae),in the nothwest Atlantic with re-descriptionsofL.gussevin.comb.,Gyrodactyloidespetruschewskii,and G.andriaschewi[J].Canadian Journal of Zoology,1983,61(2):298-306.
[8]You P,Yuan B,Yang J,Easy R,Dong Z-M&Cone DK. Pathogenic infections of Gyrodactylus brachymystacis(Monogenea)on Oncorhynchus mykiss(Walbaum)at a fish farm in Qinling Mountain region of China[J].Journal of Fish Diseases,2006,29(5):313-316.
[9]Yao WJ.A new species of Gyrodactylus Nordmann from Coreius heterodon Bleeker[J].Acta Hydrobiologia Sinica,2007,31(1):104-406.[姚卫建.铜鱼寄生三代虫一新种的记述.水生生物学报,2007,31(1):104-406].
[10]Yao WJ.Four species of Gyrodactylus from fish of the family Acheilognathinae[J].Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2002,26(5):513-516.[姚卫建.鳑鲏亚科鱼类鳃部寄生的四种三代虫的记述.水生生物学报,2002,26(5):513-516].
[11]You P,Guo ZC,King S,Cone D.A new Gyrodactylid species from Cobitis granoei(Rendahl)in central China[J]. The Journal of Parasitology,2010,96(5):897-899.
[12]Yao WJ.Three new species of Gyrodactylus from Wulung mountains region.Acta Hydrobiologia Sinica,2002,26(5):517-520.[姚卫建.武陵山地区鱼类寄生三代虫三新种.水生生物学报,2002,26(5):517-520]
[13]Yang TB,Liu SF.Gyrodactylidae(Van Beneden et Hesse). In:Zhang J-Y,Yang T-B,Liu L.et al.(eds.),Monogeneans of Chinese Marime Fishes[M].Beijing:Agriculture Press,2001,54-57.[杨廷宝,刘升发.三代虫科.见:张剑英,杨廷宝,刘琳等编著.中国海洋鱼类单殖吸虫.北京:中国农业出版社,2001,54-57].
[14]You P,Easy R,Cone D K.Gyrodactylus parvae n.sp.(Monogenea)from the Fins and Body Surface of Pseudorasbora parva(Cyprinidae)in Central China[J].Comparative Parasitology,2008,75(1):28-32.
[15]You P,Li X,King S,Cone D.Gyrodactylus rivularae n.sp.(Gyrodactylidae)from Abbottina rivularis(Basilewsky,1855)(Pisces:Cyprinidae)in central China[J].Comparative Parasitology,2011,78(2):257-260.
[16]Xie YH,Li SZ,Men QW.Wang CX.ï.Fishes.In:Liu MY,Xie Y-J&Ji D-M.(eds.),China Vertebrate[M]. Shenyang:Liaoning University Press,2000,1-970.[解玉浩,李思忠,孟庆闻,王存信.第一编鱼类.见:中国脊椎动物大全.沈阳:辽宁大学出版社,2000,1-970].
[17]Xia XQ,Wang WJ,Yao WJ.The host-specificity of monogeneans in inland waters of China[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2000,20(4):594-597.[夏晓勤,王伟俊,姚卫建.我国内陆水体单殖吸虫的宿主特异性分析.生态学报,2000,20(4):594-597].
[责任编辑 李晓霞]
Catalogue of the Gyrodactylidae(Monogenea)of China,with a Key to the Current Nominal Species
HE Huai-Ya,SHI Yan-Ru,YOU PING
(College of Life Science,Shaanxi Normal University,Xi’an,710062,China)
This paper gives a list of 54 species and 3 genera of the Gyrodactylidae from China.The distributions and known host(s)of each species are provided.A key to these species in China are included as well as a discussion on the natural diversity of these important parasites in the region.
Monogenea;Gyrodactylidae;Gyrodactylus;Laminiscus;Paragyrodactylus
S941.5
A
1004-602X(2012)03-0022-09
10.3969/J.ISSN.1004-602X.2012.03.022
20120620
中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助(Supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities,GK201002044)。
贺怀亚(1995—),男,陕西横山人,陕西师范大学硕士研究生。
*尤平(1965—),男,陕西甘泉人,陕西师范大学教授,博士。曾在延安大学生物系工作。
