An eight-year journey of Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International
2010-06-29ShuiYingLeiPanZhiWangYanPingDongCongZhuShouChuQianandShuSenZheng
Shui-Ying Lei, Pan-Zhi Wang, Yan-Ping Dong, Cong Zhu, Shou-Chu Qian and Shu-Sen Zheng
Hangzhou, China
Editorial
An eight-year journey of Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International
Shui-Ying Lei, Pan-Zhi Wang, Yan-Ping Dong, Cong Zhu, Shou-Chu Qian and Shu-Sen Zheng
Hangzhou, China
History of the journal
Founded in 2002 as a quarterly in English,Hepatobiliary&Pancreatic Diseases International(HBPD INT) has since 2007 been publishing bimonthly. Owned by the First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, the journal aims to promote the science and art of medicine and the improvement of health of the people around the world by elevating the quality of prevention, diagnosis, treatment and research of diseases. The journal was accepted byScience Citation Index Expanded (SCI-E), Index Medicus (IM)/MEDLINE, Chemical Abstract (CA), EMBASE/Excerpta Medicus (EM) and BIOSIS/ Biological Abstract (BA)from 2002 through 2007, while launching the website in 2003 with printed articles in PDF and html free to the audience. The e-version of the journal is regularly updated to keep readers abreast with the latest development of medicine in the related fields in a more accessible way. Ever since 2006, the articles published in HBPD INT could be connected via LinkOut to the database of PubMed. The monthly hits of the e-version of the journal are around 5000. Proposed by Professor Åke Andrén-Sandberg in 2004, HBPD INT established an exchange relationship withPancreatologyand both journals agreed to publish the contents pages reciprocally. Also HBPD INT has an information exchange relationship withJournal of Pancreas. In 2010 HBPD INT came under the umbrella of the ELSEVIER publisher in an attempt to expand its global influence. Recently the journal has adopted the ScholarOne ManuscriptsTMsystem for online submission, peer review and manuscript trucking as part of the efforts made by the editorial staff to foster the digital publication of the journal.
The editorial board
The journal has an international editorial board with 139 members, of whom 76 (54.7%) from China including Hong Kong (7), Taiwan (3), Zhejiang province (15) and other provinces (51). Sixty-three (45.3%) are from overseas including United States (16), Germany (11), Canada (7), Japan (5), the United Kingdom (5), Australia (4), France (4), Greece (3), Austria (1), Finland (1), India (1), Italy (1), Norway (1), Singapore (1), South Korea (1) and Turkey (1). From the very beginning of the journal, most of them have done well as advisers of the editor and editorial staff. They spent precious time evaluating manuscripts or suggesting the names of competent reviewers for specific manuscripts, without themselves acting as reviewers in some instances. Frequently they are asked to solicit material for the journal, write articles themselves, or otherwise see that the journal properly reflects activities, and the state of knowledge, in their particular disciplines.
Submissions, publication and citation
In the early years of HBPD INT, manuscripts were mostly solicited. The number of free submissions to the journal was only 158 in 2002, and this increased with year to 281 in 2009. Submissions from other countries were rare at that time. However, the number of submissions dramatically increased from 6 in 2002 to 94 in 2009. The acceptance rate decreased accordingly from 81.1% to 39.9%.
The articles published permanently in the period of 8 years were editorials, review articles, original articles, case reports, clinical imaging, new techniques, letters to the editor, etc. Most (77.3%) of them were original articles (Fig.) from China (84.8%) and the rest from India, the United Kingdom, United States, Germany,Japan, Bangladesh, Greece, Italy, etc.
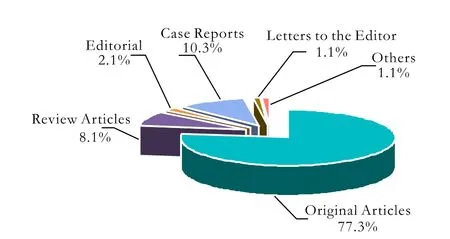
Fig. The category of the published articles.
Since the establishment of the website in 2003, the citation rate of articles published in HBPD INT has increased rapidly. But the frequently cited articles are review articles and hot-topic studies, indicating that readers are interested in concentrated information about the progress in a specific field.
A long way to go
Whether a journal is successful or not largely depends on its influence on the knowledge of the audience or indirectly the citation rate of the articles published by the journal. If the articles are never cited within two or three years they are thought to add nothing to the exiting knowledge in a given field. To solve this problem, editors have done their best to find good quality articles from submissions through the strict review process or to solicit articles in advance.
The recently released impact factor 1.183 (2009 Journal Citation Reports®) for HBPD INT indicates that there is a disparity from the international rivals although it ranks the 16th among 114 Chinese journals indexed by SCI.[1]This is not a satisfactory rate to the expectation of the editors, even our audience, but it is fair to such a young journal. This rate perhaps attributes to the following factors. First, the inclusion of HBPD INT in theIndex Medicus (IM)/MEDLINE, EMBASE/ Excerpta Medicus (EM)andBIOSIS/Biological Abstract (BA)since 2003 and the contribution of the website to quick dissemination of the knowledge or research reports published in HBPD INT. Among the databases, MEDLINE in particular has made the international audience know the journal best. And among them there are potential contributors of the journal. To attract the interest of readers is an efficient way to extend the influence of the journal. Second, editorial members and editors have spent a lot of time in soliciting good quality manuscripts in their fields including organ transplantation and hepatobiliary pancreatic surgery. In many occasions, internationally or nationally, many of them have never forgotten to say something about the journal of them or to hear opinions on the journal from colleagues in other centers. They have been deeply invested in this enterprise. Of course the development of the journal is also attributable to the efforts made by members of the editorial board and staff in reading manuscripts, writing, commissioning and editing. Third, since successful medical journals are mostly cited/ indexed in the world major databases, the inclusion of HBPD INT in such bases has obviously increased the rate of overseas submissions (94/281 in 2009).
Among specialty journals of gastroenterology worldwide, HBPD INT ranks in a low position according to its impact factor.[1]It still has a long way to go although review articles and some of the original articles are highly cited articles. In future, review articles especially systematic reviews will continue to be one of the major departments in HBPD INT. In contrast, 10.3% of case reports published are almost no citation. Are they not interesting to the readers or we should change our policies on this matter? This phenomenon is also seen in other journals.[2]However, letters to the editor especially those responding to the published articles are welcome by our readers. No matter what happens in HBPD INT the to be published material should be interesting to our readers.
It is our hope that all of the members in the international editorial board play their active part while reviewing articles and writing papers for publication in HBPD INT. Besides, the editorial staff should find time attending scientific meetings or going down to the research institute to find better research. Last but not the least, the cooperation with ELSEVIER, Thomas Reuters, and others will help to improve the quality of the journal. We know that globalization is still in some ways an aspiration and national identity is not easily discarded although the journal is international.
Funding:None.
Ethical approval:None.
Contributors:LSY wrote the first draft under the supervision of QSC. All authors contributed to the design and interpretation of the study and to further drafts. ZSS is the guarantor.
Competing interest:No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Author Affiliations: Editorial Office of Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International, First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310003, China (Lei SY, Wang PZ, Dong YP, Zhu C, Qian SC and Zheng SS)
Shu-Sen Zheng, MD, PhD, FACS, Editorial Office of Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International, First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310003, China (Tel/ Fax: 86- 571-87236559; Email: hbpdje@gmail.com)
© 2010, Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. All rights reserved.
1 ISI Journal Citation Report. ISI Web of Knowledge Database. Philadelphia, Pa: Thomson Scientific®;2009.
2 Yang H, Zhang JH, Zhang F. Citation analysis of the World Journal of Gastroenterology from 2006 to 2007. Chinese Journal of Scientific and Technical Periodicals 2010;21:190-193.
杂志排行
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International的其它文章
- News
- Resection of hepatic caudate lobe hemangioma: experience with 11 patients
- Hepatocellular carcinoma metastatic to the kidney mimicking renal oncocytoma
- Simultaneous breast and ovarian metastasis from gallbladder carcinoma
- Interferon and lamivudine combination therapy versus lamivudine monotherapy for hepatitis B e antigen-negative hepatitis B treatment: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Methods of vascular control technique during liver resection: a comprehensive review
