Ganoderma lucidum: a comprehensive review of phytochemistry,eff icacy,safety and clinical study
2024-02-15SijiWuSiyunZhngBoPengDechoTnMingyueWuJinchoWeiYitoWngHuLuo
Siji Wu,Siyun Zhng,Bo Peng,Decho Tn,Mingyue Wu,Jincho Wei,,Yito Wng,,Hu Luo,b,c,
a Macau Centre for Research and Development in Chinese Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine,Institute of Chinese Medical Sciences, University of Macau, Macao SAR 999078, China
b College of Pharmacy, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China
c Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, China
Keywords: Ganoderma lucidum Phytochemistry Eff icacy Safety Clinical study
ABSTRACT Ganoderma lucidum,one of the most well-known edible fungi,is believed to be very benef icial for longevity and vitality.A long usage history suggests that G.lucidum has various clinical therapeutic effects.And experimental studies have confirmed that G.lucidum has multiple pharmacological effects,including antitumor,anti-microbial,anti-HIV protease,and antidiabetic activity and so on.With the deepening of research,more than 300 compounds have been isolated from G.lucidum.There is an increasing population of G.lucidum-based products,and its international development is expanding.Currently,G.lucidum has drawn much attention to its chemical composition,therapeutic effect,clinical value,and safety.This paper provides a comprehensive review of these aspects to enhance the global promotion of G.lucidum.
1.Introduction
Ganodermalucidumbelongs to basidiomycete,with a woody texture,widely distributed in tropical and temperate regions in Europe,North America,and Asia[1].It is a kind of mushroom for both medicine and food,which has a long history in China,Japan,Korea,and other Asian countries.It has a common custom name in different countries,such as Lingzhi in China,Reishi in Japan,Youngzhi in Korea,and Linh chi in Vietnam.G.lucidumhas been used medicinally in China for more than 2 000 years.And it was f irst described its medicinal value inShen Nong Ben Cao Jing,the earliest pharmacopeia in China,written in the Eastern Han dynasty of China(25-220 AD).Chinese Pharmacopoeia recorded that it has the effects of invigorating qi and tranquilizing spirit (补气安神),relieving cough and asthma (止咳平喘),and can be used for restlessness,insomnia,palpitations,lung deficiency,cough and asthma,consumption and shortness of breath,and loss of appetite[2].However,the medicinal value ofG.lucidumwas unknown to Western civilization until the 20thcentury[3].G.lucidum,which is considered to be one of the most famous medicinal fungi in the world,is believed to be useful for prolonging longevity and maintaining vitality,and its industry value is estimated to be more than 2.5 billion U.S.dollars[4].
Modern scientific research and clinical trials have confirmed the ancient knowledge ofG.lucidumin Asian countries and provided a scientific basis.Modern research shows thatG.lucidumcontains polysaccharides,triterpenoids,steroids,sterols,nucleotides,fatty acids,and other active substances[5-6].Among them,polysaccharides and triterpenoids have been thoroughly investigated and widely regarded as the main bioactive components ofG.lucidum.A large number of studies have conf irmed thatG.lucidumhas a wide range of pharmacological effects,such as anti-tumor[7-8],immunomodulation[9-10],antioxidants[11-12],antimicrobial[13-14],anti-diabetes[15-16],cardioprotective[11,17],anti-inflammatory[18-19],anti-androgenic[20],antimutagenic[21],neuroprotective[12],and other pharmacological effects.
Recently,G.lucidumhas become one of the most studied and product-developed medicinal fungi because of its numerous bioactive substances and extensive pharmacological effects.In the following review,we discuss the recent research status ofG.lucidumin its chemistry and quality control,bioactivity and its mechanism,preclinical and clinical studies,safety,toxicity,and side effects evaluation.
2.Chemical constituents and quality control methods
According to the literature,there are many varieties ofGanoderma,includingG.lucidum(Curtis) P.Karst.,Ganoderma amboinase(Lam.) Pat.,G.applanatum(Pers.) Pat.,G.tsugaeMurrill,G.atrum,G.pfeifferiBres.,G.sinenseZhao,Xu et Zhang and so on.Among them,only two species,namelyG.lucidum(Curtis) P.Karst.andG.sinenseZhao,Xu et Zhang are recorded in thePharmacopoeia of the People’sRepublic of China2005-2020 edition under the heading ofGanoderma[22].G.lucidumas discussed in previous studies,has a wide variety of compounds,including triterpenoids,steroids,polysaccharides,fatty acids,amino acids,nucleosides,proteins,alkaloids and inorganic elements[22-23].And triterpenoids and polysaccharides are the main compounds because of their high content,diverse structures,and significant bioactivities[24].So far,more than 300 compounds have been isolated from the fruit body,mycelia,and spore ofG.lucidum.The nonvolatile component analysis onG.lucidumshowed that it is composed of several elements,including ash 0.72%-1.77%,carbohydrate 21.83%-27.78%,fat 1.1%-8.3%,fiber 59%-65%,protein 7%-8%[25],etc.Different extraction and analytical methods have been selected by the physical and chemical properties of complicated compounds.Herein,various compounds and quality control methods ofG.lucidumwere summarized respectively in Tables 1-16.
2.1 Chemical constituents
2.1.1 Triterpenoids
Triterpenoids,as a kind of chemical substance prevalent in nature,are also the pharmacologically active components ofG.lucidum.The fruit body and mycelium ofG.lucidumcontain different types and contents of triterpenoids[26].The structure of triterpenoid is derived from lanosterol,whose skeleton is a tetracyclic structure composed of C30H54.Most triterpenoids inG.lucidumexhibit highly oxidized characteristics[27].According to the different functional groups,triterpenoids can be divided into acid,alcohol,ketone,ester,aldehyde,and other types,and their multifarious substituent types in different positions result in a large number of triterpenoids.Over 260 triterpenoids have been identified from the fruit body,spore,and mycelia ofG.lucidum.
Most triterpenoid skeletons inG.lucidumhave 27 or 30 carbon atoms,but only a few possess 24 carbon atoms[28],changing mostly on the substituent of C-17.A typical triterpenoid carbon skeleton marking with 30 carbon atom numbers inG.lucidumhas shown in Fig.1.The skeletal types ofGanodermatriterpenoids inG.lucidumare also present in Fig.1,which are classified by carbon-carbon double bond position in rings and side chain substituent situations.Moreover,reported compounds with different substituents and formulas are shown in Tables 1-11.Skeleton 1 corresponding to compounds 1-53 has not only a double bond between C-8 and C-9 but also a carbonyl group at C-23.And different substituents appear at C-3,7,11,12,15,20,and 27.The substituents at the C-3 position includeβ-hydroxy,carbonyl group,andβ-acetoxy group.There are two main substituents on C-7,C-11,and C-15,namely carbonyl and different configurations of hydroxyl group.In the C-11 position,all of these compounds possess a carbonyl group,except ganoderic acid Df[29]possesses aβ-hydroxy substituent.In C-12,complex substituents appear in this position,such asβ-acetoxy,acetoxy,β-hydroxy,α-hydroxy,hydroxy group,and a hydrogen atom.There are two substituents attached to the same carbon in C-20,mainly methyl groups of different configurations and hydrogen atoms or hydroxyl groups.The carboxyl,formyl,acetyl,or butyryl moieties are all common substituents at C-25,which are the most common in the carboxyl group.
Different from the previous compounds in Table 1,compounds 54-92 corresponding to the skeleton 2 have two double bonds between C-8/9 and C-24/25.In addition,the substituents on C-3 and C-26 affect proliferation inhibitory activity,where the carbonyl group at C-3 is essential to inhibit cell proliferation.And the methyl group at C-26 enhances cell membrane permeability[30].All of the compounds 93-107 (Skeleton 3) have double bonds between C-8/9 and C-20/22 respectively,while their carbonyl groups at C-11 and C-23.Meanwhile,the skeleton 4 corresponding to compounds 108-115 has a double bond between C-8 and C-9 and a hydroxyl group at C-25,where lucidumol A has good inhibitory activity onα-glucosidase.And the hydroxyl group of C-3 may be an active functional group[31].Furthermore,compounds 116-121 corresponding to skeleton 5 share almost the same structure as skeleton 3,except for the double bond between C-16 and C-17 and the new substituent on C-28.The carbon number on the right-side branch of skeletons 6 and 7 is less than that of the previous skeleton,while the right-side branch of skeleton 8 has only an acetoxy group.Of all that skeleton with double bonds between C-8 and C-9,the carboxylic group in the side chain is also essential for recognizing aldose reductase inhibitory activity.Hydroxyl groups at C-3 and C-11,double bond moiety at C-20/C-22 and C-24/C-25 in the side chain are contributed to the promotion of aldose reductase inhibitory activity as well[32].Then,unlike the previous skeletons 1-7,skeletons 9 and 10 corresponding to compounds 179-234 have two double bonds between C-7/8 and C-9/11,respectively.The substituent at C-3 is a key group for various pharmacological activities and is essential for cytotoxicity[33].The inhibitory activity of sulfatase (STR) is affected by the two positions at C-3 and C-26,with ganodermenonol showing a good inhibitory effect[34]and the inhibition of 5αreductase activity is probably caused by the C-3-carbonyl and C-26-α,β-unsaturated carbonyl groups,among which ganoderic acid TR exhibited the best inhibitory activity[35].In addition,compounds 235-266 are difficult to be classified on the skeleton,so all their structures are drawn in Fig.2 and their chemical names and formulas are listed in Table 11.
2.1.2 Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are polymeric carbohydrate molecules composed of long chains of at least ten monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages.In most of the previous research,polysaccharides have been extracted from theG.lucidumfruit body,spores,mycelia,and cultivation broth[22].The structural characterization of polysaccharides isolated fromG.lucidumis listed in Table 12.The molecular weights of polysaccharides from different parts ofG.lucidumhave clear differences.The molecular weight of polysaccharides from the fruit body is between 103and 106Da[36],while that of polysaccharides from spores and mycelia is about 105-106Da.The glucans exhibit complexity in polysaccharides.Glycosidic bonds of the main chain are composed of one single type or a mixture ofα-(1→3) glucan,α-(1→6) glucan,mannan,and galactosan,withα,β-glucans or other linkages[37].Besides that,sugar components of polysaccharides inG.lucidumare glucose,mannose,rhamnose,and galactose.
2.1.3 Steroids
Steroids are also common compounds inG.lucidum,of which ergosterols and their derivatives account for the majority.Steroids usually have a variable number of double bonds,located in different positions on the similar ring system with Fig.1,including double bonds between C-7 and C-8,C-22 and C-23,C-4 and C-5.There are 27 different steroids and steroidal esters isolated fromG.lucidum,which are summarized and presented in Table 13.
2.1.4 Others
As a member of Chinese medicinal materials,there are many other types of ingredients inG.lucidum,such as meroterpenoids,alkaloids and nucleosides,which contain approximately more than 10 compounds in each category.Meroterpenoids are hybrid natural products that partially originate from the terpenoid pathway.Meroterpenoid is composed of a 1,2,4-trisubstituted phenyl group and a polyunsaturated terpenoid part.The diversity of the terpene moiety may be formed through oxidation,cyclization,isomerization,polymerization,etc[38].Up to now,no more than 10 alkaloids have been obtained inG.lucidum,which include polycyclic alkaloids,purine,pyrimidine,and cerebrosides.The chemical names,structural formulas,references and other information of all other types of ingredients are listed in Table 14.
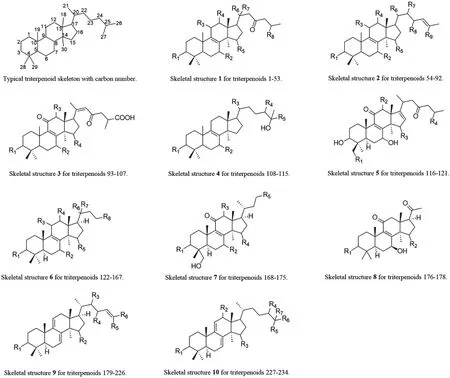
Fig.1 A typical triterpenoid skeleton and skeletal structure 1-10 for triterpenoids 1-234.
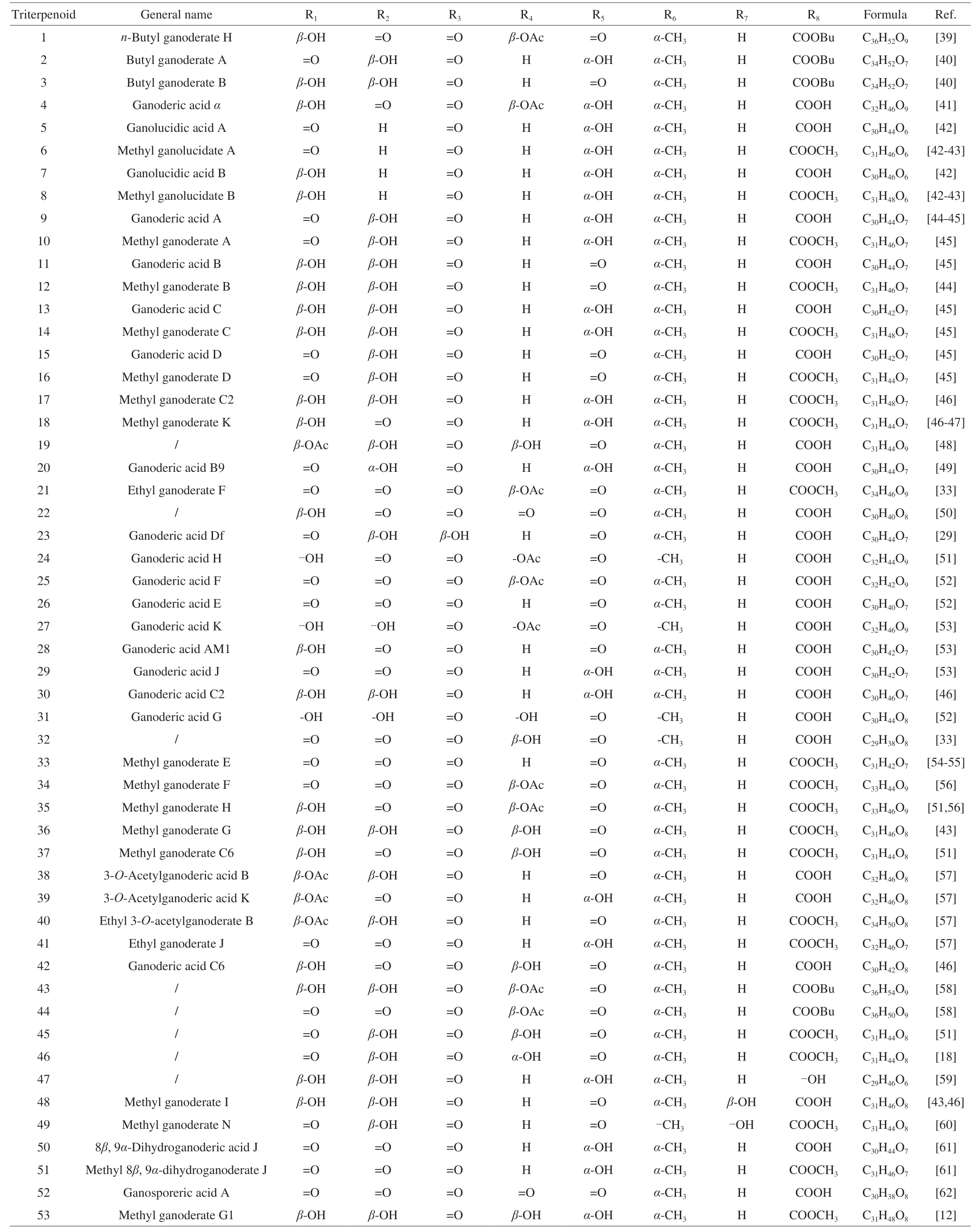
Table 1 G.lucidum triterpenoids 1-53 with skeletal structure 1.
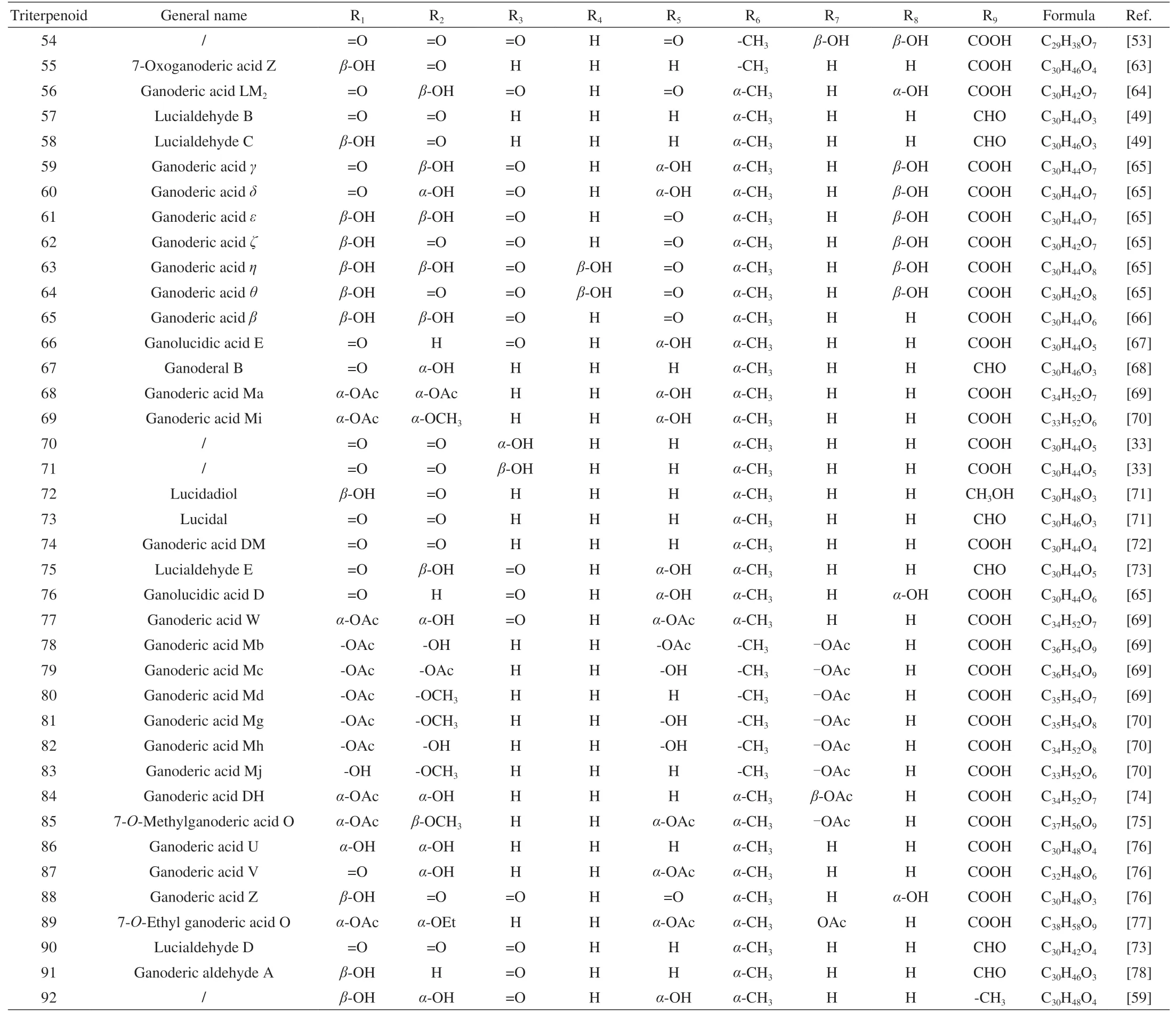
Table 2 G.lucidum triterpenoids 54-92 with skeletal structure 2.
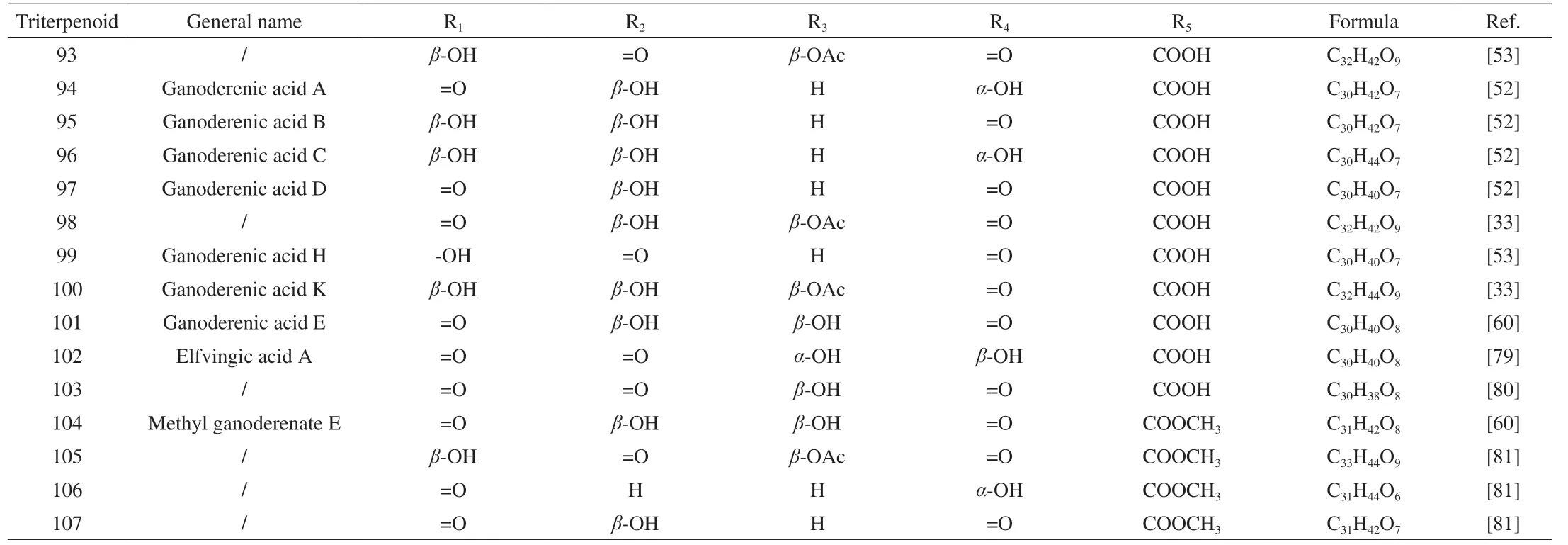
Table 3 G.lucidum triterpenoids 93-107 with skeletal structure 3.
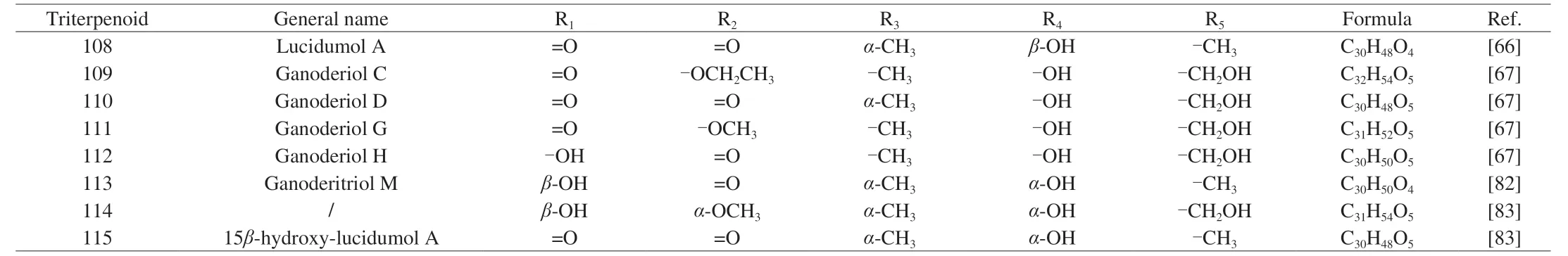
Table 4 G.lucidum triterpenoids 108-115 with skeletal structure 4.
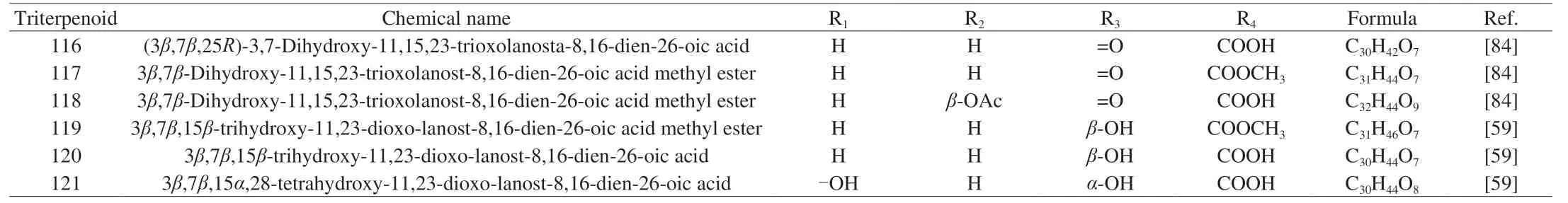
Table 5 G.lucidum triterpenoids 116-121 with skeletal structure 5.

Table 7 G.lucidum triterpenoids 168-175 with skeletal structure 7.

Table 8 G.lucidum triterpenoids 176-178 with skeletal structure 8.
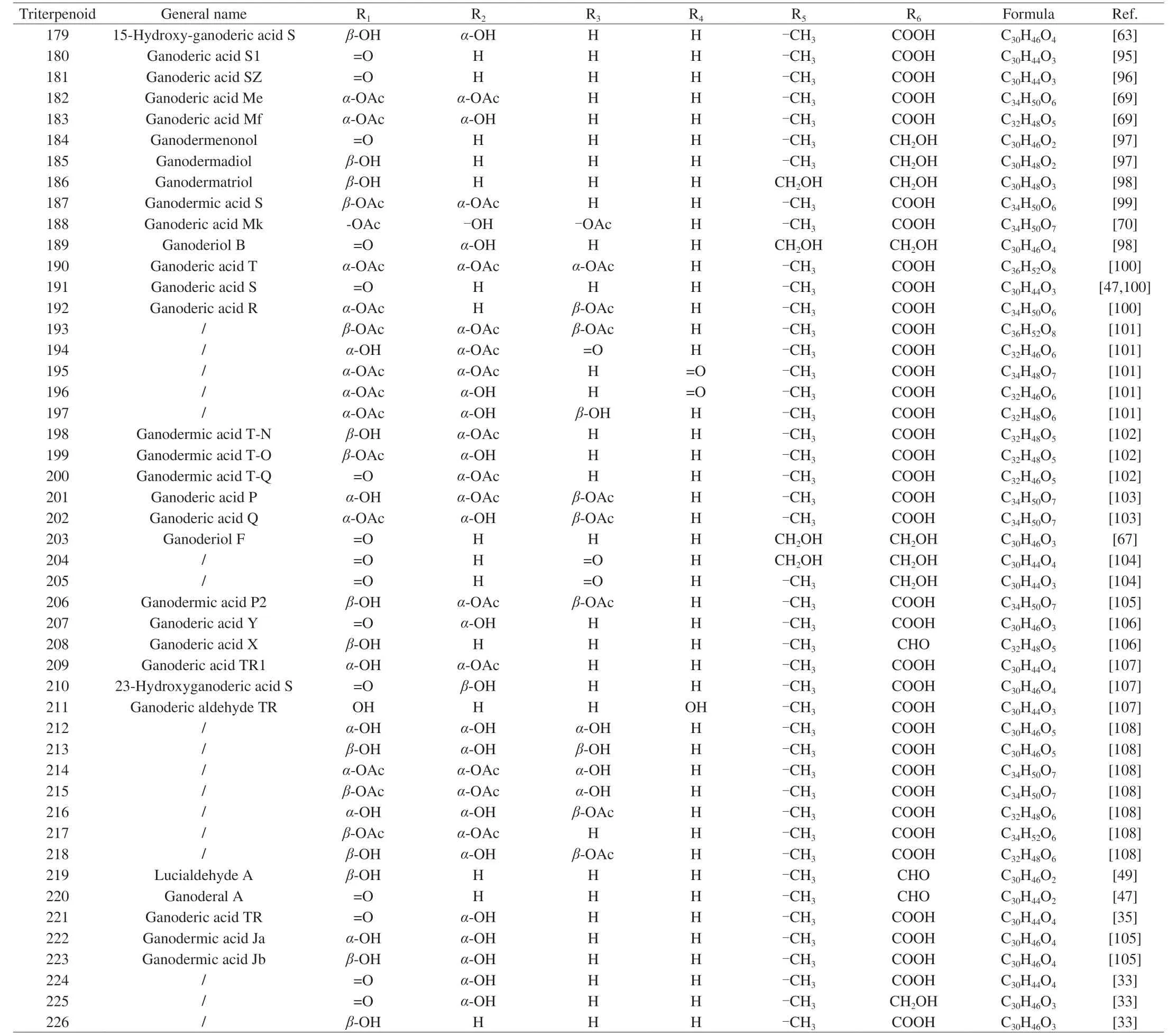
Table 9 G.lucidum triterpenoids 179-226 with skeletal structure 9.
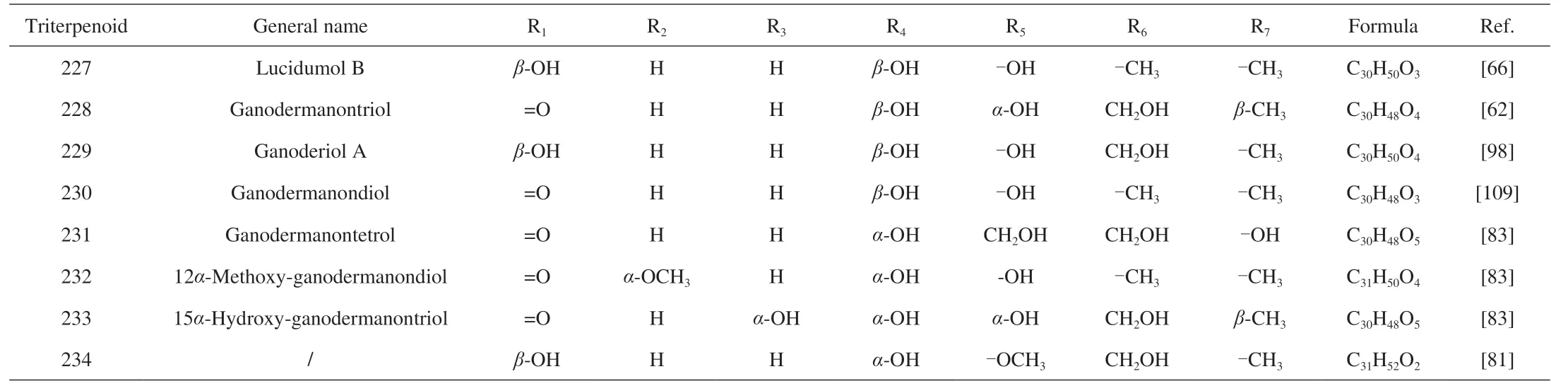
Table 10 G.lucidum triterpenoids 227-234 with skeletal structure 10.

Table 11 G.lucidum triterpenoids 235-266.

Fig.2 Structure of triterpenoids 235-266.
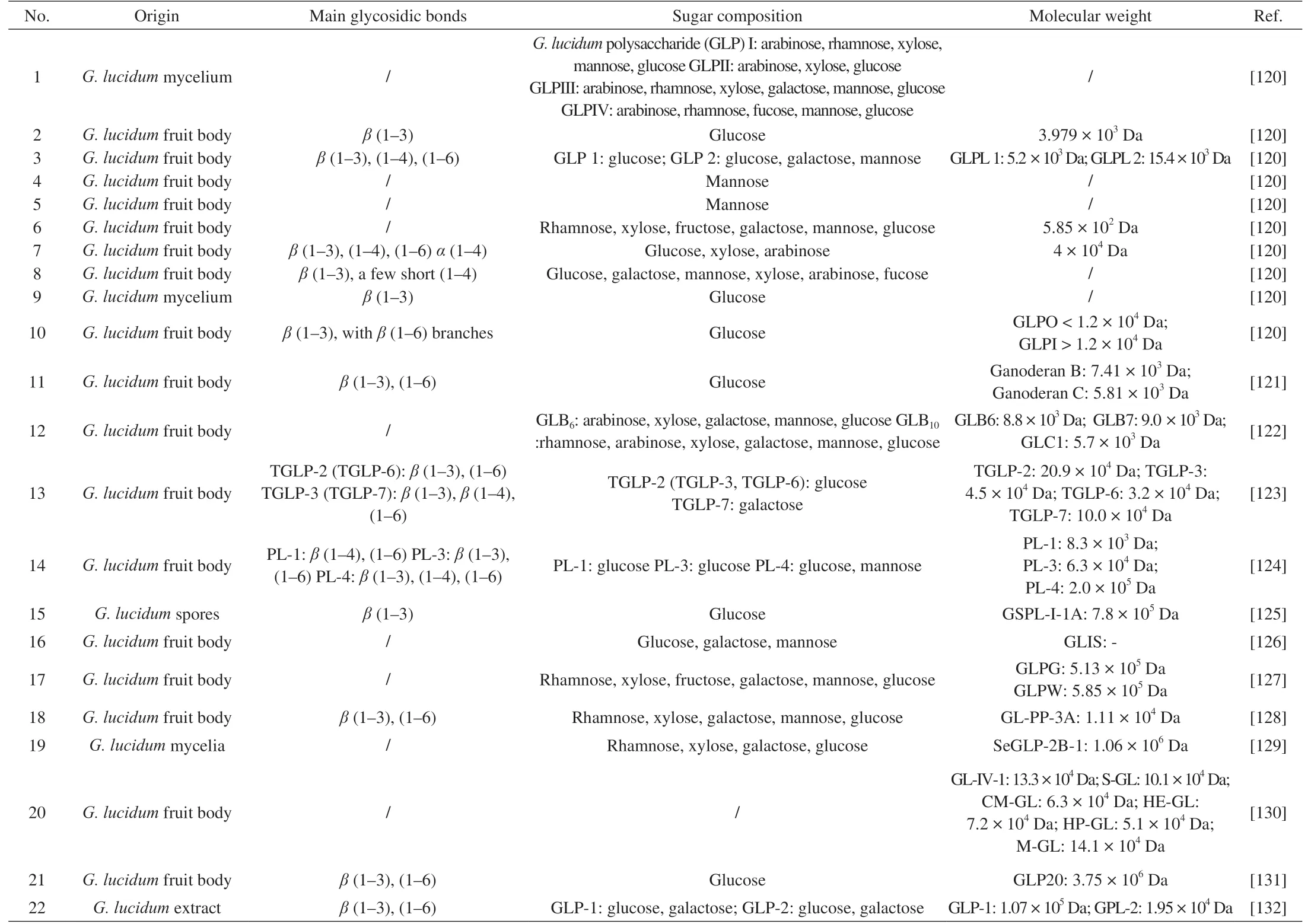
Table 12 Polysaccharide isolated from G.lucidum.

Table 13 Steroids in G.lucidum.

Table 14 Other compounds in G.lucidum.
2.2 Quality control methods
2.2.1 Small molecular substances in G.lucidum
As mentioned before,the small molecule compounds inG.lucidumare composed of triterpenes,nucleosides,alkaloids,and sterols,as well as some other types of molecules.Among them,triterpenoids are a class of important biologically active ingredients,which have strong physiological activities,such as anti-inflammatory[149-150],anti-tumor[24],protecting liver[151]and gallbladder[152],cytotoxic[33],α-glucosidase inhibitory[153],anti-malaria[154],lowering cholesterol[155],lowering blood fat[156],lowering blood sugar[15],etc.Therefore,there are relatively more studies on the quality control of triterpenoids inG.lucidumat present.Moreover,some reports focus on polar compounds such as nucleosides and nucleobases,which can participate in the regulation of various physiological processes,such as inhibiting platelet aggregation[157]and reducing memory deterioration in old senescence-accelerated mice[158].Most of the classical methods of quality control research in the past 15 years onG.lucidumsmall molecule substances are listed in Table 15,and the corresponding extraction and analytical methods are also summarized.
In general,the small molecules inG.lucidumare extracted by organic solvents or water,and the extraction solvent is selected by the requirement of polarity.Methanol[159-162],chloroform[162-166],ethanol[167-169],95% ethanol[170-173]or acetonitrile/water[174]are favored by most researchers when extracting triterpenoids,while water extraction[168,175]is the most common method for extracting nucleosides.In addition,researchers often use ultrasonic extraction[160,162,164-166,172-173,175],heating extraction[170,173,176],reflux extraction[159,163,173],shaking[169,171],vortexing[176]and other methods such as accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) system[161]to improve the extraction efficiency.After extraction,researchers would often use silica gel column chromatography or preparative high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to further purify the isolated triterpene fractions due to the insufficient sensitivity of instrument[22].
With the rise of fingerprints in the field of quality control of traditional Chinese medicine and the renewal of analytical instruments,researchers are more inclined to directly analyze the extracts of herbs through instruments.Many previous studies[159-161,163-168,170-178],as shown in Table 15,have also focused on the quantitative measurement of the chemical composition ofGanoderma,to distinguishG.lucidumfrom different species or origins and to control the quality of herb of the same batch.And in terms of the instruments employed in the research,ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy(UV-Vis),HPLC,infrared spectroscopy (IR) and Raman spectra,near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy,gas chromatography (GC),ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) and high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) are the popular ones.Abundant detectors have also provided favorable conditions for the detection of different types of compounds,such as ultraviolet detector/ultraviolet-visible detector (UV/UVD),mass spectrometry (MS),multilevel mass spectrometry (MSn),etc.These instruments have their advantages and disadvantages.Among them,ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry is an analytical method that has been utilized extensively for decades,which has the advantages of low analysis cost and wide applicable concentration range.For the quality control ofGanodermain the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia,the total contents of triterpenoids and sterols were measured by ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry[179].The authenticity ofG.lucidumspore powder samples can be identified by NIR spectroscopy,and its adulteration content can be predicted[180].LC-MS can also achieve high sensitivity,improve the analysis efficiency and obtain specific compound information.This method has been used by the United States Pharmacopoeia to specify the retention time of specific ganoderic acid,ganoderic acid and monosaccharide,such as ganoderic acid A,B,C,D and ganoderenic acid B,C,D and mannose,galactose[181]and etc.Zhang et al.[162]combined the HPLC-MS analysis of theGanodermaextract with the pharmacological activity research on three cancer cells and found that 6 compounds for example 12-acetoxyganoderic acid F and ganoderic acid A had significant anti-proliferative activities.Compare with LC-MS,GC-MS has higher separation efficiency for sterols analysis than LC-MS,and exhibits high sensitivity,high accuracy and high interference removal ability,which are very suitable for quantifying several steroid compounds simultaneously[182].Moreover,the sterol chromatogram combined with pattern recognition analysis,such as hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA) and discriminant analysis (DA),could distinguishGanodermafrom different species and regions[170].IR and Raman spectroscopy could overcome the shortcomings of the large number of organic solvents required for LC with a simplified sample preparation process.HPTLC method also uses less solvent and reduced the time for analysis and sample preparation[169].The result of fingerprinting is a complex and broad data matrix,which is characterized by a large number of variables[159].Principal component analysis (PCA)[159,166,168,172,177],partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA)[159,162],HCA[159,170-171,174-175],DA[170-171,177],soft independent modeling of class analogy (SIMCA)[159]and cluster analysis (CA)[166,172-173]have been regarded as the feasible data analysis methods in massive and complex data.Among them,PCA and CA mainly focus on the features that contribute most to the variance by highlighting the high or low regulatory levels of certain metabolites.And HCA,DA and SIMCA could be used to distinguish or predict different samples[183].Furthermore,PLS-DA can quantitatively predict the target component in the mixture through a large amount of data.
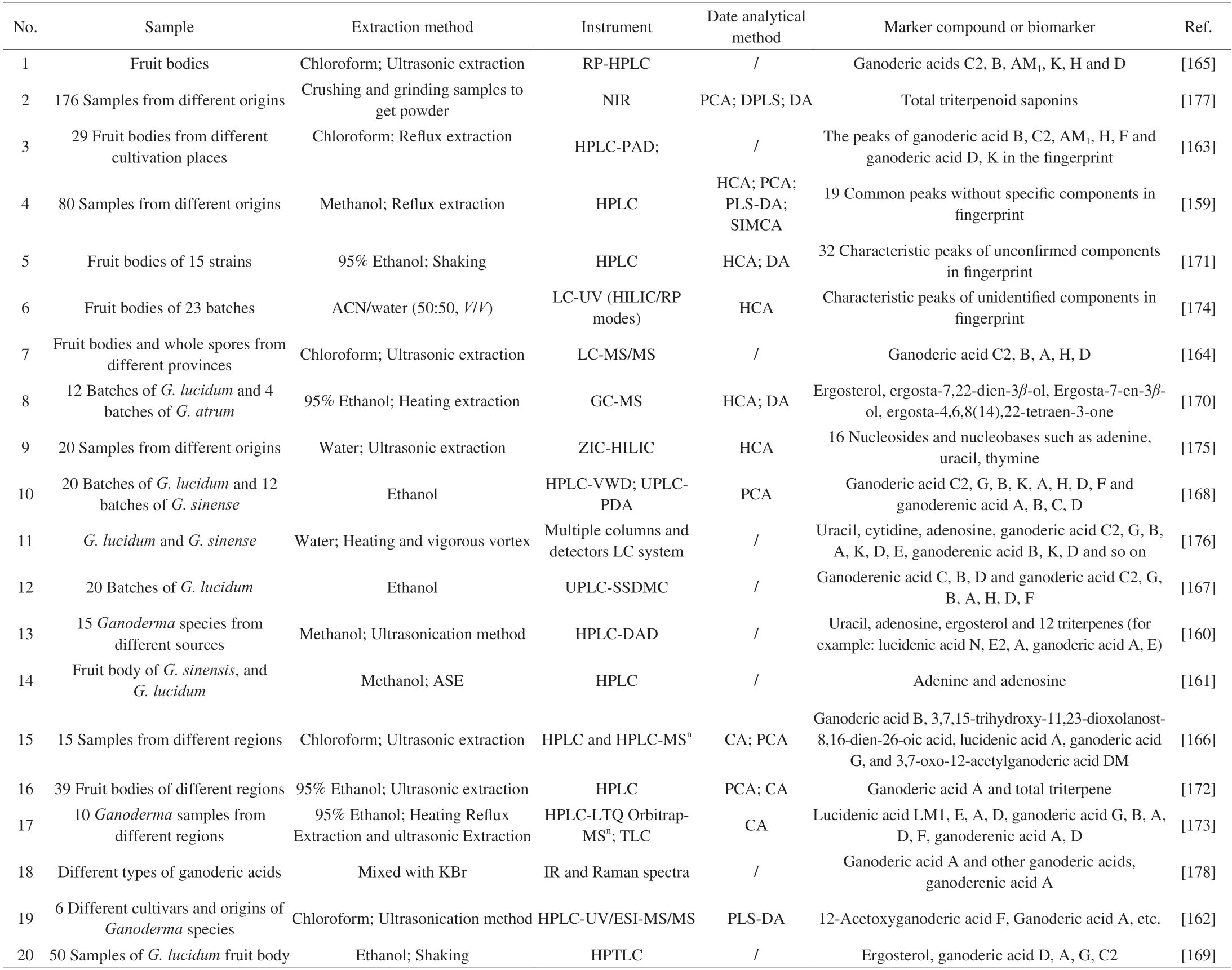
Table 15 Small molecule marker compounds in G.lucidum.
2.2.2 Macromolecular substances in G.lucidum
The macromolecular compounds inG.lucidumare mainly carbohydrates,including glycoproteins and polysaccharides[184],in which polysaccharides represent one of the most abundant components inG.lucidum[37].Since Miyazaki et al.[185]reported that a branched arabinoxyloglucan isolated fromG.lucidumfruit body possesses the anti-tumor effect,researchers have become more interested in polysaccharides with more studies only their chemical structure and activity.Therefore,the quality control of polysaccharides inG.lucidumhas become an important criterion of its quality.
The extraction methods of GLP mainly include hot water extraction,salt solution extraction,alkaline solution extraction and so on.Water extraction conforms to the traditional Chinese medicine decoction principle and is the most common basic extraction method.And the salt solution can remove the influence of protein by 0.9% sodium chloride[186].Water-insoluble polysaccharide could also be obtained by alkaline solution extraction,which needs to be combined with sulfate modification polysaccharide method[187].Since GLP are also insoluble in alcohol,the isolation method normally involves water extraction and alcohol precipitation[37].In addition,ultrasonic[188]and microwave-assisted extraction[189-191]are also new methods for isolating GLP.The commonly used method of purifying polysaccharides is column chromatography,including anion exchange column chromatography[124,188-189],gel permeation chromatography[124,188]and affinity chromatography.In the meantime,researchers use fermentation methods to purify polysaccharides,such as fermented soybean curd residue[192].
Different from the analysis of small molecular compounds with single type of analysis method,GLP requires the combination of multiple analysis methods to characterize the various information of it clearly.Research on the structure of GLP mainly includes the range of molecular weight,monosaccharide composition,glycosidic bond types,repeating units,etc.The main methods for analyzing the monosaccharides composition of polysaccharides include GC[124,187,189,193-196],LC[194-195,197-200]and high-performance anion-exchange chromatography (HPAEC)[201].High-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC)[202],carbohydrate gel electrophoresis (PACE)[203],and HPSECELSD[124,187,189,193,204]methods are also used to detect polysaccharides.After the sample be processed by acid hydrolysis,the glycosidic bond of the polysaccharide is cleaved,so that the monosaccharide composition can be conveniently detected by the GC and GC-MS method.In addition,GC-MS combined with methylation treatment can help determine the connection mode of sugar residues in polysaccharides,and periodic acid oxidation and Smith degradation can determine the type of glycosidic bonds[205].Furthermore,by derivatizing the sample with 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP),the monosaccharide molecules are given ultraviolet or fluorescent absorbing groups to determine the composition of monosaccharides by HPLC[206].As one of the factors affecting the biological activity of polysaccharides,molecular weight is mainly detected by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and gel permeation chromatography(GPC)[187].Some researchers have utilized matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry to test molecular weight[207].The connection mode of glycosidic bonds can be analyzed by infrared spectroscopy,and NMR technology can help analyze the anomeric configuration,the connection mode of glycosidic bonds,the connection sequence of sugar residues,etc.The different techniques for determining the relevant information of polysaccharides are listed in Table 16,and the different pre-treatment methods required are also listed.
The activity ofGanodermapolysaccharide has been reported many times,andGanodermapolysaccharide has been included in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia as a quality control marker[179].Many researchers have studied the fingerprint of triterpenoids and polysaccharides fromGanodermaand judged the total content of the composite components at the same time,in order to distinguishGanodermaspecies from different origins and different growth conditions.At present,the research on quality control ofG.lucidumpolysaccharide is mainly about the monosaccharide or oligosaccharide composition of polysaccharide hydrolysate by acid hydrolysis combined with instrument detection,based on whichG.lucidumin different regions could be distinguished.For instance,Zhao et al.[212]discriminatedG.lucidumorigins by HILIC-ELSD/ESI-TOF/MS combined with acid hydrolysis,and polysaccharides andD-galactose could be considered as promising quality control markers.The fingerprinting method of HPTLC can distinguish the polysaccharides ofG.applanatumandG.lucidum.However,forG.lucidum,G.nigrolucidumand different parts (fruit bodies and spores) ofGanoderma,the difference in their fingerprints are not very obvious,and the differences between the samples could hardly be detected[202].In addition to monosaccharide composition analysis,molecular weight and conformation also affect the activityof GLP.Li et al.[132]found that the structural features of GLP are related to immunoregulatory activity.The polysaccharides degraded by ultrasound exhibited higher lipid-lowering and antioxidant activities than natural polysaccharides[207].In recent years,with the advancement of analytical technology,breakthroughs have also been made in data processing methods.Multivariate statistical analysis is an analytical method suitable for quality control of Chinese herbal medicines,including PCA,hierarchical cluster analysis and(orthogonal) projection-to-latent-structure discrimination analysis((O)PLS-DA)[212].Among them,the PCA and OPLS-DA methods are the most popular in traditional Chinese medicine fingerprint.Both the PLS-DA and OPLS-DA methods each have their advantages and disadvantages so the selection method should be based on the specific data situation[213].

Table 16 Analytical method of polysaccharides in G.lucidum.
At present,most of the studies have focused on the chemical composition alone or the efficacy of the polysaccharides.And no consensus has been reached on the structure-activity relationship through the research on GLP.Further,studies on the activity of GLP and the summary of its chemical structure similarities require the future efforts of researchers.
3.Bioactivity and its mechanism
3.1 Anti-tumor effect
Numerous laboratory researchers and preclinical trials have shown thatG.lucidumhas extensive anticancer activity.It was reported thatG.lucidumcould induce cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis[214],inhibit angiogenesis,invasion and metastasis,and tumor growth to exert its anticancer activityin vitroandin vivo[215-216].And there are accumulating evidence implicating thatG.lucidumalso exerts anticancer action by affecting autophagy[217-222],immune function[223-229],chemotherapy,and radiotherapy sensitivity[230-236].
G.lucidumextract,which contains 6% triterpenes and 13.5%polysaccharides,inhibited the proliferation of ovarian cancer HOCC cells by up-regulating Cx43 expression and down-regulating the expression of VEGF[237].GLP and enzymatically hydrolyzedG.lucidumpolysaccharide (EGLP) induced apoptosis in U14 cells and suppressed tumor growth in U14 cervical tumor-bearing mice,in which the anticancer activity of EGLP is better than GLP.Moreover,EGLP exerted anticancer activity by regulating the apoptotic process,decreasing the expression of Bcl-2 and COX-2,and increasing the expression of Bax and cleaved caspase-3[238].Anti-angiogenesis ofG.lucidumshowed as the viability of HUVEC or the formation of HUVEC capillary tubes was inhibitedin vitro[239-240],and decreased the expression of VEGF and bFGF or microvessel density of tumorin vivo[241].G.luciduminhibited breast cancer migration and invasion by regulating the Rac/Lamellipodin pathway[242]and suppressed breastto-lung cancer metastases[243].
The extracts ofG.lucidumfruiting body (GLE) induced HCT116 cell cycle arrested in G0/G1 correlated tightly with the decreasing gene expression of E2F-1,CDK2,CDK4,CDK6,Cyclin A2,Cyclin B1,Cyclin E1 and increasing expression of P21[222].Apoptosis was induced after GLE treatment via decreasing the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax and increasing cleaved caspase-3 and poly ADP-ribose polymerase protein expression[222].An increase in HCT116 cell autophagy was observed with the treatment of GLE,which was induced by regulating the related protein expression in the mTOR pathway[222].Consistently,the antitumor effect ofG.lucidumis regulated by caspase-dependent apoptosis[221,244-246]and inducing initiation of autophagy[217,221]was proved in other studies.Sporoderm-broken spores ofG.lucidumwater extract (BSGLWE) was studied to show that it disrupted cell cycle progression and induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer HCT116 cells[244].Moreover,BSGLWE suppressed tumor growthin vivoby regulating the expression of genes and proteins associated with the cell cycle and apoptosis (Fig.3)[244].G.lucidumexerts its anticancer activity for inhibiting proliferation and inducing cell death via caspase-dependent and cyclin-CDK2 pathways and regulating mTORC1/2-mediated signaling pathways by activating AMPK and inhibiting IGFR/PI3K/Rheb (Fig.3)[247].Water extract fromG.lucidumalso induced mitochondriamediated apoptosis,arrested the cell cycle at the S phase via the cyclin-CDK2 pathway,and inhibited cell migration associated with EMT in glioblastoma cells GBM8901 and U87 (Fig.3)[248].G.lucidumspore oil (GLSO) induced apoptosisin vitroandin vivovia the caspase pathway (Fig.3)[249].
The clerk comforted them as best he could; he also was greatly distressed13 that Peter should have behaved in such a way just when he should have gained honour from his pupil
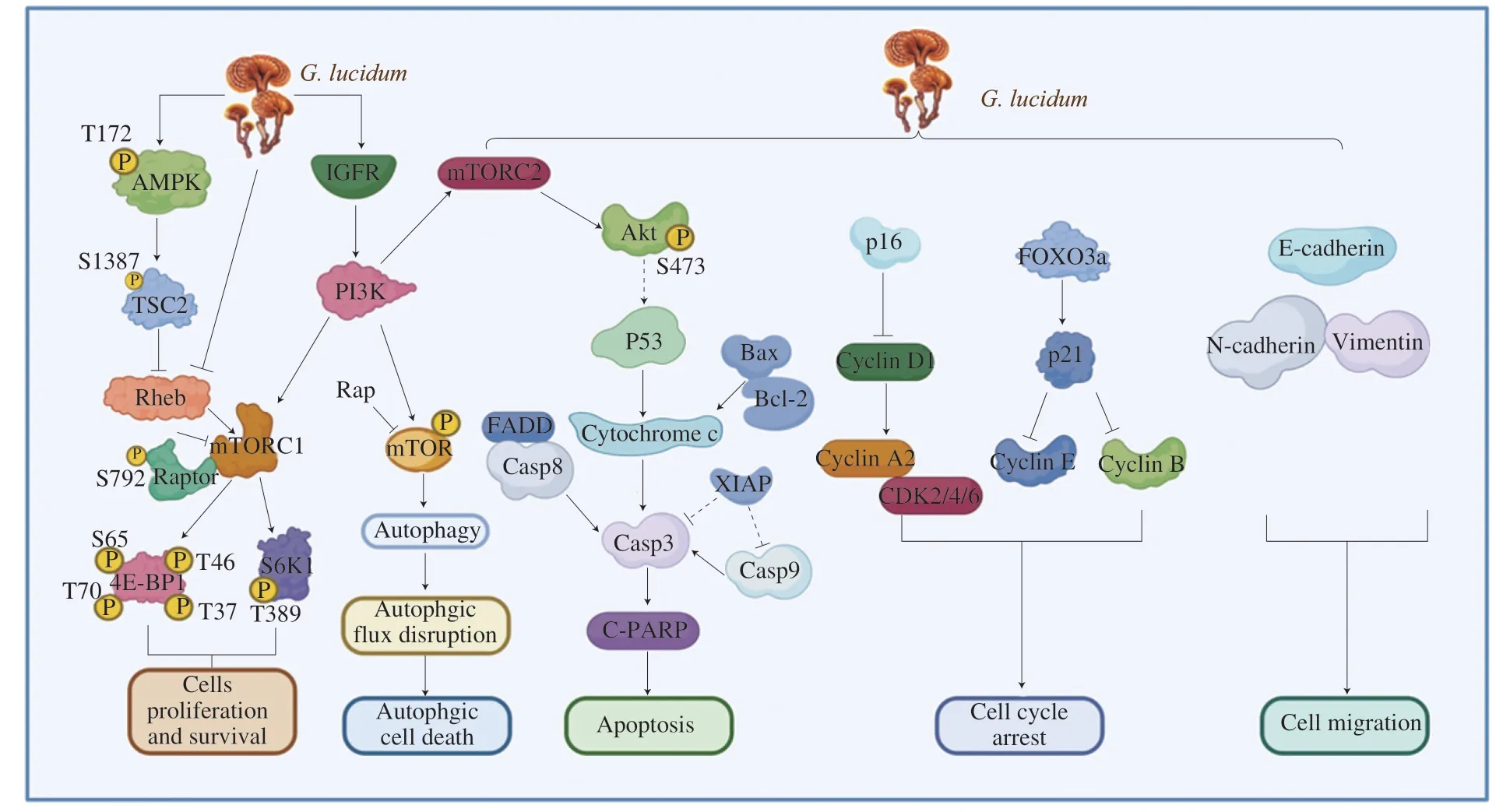
Fig.3 Anti-tumor mechanisms of G.lucidum.
Autophagy affected byG.lucidumin vitroandin vivo,which was increased autophagosome accumulation and blocked autophagic flux[217,221,250].Moreover,autophagosome accumulation is responsible for apoptosis in colorectal cancer,which is mediated via MAPK/ERK activation[217].Ganoderic acid D,a representative active triterpenoid fromG.lucidum,would inhibit cell proliferation,cycle arrested,induce apoptosis and autophagic cell death to exert its anticancer effect,which through the mTOR pathway to lead the synergistic effect on apoptosis and autophagic cell death in the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells[250].However,cell cycle arrest for antitumor activity ofG.lucidumnot only arrested in G0/G1 phase[218-219,222,247]but also arrested in the G2/M phase[221,244,250],S phase[248]and subG1 phase[245].GLP conjugated with bismuth sulfide nanoparticles (GLP-BiNP) increased the sensitivity of radiotherapy to inhibit invasion,metastasis,and tumor growth,and alter the radiationinduced immunosuppression microenvironment[235].Moreover,hepatic carcinoma HepG2 cells could be suppressed by GLP,which regulates the expression of hepatic miRNAs and immune-related miRNAs[226].
3.2 Anti-microbial activity
3.2.1 Antibacterial activity
Fungi are a widespread kind of microorganism.As a notable kingdom of fungi,mushrooms can be edible and play an indispensable role in alternative and supplementary medicine.Owing to a set of bioactive functions,G.lucidumis of significant ability against microbiota,including bacteria and fungi.The capacity ofG.lucidumagainst bacteria is characterized by the inhibition of both Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria[184].Interestingly,reports facilitated by different extracts ofG.lucidumcommonly indicated anti-bacteria ability,which enhanced the practicability ofG.lucidumbut puzzled determination in defined bioactive compounds.
Extract parameter,yield region,and chosen organ ofG.lucidumdetermine the resultant content of bioactive compounds and direct efficacy of anti-bacteria ability.Scientists have used water,methanol,dichloromethane[251],acetone[252],and chloroform as solutions to obtain a prepared extract ofG.lucidum.An interesting design,in which driedG.lucidumpowder was added to beef sausage,demonstrated the anti-bacteria ability of rawG.lucidumwas similar to nitrite[253].With a spectrum of components in different categories,G.lucidumshowed to protect from oxidant stress,while its anti-bacteria ability is closely associated with the generation of reactive oxidant species oppositely.In addition,the leakage of bacterial inner proteins is another mechanism of the phenolic-rich fraction ofG.lucidumwater extract[254].Another report compared the antibacterial ability of per ether,chloroform,and methanol extract.Methanol extract exhibited the smallest IC50value implying variable anti-bacterial efficacy attributed to extraction conditions[255].Gokcen[256]considered phenolic compound,β-carotene and lycopene components as significantly bioactive components of methanol extract.
When the discrimination in species was considered,the sensitivity of different tested bacteria toG.lucidumvaried.To detect whetherG.lucidumacted on drug resistance,multidrug-resistant tuberculosis was considered.After the administration ofG.lucidumextracts in different concentrations,the growth of tuberculosis was inhibited[257].In addition,extended-spectrumβ-lactamase-producing and multidrugresistantPseudomonas aeruginosawas examined for supporting the specific antibacterial ability ofG.lucidum[13].Several studies also established test models using an array of bacteria,which might provide a detailed description ofG.lucidum.G.lucidumcould suppress either special species,like drug-resistant ones or common species extract to widen its anti-bacteria applications.General lines,includingEscherichia coli,Pseudomonasaeruginosa,Staphylococcus epidermis,Enterococcus raffinosuswere inhibited byG.lucidum,respectively[258].
There remained several reports about mono-components for anti-bacterial ability despite raw extract ofG.lucidum.Peptides ofG.lucidumobtained from fruiting bodies and mycelium showed anti-bacterial potentially.The structural presence of cationic and hydrophobic amino acids facilitated its efficacy[259].This effect also appeared in another research focused on crude proteins ofG.lucidum[260].P-hydroxybenzoic and cinnamic acids found inG.lucidumpossessed anti-bacterial effects compared with the methanol tract ofG.lucidum[261].Richly produced in the fruiting body ofG.lucidum,polysaccharides,especially with non-reducing sugars,exhibited anti-bacterial performance directed to foodstuffs and human healthassociated microorganisms[262-263],while exopolysaccharide and chitosan did as well[264-265].These proofs congruously indicated the anti-bacterial ability ofG.lucidum.However,fewer studies concentrated on the affirmatory bio-compounds with mechanisms ofG.lucidumlimited its applications.With anticipated extraction and separation methods improving,the effect and mechanisms ofG.lucidumanti-bacterial will be further studied when the purified components can be prepared.
3.2.2 Anti-fungal activity
Although bacteria and fungi are different in structures and characters,both microorganisms are negatively regulated byG.lucidum.Research has wildly examined the suppressive effects ofG.lucidumon an array of pathogenic fungi,includingCandida albicans,Candida krusei,Candida glabrata[251],andAspergillus fumigatus[261].The anti-fungi ability ofG.lucidumattracted growing interest in this natural substance rather than standard agents resisted by vicious fungi.Dejan S.compared the efficacy ofG.lucidumfrom China with that from Serbia.The variable sources resulted in different sensitivity of tested fungi to the administration ofG.lucidum,which performed better than bifonazole and ketoconazole.When treated by that from China,Trichoderma virideandPenicillium funiculosumwere best suppressed while extract ofG.lucidumfrom Serbia sensitively impactedAspergillus versicolor[266].The hypothesis that diverse strains brought out different anti-fungi efficacy was also proved by Swati’s discovery[267].Two strains ofG.lucidum,DARL-4,and MS-1,showed moderate anti-fungi ability compared to fluconazole.Monica measured the performances of proteins ofG.lucidumextract acting as deoxyribonuclease,ribonuclease,protease,glucanase,and chitinase.The anti-fungi efficacy ofG.lucidummight partially associate with proteins ofG.lucidumfor the degradation of nutrient components that were necessary for phytopathogen fungi[268].
3.2.3 Anti-viral efficacy
People hitherto have found a variety of viruses and driven away at the development of broad-spectrum anti-viral agents.In addition to the frequent mutation of viruses,drug resistance is also a vital problem in clinical practice.Some active components isolated from fungi show potent pharmacological action in treating infectious diseases.G.lucidumhas been proven with specific efficacy in treating various internal diseases for thousands of years,and its efficacy in anti-virus gradually comes into notice.Based on the development of modern pharmacology,several studies isolated and purified many active components fromG.lucidum,and part of them have been verified with efficacy in anti-virusin vivoorin vitro.Some early studies show that ganoderic acid could inhibit the excretion of HBsAg and HBeAg in a dose-dependent manner and protect liver tissues from injury[269-270].Otherwise,the proteoglycans ofG.lucidumprohibited herpes virus-associated pain was provedin vitro[271]and in a clinical study on 5 patients in Japan[272].But the anti-hepatitis virus and antiherpes virus molecular mechanisms induced byG.lucidumstill lack molecular level studies.
Dengue is prevalent in several countries and regions,and the symptoms are characterized by hyperpyrexia,fatigue,and bleeding.The replication and assembly of DENV viruses mainly depend on NS2B-NS3 protease (PR) activation,which becomes a potential target for treatment.By comparison with an inhibitor of NS2B-NS3 PR,four triterpenoids isolated fromG.lucidumare probable inhibitors of NS2B-NS3 protease.In a consequential studyin vitro,Ganodermanontriol was further put forward as a potent inhibitor[273],but the interaction between Ganodermanontriol and DENV NS2B-NS3 PR is elusive.Six active components were isolated from another form ofG.lucidumin another study that showed better inhibitory efficacy on DENV-2 NS2B-NS3 PL at (84.6 ± 0.7)%[274].Additionally,the molecular interactions between these components and DENV-2 NS2B-NS3 PL have been confirmed as van der Waals,hydrogen bonding,and pi-pi interactions.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a human herpes virus that exists as a DNA loop in the B lymphocyte.Infection of EBV contributed to about 1.5% of human cancer patients and is expressed in malignant tumors[275],in which the treatment of anti-EBV has become a preventative strategy.Co-treatment ofG.lucidumextracts and quercetin in a low concentration suppressed the development of EBV-associated gastric cancer and the increased PAPR1 cleavage,caspase 3 and decreased Bcl-2 were observed,which proved theG.lucidumextracts enhanced the quercetin induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner.Mechanically,G.lucidumextracts and quercetin upregulated the expression of EBV latent and lytic genes,triggering lytic reaction,and consequently leading to the apoptosis of EBV[276].Zheng et al.[277]isolated 5 active components,including ganoderic acid A,ganoderic acid B,ganoderol B,ganodermanontriol,and ganodermanondiol fromG.lucidumby dichloromethane,all of them inhibited the activity of telomerase and EBV capsid antigens to the almost same degree.But the ganoderic acid A and B exhibited more effectiveness than the other three in inhibiting EBV early antigens.Furthermore,the hydrogen bonds,van der Waals force,and hydrophobic interaction were confirmed in the combination of ganoderic acid A and amino acid residues.
In a clinical study containing 61 patients with gingivitis and positive for human papillomavirus 16 serotype (HPV16) or human papillomavirus 18 serotypes (HPV18),the group with combination therapy ofG.lucidumandTrametes versicolorperformed better than that withLaetiporus sulphureusonly[278],which indicated the potential anti-HPV efficacy ofG.lucidum.Another study further confirmed the pharmacological effects ofG.lucidumextracts in inhibiting the proliferation,apoptosis,and cell cycle of HPV transformed cells[279].Zhang et al.[280]discoveredG.lucidumtriterpenoids (lanosta-7,9(11),24-trien-3-one,15;26-dihydroxy) and ganoderic acid Y exhibited anti-enterovirus 71(EV71) effectsin vitro.This efficacy probably depended on the binding of active components and viral capsid proteins,associated with the adhesion of the EV71 to the cell membrane.In addition to the inhibition of adsorption of EV71,these two components also interfered with the replication of EV71 RNA.TheG.luciduminduced immunomodulation is also related to the polysaccharide,which interacts with the innate immune receptors,including Dectin-1,DC-SIGN,Langerin,and TLR2[281].The relatively broad-spectrum anti-viral efficacy of active components inG.lucidummostly depends on the interruption of adsorption,invasion,and cell cycle.Some studies also illustrated the molecular mechanisms in this progress,at least in part.
3.3 Anti-HIV protease efficacy
Although various anti-viral efficacy ofG.lucidumhas been confirmed in the past decade,the development of anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) drugs is still a complicated issue[282].It has been found that the ganoderic acidβ,lucidumol B,and ganolucidic acid A isolated fromG.lucidumexhibited dramatic inhibition effects on HIV-1 protease activity as early as the end of the 20thcentury[66],but the molecular mechanisms of these effects are still unclear.
The HIV-1 protease (PR) is associated with the proliferation of HIV-1,which cleaves precursor protein and promotes HIV maturity,and is targeted by some active components inG.lucidum.Five active components isolated from the fruiting bodies and spores ofG.lucidum,namely ganoderic acidβ,lucidumol B,ganodermanondiol,ganodermanontriol,and ganolucidic acid A,had potent anti-HIV1 PR activity in a value of IC50within 20-90 µmol/L[66].Another study proved extractive ganoderiol F inhibited HIV at a concentration of 7.8 mg/mL,and other active components such as ganoderiol B and ganoderic acid C1 also inhibited HIV PR moderately[41].In a molecular docking study on the interaction between ganoderic acid with 1HVR and 1DIF,which are 2 types of HIV-1 PR,ganoderic acid B performed the lowest cluster number and IC50value.Triterpenes inG.lucidumsignificantly inhibitedα-glucosidase andα-amylase activity with IC50value of 0.1 µmol/L.Furthermore,the model of ganoderic acid B formed 4 hydrogen bonds with 1HVR in a manner of ILE50,ILE50,ASP29,and ASP30 residues[283].HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) is another target for pharmacological inhibitor extract fromG.lucidum.A laccase isolated from fresh fruiting bodies ofG.lucidumis characterized by novel N-terminal,high molecular weight,and Con A-Sepharose adsorption only.Its anti-HIV RT efficacy is probably based on the interaction between protein-protein[284].
The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) caused by HIV is still a serious illness in the world and inhibition of HIV PR and HIV RT are principal strategies in existing therapies.Whereas the side-effects elicited by tipranavir,saquinavir and ritonavir have become a new problem for AIDS treatments[285]and complementary and alternative medicine therapies could provide more selectable solutions.Studies proved some active components isolated fromG.lucidumhave anti-HIV efficacy,but the molecular mechanisms of these effects are still unclear.
3.4 The regulation of G.lucidum in diabetes mellitus
Bioactive components isolated fromG.lucidumexhibit potent anti-diabetic efficacy via various pharmacologic actions,but the protection of renal insufficiency is needed to study further.According to the International Diabetes Federation database,the burden of global diabetes mellitus (DM) has risen to 463 million adult patients in 2019.Although insulin injection and oral glucose-lowering drugs,including Metformin,Acarbose,DDP-4 inhibitors,and SGLT-2 inhibitors,are recommended as the first-line therapies,diet and regular exercises are still needed and undesirable side effects are inevitable[286].Most make us anticipate the exploration of more effective and glucose-lowering drugs and permanent remedies,which are ongoing and extracts isolated from plants play a vital role in the study of DM treatment[287].
In addition to the pharmacological effects,the extraction process influences the efficacy ofG.lucidum.In the condition of 65.8-70.0 °C for 2.8-3 h,the bioactive components acquired optimal anti-diabetes activity and more than 39%α-glucosidase inhibition effects[288].
In a study with T2DM rats induced by streptozotocin,GLPs treatment dramatically reduced fasting blood glucose (FBG) and insulin,mediated the aberrant gut microbiota and enhanced the antioxidant ability[289].GLPs also involved in regulating lipid metabolism indb/dbmice.In the high-fat dietdb/dbmice treated with GLPs,the body weight,FBG,and HbA1C levels decreased and aberrant lipid metabolism was corrected and consequently inhibited lipid anabolism[290].Triterpenes inG.lucidumsignificantly inhibitedα-glucosidase andα-amylase activity with IC50values of(10.02 ± 0.95) and (31.82 ± 4.30) µg/mL,respectively[291],which indicated the triterpenes are promising to act as a substitution of acarbose and voglibose.Furthermore,the triterpenoids isolated fromG.lucidumimprove glucose consumption in insulin resistance cells.The concentrations of triterpenoids at 0.03 and 0.06 mg/mL contributed to glucose consumption values at (1.80 ± 0.12) and(2.21 ± 0.29) mmol/L,respectively,and without cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells[292].
Impairment of the pancreas organ is a major feature of DM,especially in T1DM,which can be observed in the early years of the patients.The impaired islet β cells trigger the decreased secretion of insulin and consequently result in hyperglycemia,so restoring the pancreas function and regulating blood glucose are two principal strategies in treating DM.Protection of pancreas organ induced by recombinant LZ-8,an analog of immunomodulatory protein Ling Zhi-8,promotes insulin excretion,relieves symptoms of T1DM,decreases blood glucose and HbA1c and inhibits TNF-α and IL-1β,which is mainly depended on its anti-inflammation and regulatory T cells mediation[293].A proteoglycan isolated fromG.lucidumwas named FYGL and had similar efficacy in inhibiting pancreatic β cells injury accompanying decreased ROS and NO levels[294].In an early study,researchers illustrated the mechanisms of insulin resistance restoration induced by FYGL.Activation of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 B(PTP1B) dephosphorylated insulin receptor substrate(IRS) contributed to the dysfunction of the insulin signal pathway.This aberrant phenomenon was corrected by FYGL,accompanied by activation of PI3K/Akt,and finally restored the glucogen synthesis by insulin in HepG2 cells[295].Furthermore,treating myoblast L6 cells with FYGL also led to the activation of AMPK and increased the expression of GLUT4,promoting glucose uptake[16].
A novel complex GLP-chromium (III) (GLP-Cr III) treated pre-diabetic mice with administration of 50 mg/kg per day decreased the level of FBG,total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG)B[296],which provided a novel form of GLP.The vasculopathy is still a frequent pathologic change in DM patients with the long course,which results in increased risk factors of cardiovascular disease,renal insufficiency,and fundus lesions.In terms of these challenges,a clinical study confirmed thatG.lucidumadministration could not increase cardiovascular risk[297].G.lucidummycelia mediated the leukocyte metabolism and oxidative stress in DM rats[298].The ROS and chronic inflammation induced by advanced glycation end products (AGE) are associated with hyperglycemia and finally result in vasa vasorum angiogenesis,but this pathologic process can be interfered with by polysaccharide peptide (PSP) isolated fromG.lucidum[299].PSP inG.lucidumalso promotes the repair of blood vessels.A study with 35 Wistar rats showed that the PSP promoted endothelial repairment and downregulated the risk factors in an optimum dose with 300 mg/kg body weight,which was proved by the alteration of endothelial progenitor cells and circulating endothelial cells level[300].Xiao et al.[301]confirmed an anti-diabetic bioactive component F31 in GLP.Mechanistically,F31 promoted the phosphorylation of AMPK and decreased the level of hepatic glucose regulatory enzyme mRNA in liver tissues.The increased GLUT4 was also observed in the T2DM mice and was accompanied by decreased epididymal fat/body weight.
3.5 Liver and gastric injury
Protection from liver damage was another application ofG.lucidum.There remained a set of articles usingin vivoandin vitromodels to assess howG.lucidumpossessed anti-hepatitis ability[151,302].G.lucidumcould treat acute liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride[303].Shi[304]and Han[305]also discovered that treatment ofG.lucidumameliorated the insult ofD-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide in hepatitis mice.With good ability in radical scavenging,mitochondrial enzyme normalization,and membrane potential restoration,G.lucidumprotects from disruption of liver injury-associated indications followed by attenuated MDA,superoxide dismutase (SOD),and glutathione (GSH)[306].As disruption of aminotransferase,aspartate aminotransferase,and lactate dehydrogenase were assessed after treatment ofG.lucidumin preclinic[307-308],a randomized controlled trial using a commercial drug mainly consisting ofG.lucidumgave support for the translational medical potentiality ofG.lucidumin liver protection.More attention was then put on triterpenoids[309-310]and GLP[311]because of structural identification and detectable antioxidant profile compared with raw extract ofG.lucidumwith water,ethanol,or methanol[21].
Like the role in hepatocellular carcinoma,theG.lucidumand its extracts also can contribute to reversing the gastroblastoma,which may interfere with intracellular autophagy.Methanolic fruiting body extract ofG.luciduminhibited the growth of gastric cancer cells by prohibiting the cellular autophagy and cell cycle by increasing the LC-II and p62 adaptor[220,312].Meanwhile,G.lucidumand its extracts regulate the fungal immunomodulatory protein Lz-8 and induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated autophagic cell death in the human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901[313].Further investigations need to elucidate whether those autophagic regulations are going through the phagosome-autophagosome-lysosome procedure and mediate aiming protein degradation.
3.6.Cardiovascular potential
As a multi-pathway regulation,G.lucidumworks on the cardioprotective effects[314].Selenium-enriched GLP (Se-GLP) was discovered to prevent oxidative damage in a mouse model of heart reperfusion injury and made the role of anti-oxidative regent.In such a model,the antioxidant enzymes,including SOD,catalase (CAT),glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px),and GSH were all compromised,which also contributed to reversing the heart injury-induced failure[315].Accordingly,Ganoderic acid A extracted fromG.lucidumwas correlated to a hypoxic injury of the heart going through the PI3K/AKT pathway mediated rat H92 cardiomyocyte proliferation and apoptosis attenuation[316].Furthermore,in the pressure-boosting irradiated cardiomyopathy mice model,one extract of spore oil was confirmed for the modification of cardiac function improvement through the circle RNA-FOXO3 axis,which is an important pathway associated with heart failure[317].
G.lucidumand its extraction ingredients were not only directly used in myocardial disorders,but also effective in the following complications[318-320].Interestingly,G.lucidumand its ingredients can alleviate cardiovascular collapse and damage caused by diastolic dysfunction[321].At the same time,polysaccharide peptide extracted fromG.lucidumwas reported to hinder diabetes and reduce the cardiac disease risk by releasing the vascular damage level in Wistar rat models[300].Besides,G.lucidumspores declined the total cholesterol and triglycerides in diabetic rats through upregulating the acyl-CoA oxidase 1,acetyl-CoA carboxylase,INSIG1,and INSIG2 gene expression[322].Another major complication of cardiovascular disease is dyslipidemia,for instance,polysaccharide peptide was applied to protect the atherogenesis process in the context of dyslipidemia from atherosclerosis and blood vessel damage[323].Polysaccharides as hypolipidemic ingredients can also exhibit antioxidant and antiapoptotic effects in high-fat diet mice[324].
4.Preclinical and clinical studies
Before the common era,G.lucidumhas been widely used by Asia populations to improve general health.In recent years,novel applications ofG.lucidumhave been suggested,such as treatment alongside Western chemotherapy to inhibit cancer and reduce side effects.In addition,other diseases,such as brain,renal,immune,infection,and myopathy-related problems,have also been regulated byG.lucidum.
4.1 Protective effects of G.lucidum against cancer
G.lucidumwas used as adjuvant therapy with chemotherapy or radiotherapy in cancer treatment to prolong long-term survival,promote life quality,and regulate immunity.To evaluate the effects ofG.lucidumin cancer treatment,clinical studies since 1997 have been published[325-329].Alteration of the immune system after administration ofG.lucidumis discussed most.Evidence revealed that cancer patients displayed a series of cellular immunological enhancements,such as NK cell activity and CD4/CD8 ratios were changed after Lingzhi capsule,G.lucidumextracts orGanodermaspore powder supplementation[325,330-332].The quality of life is also evaluated after the administration ofG.lucidum.Studies show that the administration ofG.lucidumextracts improves the quality of life of patients with lung cancer[333].After oral administration ofGanodermaspore powder capsules,one hundred patients with digestive system tumors obtained more remarkable points of quality of life score than the control[334].In addition,oral administration withGanodermaspore powder can also improve physical well-being and fatigue subscale for breast cancer patients undergoing endocrine therapy[335].Although accumulative clinical studies aboutG.lucidumin cancer therapy emerged,there is no sufficient evidence to encourage the use ofG.lucidumas a firstline treatment for cancer.Also,long-term treatment has not been followed,and it remains uncertain whether the treatment can help prolong cancer patient survival.However,G.lucidumis an alternative adjunct that potentially enhances immune response,promotes quality of life,and shows minor adverse effects for patients with cancer.
4.2 Renal protective effects of G.lucidum
Shieh et al.[336]first observed the protective function ofG.lucidumon renal cells and hepatocytes.Subsequently,several clinical trials have been started to evaluate the effects.Futrakul et al.[337]found that 5 patients with impaired renal function showed significantly decreased proteinuria after taking a crude extract of fungusG.lucidumfor 1 year.In 2003,Xiao et al.[338]observed thatG.lucidumdecoction is useful in markedly lowerRussula Subnigricans-induced kidney injury in patients.In addition,Nephrotic patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis also ameliorated injured kidneys after administration ofG.lucidum,such as inhibiting endothelial cell cytotoxicity,restoring immune-circulatory balance,and suppressing proteinuria[339].These clinical results confirmed the potential protective roles ofG.lucidumin renal health and proved the safety of administration ofG.lucidumin the human body.
4.3 Neuroprotective effects of G.lucidum
G.lucidumis neuroprotective in ischemia/reperfusion or traumatic spinal cord injury in experimental models,which drives clinical trials to determine its effects on neuroprotection.G.lucidumhas been reported to show effects on pain relief.Administration of hot water extracts from various herbs,includingG.lucidumhas been tested to relieve herpes zoster pain within a few days.No patients developed post-herpetic neuralgia after more than one year of follow-up[340].In 2018,a clinical study reported that weekly seizure frequency was reduced in patients with epilepsy after administeringG.lucidumspore powder[341].In addition,G.lucidumalso shows curative effects on depression in combination therapy[342].However,the effects ofG.lucidumspore powder on Alzheimer’s disease are limited.G.lucidumspore powder treatment for 6 weeks did not show more encouraging results in symptom improvements[343].Taken together,the evaluation of the neuroprotective effects ofG.lucidumis limited in clinical trials.
4.4 Protective effects of G.lucidum on other diseases
Considering the potential immune regulation effects ofG.lucidum,immune status has been checked in rheumatoid arthritis(RA) patients and hemophiliacs with positive HIV antibodies after administration ofG.lucidum[344-345].RA patients’ global score improved significantly,but no obvious alteration in immune status for hemophiliacs after eatingG.lucidum.In addition,Ji 731 injection,which containedG.lucidum,was evaluated to be useful for atrophic rhinitis[346].
In conclusion,G.lucidumor its related products were potentially effective for several diseases,especially for immune regulation after chemotherapy for cancer patients.Moreover,immune regulation has also been applied to other immune or inflammation-related diseases,such as RA or atrophic rhinitis.Not only immune regulation,but neuron system-related diseases were also possible to be modulated byG.lucidum,such as pain relief and neurodegenerative diseases.However,as the potential mechanism ofG.lucidumin biological function and there is no long-term treatment trial,the effects ofG.lucidumis hard to observe and evaluate.
5.Safety,toxicity,and side effects evaluation
G.lucidumincludes triterpenes,polysaccharides,nucleosides,steroids,fatty acids,alkaloids,proteins,peptides,amino acids,and inorganic elements[347].Most reports illustrated that one or some of them are not causing apparent toxicity or safety problems.Rodent animals,for example,can tolerate up to 5 000 mg/kg dose ofG.lucidumadministration,and no mortality rate was reported during the integral progression[348].In addition,extracted ingredients from GLP were administrated in Wistar rats compared with a placebo.The result indicated no significant differences in abnormal clinical symptoms as well as body weight and food intake,even the same for the hematology and clinical chemistry values[349].This phenotype matched the data in multiple human clinical trials.Health volunteers 1.5 g/day and 4 consecutive weeks of exposure would not affect their hemostatic parameters as well as platelet and global hemostatic functions,while it cannot cause breeding or tissue damage problems[350].After a 12-week stable dose ofG.lucidumtreatment,23 dyslipidemia volunteers accompanied mild hypertension that did not affect the physiological expression,only found a few side symptoms considered not clinically significant such as headache,influenza/running nose[17].However,minors reported higher doses of it to induce some hematologic abnormal and immune responses.For example,atherosclerotic patients who receive the above amount ofG.lucidumtreatment with 3 000 mg/day can inhibit their platelet aggregation progression[351].After a 10-day trial,participants supplemented with 2 g ofG.lucidumwere found to boost CD56,the cell surface glycoprotein involved in embryonic development and nerve growth in their blood samples[352].Besides,GLP can enhance the sheep’s red blood cells though no phagocytic function or macrophages were manifested during the procedure[349].Overall,appropriate doses ofG.lucidumunder expert advice may not trigger toxicity,side effects,and safety problems for the patients.
6.Conclusion
G.lucidum,as a medicinal and edible plant,has been used for a long history.After years of research,more than 300 compounds have been isolated from the fruit body,mycelia and spore ofG.lucidum.These ingredients have also been shown to have various pharmacological effects.One of the most studied is tumor and immune regulation.G.lucidumhas also been developed into various products,of whichG.lucidumspore-related functional food is the most famous.In these years of the outbreak of COVID-19,G.lucidumhas also been studied on COVID-19,showing a good effect in inhibiting the COVID-19 virus.Despite the wide application ofG.lucidum,the therapeutic mechanism ofG.lucidumfor various diseases is still unclear.Long-term follow-up is also lacking in clinical studies.As a popular medicinal and edible plant,G.lucidumneeds more research on its therapeutic mechanism and clinical research.
Declaration of competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Macao Science and Technology Development Fund (001/2023/ALC and 0006/2020/AKP),the Research Fund of University of Macau (CPG2023-00028-ICMS),the Guangxi Science and Technology Major Project (GUIKEAA22096029) and Macao Young Scholars Program (AM2022022).
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- Protective effects of oleic acid and polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil on cardiovascular diseases
- Diet and physical activity inf luence the composition of gut microbiota,benef it on Alzheimer’s disease
- Inf luence of nitrogen status on fermentation performances ofnon-Saccharomyces yeasts: a review
- Resveratrol combats chronic diseases through enhancing mitochondrial quality
- Demonstration of safety characteristics and effects on gut microbiota of Lactobacillus gasseri HMV18
- Cyanidin-3-glucoside protects the photooxidative damage of retinal pigment epithelium cells by regulating sphingolipid signaling and inhibiting MAPK pathway
