Clinical Observation on the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease with Damp-heat Stasis Syndrome in Clinical Proteinuria Stage by Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste
2024-03-07YingTANQilingZHANGJuanCHENXuYUQianhuaYANJiangyiYU
Ying TAN, Qiling ZHANG, Juan CHEN, Xu YU, Qianhua YAN, Jiangyi YU*
1. Department of Endocrinology, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210004, China; 2. The First Clinical Medical College, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
Abstract [Objectives] To evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) patients with damp-heat stasis syndrome in the clinical proteinuria stage. [Methods] Retrospective analysis was made on 30 patients with DKD who were diagnosed with damp-heat stasis syndrome in the clinical proteinuria stage from March 2021 to March 2023 in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, and who took Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste continuously for six months. The urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (UACR), urinary complement C3, and urea nitrogen (BUN) of DKD patients before and after treatment were compared, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), blood creatinine (Scr), and cystatin C (CysC) were estimated, and the therapeutic effects on renal function and urinary protein were evaluated. [Results] After treatment, UACR significantly decreased (P<0.01), and urinary complement C3 and Scr decreased (P<0.05), while other indicators showed no significant statistical difference (P>0.05). In terms of evaluating the efficacy of urinary protein therapy, 8 cases showed recent relief; 8 cases showed significant effect; 9 cases were effective, and 5 cases were invalid after treatment, with a total effective rate of 83.33%. In terms of renal function efficacy evaluation, 8 cases showed significant effect; 4 cases were effective; 11 cases were stable, and 7 cases were invalid, with a total effective rate of 76.67%. In the safety evaluation, there were no obvious adverse reactions. [Conclusions] The Kunkui Kidney Preserving Past has significant clinical efficacy and safety in treating DKD patients with damp-heat stasis syndrome in the clinical proteinuria period. It has significant advantages in reducing urinary protein and protecting renal function, which is worthy of clinical promotion.
Key words Diabetic kidney disease, Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste, Proteinuria, Clinical efficacy, Safety
1 Introduction
The incidence rate of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is increasing year by year. It is one of the major microvascular complications that lead to disability and death in diabetes, and also one of the main reasons that lead to end-stage renal disease and cardiovascular death. It has become a major social and economic burden in China[1]. DKD is mainly characterized by proteinuria and renal function decrease, and its early symptoms are relatively insidious. When proteinuria is detected clinically, most DKD patients have entered the phase of massive albuminuria. At this stage, the risk of DKD patients progressing to end-stage renal disease is approximately 14 times higher than other kidney diseases[2]. However, the metabolic control strategies recommended by existing Western medical guidelines (such as RASi, SGLT-2i,etc.) can only delay some early progression of DKD. Once it progresses to the clinical proteinuria stage, the clinical efficacy of these measures is often unsatisfactory. Therefore, how to reverse the clinical proteinuria stage of DKD remains a difficult and bottleneck issue. In the past decade, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has gradually become a research hotspot in the field of treating DKD with its advantages of multi-form, multi-component, multi-target, multi-pathway and considerable clinical efficacy. In this retrospective study, the Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste was used to treat DKD according to the pathogenesis characteristics of damp-heat and blood stasis in DKD patients in the clinical proteinuria period, and good clinical efficacy has been achieved.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Research objectsThis study included 30 patients with DKD who were diagnosed as the syndrome of damp heat and blood stasis in the clinical proteinuria period from March 2021 to March 2023 in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, and who had taken the Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste for six months continuously. Inclusion criteria: conforming to the diagnosis standard of DKD in the western medicine by theExpertConsensusonthePreventionandTreatmentofDiabeticKidneyDiseasebyCombiningTraditionalChineseandWesternMedicine(2023)[3]; the diagnosis of TCM syndrome type referred to the standard of theGuidetoDiagnosisandTreatmentofDiabeticKidneyDiseaseCombinedwithDiseaseandSyndrome[4], and the clinical differentiation is the syndrome of dampness and blood stasis blocking collaterals. Exclusion criteria: serious infection or acute complications of diabetes within one month; undergoing dialysis treatment; recent history of critical illness; pregnant or lactating women patients; not continuously taking the Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste for treatment for 6 months. This study has been reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine (ethical approval number: 2021NL-017-02).
2.2 Treatment measuresAccording to theExpertConsensusonthePreventionandTreatmentofDiabeticKidneyDiseasebyCombiningTraditionalChineseandWesternMedicine(2023)[3], basic treatment was carried out, and the Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste (30 g ofAbelmoschusmanihotflower, 15 g of Huobahuagen, 30 g ofAstragalusmembranaceus, 10 g ofCornusofficinalis) was given, 200 mL each time, once after breakfast and dinner. It was taken continuously for 6 months.
2.3 Efficacy evaluation
2.3.1Efficacy evaluation of urinary protein. With reference to theCriteriaforDiagnosis,SyndromeDifferentiationandTherapeuticEffectEvaluationofDiabeticKidneyDisease(TrialScheme)[5]issued by the Nephropathy Branch of the Chinese Society of Traditional Chinese Medicine, it was proposed that: (i) recent relief: UACR decreased by ≥ 50%, or fell to the normal range; (ii) significant effect: UACR decreased by ≥ 30%, but less than 50%; (iii) effective: UACR reduction, but less than 30%; (iv) invalid: those who did not meet the above valid standards. Total effective rate=(Recent relief+Significant effect+Effective)/Total number of cases×100%.
2.3.2Efficacy evaluation of renal function. With reference to theStudiesaboutSpecificationofSyndromeDifferentiationonDifferentStagesandEfficacyEvaluationProposalforDiabeticKidneyDisease[6], it was proposed that: (i) significant effect: blood creatinine reduced by ≥ 20%; (ii) effective: blood creatinine decreased by 10% to 20%; (iii) stable: there was no increase in blood creatinine, and the decrease was less than 10%; (iv) invalid: elevated blood creatinine. Total effective rate=(Significant effect+Effective+Stable)/Total number of cases×100%.

3 Results and analysis
3.1 Changes in urinary protein indicators before and after treatmentSeen from Table 1, the UACR of DKD patients significantly decreased after treatment, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.01). After treatment, the patient’s urinary complement C3 decreased, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).

Table 1 Changes in urinary protein indicators of DKD patients before and after treatment [n=30, M (P25,P75)]
3.2 Changes in renal function indicators before and after treatmentSeen from Table 2, the Scr of patients decreased after treatment, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); after treatment, the eGFR of patients showed an upward trend, but no significant statistical significance was observed (P>0.05); after treatment, the BUN and CysC of patients showed an increasing trend compared to before treatment, but there was no significant statistical significance (P>0.05).
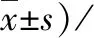
Table 2 Changes in renal function indicators of DKD patients before and after treatment (n=30, [M(P25, P75)]
3.3 Efficacy evaluation of proteinuriaSeen from treatment results, among 30 patients, 8 patients had recent relief; 8 patients showed significant effect; 9 patients were effective, and 5 patients were invalid, with a total effective rate of 83.33%.
3.4 Efficacy evaluation of renal functionSeen from treatment results, among 30 patients, 8 patients showed significant effect; 4 patients were effective; 11 patients were stable, and 7 patients were invalid, with a total effective rate of 76.67%.
4 Discussion
Traditional Chinese medicine believes that the pathogenesis of DKD is deficiency in origin and excess in superficislity, with "qi and yin deficiency, dampness and stasis obstructing the meridians" as the core pathogenesis. Dampness and stasis are both pathogenic factors and pathological products that run through the entire process of DKD. The pathogenesis of dampness and stasis obstructing collaterals has two meanings: firstly, it refers to dampness and heat accumulating in the kidney, and blood stasis obstructing the meridians; secondly, it refers to the intertwining and interweaving of dampness and blood stasis. Damp-heat stagnation in the kidney, and blood stasis obstructing the collaterals, lead to the loss of kidney sealing and storage of essence, and the essence will flow downwards, resulting in proteinuria, which is the central link in the occurrence and development of DKD.
The Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste is formulated based on the pathogenesis of DKD mentioned above, combined with the clinical experience of Professor Yu Jiangyi, a renowned traditional Chinese medicine practitioner in Jiangsu Province, and modern pharmacology. It is composed of four traditional Chinese medicines:A.manihotflower, Huobahuagen,A.membranaceus, andC.officinalis. It has the effects of nourishing qi and yin, clearing and promoting blood circulation and unblocking collaterals. The results of our study found that it had significant clinical efficacy in reducing proteinuria, protecting renal function, and reversing DKD when using the Kunkui Kidney Preserving Paste to treat DKD patients with the syndrome of damp heat and blood stasis in clinical proteinuria stage, and there are no significant adverse reactions. Among them,A.manihotflower is the monarch drug in this prescription, with the main efficacy of clearing heat, promoting dampness and blood circulation, and unblocking collaterals. Related evidence-based medical research has confirmed thatA.manihotflower preparation significantly reduced proteinuria than RASI[7], and has been widely used in clinical practice for the treatment of DKD. Huobahuagen is the root ofTripterygiumhypoglaucum(Levl.) Hutch, a plant similar toT.wilfordiiHook F. It has the effects of clearing heat, detoxifying, dehumidifying, and activating collaterals. Modern pharmacological research has confirmed that Huobahuagen has various effects such as improving microcirculation and anti-glomerulosclerosis, which are beneficial for reducing proteinuria and protecting kidney function, and can play a multi-target role in preventing and treating DKD[8]. The combination ofA.membranaceusandC.officinalisis used to tonify qi and yin. The four herbs treat both manifestation and root cause of DKD, and have excellent clinical effects by clearing heat and dampness, promoting blood circulation, and nourishing qi and yin.
杂志排行
Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Effects of Exogenous Plant Hormones on Growth Status and Secondary Metabolism of Houttuynia cordata Thunb.
- Identification of Xunxi Shujin Decoction by TLC
- Preparation of 20 (S)-protopanaxadiol PLGA Nanoparticles
- A Network Pharmacology Study on Active Components and Targets of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium for Treating Keloids
- Pharmacognostic Identification of Hedyotis auricularia and Mitracarpus villosus
- Determination of Salvianolic Acid B in Yiqi Huayu Prescription by HPLC
