Mogroside IIE,an in vivo metabolite of sweet agent,alleviates acute lung injury via Pla2g2a-EGFR inhibition
2024-02-16WeichoGuoqingRenKuniyoshiShimizuRenshiLiChofengZhng
Weicho Lü,Guoqing Ren,Kuniyoshi Shimizu,Renshi Li,b,*,Chofeng Zhng,b,*
a State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines,School of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy,China Pharmaceutical University,Nanjing 211198,China
b Sino-Jan Joint Lab of Natural Health Products Research,School of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy,China Pharmaceutical University,Nanjing 211198,China
c Faculty of Agriculture,Kyushu University,Fukuoka 819-0395,Japan
Keywords:Mogroside IIE Acute lung injury Secreted phospholipase A2 type IIA (Pla2g2a)Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
ABSTRACT In the face of increasingly serious environmental pollution,the health of human lung tissues is also facing serious threats.Mogroside IIE (M2E) is the main metabolite of sweetening agents mogrosides from the anti-tussive Chinese herbal Siraitia grosvenori.The study elucidated the anti-inflammatory action and molecular mechanism of M2E against acute lung injury (ALI).A lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI model was established in mice and MH-S cells were employed to explore the protective mechanism of M2E through the western blotting,co-immunoprecipitation,and quantitative real time-PCR analysis. The results indicated that M2E alleviated LPS-induced lung injury through restraining the activation of secreted phospholipase A2 type IIA (Pla2g2a)-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).The interaction of Pla2g2a and EGFR was identified by co-immunoprecipitation.In addition,M2E protected ALI induced with LPS against inflammatory and damage which w ere significantly dependent upon the downregulation of AKT and mTOR via the inhibition of Pla2g2a-EGFR.Pla2g2a may represent a potential target for M2E in the improvement of LPS-induced lung injury,which may represent a promising strategy to treat ALI.
1. Introduction
The fruits ofSiraitia grosvenorii(Swingle) C.Jeffrey has been used to nourish the lung arrests cough for hundreds of years[1,2].In China,S.grosvenoriifruits also are used as food for making tea,cooking soup,and so on.Pharmacological research shows that mogrosides fromS.grosvenoriifruitsprovide anti-inflammatory,anti-oxidant,hypoglycemic,and hypolipidemic benefits[3,4].Mogrosides V (M5) can gradually break off the glucosyl groups to translate into mogrosides containing 4,5,6,and 1 sugar groups or aglycon during the metabolism in rats,among these metabolites of M5,mogroside IIE (M2E) with the ability to relieve pancreatitis[5]is the most abundant metabolite especially in the liver and lungs[6].In addition,M2E is also a major compound in the immature fruit ofS.grosvenorii.However,the protective effects of M2E against lung injury have not been elucidated.
Due to industrialization and global warming,the living environment is continuously deteriorating.Air pollutants ozone,sulfur dioxide,carbon monoxide,and PM2.5are constantly increasing[7],which would be associated with the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in the setting of acute traumatic injury[8].Acute lung injury (ALI) and ARDS (a more form of ALI) are deemed as an acute and serious inflammatory process in lung,which is committed to several direct and indirect insults[9].Inflammation is considered a crucial defining event involved in the pathological process of ALI[10].Therefore,inhibition or downregulation of inflammation could be a useful strategy for the treatment of ALI.
Secreted phospholipase A2 type IIA (Pla2g2a) is an acute-phase protein in response to various proinflammatory cytokines[11].Increased plasma levels of Pla2g2a are reported in patients experiencing acute and chronic inflammatory conditions which serve as a surrogate marker for these pathologies[12].In addition,Pla2g2a is significantly upregulated in PM2.5-induced lung injury[13].Pla2g2a is present in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) of patients with ARDS,which is believed to be related to the occurrence and transmission mechanism of lung inflammation in ARDS[14].And our previous research showed that mogrosides had a significant alleviating effect on the increase of lysophosphatidylcholine (a catalytic product of Pla2g2a) in the lung caused by PM2.5[15].Therefore,Pla2g2a could be a potential new strategy for the protection of lung injury.
We hypothesized that M2E was promising as a therapeutic agent and dietary supplement in the improvement of lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-induced lung injury by inhibiting Pla2g2a.In the present study,we established an animal model of LPS-induced ALI and an LPS-induced MH-S cell model to explore the protective effects of M2E.The influence of M2E on the Pla2g2a-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway was investigated.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
M2E was purchased from Chengdu Biopurity Phytochemicals Ltd.(Chengdu,China).3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) was from Biosharp Technology Inc.(Hefei,China).Acetonitrile and methanol were purchased from Merck &Co.,Inc.(New Jersey,USA).Formic acid was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (USA),Pla2g2a (Affinity,DF6366,China),EGFR(Proteintech,18986-1-AP,China),p-EGFR (Santa Cruz,sc-57545,USA),AKT (Wanleibio,WL0003b,China),p-AKT (Wanleibio,WLP001a,China),mTOR (Abcam,ab134903,USA),p-mTOR(Abcam,ab109268,USA),NO,protein A+G Agarose (Beyotime,P2055,China),glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)(Proteintech,60004-1-Ig,China).LPS (L8880;Escherichia coli055:B5) was purchased from Solarbio LIFE SCIENCES(Beijing,China)
2.2 Animals
Adult male ICR mice (20−23 g) were from Yangzhou University Comparative Medicine Center of Jiangsu Province (Jiangsu,China).These mice were maintained with controlled temperature,humidity,adequate light.For experiments,animals were randomly divided into 3 groups (M2E,M5,and control group),intragastrically administered once a day for 20 days.The dose of M5 was 32.1 mg/kg in M5 group.The dose of M2E was 20 mg/kg in M2E group,and the control group was given physiological saline.The mouse plasma was collected at 12 h after the last dose of M2E administration.
ALI induced with LPS in mice is a classic model for research and screening of ARDS drugs and pharmacological mechanisms[16].Adult male ICR mice (20−22 g) were divided into 5 groups:(1) control group,(2) model group,(3) low dose of M2E (10 mg/kg),(4) middle dose of M2E (20 mg/kg),(5) high dose of M2E(40 mg/kg).Prophylactic M2E was administered for 7 days.5 mg/kg LPS intratracheal instillation induced ALI,and 24 h after stimulation,blood was collected and mice were euthanized[17].
2.3 Sample preparation and analysis for metabolomics study
To 100 μL of plasma sample thawed at 4 °C,300 μL of acetonitrile was added,allowed to stand at 4 °C for 3 h,centrifuged for 10 min at 15 000 ×g,and the supernatant was transferred to a new tube and dried by nitrogen.The residue was reconstituted in 200 μL water-acetonitrile solution (1:1),centrifuged for 15 min at 15 000 ×g.Thereafter,the supernatant was analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HPLC-TOF/MS)(6530 Accurate-Mass Q-TOF system,Agilent Technologies,USA).Chromatographic conditions: flow rate was 0.4 mL/min,injection volume 10 μL,column temperature 35 °C,mobile phase 0.1% formate water (A),and acetonitrile (B).The gradient of the mobile phase was:0−10 min,5%−40% B;10−25 min,40%−95% B;25−35 min,95% B.Mass spectrometry conditions: positive ion mode acquisition,scan rangem/z30−1 500.
2.4 Preparation of mRNAs and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis
For qRT-PCR,total mRNAs were extracted from the MH-S cells,lung,spleen,or thymus tissue using a commercial purification kit(Esunbio,China).The expression levels of genes were determined with qRT-PCR.Primers and amplicon sizes are shown in Table S1.
2.5 Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation
Pla2g2a (1cjy) was docked with compounds by AutoDock Vina (an open-source program).The protein structures of PLA2were obtained from PDB database (Pla2g2a crystal: 1cjy).The Pla2g2a-M2E complex or Pla2g2a was subjected to 5 ns molecular dynamics simulation through the Gromacs5.0.7 platform.The results of molecular dynamics simulation were analyzed by xmgrace and dssp platforms.
2.6 Network construction and bioinformatics analysis
To predict the target,the three-dimensional structure of M2E was uploaded onto the PharmMapper database.After comparing the anti-inflammatory targets from GeneCards database,the inflammation-related targets of M2E were obtained.Cytoscape and STRING were used to acquire a protein interaction network(PPI) of M2E anti-inflammatory targets.
Microarray and RNA-seq datasets of whole blood within 48 h of admission from patients with 13 patients with ALI +sepsis and 21 patients with sepsis (GSE10474) were reanalyzed for the genetic correlation amongPLA2G2A,IL6,IL1B,NOX2,IL17A,CD86,CD163,SFTPC,andEGFR.
2.7 Cell culture
MH-S cells were seeded into 96-well plates or 6-well plates(4 × 104/cells well).The serum-containing medium was discarded,serum-free medium and corresponding drugs were added to 96-well plates.After 44 h of culture,MTT solution was added and measured at 570 nm.5 μg/mL LPS and corresponding drugs were added to 6-well plates.After 24 h of culture,cells were collected.
2.8 Epifluorescence microscopy
To localize p-EGFR,Pla2g2a immunofluorescence staining was performed.Lung tissue sections were dewaxed with xylene,incubated in 0.1% Triton X-100 solution,and washed with 1× PBS (MH-S cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde).Tissue sections were blocked with bovine serum albumin (BSA),incubated with the primary antibody in a humidified chamber,and stained with a secondary antibody conjugated with fluorescent dye.Slides were examined and images were photographed under an epifluorescence microscope at room temperature.
2.9 Co-immunoprecipitation and western blotting
Radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) solubilization buffer was subjected to extract the total proteins from lung tissues and cells.The concentration of proteins was determined using a BCA kit.After total proteins incubating with the appropriate antibodies and the Protein A/G Plus Agarose,immune complexes were washed and mixed with SDS sample loading buffer.Equal amounts of immune complexes or lysates were separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)gels and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF).After incubating with the primary and thereafter secondary antibodies,the western blotting signals were analyzed.
2.10 Cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA)
After MH-S cell lysis,the solution was centrifuged at 15 000 ×gfor 15 min,the supernatants were divided into two parts,one part treated with M2E (10 μmol/L) and the other part with 0.1% DMSO.Then,the corresponding lysates were divided into 6 aliquots.The lysates were heated respectively at 37,42,47,52,57,62,and 67 °C.After centrifugation at 15 000 ×g,the heated lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE (La Jolla,CA,USA).
2.11 Data processing and analysis
The raw profile was processed by the Agilent masshunter profinder for directional regression characterization,peak detection,and alignment.Data was imported into Mass Profiler Professional (MPP) for data difference analysis,and the control group was selected as a reference.Principal component analysis(PCA) and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA) were used to analyze the difference between groups.The VIP score >1,P<0.05 and |log2FC| >1 were used to screen the differential metabolites between control and M2E group.
All the data were analyzed with one-way analysis of variances (ANOVAs),the following was Tukey’s range test.All data were expressed as the mean ± standard error (SD) of the mean andP<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1 M2E relieves lung injury induced with LPS in mice
The rate of body weight change in mice and lung weight/body weight was significantly increased in the model group,compared with the control group.Whereas M2E inhibited LPS-induced ratio increased (Figs.1A,B).A preliminary evaluation of lung specimens collected from the LPS group indicated visibly pathological lesions,including severe leukocyte infiltration,thickened alveolar wall,pulmonary edema,and hemorrhage,which were markedly alleviated in the M2E-pretreated mice(Figs.1C,D).As shown in Fig.1E,applying a semiquantitative methodology to score for lung injury,we observed that LPS significantly increased lung injury scores,which were decreased by M2E pretreatment.Meanwhile,NO content in the lung was increased in model mice (Fig.1F).In addition,compared with the control group,the expression ofIL-6,CD68,andCD86genes in the lung was increased in the model group (Figs.1G-I).M2E administration suppressed the increase of IL-6,CD68,CD86,and NO levels.The up-regulated protein expression of CD86 induced with LPS was performed that macrophage was diffuse in the lung tissue and manifested type I of polarization to secrete proinflammatory factors.At the same time,M2E could attenuate the fluorescent intensity of CD86 (Fig.1J),which identified that the effect of LPS on macrophage activation was weakened.
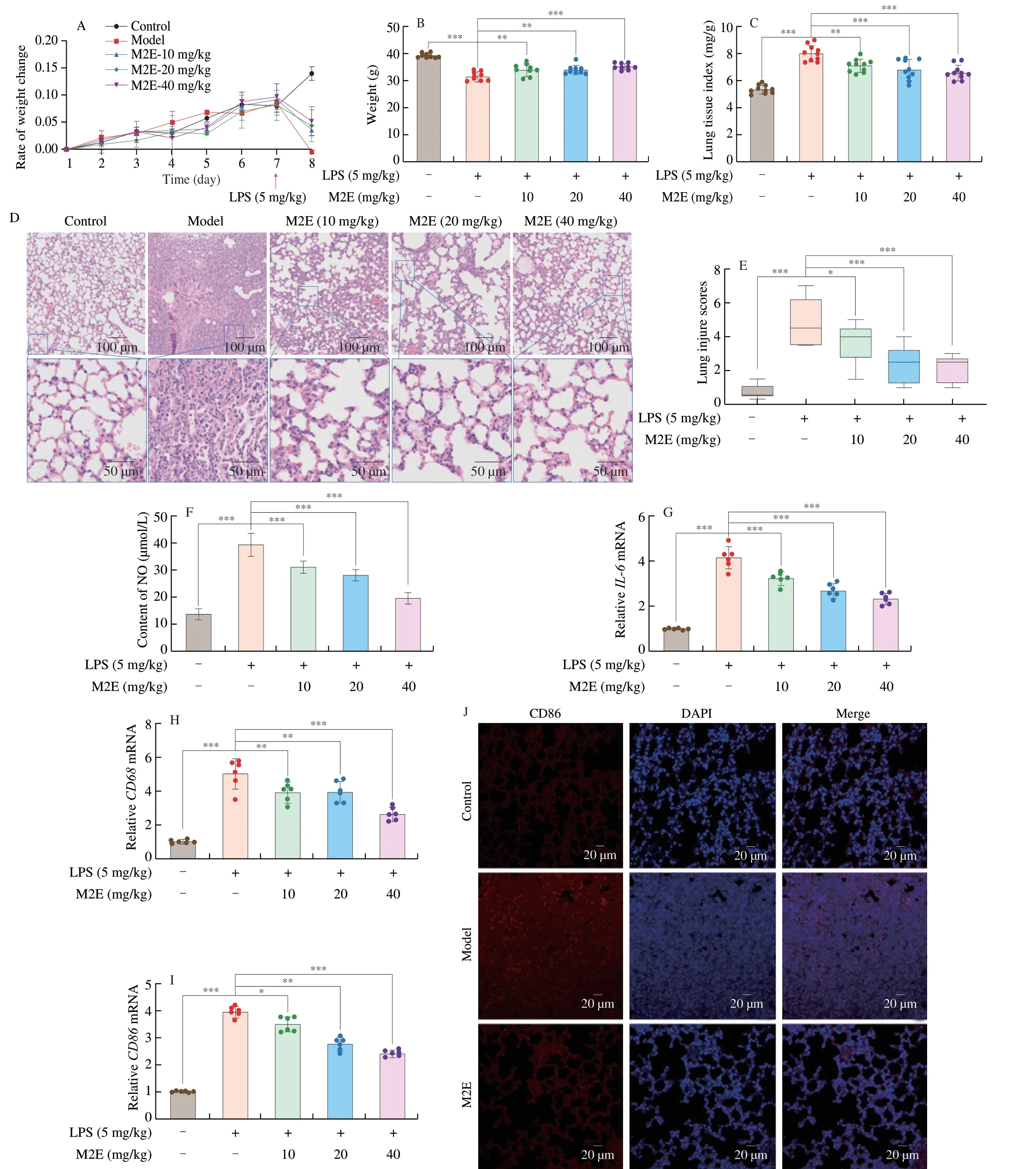
Fig.1 M2E markedly ameliorated lung acute injury in LPS-treated mice.(A) Change in body weight of mice after M2E administration and LPS-induced.(B) Final body weight of mice 24 h after LPS-induced.(C,D) Mouse lung tissue index and lung histopathology were observed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE)staining.(E) The score of HE stained sections of mouse lung tissue.(F) NO expression in the control,model,and M2E administration group in lung tissue.(G-I) Gene expression of IL-6,CD68,and CD86 in the control,model,and M2E administration group in lung tissue.(J) Representative immunofluorescent staining images of CD86 in the lungs.The values are expressed as the mean ± SD of at least three independent assays.ns.no significant difference,* P <0.05,** P <0.01,*** P <0.001.The same below.
3.2 M2E directly binds to Pla2g2a and inhibits its expression in MH-S cells
The PharmMapper predicted targets for M2E (Table S2)and screened 26 targets whose Norm Fit was more than 0.7.Topological parameters (Degree,BetweennessCentrality,and BottleNeck) were used to evaluate the key position of the protein target in the protein interaction network (Figs.2A,S1A).Topological results showed that Pla2g2a and EGFR were likely the key targets in the protein interaction network.Based on the ClueGO assessment,M2E targets were enriched to achieve 9 groups of biological processes (Fig.S1B).M2E was docked with Pla2g2a.The docking results showed that the binding energy of M2E and Pla2g2a was −7.7 kcal/mol.It was worth noting that M2E interacted with Ca2+in the Pla2g2a (Fig.2B).M2E and Pla2g2a have performed a 5 ns molecular dynamics simulation for the complex and Pla2g2a.The complex of Pla2g2a and M2E started to stabilize at 0.8 ns (Fig.2C),in contrast,only Pla2g2a stabilized after 3 ns.Pla2g2a was a Ca2+dependent enzyme,and molecular docking results indicated the ability of M2E to interact with the Ca2+in Pla2g2a.Compared with Pla2g2a,it was obvious that the RMSD change of the complex was relatively stable,and the fluctuation was not clear (Fig.2D),which showed that the interaction of M2E limited movement of Ca2+.There was compelling evidence of combination between M2E and Pla2g2a,and the combination had a stabilizing effect on the protein structure of Pla2g2a and limited the movement of Ca2+.The results of M2E investigations on cell viability of MH-S(Fig.S1C) suggested that M2E did not impact the cell viability when the doses of M2E were lower than 100 μmol/L.M2E reduced the gene and protein expression of Pla2g2a,which were significantly elevated in the MH-S cells in response to LPS treatment(Figs.2E-F).We employed CETSA approaches to identify Pla2g2a that interact with M2E.Compared with the control group,M2E could reduce the degradation rate of Pla2g2a at high temperatures.The results showed that M2E had a higher affinity with Pla2g2a(Fig.2G).Collectively,results suggested that M2E directly interacted with Pla2g2a in MH-S cells and inhibited the expression of Pla2g2a.

Fig.2 Identified that the M2E bonded with Pla2g2a and inhibited the expression of Pla2g2a.(A) M2E activity protein interaction network.(B) Molecular docking results of M2E and Pla2g2a.In molecular dynamics simulation of M2E and Pla2g2a,the red line was the Pla2g2a track,and the black line was the complex of Pla2g2a and M2E.(C) RMSD analysis of complex and Pla2g2a (the red line represents the motion state of the Pla2g2a protein,while the black line represents the motion state of the Pla2g2a protein containing M2E).(D) RMSD analysis of Ca2+ of complex and Pla2g2a (the red line represents the motion state of the Pla2g2a protein,while the black line represents the motion state of the Pla2g2a protein containing M2E).(E) Effect of different concentrations of M2E on the protein expression of Pla2g2a.(F) Effect of different concentrations of M2E on the gene expression of Pla2g2a in LPS-induced MH-S cells.(G) M2E administration or non-administration sample data of the cellular thermal shift assay for Pla2g2a.
3.3 M2E relieves LPS-induced inflammation by inhibiting Pla2g2a-EGFR
Analysis of transcriptomic data derived from patient samples with clinical ALI showed a strong correlation between Pla2g2a and several inflammatory factors (Fig.3A),including IL6,IL1B,IL17A,and NOX2.Pla2g2a showed a higher correlation with CD86,but a lower correlation with CD163,suggesting that Pla2g2a may be closely associated with polarization of type I macrophages and less with type II macrophages[18,19].M2E had an IC50of 20.82 μmol/L for NO inhibition in the LPS-induced macrophage inflammation model (Fig.3B).Ulteriorly,M2E (0.1,1,10 μmol/L) significantly reduced the LPS-induced upregulation ofIL-1β,IL-6,andTNF-αgene expression in MH-S cells (Figs.3C-E).In addition,it should note that M2E down-regulated the activation of EGFR (Fig.3F-G).Based on the results of immunoprecipitation,it was found that LPS stimulation increased Pla2g2a binding to EGFR in MH-S cells compared with the control group,which indicated that M2E could significantly interfere with the binding of the two proteins and in turn inhibite the activation of EGFR (Figs.3H-J).Pretreatment with LPS increased the fluorescence intensity of Pla2g2a and p-EGFR in the MH-S cells,which uncovered the temporal and spatial consistency of Pla2g2a and p-EGFR expression after LPS pretreatment.At the same time,M2E significantly inhibited the fluorescence intensity of Pla2g2a and p-EGFR (Fig.3K).

Fig.3 Pla2g2a-EGFR was performed a significant role during M2E released the inflammation-induced with LPS.(A) Correlation between Pla2g2a and inflammation-related indicators in human acute lung injury transcriptome sample.(B) Inhibition rate of different concentrations of M2E on NO concentration.(C-E) Gene expression of IL-1β, IL-6,TNF-α in LPS-induced MH-S cells.(F-G) Effect of different concentrations of M2E on the activation of EGFR of LPS-induced MH-S cells.(H-J) Interaction between Pla2g2a and EGFR was investigated using immunoprecipitation assays.(K) MH-S cells in dishes were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde,stained with DAPI (blue),Pla2g2a (green),and p-EGFR (red),and imaged by confocal microscopy.
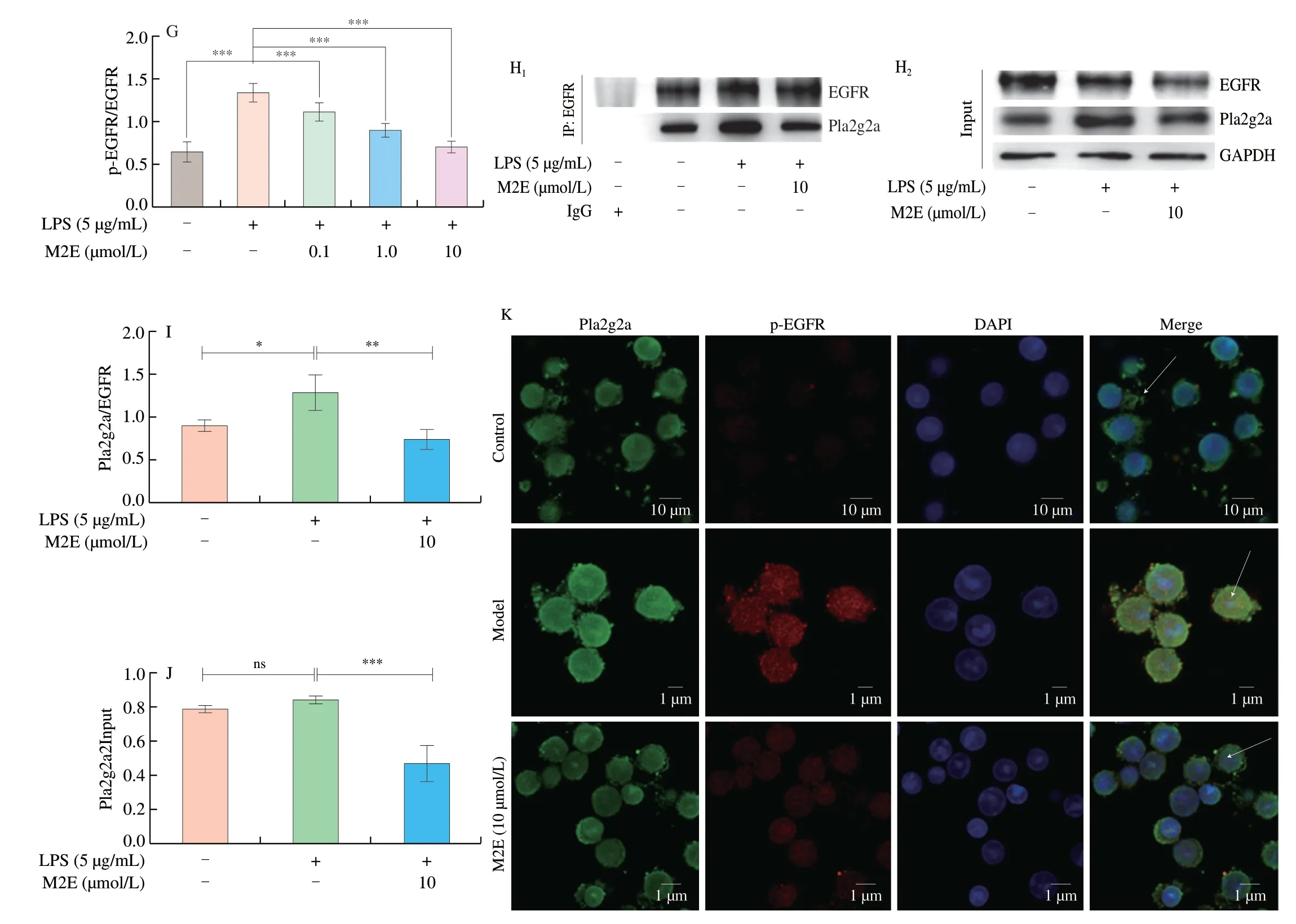
Fig.3 (Continued)

Fig.4 Altering Pla2g2a expression changed the anti-inflammation and anti-oxidant activity of M2E.(A-B) Protein and gene expression of Pla2g2a knocked down by siRNA in MH-S cells.(C-D) mRNA expressions of inflammation gene were analyzed by qRT-PCR after Pla2g2a was knocked down.(E) Expressions of NO were analyzed after Pla2g2a was knocked down.(F-I) Protein expressions of EGFR,AKT,and mTOR were analyzed by Western blotting.
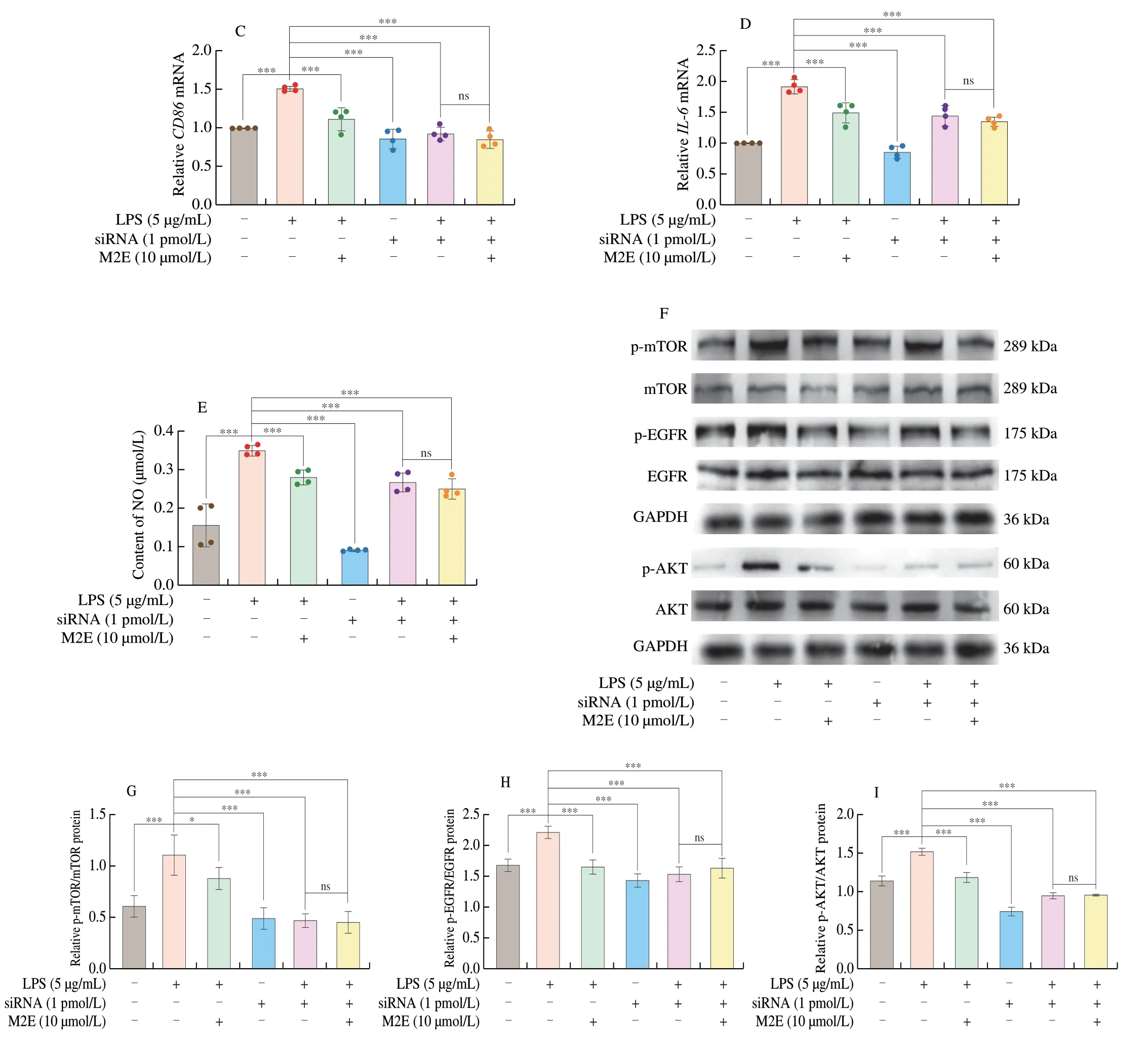
Fig.4 (Continued)
3.4 M2E inhibits EGFR-AKT-mTOR to recede LPS-induced inflammation
We investigated whether the Pla2g2a was involved in the anti-macrophage type I polarization of M2E in the following study.First,we identified the knock-down of Pla2g2a protein expression and mRNA expression in MH-S cells (Figs.4A-B).The expression ofCD86,IL-6genes,and content of NO were significantly down-regulated after Pla2g2a knock-down,and M2E did not affect the expression ofCD86,IL-6genes,and NO content (Figs.4C-E).MH-S stimulated with LPS not only activated EGFR but also induced the ATK/mTOR signaling cascade,the downstream target of EGFR[18].Next,we sought to reveal the relationship between Pla2g2a and EGFR-AKT-mTOR signaling.The activation of EGFR,AKT,and mTOR in MH-S cells treated with LPS were all inhibited after knocking-down Pla2g2a (Figs.4F-I).Accordingly,M2E could not further decrease the EGFR,AKT,and mTOR phosphorylated expression in the MH-S cells lacking Pla2g2a.
Plasmid transfection accomplished Pla2g2a overexpression in the MH-S cells (Fig.5A).The results of detecting the expression of inflammatory factors and NO in LPS-treated overexpression Pla2g2a and normal MH-S showed that overexpression of Pla2g2a mediated up-regulation of NO content,expression ofIL-6andCD86genes,and reversed M2E-mediated inhibition of the aforementioned proteins(Figs.5B-D).In MH-S cells,CD86 fluorescence staining showed that after Pla2g2a was overexpressed,CD86 fluorescence was more significant,and M2E could reduce the fluorescence intensity of CD86 (Fig.5E).
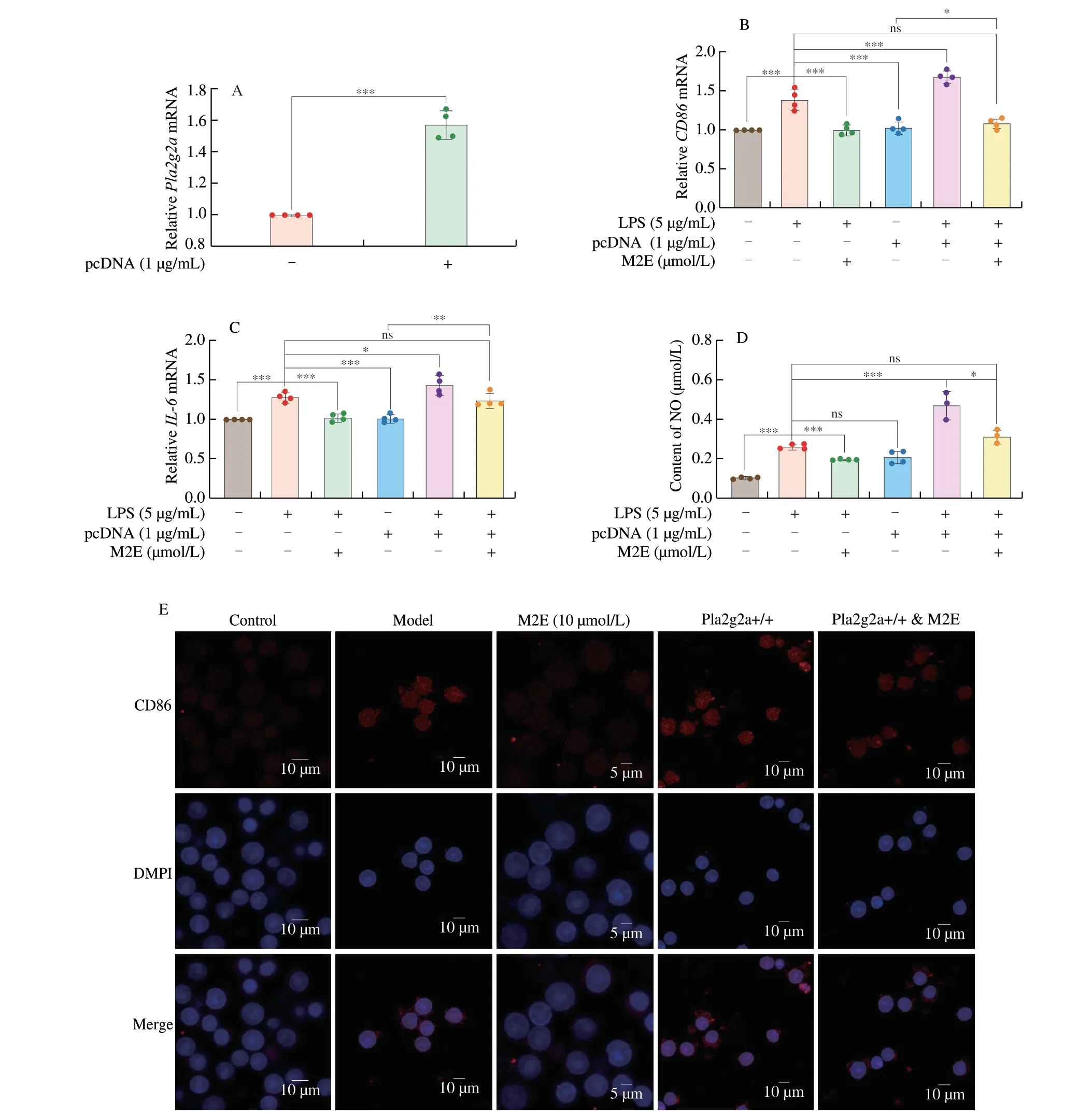
Fig.5 Overexpression of Pla2g2a disturbed the therapeutical effect for LPS-induced MH-S of M2E.(A) Gene expression of Pla2g2a after pcDNA overexpression in MH-S cells.(B,C) mRNA expressions of inflammation gene were analyzed after Pla2g2a overexpression.(D) Expressions of NO were analyzed after Pla2g2a overexpression.(E) Stained with DAPI (blue) and CD86 (red),and imaged by confocal microscopy.
The above results indicated that Pla2g2a was the critical component of M2E suppressed inflammatory factors and polarization of macrophages.Pla2g2a inhibited the activation of the EGFR/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by inhibiting Pla2g2a,thereby significantly improving the LPS-induced inflammation in MH-S cells.
3.5 M2E inhibits Pla2g2a-EGFR to relieve LPS-induced lung injury in mice
Western blotting and qPCR analysis of lung tissue proteins showed that M2E significantly improved the protein and gene expression of Pla2g2a in mouse lung tissue induced by LPS(Figs.6A-C).At the same time,the EGFR/AKT/mTOR pathway,which was significantly activated by LPS induction in lung tissue,was also inhibited after M2E administration (Figs.6B,D-F).As shown in Fig.6G,the microscopic evaluation revealed increased fluorescence intensity of FITC labeled Pla2g2a and tetramethylrhodamine (TRITC) labeled p-EGFR was found in lung tissue of mice subjected to LPS treatment.In addition,green fluorescence of FITC-Pla2g2a and red of TRITC-EGFR were co-localized.M2E pretreatment decreased the fluorescence intensity of Pla2g2a and p-EGFR in the lung,which indicated the temporal and spatial consistency of the inhibition of Pla2g2a and p-EGFR expression after M2E pretreatment.

Fig.6 M2E relieves the lung injury induced with LPS through inhibiting Pla2g2a-EGFR.(A) Gene expression of Pla2g2a in the control,model,and M2E administration group in lung tissue.(B-F) Protein expression of Pla2g2a,EGFR,AKT,and mTOR in the control,model and M2E administration group in lung tissue.(G) Representative immunofluorescent staining images of Pla2g2a and p-EGFR in the lungs.
3.6 The relationship between mogrosides and Pla2g2a
As the processing of the fruit matures,the content of M2E decreases while mogroside III (M3) and mogroside IV (M4)increase.What continues to accompany fruit ripening was the increase in M5 content and the decrease in M3 and M4 content(Figs.S2A-C).Therefore,we next compared the effects of various mogrosides on Pla2g2a.Based on the binding energy of molecular docking,it was found that M2E,mogrol,and bryodlcosignenin had the lowest binding energy (Fig.7A).At the same time,compared with other compounds,the amino acid residues bound by M2E had the highest degree of overlap(Fig.S3A).M5 would be metabolized to M2E in rats and accumulate in lungs and other tissues.Therefore,to further study the pharmacological differences between the two important compounds forS.grosvenoriifruits (Fig.7B),we administered M2E and M5 to normal mice for 20 days.After 20 days of administration,there was no significant difference in the weight change trend and no significant effect on the number of T cells and B cells in mesentery lymphadenites of mice among the control group,the M2E,and the M5 group (Figs.S3B-F).The results identified that M2E and M5 had no obvious effect on the normal growth of mice.However,in the M2E group,not M5 group,mRNA expression ofPla2g2awas reduced significantly in the lungs (Fig.7C).To explore the differences in the metabolites in plasma after M2E and M5 administration,a comprehensive metabolomics study was carried out.The study established the PCA and OPLS-DA models of the M2E and control group or M5 and control group (Figs.7D-E,S4A-B,Table S3),which showed that the difference of metabolism between the M2E group and control group was significant.A total of 12 differential metabolites were obtained by analysis between the M2E group and the control group,but there is no metabolite between M5 and control group,which were screened through VIP score >1,P<0.05,and |log2FC| >1 (Figs.7F-G,S4C-D).Next,we determined the structure of the biomarker by secondary mass spectrometry data and HMDB database analysis,and finally,the differential metabolites obtained are shown in Fig.7H and Table S4.LysoPCs were the primary differential metabolites caused by M2E administration.Analysis of the KEGG pathway of differential metabolites showed that administration of M2E could significantly affect glycerophospholipid metabolism (Fig.7I;Table S5).LysoPC (15:0),LysoPC (18:0),LysoPC (20:3),LysoPC (22:4),and LysoPC (24:0) participated in and affected the glycerophospholipid metabolism.
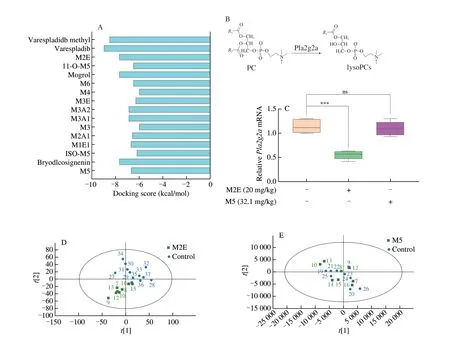
Fig.7 M2E holds the better pla2g2a inhibition among the mogrosides.(A) The docking results of mogrosides bond with Pla2g2a.(B) PLA2 enzyme catalyzes the production of lysoPCs.(C) Pla2g2a gene expression level in the lung.(D) PCA analysis of plasma metabolomics in the group of M2E administration and the group of control.(E) PCA analysis of plasma metabolomics in the group of M5 administration and the group of control.(F) Volcanic maps between M2E and control groups;(G) Maps between M5 and control groups,metabolites in red are metabolites that are up-regulated relative to the control group,and metabolites in blue are metabolites that are down-regulated relative to the control group.(H) Heatmap of the differential metabolites between M2E and control.(I) KEGG pathway analysis of differential metabolites.
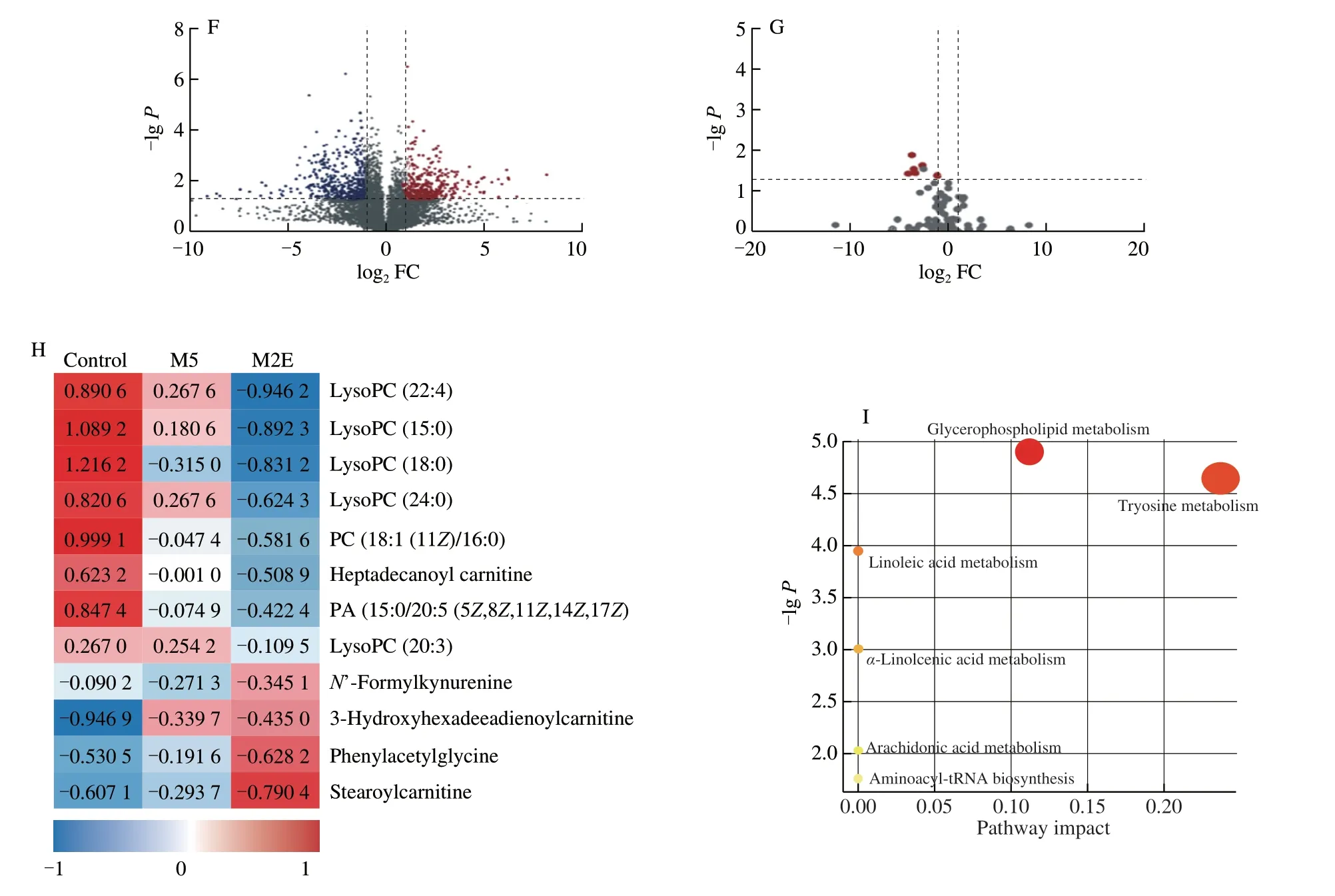
Fig.7 (Continued)
4. Discussion
ALI refers to a series of clinical criteria,manifested as progressive hypoxemia,dyspnea,and increased work of breathing.ARDS account for more than 10% of all intensive care unit (ICU) admissions and 4% of all hospitalizations[20].Traditional Chinese medicineS.grosvenorii,traditional medicine and food,has been used for the treatment of lung diseases for a long time.M2E is a primary component in the immature fruit ofS.grosvenorii.During the maturation process.Our research had shown that M2E had a better Pla2g2a inhibitory effect in mogrosides.In the mouse model of LPS-induced lung injury,M2E significantly protected the lung tissue of mice,reduced inflammation,and leukocyte infiltration,and NO expression.
Recent studies have shown persistently elevated levels of Pla2g2a in deceased COVID-19 patients.Pla2g2a levels of deceased COVID-19 patients were as high as 1 020 ng/mL,which was 9.6 or 5 folds higher than those in mild or severe COVID-19 patients[21].Pla2g2a had immediate and organism-wide pathogenic potential[22-26],which indicated that Pla2g2a could exacerbate tissue and organ damage.The role of Pla2g2a had been described in inflammation,tumorigenesis,and metastasis.LPS mediated the phosphorylation of extracellular signalregulated protein kinase (ERK)1/2.The accumulation of ERK1/2 levels modulated the downstream activities of human cytosolic phospholipase A2-alpha (cPLA2a),in turn,cPLA2a regulated activations of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase (mPGES)-1 enzymes,which led to the production of Pla2g2a[27].EGFR had been reported to initiate the inflammatory response[28].The EGFR family and its ligands served as a switchboard for the regulation of multiple cellular processes.EGFR,via transactivation,had the potential to mediate signaling of non-EGFR ligands and thereby served as a heterologous transducer of cellular signaling[29].The results of network pharmacology and human transcriptome data mining indicated that Pla2g2a and EGFR might be the pivotal points of M2E regulation.Pla2g2a was able to bring into play EGFR to trigger downstream pathway signaling[11].
The expression of Pla2g2a was significantly reduced in lung tissue induced with LPS after M2E administration.CETSA,molecular docking,and molecular dynamics simulations further demonstrated that M2E could inhibit Pla2g2a.In the meantime,Pla2g2a,EGFR/AKT/mTOR,and a variety of inflammatory indicators were significantly upregulated and activated in the LPS-induced lung injury,while M2E could significantly inhibit the production of the above proteins.Relying on the methods such as immunoprecipitation,immunofluorescence,and CETSA confirmed the up-regulated expression of Pla2g2a in MH-S cells stimulated by LPS,thereafter Pla2g2a bound with EGFR and activated EGFR.At the same time,M2E bound to Pla2g2a and prevented its binding to EGFR,thereby reducing the expression of Pla2g2a and the activation of EGFR.Furthermore,knock-down and overexpression of Pla2g2a in MH-S showed that M2E inhibited the activation of EGFR by inhibiting Pla2g2a,thereby blocking the EGFR/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway activated by LPS.The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway regulated cell growth,proliferation,migration,invasion,survival,apoptosis and autophagy[30].During LPS-induced inflammatory response,LPS mediated PI3K,p-AKT and p-mTOR protein levels through toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4),and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis was the key point for TLRs/NF-κB to coordinate inflammatory responses[31,32].At the same time,the activation of EGFR participated in the increased expression of TLR4 and activated the AKT/mTOR pathway[33,34].By inhibiting the binding of Pla2g2a and EGFR,M2E affected the activation of EGFR and thereby truncated the LPS-induced AKT/mTOR activation,which alleviated the LPS-induced inflammatory response.
Furtherly,the results of the study on a variety of mogrosides identified that M2E could be a better Pla2g2a inhibitor.As a metabolite of M5in vivo,M2E significantly inhibited the activity of Pla2g2a,while M5 could not.M5 had no effect on the metabolism of normal mice,which indicated that in the body,M5 was likely to be metabolized into M2E and exert its efficacy.Therefore,this article explores the interventional effect of M2E on lung inflammation,further showing that the use ofS.grosvenoriican resist lung inflammation and injury.
5. Conclusions
In summary,M2E is a low molecular weight component of the traditional Chinese medicinal plant.we identified the ability of M2E to ameliorate ALI in LPS induced mice and first analyzed the target of M2E,Pla2g2a was determined.Importantly,we determined the anti-inflammatory effect of M2E on lung tissues and revealed that the underlying mechanism of M2E action involved inhibition of EGFR/AKT/mTOR signaling mediated by Pla2g2a.This study is the first to demonstrate that the ability of M2E to inhibit the formation of the Pla2g2a-EGFR complex.These findings,therefore,showed that M2E exerted therapeutic effects in models of ALI,thus supporting this phytochemical as a novel candidate for the treatment of ALI shortly.On the other hand,it further explained the potential mechanism by which mogrosides might be metabolized into M2E in the body to exert pharmacological effects and also provided part of the theoretical basis for the application of immature fruits ofS.grosvenorii.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation(81 773982;82003937),and Youth Academic leaders of the Qinglan Project in Jiangsu province for financial support.We would like to express our gratitude to EditSprings (https://www.editsprings.com/)for the expert linguistic services provided.
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at http://doi.org/10.26599/FSHW.2022.9250025.
杂志排行
食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- Modifications in aroma characteristics of ‘Merlot’ dry red wines aged in American,French and Slovakian oak barrels with different toasting degrees
- Effect of different drying methods on the amino acids,α-dicarbonyls and volatile compounds of rape bee pollen
- Dynamic changes in physicochemical property,biogenic amines content and microbial diversity during the fermentation of Sanchuan ham
- A comparison study on structure-function relationship of polysaccharides obtained from sea buckthorn berries using different methods:antioxidant and bile acid-binding capacity
- Yolk free egg substitute improves the serum phospholipid profile of mice with metabolic syndrome based on lipidomic analysis
- Underlying anti-hypertensive mechanism of the Mizuhopecten yessoensis derived peptide NCW in spontaneously hypertensive rats via widely targeted kidney metabolomics
