Transcriptomic analysis of Andrias davidianus meat and experimental validation for exploring its bioactive components as functional foods
2024-02-16ChnggGunZhnglinTnShuchngLiYiWngNoyukiYmmotoChongZhngdSongjunWngJunjiChnXinhuiXingd
Chngg Gun*,Zhnglin Tn,c,Shuchng Li,Yi WngNoyuki Ymmoto,Chong Zhngd,Songjun Wng,Junji Chn,Xinhui Xingd,g,h,*
a Key Laboratory for Industrial Biocatalysis,Ministry of Education of China,Department of Chemical Engineering,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
b School of Life Science and Technology,Tokyo Institute of Technology,Yokohama 226-0026,Japan
c Sensing System Research Center,National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology,Tsukuba 305-8565,Japan
d Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
e Henan Giant Salamander Protection and Development Association,Luoyang 471000,China
f Intelligent Computing Research Center,Harbin Institute of Technology,Shenzhen 518071,China
g Institute of Biopharmaceutical and Health Engineering,Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School,Shenzhen 518055,China
h Institute of Biomedical Health Technology and Engineering,Shenzhen Bay Laboratory,Shenzhen 518067,China
Keywords:Chinese giant salamander Transcriptomic analysis Bioactive components Functional peptides mining
ABSTRACT Andrias davidianus (Chinese giant salamander,CGS) is the largest and oldest extant amphibian species in the world and is a source of prospective functional food in China.However,the progress of functional peptides mining was slow due to lack of reference genome and protein sequence data.In this study,we illustrated full-length transcriptome sequencing to interpret the proteome of CGS meat and obtain 10 703 coding DNA sequences.By functional annotation and amino acid composition analysis,we have discovered various genes related to signal transduction,and 16 genes related to longevity.We have also found vast variety of functional peptides through protein coding sequence (CDS) analysis by comparing the data obtained with the functional peptide database.Val-Pro-Ile predicted by the CDS analysis was released from the CGS meat through enzymatic hydrolysis,suggesting that our approach is reliable.This study suggested that transcriptomic analysis can be used as a reference to guide polypeptide mining in CGS meat,thereby providing a powerful mining strategy for the bioresources with unknown genomic and proteomic sequences.
1. Introduction
Andrias davidianus(Chinese giant salamander,CGS) is the largest and oldest extant amphibian species in the world.It has been revealed to have unique nutraceutical functions including high quality nutrients,antioxidant,anti-tumor,antibacterial,and anti-aging activity and the ability to treat burns,infections,and radiation exposure.Particularly,the meat (muscle) of CGS is long known to be functional food and medicine in China[1,2].Although the protein contents in the meat of CGS is lower than in aquaculture,it is rich in essential amino acids,particularly in lysine and tryptophan[1,2].However,wild CGSs have been listed as a class II endangered and protected species of China since 1988,therefore Chinese aquatic scientists have made great efforts in the artificial breeding of CGS for population protection since the 1970s and succeeded in the development of the farming industry of CGSs,which has enabled rational utilization of farmed CGSs from the second generation[3,4].
Recent studies have discovered that polypeptides in the meat of CGS could contribute to various health benefits.Enzymatic hydrolysate of the meat of CGS possesses high antioxidant activity compared to those from beef,pork,chicken,and fish[5].Furthermore,the anti-aging effects of the meat of CGS were also demonstrated in the aging mice model[6]andDrosophila[7].Despite the health benefits exhibited in the meat,most studies on bioactive components from CGS have focused on the mucus-and skin-derivatives[8-10]and cartilage[3]by the established extraction methods of bioactive components due to various challenges in enzymatic hydrolysis and separation of bioactive components from meat.
On the other hand,multi-omics analysis,particularly transcriptomic analysis of food-borne proteins is a useful tool for functional analysis for developing animal-derived functional foods in which the extraction of bioactive components is difficult.Zhang et al.have conducted a comparative analysis of the region-specific expression patterns in different beef cuts,and suggested that these analyses could be used to aid the selection of health-beneficial meat in beef[11].A similar approach has also been used in analyzing the nutritional value of various livestocks[12,13].These studies have shown that transcriptomic analysis is a viable method for analyzing nutraceutical values of animal-derived proteins.As traditional chemical or enzymatic extraction of bioactive compounds from CGS requires trail-and-error approaches with substantial uncertainties,they have hindered the progress in the systematic mining of the healthbeneficial components of CGS.Therefore,it is important to develop the multi-omics analysis of CGS tissues or organs to identify the bioactive components,particularly transcriptomic analysis of proteins,to accelerate the progress in exploring bioactive peptides.However,multi-omics analysis of CGS is a complicated and laborious task.CGS has a huge genome of approximately 50 Gb[14–15],which has rendered it impractical to conductde novoassembly with huge genome of CGS,thus,limited the progress of genome sequencing of CGS.To address this limitation,proteomic methods and next-generation sequencingbased RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) have been used to investigate the transcriptome of CGS,particularly the transcriptome of skin[16-19].
Meanwhile,research on the discovery and production of functional polypeptides in the meat of CGS is limited by various bottlenecks,which include: (1) no reference data on the protein composition of the meat of CGS,which in turn results in the difficulty in identifying amino acids sequence which matches the mass spectrum[17],(2) short read length,GC bias and incapability to provide coverage of repetitive regions result in low accuracy of transcriptome assembly based on RNA-seq[20,21],and (3) lack of efficient design strategy and screening method due to the laborious process of traditional enzymatic hydrolysis of the meat.These limitations have obstructed the progress of mining the bioactive components from the meat of CGS.
In this study,we have used real-time long-read technology of RNA-seq to counteract the errors produced by next-generation sequencing on short reads,with the objective to generate an accurate full-length meat transcriptome of CGS,which can be used as a reference dataset to guide the mining of nutraceutical peptides based on the estimated meat protein sequences of CGS.In order to prove the reliability of this strategy,valine-proline-isoleucine (VPI),which is an inhibitor of diabetes targeting dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV)[22],was successfully screened from the meat protein sequences of CGS by enzymatic hydrolysis.
2. Methods and materials
2.1 Animal materials
A healthy farm-raised CGS (female,4 years old,70 cm in length,4 kg) was obtained from Henan Huani Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.(Henan,China).The CGS was sacrificed,the meat was immediately isolated from CGS body and washed with sterile phosphate-buffered saline.For RNA extraction,meat tissue was snap-frozen with liquid nitrogen immediately after isolation and stored at -80 °C until the further experimental procedure.
2.2 RNA sequencing
RNA was extracted with a kit as manufacturer’s protocol by GENEWIZ.The quantity,and quality of RNA were evaluated with NanoDrop Spectrophotometer and sequenced by PacBio Platform of GENEWIZ[23].
2.3 Pre-processing of sequencing data
The data was processed with Iso-Seq process (SMRTLink software,v11.0,PacBio) to obtain full-length transcriptome,which includes circular consensus sequence (CCS) acquisition,fulllength sequence identification (classify) and isoform horizontal clustering (cluster).
First,the CCS was extracted from the bam file of offline subread,and the minimum predicted accuracy was defined as >0.8.
Then,the CCS was divided into full-length sequence or non-fulllength sequence based on existence of 3’ primers,5’ primers and PolyA.Primers and polyA/T tail sequence from both end of CCS was removed,and the artificial concatemers of the full-length sequence were filtered to obtain full-length non-chimeric sequence and nonfull-length sequence.The information of sequence strand was also identified based on primer information and polyA/T tail.
A consensus isoform was obtained from each cluster of full-length non-chimeric grouped with iterative isoform clustering algorithms.Consensus isoform was corrected with Quiver algorithms and highquality sequences were screened for subsequent analysis with predicted accuracy ≥ 0.99 and more than 2 full-length sequences were supported.
Open reading frame (ORF) prediction and annotation analysis were conducted with high quality sequences analysis obtained after pre-processing.
2.4 Functional annotation
In order to analyze the function of CGS meat transcripts,6 databases were used for annotation.To obtain annotation information,transcripts were screened against the following databases: NCBI non-redundant protein sequences (nr);KOGs (eukaryotic orthologous groups)[24];Swiss-Prot,a manually annotated and reviewed protein sequence database[25];KEGG Ortholog database (KO)[26];Gene Ontology (GO)[27],and the public database Protein family (Pfam)[28]using basic local alignment search tool (BLAST) software and HMMER software.
2.5 Open-reading frame prediction
TransDecoder v 5.5.0 was used to predict ORF based on: (1)identification of the longest ORF sequence in the transcript;(2) the longest 500 ORF sequences were chosen as training set,and Markov model prediction was conducted;(3) scoring of the possible six-code box based on Markov model.ORF is determined by ORF coding structure with a positive score and higher than other assumed error ORF structure scores.(4) The condition of ORF exclusion is defined as high scoring ORF included in all other different reading frames of long ORF.(5) ORF annotated with Pfam domain or Swiss-Prot data was prioritized.ORF sequences were translated to CDS sequences of amino acids after the process.
2.6 Analysis of the composition of amino acids in CGS meat
Amino acid composition analysis for dried meat floss of CGS was conducted by Beijing Tailian Biotechnology Co.,Ltd[29].
2.7 Longevity gene analysis
137 reported genes related to longevity were collected from 88 rockfish species (Table A.1)[30].Then,we compared the genes in CGS meat based on the results from Swiss-Prot database functional annotation to the 137 longevity genes.
2.8 Functional peptide analysis
Six functional peptide databases were collected including antioxidative peptides,antithrombotic peptides,antihypertension peptides,antidiabetic peptides,antiviral peptides,and antimicrobial peptides[31-35].After that,we analyzed the CDS sequences obtained from the transcriptome to identify the functional peptides which were included in them.We developed a Python script pipeline (Python 3.7)to compare the functional peptides in CDS sequences to databases.
2.9 Detection of DPP IV-inhibiting peptides in vitro
Papain,pepsin,flavor protease,complex protease and trypsin were used to release VPI from CGS meat proteins,which is a DPP-IV inhibitory peptide (IC50=20.2 μmol/L)[22].Among them,pepsin,flavor protease,and complex protease were purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co.,Ltd.,and papain was obtained from Beijing Solarbio Science &Technology Co.,Ltd.The enzymes were used either in pair or alone to hydrolyze CGS meat.20 mL suspension of the meat of CGS (10 mg/mL) was hydrolyzed with 1 mg/mL of each enzyme and incubated in optimal temperature and temperature as listed in Table 1 for 24 h.When the optimal pH and temperature were different for combination of enzymes,the reaction pH was taken as average optimal pH of the pair,and the temperature was taken as the lower temperature in the pair.The products were collected by centrifugation at 10 000 ×gfor 5 min,filtered through 0.2 μm membrane,and analyzed with quadruple time of flight spectrometer to identify VPI.
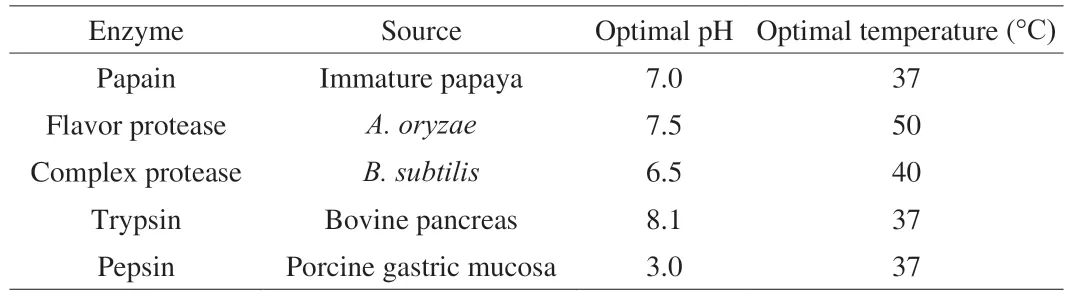
Table 1 Details of enzymes used in this study.
3. Results
3.1 Sequencing of the CGS meat transcriptome using the PacBio Sequel system
To investigate the transcriptome of CGS meat for functional peptides mining,single molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing was used to sequence the CGS meat transcriptome and 11 688 transcripts were obtained.The statistics of transcriptome showed that the mean length of transcripts and GC contents were 2 999.8 bp and 47.1%respectively.The maximum and minimum length of transcripts were 8 888 and 63 bp,respectively,and the maximum and minimum GC content were 23% and 63.2% (Figs.1a and b).Therefore,the transcriptome composition of CGS meat was successfully resolved and can be used as the basis for the gene function analysis and functional peptide mining[36].
3.2 Functional annotation of transcripts of CGS meat
Unique CGS transcripts were annotated using BLAST software[37]through homology searches against different protein and nucleotide databases.A total of 10 103 (86.4%),8 364 (71.6%),9 519 (81.4%),and 6 788 (58.1%) unique transcripts have generated significant hits in the Nr,KOGs,Swiss-Prot,and KEGG databases (Table A.2,Fig.2).Then,the transcripts were further annotated with HMMER 3.1b2[38]using data in the Pfam database[28].8 995 (77.0%) unique transcripts were assigned,1 531 transcripts (13.1%) were not identified,10 157 transcripts (86.9%) were identified in at least one database,and 6 323 transcripts (54.1%) were identified in all databases (Fig.2).The distribution of the top BLAST hits indicates that putative proteins were similar to those of theXenopus tropicalisandChrysemys picta belliiwhich are amphibians (Fig.1c),suggesting that the CGS transcriptome was well-assembled and approximate previous study[39].
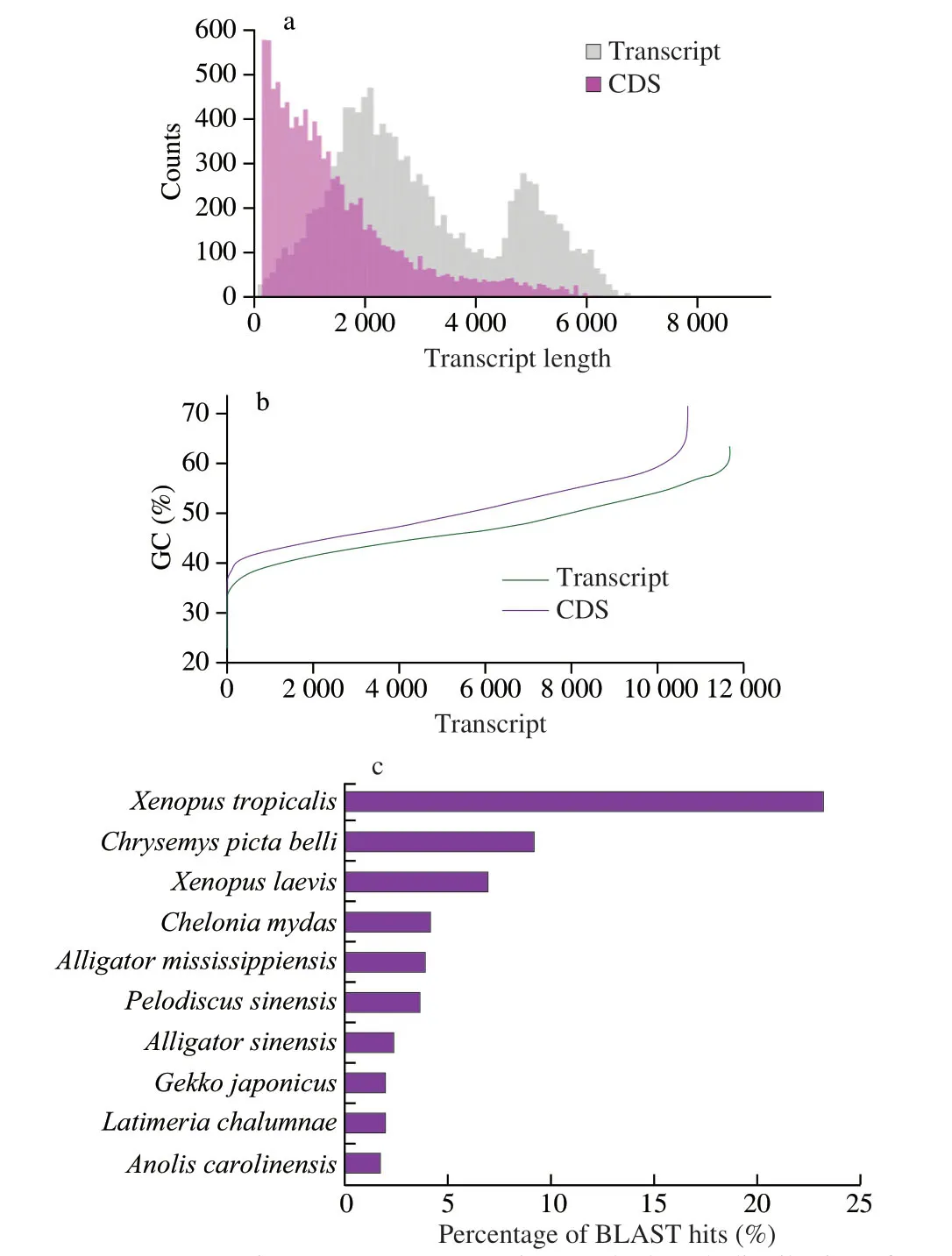
Fig.1 The statistical analysis of transcript.(a) the length distribution of transcript and CDS.(b) the GC content percentage of transcript and CDS.(c) distribution of the top 10 species producing the most BLAST hits for transcripts in the nr database.
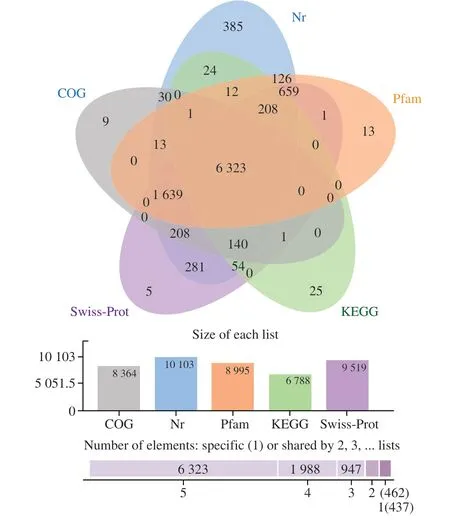
Fig.2 The annotation statistical analysis of transcript.Venn diagram was obtained by analyzing the results of 5 annotation analyses (Upper).The number of transcripts annotated by each database (Middle).Statistics on the number of transcripts simultaneously annotated by multiple databases (Lower).
3.3 Composition of amino acids of CGS meat
The composition of amino acids in the meat of CGS was analyzedin silicoandin vitro(Fig.3).L,S,and R were the most abundant amino acids based on the result obtained from CDS analysis,while R,E and D were the most abundant amino acids found in meat hydrolysate.Comparing the results obtained fromin silicoandin vitroanalysis,the composition of G,K,I,H,and M was similar,while Q,N,and W were not detectable probably due to degradation and conversion of amino acids after acid treatment.

Fig.3 The statistical analysis of amino acid content.(a) the amino acid content distribution was obtained by calculating the percentage of each amino acid in the transcripts.(b) each amino acid content was measured by experiment.
3.4 Prediction of potential CDSs
CDSs were predicted using TransDecoder v 5.5.0[40].A total of 10 703 CDSs were obtained from 11 688 unique transcripts.The length statistics of CDSs showed that the mean length of CDSs was 1 507.8 bp,the mean GC content was 50.1%,and the maximum and minimum length of CDSs was 6 759 and 147 bp respectively (Fig.1a and b).The length distribution of CDSs is an approximately normal distribution which suggests that the result of sequencing was reliable.The acquisition of CDS sequences also laid the foundation for the mining of functional peptides,the CDS sequences library can be used as a reference database for the interpretation of data obtained from liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry,and as a rapid discovery tool for existing functional peptides in the CGS meat protein.
3.5 KEGG analysis
The KEGG metabolic pathway annotation results are shown in Fig.4a.The results reveal that most proteins from CGS proteins are involved in signal transduction,cellular community,and endocrine system.The proteins responsible for signal transduction belong to the category of environmental information processing,which is related to strong environmental adaptability of CGS.For instance,the highest number of proteins are involved in immunity and endocrine system at organismal systems level,which suggests that proteins involved in signal transduction are also involved in perception and regulation.Furthermore,the result also suggests that the blood of CGS exhibits high antimicrobial activity.The rich internal regulatory system can also be a source of longevity,immune,and antioxidant factors in meat.In addition,KEGG metabolic pathway annotation has also found agingrelated proteins,which may be related to the longevity of CGS.
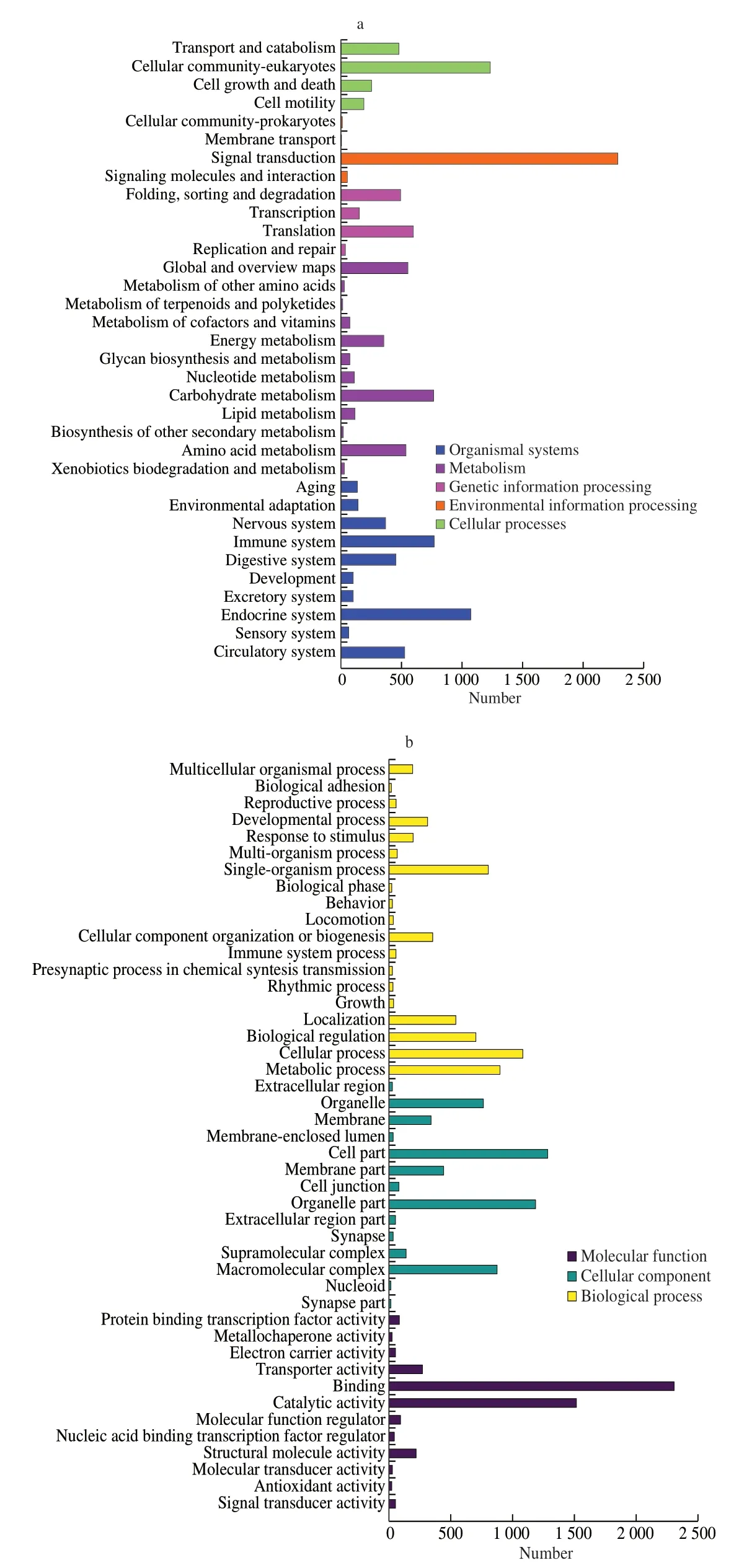
Fig.4 Annotation analysis of CGS meat transcripts.(a) KEGG pathway classification.(b) GO classification.
3.6 GO analysis
To identify the functional distribution of unique genes expressed in CGS meat,a total of 3 270 transcripts were classified into 45 GO term categories in three main classes: biological process,cellular component,and molecular function (Fig.4b).The largest numbers of annotated transcripts were involved in biological processes;among these transcripts,the highest proportion were categorized as “cellular process” (20.5%),“metabolic process” (17.0%),“single-organism process” (15.2%),“biological regulation” (13.2%),and “localization”(10.2%).In the cellular component,transcripts were mainly enriched in the terms “cellular part” (24.6%),“organelle part” (22.7%),and“macromolecular complex” (16.8%).In molecular function,the term“binding” (49.8%) and “catalytic activity” (32.8%) contributed to the majority of transcripts.Besides,we have also observed biopolymers and sequences related to linkage and catalysis in the transcripts,which indicates that the meat of CGS may have antioxidant,longevity,and anti-tumour functions.
3.7 Analysis of eukaryotic orthologous groups (KOGs)
To identify orthologous protein sets and characterize the functional distribution characteristics of the CGS meat transcriptome,a total of 8 364 transcripts were classified into 24 KOG categories(Fig A.1).The percentage of annotated unigenes in “cytoskeleton” (Z)and “signal transduction mechanisms” (T) were the highest categories.However,more than 8 000 cytoskeletal proteins were discovered,which suggests that proteins in CGS meat might possess multiple functions.
3.8 Lifespan gene analysis
CGS is known for its effect in promoting human longevity in ancient Chinese records.Therefore,it is also of our interest to investigate if the meat of CGS contains component which could promote longevity and health span.The function of annotated CGS meat transcripts was analyzed.The lifespan genes were screened,and 16 genes were reported to contribute to longevity (Table A.3).Based on this result,we speculated that these genes are responsible for the CGS’s longevity.These results also demonstrated that our method was feasible by leveraging transcripts to interpret the functional genes.
3.9 Functional peptide analysis
To investigate the richness of functional peptides in the meat of CGS,the existing functional peptides were screened in the CDS sequences obtained.8 142 peptides containing six kinds of functions,including antioxidative,antithrombotic,antihypertensive,antidiabetic,antiviral,and antimicrobial were selected.Then we screened these peptides in the CDS sequence libraries and 1 712 peptides were found to be contained in CDS sequences (Table A.4). Antihypertensive peptides contributed to the greatest fraction of all peptides screened,followed by antioxidative peptides,antidiabetic peptides,antiviral peptides,and antithrombotic peptides.At least 9 antimicrobial peptides were found.
The detection rate of antimicrobial peptides is the lowest (0.3%),while antidiabetic (74.2%),antihypertensive (58.5%),antioxidation(55.8%),and antithrombotic (40.6%) are the 4 types with the highest detection rate.These 4 types of functional peptides are of great significance to human health,therefore,the CGS meat can be used to produce bioactive peptides as functional food components.These results suggested that the CGS meat contains many kinds of functional peptides and can be used as bioactive additives for functional foods.
3.10 Experimental validation of the content of VPI from the estimated meat protein sequence of CGS in vitro
The aforementioned result obtained fromin silicoanalysis was verified with wet-laboratory experiment.VPI was chosen as model because we have found the sequence of VPI existing in 21 proteins from the meat of CGS.In addition,VPI is known to exhibit DPP-IV inhibitory activity,which could help in glycaemic control.Enzymatic hydrolysis of the meat of CGS showed that 170.66 nmol/L VPI tripeptide was produced from 200 mg meat of CGS by papain,while 78.16 nmol/L and 67.30 nmol/L VPI were produced after treatment with the combination of papain+pepsin and papain+trypsin,respectively.Further evaluation of anti-diabetic effect of enzymatic hydrolysate of the meat of CGS is in progress.
4. Discussion
To the best of our knowledge,this article is the first study to investigate the transcriptome of CGS meat using SMRT sequencing and its function by functional annotation.This approach of transcriptomic analysis is more advantageous than genomic analysis for species with limited genomic information,particularly in functional gene mining and regulatory mechanisms[41].Next-generation sequencing method has been used in some studies to investigate the transcriptomes of CGS meat and reported that there are 93 366 and 158 103 transcripts,respectively,with an average length of transcripts of 1 326 bp and 810 bp[16,42].However,our method yields 11 688 transcripts with a mean length of 3 000 bp.There are two potential reasons for the low number of transcripts obtained in our study compared to previous studies.Firstly,we have measured the transcripts of only the meat of CGS compared to multiple tissues,which range from 10– 20 tissues in prior studies.Secondly,splicing processes in next generation sequencing technology might have contributed to a greater number,but shorter transcriptomes.Nevertheless,the transcript sequences obtained by our method has increased significantly,which are 2.27-fold and 3.70-fold higher than prior reports,indicating that this method can counteract the disadvantage of next-generation sequencing and can obtain transcripts precisely.
By annotation analysis,we have interpreted the function of transcripts and found many genes relating to signal transduction and longevity.In addition,we have found 16 genes that were reported to contribute to lifespan[30],which explained the longevity of CGS.On the other hand,in silicoanalysis which we have proposed is more advantageous thanin vitroanalysis conducted.some prior studies have reported a lack of W,Q,and N in the meat of CGS[43].However,these amino acids can be detected based on CDS analysis.By comparing the sum of Q and E,and N and D,equal relative concentrations were observed,suggesting that these amino acids were not undetectable,but converted or degraded into other molecules due to acid treatment,i.e.,degradation of W,and conversion of Q to E,and N to D.
Although various studies have already shown that various tissues from CGS,e.g,skin and mucus exhibit unique nutraceutical functions[1,2],the sources of these functions remained unknown.To demonstrate the potential of CGS meat,1 712 reported functional peptides with functions including antioxidation,antithrombotic,antihypertensive,antidiabetic,antiviral,and antimicrobial were found in CDSs of CGS meat.Among them,the antidiabetic peptides and antioxidation peptides contribute to the majority of peptides,suggesting that CGS meat can be used to improve some chronic diseases,e.g.,type 2 diabetes.
As a proof of concept,we have validated that the method we proposed can be used to guide the mining of functional peptides from the meat of CGS.VPI,a DPP-IV inhibitory peptide[22],which can be used as antidiabetic drug was selected as our model.By optimizing the composition and conditions for enzymatic hydrolysis,we have successfully released VPI from the meat of CGS.After papain hydrolysis,170.66 nmol/L VPI was obtained from the meat of CGS.Considering that the protein content in the meat of CGS is 15.37%[2],the content of VPI in the proteins in CGS was 36.35 μg/g.Considering that most proteins obtained from tissues of CGS range from 10–100 kDa[44],the molar ratio of VPI to proteins was 0.1%–1%.As there were 21 proteins among 10 703 proteins in the meat of CGS containing VPI in their sequence,the fraction of VPI among the CGS meat proteins was covered in the range 0.1%–1%.VPI is a DPP-IV inhibitory peptide,which could help in glycemic control and used as novel class of antidiabetic drugs.Discovery of DPP-IV inhibitory peptides,particularly VPI,and the capability to release it from the meat of CGS,suggested that the meat of CGS might be used as functional food and drug to treat diabetes.
In conclusion,the transcripts and CDSs of CGS meat were parsed by SMRT sequencing.Annotation analysis was performed and 16 genes related to longevity were mined.The potential of CGS meat peptides as functional foods was demonstrated by meat protein enzymolysis to generate DPP IV-inhibitory peptides.This work can contribute to accelerating the functional peptide mining of CGS meat and other tissues.
Conflict of interests
Yi Wang,Chong Zhang and Xinhui Xing are the editorial board members forFood Science and Human Wellnessand was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article.All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Data available
The raw data of sequencing has been submitted to NCBI and the accessible number is SRR17332551.The high-quality (HQ,polished High Quality) sequences file,ORF sequences file,CDS protein sequences file and six kinds of functional peptide databases file can be access at https://github.com/guanchangge/Chinese-Giant-Salamander.
Acknowledgment
This work was funded by Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission (KCXFZ20201221173207022).
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at http://doi.org/10.26599/FSHW.2022.9250014.
杂志排行
食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
- Targeting gut microbiota in osteoporosis: impact of the microbial based functional food ingredients
- Weizmannia coagulans: an ideal probiotic for gut health
- Natural sources,refined extraction,biosynthesis,metabolism,and bioactivities of dietary polymethoxyflavones (PMFs)
- A review of salivary composition changes induced by fasting and its impact on health
- Minerals in edible insects: a review of content and potential for sustainable sourcing
