Natronococcus zhanjiangensis sp.nov.,a halophilic archaeon isolated from a saltern sediment in Zhan Jiang,Guangdong Province,China
2012-01-12CHENDiHEWeihong
CHEN Di,HE Wei-hong
(Marine Environmental Engineering Center,South China Sea Institute of Oceanology,CAS,Guangzhou 510301,China.)
Members in the family Halobacteriaceae are well-known for its strong ability to inhabit at extremely hypersaline environments including soda lake,salt mine,sea food,marine environment,etc.Some of them also require alkaline pH for growth,including genera Natronococcus,Natronbacterium,Natronolimnobius,Natronorubrum,Natrinema,etc.The genus Natronococcus,first proposed by Tindall et al.in 1984[1],is one typical genus of the extremely haloalkaliphlic archaea,and currently,contains only three species:Natronococcus occultus[1],Natronococcus amylolyticus[2]and Natronococcus jeotgali[3].The first two species were isolated from Soda lake(Magadi,Kenya),and the third species was isolated from fermented seafood.All of them are cocci and can grow above 5.0 mol/L NaCl with an optimum at pH 9.0~10.Strain SCSIO CD13T,was isolated from a red saline sediment sample collected from a saltern sediment after incubation at 37℃and pH 7.2~7.5 on the modified salt-minerals medium.The polyphasic taxonomic data including physiological,chemtaxonomic and 16S rRNA gene sequences analysis revealed that strain SCSIO CD13Trepresented a new member of the genus Natronococcus.Here,we report the taxonomic description of this new isolate based on these polyphasic data.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Isolation of SCSIO CD13T
The sample was collected from the sediment of a saltern(20°48.212'N,110°18.379'E)at Zhan Jiang City,Guang Dong province,China.Strain SCSIO CD13Twas isolated by using a standard serial dilution plating method.The specific medium were the following:casamino acid 5 g,Yeast extract 5 g,NaCl 250 g,KCl 2 g,MgSO4·7H2O 2 g,NH4Cl 2 g,agar 20 g,trace salt solution 1 mL,distilled water 1 liter,pH 7.2~7.5,after incubation at 37℃for 10 days.The colonies were purified and maintained on modified DSMZ standard medium No.372(modified with MgSO4·7H2O,2 g instead of 20 g,pH 8.0~8.5 adjusted with sterile Na2CO3solution),which was also used as the basal medium for following identification tests.
1.2 Phenotypic characterisation
Phenotypic tests were carried out according to the proposed minimal standards for the description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales[4].Microscopical characterization was performed using light and transmission electron microscopy(TEM)after incubation at 37℃for 10 days on modified DSMZ standard medium No.372.Carbon(each at a final concentration of 1.0%)and nitrogen sources(0.5%)for growth were tested on modified DSMZ standard medium No.372 by substituting of yeast extraction,casamino acids and trisodium citrate.The variable pH values from 5.5 to 11 for growth were determined by using 50 mmol/L pH buffers(MES pH 5.5~6.5,PIPES pH 6.1~7.5,HEPES pH 6.8~8.2,Tricine pH 7.4~8.8,CHES pH 8.6~10 and CAPS pH 9.7~11.1).Gram reaction was tested based on the procedure described by Dussault[5].Hydrolysis of casein,gelatin,and tween 80 were carried out on plates of modified DSMZ standard medium No.372 supplied with 1%test substances.Magnesium for growth was done based on DSMZ standard medium No.372(modified by deleting MgSO4·7H2O,pH 8.0~8.5 adjusted with sterile Na2CO3solution).NaCl tolerant for growth(0~5.5 mol/L at 0.5 mol/L intervals)was tested by using DSMZ standard medium No.372 as the basal meidium).Anaerobic growth on nitrate,L-arginine and DMSO(Dimethyl Sulphoxide)were examined using solution of modified DSMZ standard medium No.372 covered with paraffine and incubation at 37℃for 10 days in the dark.Antibiotic susceptibility were examined by as described by Groth et al.[6]using antibiotic discs on modified DSM 372 medium with the tested organisms.
1.3 Chemotaxonomic characterization
Menaquinones were isolated using the methods of Minnikin et al.[7]and separated by HPLC[8-9].Polar lipids were extracted and determined by published procedures of Ross et al.[10]with freeze-drying biomass collected by shaking incubation at 37℃for 7 days in broth of modified DSMZ standard medium No.372.
1.4 Molecular Characterization
Extraction of genomic DNA was performed as described by Xu et al.[11].PCR-mediated amplification of 16S rRNA gene was done by using universal primers for archaeal 16S rDNA[12]P1:5'-ATTCCGGTTGATCCTGCCGGA-3'and P2:5'-AGGAGGTGAT CCAGCCGCA-3'.PCR product was directly sequenced.The genomic DNA G+C content was determined by the thermal denaturation method[13]with the chromosomal DNA extracted and purified according to Marmur[14].The similarity and homology of the sequence was compared with the existing sequences available in the data bank using BLAST search.Multiple alignments with sequences of the recognized species in the family Halobacteriaceae that appeared most closely related to the novel strain and evalution of the levels of sequence similarity were carried out using CLUSTAL X[15].The phylogenetic tree(Fig.1 )was constructed using the neighborjoining method of Saitou and Nei[16]from Knucvalues[17-18]using the MEGA 5.0 software package[19].The topology of the phylogenetic tree was evaluated by the bootstrap resampling method of Felsenstein[20]with 1 000 replicates.DNA-DNA hybridization experiments were done between strain SCSIO CD13Tand the type strain Ncc Jeotgali B1Taccording to the optical renaturationmethod[21-22]andaUV1601 spectrophotometer(Shimadzu).
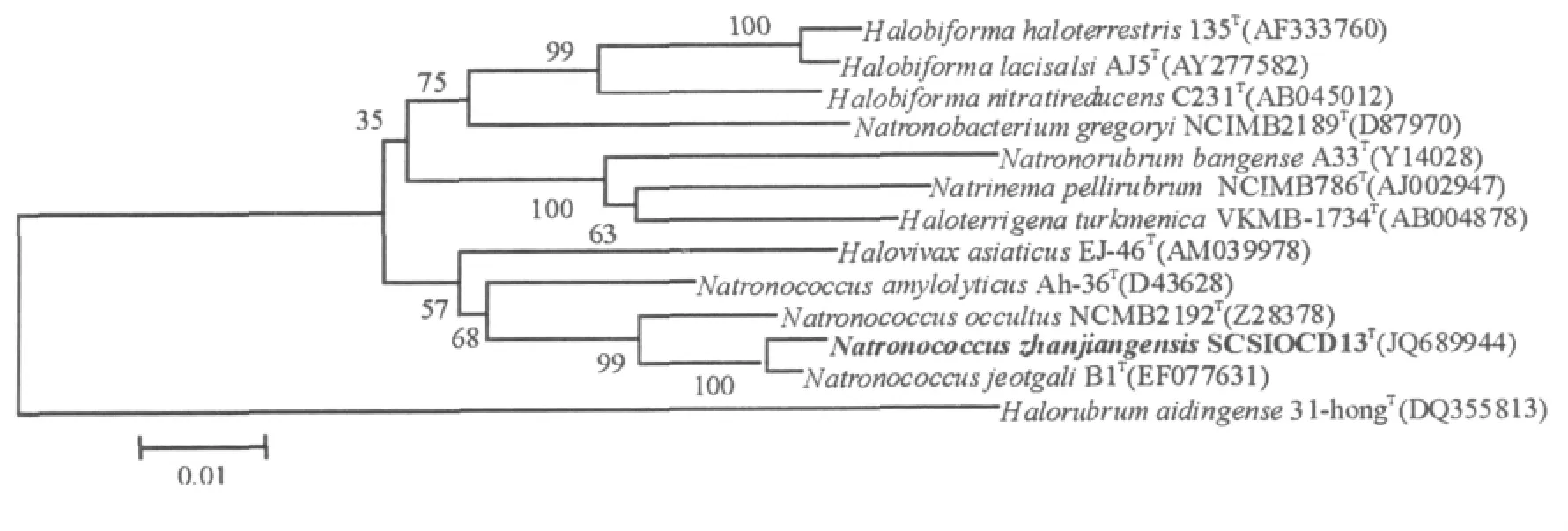
Fig.1 Phylogenetic tree of strain SCSIO CD13Tand its closely related species based on 16S rRNA gene sequences.Numbers on branch nodes are bootstrap values(1 000 resamplings).Bar,1%sequence divergence.Species Halorubrum aidingense 31-hongTwas used as the outgroup
2 Result
Colonies of strain SCSIO CD13Tare orangered,smooth,1~3 millimeters in diameters after incubation at 37℃for 10 days.Cells size 1.0~1.5 μm,cocci,aerobic,non-motile,as shownin Fig.2 .Growth occurs at NaCl concentration ranges of 2.5 to 5.5 mol/L(optimum 3.5~4.0 mol/L),with temperature 37℃and pH 8.5.Gas vesicles were not found.Cell leakage occurs in distilled water and gram reaction was variable.Oxidase reaction was negative.Magnesium ions for growth were not required.Hydrolysis of casein,gelatin,and tween variable and not produced gas vesicles.Maximum growth was observed at 2.5 to 5.5 mol/L of NaCl concentration with optimum pH 8.0~8.5.Magnesiumions were not indispensable.Nitrate reduced to nitrite and starch,tween 20 can be hydrolyzed.The major polar lipids were phosphatidylglycerol(PG)and phosphatidylglycerol phosphate methyl ester(PGP-Me).Glycolipids were not present.All above characteristics and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis further supported the affiliations of the strain to the genus Natronococcus.However,strain SCSIO CD13Tfollowing biochemical parameters,such as grow at pH 7.0 and no growth occurs at pH 10,temperature range,NaCl concentration and magnesium for growth,H2S production,hydrolysis of starch and gelatin,all of these properties were different to its closest phylogenetic neighbour Ncc Jeotgali B1Tand the other two closest relations.Detailed characteristics of four strains were listed in table 1 .Moreover,23%of DNA-DNA hybridization between the isolate and its phylogenetic neighbor Ncc jeotgali B1Twas far below the 70%cut-off point recommended for the delineation of genomic species[23].Based on the polyphasic taxonomic data in the present study,strain SCSIO CD13Trepresents a hitherto unknown species of the genus Natronococcus,for which the name Natronococcus zhanjiangensis sp.nov.,was proposed.
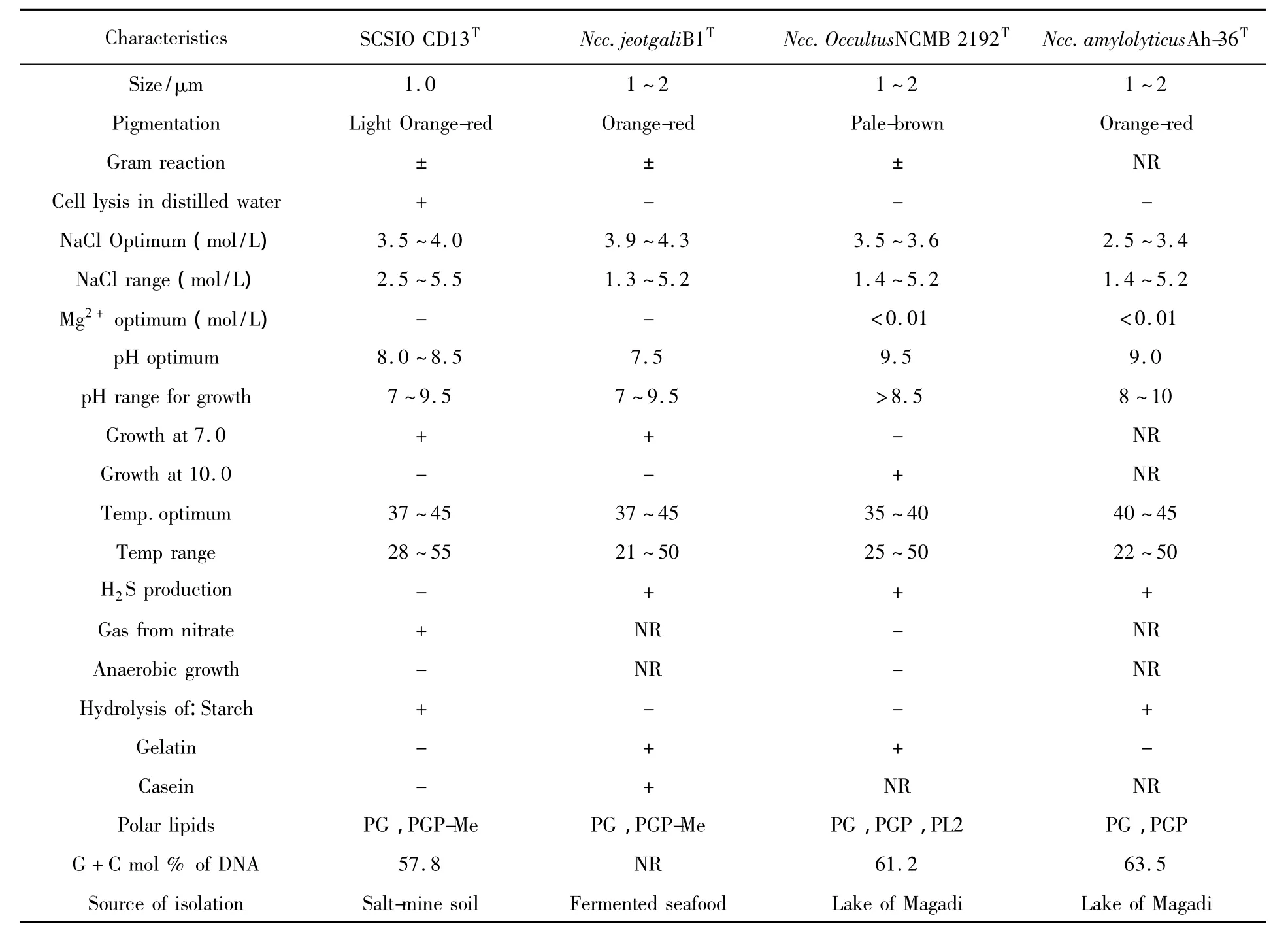
Table 1 Differential properties of strain SCSIO CD13Tand related Natronococcus species
4 Description of Natronococcus zhanjiangensis sp.nov.
Natronococcus zhanjiangensis(zhan.ji.ang.engsis.N.L.fem.adj.zhanjiangensis pertaining to Zhanjiang,a city in China near where the sample was collected).
Colonies are orange-red,smooth,circular,1~3 millimeter in diameters after incubation at 37℃for 10 days.Cells are cocci(1~1.5 μm in diameters),no-motile,strictly aerobic,gram variable and leak in distilled water.Gas vesicles are not found.Growth occurs in media containing 2.5 to 5.5 mol/L NaCl and the optimum is 3.5~4.0 mol/L with the optimum pH range 8.0~8.5.Temperature range for growth is 25℃to 55℃with the optimum 37~45℃.Magnesium ions are not required.Nitrate reduced to nitrite.Starch,tween 20 can be hydrolyzed,but not tween 80,gelatin,casein.Indole from tryptophan occurs.Catalase-positive and oxidase-negative.H2S production was negative.The major polar lipids are C20-C20and C20-C25derivatives of PG and PGP-Me.Glycolipids and PGS are not present.The G+C content of chromosomal DNA is 57.8 mol%(Tm).The type strain is SCSIO CD13T,isolated from a saltern sediment soil collected from Zhan Jiang City,in Guangdong province,China.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTWe gratefully acknowledge Dr.Fredimoses Mangaladoss for revising the final version of the manuscript based on the standard format of Microbiology China,on the grammar,correcting and offering good suggestions etc.
Reference
[1] Tindall BJ,Ross HNM,Grant W D.Natronobacterium gen.nov.and Natronococcus gen.nov.,two new genera of haloalkaliphilic archaebacteria[J].Syst Appl Microbiol,1984,5(1):41-57.
[2] Kanai H,Kobayashi T,Aono R,et al.Natronococcus amylolyticus sp.nov.,a haloalkaliphilic archaeon[J].Int J Syst Bacteriol,1995,45(4):762-766.
[3] Roh SW,Nam YD,Chang HW,et al.Natronococcus jeotgalisp.nov.,a halophilic archaeon isolated from shrimp jeotgal,a traditional fermented seafood from Korea[J].Int J Syst Evol Microbiol,2007,57(9):2129-2131.
[4] Oren A,Ventosa A,Grant WD.Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales[J].Int J Syst Bacteriol,1997,47(1):233-238.
[5] Dussault HP.An improved technique for staining halophilic bacteria[J].J Bacteriol,1955,70(4):484-485.
[6] Groth I,Rodrıguez C,Schutze B,et al.Five novel Kitasatospora species from soil:Kitasatospora arboriphila sp.nov.,K.gansuensis sp.nov.,K.nipponensis sp.nov.,K.paranensis sp.nov.and K.terrestris sp.nov[J].Int J Syst Evol Microbiol,2004,54(6):2121-2129.
三组产妇麻醉前的平均动脉压(MAP)比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);三组产妇硬膜外给药后,MAP均有不同程度的降低,与麻醉前比较,三组产妇麻醉阻滞平面达T8及胎儿娩出时的MAP显著降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);三组产妇在麻醉平面达T8时及胎儿娩出后的MAP比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
[7] Minnikin DE,O’Donnell AG,Goodfellow M,et al.An integrated procedure for the extraction of isoprenoid quinines and polar lipids[J].Microbiol Methods,1984,2(5):233-241.
[8] Kroppenstedt RM,Korn-Wendisch F,Fowler VJ,et al.Biochemical and molecular genetic evidence for transfer of Actinoplanes armeniacus into the family Streptomycetaceae[J].Zentbl Bakt Hyg Abt Orig,1981,2(3):254-262.
[9] Kroppenstedt RM.Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase(RP 18)and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases[J].J Liquid Chromato,1982,5(12):2359-2387.
[10] Ross HNM,Grant WD,Harris JE.Lipids in archaebacterial taxonomy[M].In Chemical Methods in Bacterial Systematics,Edited by Goodfellow M,Minnikin DE[J].New York:Academic Press,1985:289-299.
[11] Xu P,Li WJ,Xu LH,et al.A microwave-based method for genomic DNA extraction from Actinomycetes[J].Microbiology(in Chinese),2003,30(4):82-84.
[12] Wang ZX,Yu Y,Zhou PJ.Taxonomy of a new species of Haloalklophilic archaeon[J].Acta Microbiologica Sinica(in Chinese),2000,40(2):115-120.
[13] Marmur J,Doty P.Determination of base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its denaturation temperature[J].J Mol Biol,1962,5:109-118.
[15] Thompson JD,Gibson TJ,Plewniak F,et al.The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface:flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools[J].Nucleic Acids Res,1997,25(24):4876-4882.
[16] Saitou N,Nei M.The neighbor-joining method:A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees[J].Mol Biol Evol,1987,4(4):406-425.
[17] Kimura M.A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequence[J].J Mol Evol,1980,16(2):111-120.
[18] Kimura M.The neutral theory of molecular evolution[M].Cambridge University Press,Cambridge,1983.
[19] Tamura K,Peterson D,Peterson N,et al.MEGA5:Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using Maximum Likelihood,Evolutionary Distance,and Maximum Parsimony Methods[J].Mol Biol Evol,2011,28(10):2731-2739.
[20] Felsenstein J.Conference limits on phylogenies:an approach using the bootstrap[J].Evolution,1985,39(4):783-789.
[21] Huss VAR,Festl H,Schleifer KH.Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates[J].Syst Appl Microbiol,1983,4(2):184-192.
[22] Jahnke KD.BASIC computer program for evaluation of spectroscopic DNA renaturation data from GILFORD SYSTEM 2600 spectrophotophotometer on a PC/XT/AT type personal computer[J].J Microbiol Methods,1992,15:61-73.
[23] Wayne L,Brenner DJ,Colwell RR,et al.International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology.Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics[J].Int J Syst Bacteriol,1987,37:463-464.
