Mechanism of AiTongXiao granule in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma based on network pharmacology and rat transplanted liver cancer model
2024-01-22LIUHuanLIUXianJINLijieLIUShashaWEIYanfei
LIU Huan, LIU Xian, JIN Li-jie, LIU Sha-sha, WEI Yan-fei
1.The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530024, China
2.Guangxi Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology of Preventive Medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530024, China
3.Teaching Experiment Training Center of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
4.College of Basic Medicine of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1.Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a kind of malignant tumor with strong heterogeneity and high mortality.The harm of liver cancer in China is more serious, about 380,000 people die from liver cancer every year, accounting for 51% of the global liver cancer deaths[1].Due to the complex etiology and pathogenesis of liver cancer, relying on a single means often cannot obtain the ideal therapeutic effect.Therefore, the combination of traditional Chinese and western medicine and multi-disciplinary combined treatment has important status and practical significance for the prevention and treatment of liver cancer.Traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation is one of the most important means of TCM clinical disease treatment, and the modern scientific explanation of its pharmacodynamic material basis and its mechanism of action is the key field of TCM modernization research.However, due to the characteristics of multi-components and multi-targets, a relatively complete scientific research system has not been formed in terms of its material basis and mechanism of action.In recent years, the rapid development of network pharmacology has provided strong support for the analysis of the molecular mechanism of Chinese medicine compounds.This method has been gradually applied to the mechanism research of more and more TCM monomers, single herbs or TCM compounds, and has become a hot topic in current research[2].
AiTongXiao granule (ATXF) is developed by Professor Wei Ailing on the basis of “GexiaZhuyu Decoction”, which utilizes “clearing heat, detumescence and reinforcing qi” in the treatment of HCC.Among them, hedyotis alba and schelderwort are royal medicines,which have the effect of clearing heat and detoxifying.Meanwhile,Safflower, Tricolor, Zedoary and Red peony are the products for removing blood stasis and dispersing knot, moving qi and relieving pain.Due to the body poison stasis mutual knot, positive qi depletion injury, astragalus, rhizoma corydalis, gynostaphylla, Radix aconitum,Radix aconitum, Radix aconitum were added to support healthy qi.ATXF has been clinically applied in the treatment of liver cancer for more than ten years, which has proved to effective in preventing and treating liver cancer and improving the quality of life of patients[3-5].The experimental results of transplanted hepatocellular carcinoma model in rats showed that ATXF could inhibit the proliferation of liver cancer cells, induce cell cycle arrest, and significantly increase the apoptosis rate of cancer cells and downregulated the expression level of Bcl-2, Survivin, vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF),micro vessel density (MVD)[6, 7].The above studies provide a certain scientific basis for the clinical efficacy of ATXF, but its material basis and specific molecular mechanism are not fully understood.Therefore, in this study, the active ingredients and core action targets of Huatongxiao granules were screened by constructing a “drug component-disease target” network using network pharmacology.On the basis of the previous results, the molecular verification of the transplanted liver cancer model in rats was carried out, in order to provide a scientific basis for elucidating the molecular mechanism of the treatment of liver cancer by ATXF.
2.Materials and Methods
2.1 Network pharmacology analysis
2.1.1 Screening of active ingredients and target information of ATXF
All of the known chemical components of the 12 traditional Chinese herbal medicines including hedyotis diffusa, sculellaria barbata,radix paeoniae rubra, curcuma zedoary, astragalus membranaceus,rhizoma sparganii, glycyrrhiza, Lindera aggregate, coco grass,corydalis tuber, gynostemma pentaphylla and carthamus tinctorius L were obtained in the pharmacology database and analysis platform TCMSP (http://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php).Oral Bio-availability (OB)30% and Drug-likeness (DL)0.18 were used as screening thresholds to collect the active components of each herb and obtain the target information of each herb.
2.1.2 Collection of liver cancer disease target
“Hepatocellular carcinoma” was used as key word and searched in biological information databases GeneCards(http://www.genecards.org/), OMIM(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim), TTD(http://db.idrblab.net/ttd/)and DrugBank(https://go.drugbank.com/), the liver cancer disease targets were collected respectively and the Venn diagram was used to collect and combine the results of the above 4 databases to obtain the information of all liver cancer disease targets
2.1.3 Construction of “active ingredient-potential target network” for prevention and treatment of liver cancer by ATXF
VENNY2.1.0 software was used to make an intersection pie chart between the target of liver cancer disease and the target of the active ingredient of the Chinese medicine of ATXF to obtain the potential target of Uantongxiao granule for prevention and treatment of liver cancer.Then Cytoscape 3.8.2 was applied to import drug ingredient and disease target information, construct disease network diagram of active ingredient and potential target, and analyze the correlation.
2.1.4 Construction of protein interaction network, enrichment analysis of KEGG pathway and GO biological process
String online platform (http://string-db.drg/) was used to construct the protein interaction network among the potential targets of the prevention and treatment of liver cancer(protein-protein interaction,PPI).The protein species was set as “homo sapiens” and “minimum required interaction score” was 0.95; “hide disconnected in the network” was selected to screen the core targets of ATXF in the treatment of HCC.Furthermore, another online platform Metascape(http://metascape.org) was used for GO and KEGG analysis.According to the converted EntrezIDs, the Omicshare online analysis platform was used to visually analyze the enrichment results with P< 0.05 as the threshold.
2.2 Experimental Validation
2.2.1 Cells, animals and main reagents
Rat abdominal fluid cancer cell line Walker-25 (LLC-WRC 256)is obtained from Guangxi Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology of Preventive Medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine.30 male SPF Sprague-dawley rats(200~220g)were purchased from Changsha Tianqin Biotechnology Co., LTD (License number:SCXK (Hunan)2019-0014).Aitongxiao granule was prepared by Jiangyin Tianjiang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd into non-decoction granules (15 g/packet).High sugar DMEM culture solution purchased from Gibco, USA;Fetal bovine serum was purchased from Biological Industries; Rabbit anti-p53 polyclonal antibody(10442-1-AP), rabbit andti- phosphop53 (Ser 15) polyclonal antibody (29961-1-AP), mouse anti-AKT monoclonal antibody (60203-2-Ig) and mouse anti-phospho-AKT(Ser473) monoclonal antibody (66444-1-Ig) were all purchased from Proteintech, USA; Rabbit anti- p44/42 (Erk1/2) monoclonal antibody(#4695s)was purchased from CST.
2.2.2 Establishment of transplanted rat liver cancer model and treatment of ATXF
Referring to Wang’s method of modeling transplanted liver cancer in rats[6], 30were divided into control group and treatment group.On the 8th day after modeling, the same amount of drug solution was administered at 10 mL/kg body weight per day.The treatment group rats were given a gavage of ATXF granule solution (75 mg/L) daily, while the control group was given a gavage of distilled water twice a day, and the drug was discontinued after 15 d.By the end of the treatment, blood was collected from abdominal aorta after fasting anesthesia; The liver was removed and the tumor tissue was completely removed.The weight of the tumor was determined.The animal experiment program has been reviewed by the Ethics Committee of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,and conforms to the principles of animal protection, animal welfare and ethics, as well as the relevant provisions of the national experimental animal welfare ethics.The approval number is No.DW20230620-118.
2.2.3 Pathology and liver function test
Part of the transplanted tumor tissue was fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde at room temperature, dehydrated with alcohol of different concentrations, transparent with xylene, and embedded in paraffin wax.Hematoxylin-eosin staining (HE) was sectioned, dried,and dewaxed.Hematoxylin-eosin staining (HE) was used to observe the morphological changes of HCC cells under a microscope.Serum of control group, treatment group and normal rats were collected and tested by Asparagine amino acid transferase (AST) and Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ELISA kit according to the manufacture’s instruction.
2.2.4 Western blot
50 mg tumor tissue was weighed, 500 μL RIPA lysate containing protease and phosphatase inhibitor was added, and total tissue protein was extracted after homogenization.The concentration of total protein was determined by BCA method, and the sample was prepared by SDS-PAGE loading buffer after treatment with boiling water bath.The target protein was separated by 10%PAGE gel electrophoresis.The protein was transferred to PVDF membrane by semi-dry method.The protein was blocked in 5%skim milk powder at room temperature for 1 h.After blocking, the membranes were incubated with primary antibodies and the internal reference antibody β-actin at 4 ℃ overnight.The membranes were further washed by TBST buffer for three times and incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) labeled secondary antibody for 1 hour at room temperature.At last, the membranes were washed triple times and detected by luminol chemiluminescence method, The gray value of each target genes and internal gene β-actin were measured by using Image J software.
2.2.5 Statistical analysis
The experimental data were analyzed by SPSS 17.0 statistical software, and the measurement data were represented.Independent sample t test was used for statistical analysis between the two groups, and P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Results of network pharmacological analysis
3.1.1 Active constituents and their targets of ATXF
By searching “Hedyotis Diffusae Herba”, “Scutellariae Barbatae Herba”, “Radix Paeoniae Rubra”, “Curcumae Rhizoma”, “licorice”,“Carthami Flos”, “Hedysarum Multijugum Maxim”, “Gynostemmae Pentaphylli Herba”, “Sparganii Rhizoma”, “Linderae Radix”,“Cyperi Rhizoma”, “Corydalis Rhizoma” as key words in the TCMSP database, the number of active ingredients and target points of Chinese medicine collected and shown in table1.257 kinds of active ingredients were obtained after the collection of all the active ingredients of Chinese medicine, of which 18 were common ingredients, their names and code of this paper were stigmasterol(A1), beta-sitosterol (A2), quercetin (A3), baicalin(B1), cholesterol(B2), baicalein (B3), rhamnazin (B4), sitosterol (B5), luteolin (B6),spinasterol (C1), hederagenin (C2), formononetin (C3), kaempferol(C4), mairin (C5), jaranol (C6), isorhamnetin (C7), calycosin (C8),hyndarin (C9).Quercetin, stigmasterol, sitosterol and sitosterol are the common components of 7-9 Chinese herbs in ATXF.The active ingredients in the recipe correspond to 24-223 targets respectively,and a total of 289 drug action targets were obtained (Table1).
3.1.2 Analysis of potential targets for preventing and treating hepatocarcinoma with ATXF
The targets of liver cancer disease collected by GeneCards, OMIM,TTD and DrugBank were imported into VENNY 2.1 software to make a Venny map, and 7993 targets of liver cancer disease were obtained.It can be seen from the figure that most of the targets come from the GeneCards database (Figure 1A).Then, the above targets of liver cancer disease and the targets of the active ingredients of various Chinese medicines were used to make Wayne diagram, and 231 potential targets were obtained by intersection of the two subsets(Figure 1B).

Tab 1 The number of active components and targets of each herb in ATXF
3.1.3 Construction of potential target network of active ingredient of ATXF for prevention and treatment of liver cancer
The main active components of ATXF granules and 231 potential targets for prevention and treatment of liver cancer were imported into Cytoscape 3.8.2 software to construct the network topology diagram of “Active ingredients-potential Targets”, which involves 512 nodes and 5798 edges (Figure2).Licorice, rhizoma corydalis and meliopsis contain more special active ingredients.In terms of the number of targets, the common components quercetin (A3),stigmosterol (A1), glutsterol (A2), kaempferol (C4) and luteolin(B6) had a large number of linking targets (Figure2).n terms of the number of binding targets of specific components, there were wogonin (BZL13), Cryptopin (YHS3) contained in Rhizoma corydalis, 6,7-dimethoxy-2-(2-phenylethyl) chromone (WY1)contained in Rhizoma corydalis.Beta-carotene (HH9) of safflower,ellagic acid (CS1) of paeony, Chryseriol (XF1) of Chrysophane,7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone (7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone,GC6), 3’-Methoxyglabridin, GC60, licochalcone a, GC60 GC59)connected more targets (Figure2).
3.1.4 PPI network construction and core target screening
The 231 “drug-disease” intersection targets obtained were uploaded to the String platform to obtain the interaction relationship between the targets.The results showed that five targets, including MAPK3,IL6, TP53, ALB and AKT1, had the highest level of interaction with other targets, as shown in Figure 3.The “drug-disease” targets were uploaded to CytoNCA for topological analysis.Based on the median of Degree, Eigenvector, LAC, Betweenness, Closeness and Network values as the screening criteria, 11 core genes were obtained after secondary screening.They are AKT1, CASP3, IL6, JUN, MAPK1,MAPK3, MMP9, MYC, PTGS2, TNF and TP53.The specific topological parameters of each gene are shown in Table 2.
3.1.5 Analysis of KEGG, the core target of treating liver cancer with ATXF granules
The metascape website was used to conduct KEGG pathway Enrichment analysis (Min overlap: 3, P value Cutoff: 0.01, Min Enrichment: 1.5) for 11 selected core targets.The results showed that the top 20 pathways were Hepatitis B, TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis(TWEAK) signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway,Hepatitis C and hepatocellular carcinoma, Signaling by interleukins,Spinal cord injury, Chromosomal and microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer, Pathways in cancer, Apoptosis, positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation (Figure 4).
3.2 Animal experiment results
3.2.1 Antitumor effect of ATXF on Walker-256 transplanted tumor rats
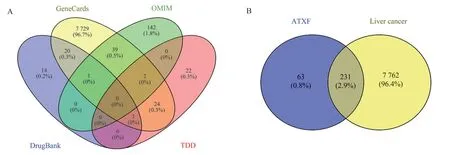
Fig 1 Screening of therapeutic targets of ATXF for hepatocellular crcinoma
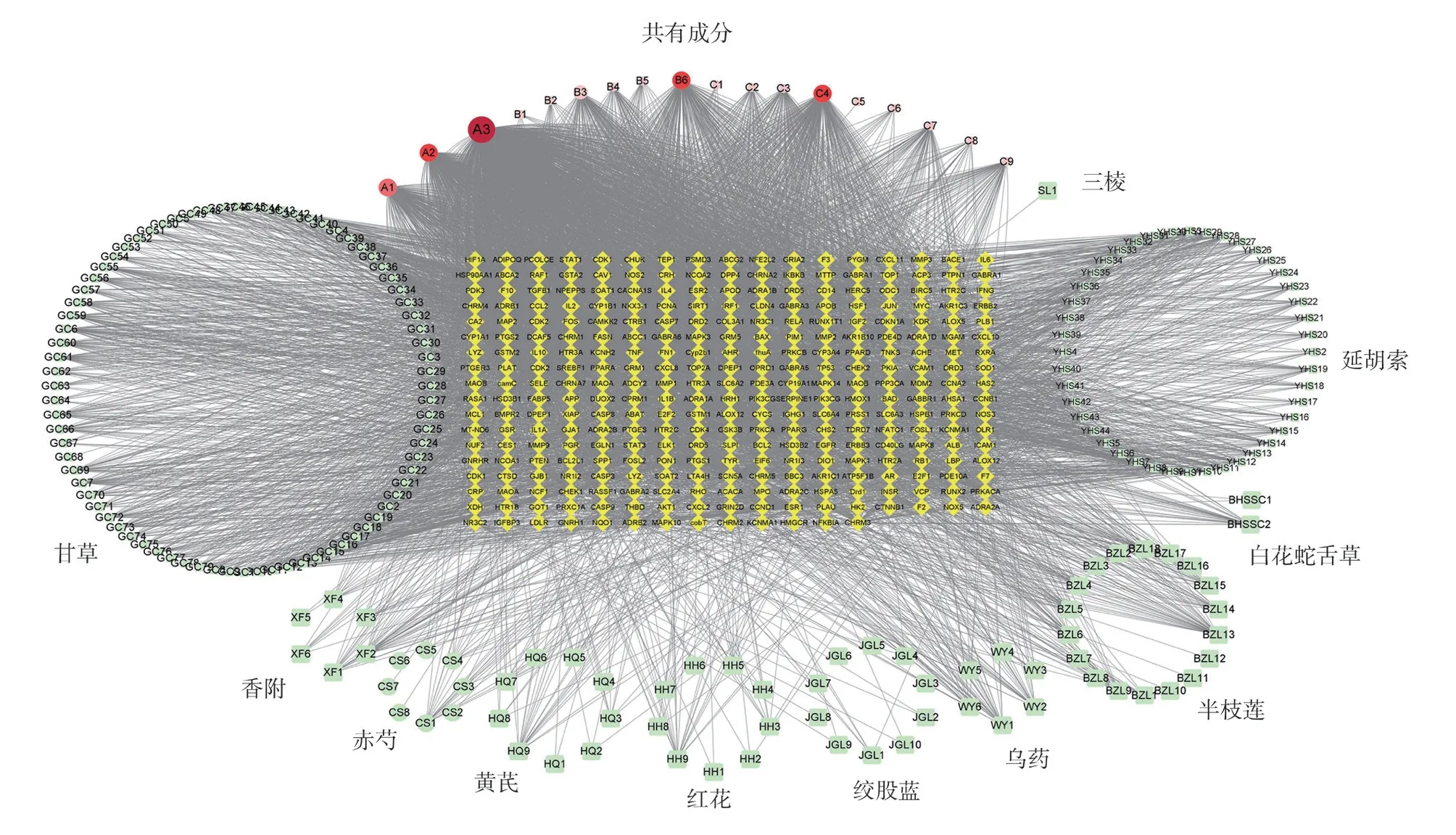
Fig 2 Network diagrams of active ingredients-potential targets of ATXF
The experimental results of the rat model showed that after 15 d of treatment, the mental state of the treatment group was better, the survival rate was higher (80%, 12/15), and there was no death after 10 days of intervention.The mental state of the control group was poor, death occurred every 1-2 d, and the final survival rate was only 40% (6/15), indicating that ATXF could significantly prolong the survival period of SD rats bearing tumor (P < 0.05) (Figure 5A).Comparing the weight of intrahepatic transplanted tumor between the two groups, it was found that the tumor growth could be significantlyinhibited in the treatment group of ATXF (Figure 5B).Anatomical observation showed that the liver morphology of rats in the treatment group was better and the volume of intrahepatic tumor was smaller(Figure 5C).However, in the control group, the intrahepatic tumors grew too fast, were too large, the liver was compressed, and a few suspected metastases appeared on the external surface (Figure 5D).

Tab 2 Topological parameters of the key targets of ATXF in the treatment of HCC

Fig 4 KEGG pathway of ATXF in the treatment of HCC (top 20)
3.2.2 Effect of ATXF on liver function in rats
ELISA method was used to detect the content of AST and ALT in serum of rats in treatment group, model control group and blank group, The results showed that the serum AST and ALT in control group and treatment group were significantly higher than those in blank group (P<0.01), suggesting that the use of intrahepatic modeling and subsequent liver cancer transplantation could damage the liver function of rats.Compared with the control group, AST and ALT contents in the treatment group were significantly decreased(P<0.05), which may be caused by the inhibitory effect of ATXF on transplanted tumors (Figure 6A).HE pathological examination of the transplanted tumor tissues of the two groups showed that there were more vacuoles and unclear nuclear boundaries in the transplanted tumor cells of the treatment group.The morphology of the transplanted tumor cells in the model group was intact,suggesting that AXTF had a killing effect on the transplanted tumor tissue (Figure 6B-6C).
3.2.3 Validation of the targets of ATXF Total protein was extracted from the tumors of the two groups,and Western blot analysis showed that the expression levels of AKT and pAKT in ATXF group were significantly lower than those in control group (P < 0.01).There were no significant differences in the expression levels of p53 and ERK1/2 proteins between the two groups, but the levels of p-p53 and pERK1/2 in the ATXF group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.01)(Figure 7A-7B).

Fig 5 The intervention effect of ATXF on transplanted tumor model rats, compared to the control group, **P < 0.01

Fig 7 Western blot analysis of transplanted tumor tissue in rats
4.Discussion
The etiology and pathogenesis of primary liver cancer are complicated, and it is difficult to reach the therapeutic expectation by relying on single treatment.In clinical practice, ATXF combined with hepatic artery chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation can significantly improve the quality of life of patients with advanced liver cancer, but the material basis and mechanism of its prevention and treatment of liver cancer remain to be clarified[5].n this study, 257 kinds of active ingredients were collected by network pharmacology, including many anti-tumor active ingredients.For example, quercetin, a flavonoid component that exists in a variety of foodborne drugs, is also a common component of up to 9 traditional Chinese medicines in ATXF.Studies have shown that quercetin is cytotoxic to tumor cells and can play an anti-tumor role by blocking cell cycle, inducing cell apoptosis and inhibiting tumor cell invasion and metastasis[8].Another recent network pharmacological study pointed out that quercetin is also a common active ingredient in five classic prescriptions for liver cancer[9],suggesting that quercetin may have important significance in the clinical prevention and treatment of liver cancer, and it is worth further research.In addition, stigmasterol can cause endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial dysfunction of oral cancer cells, and then induce cell apoptosis[10].Another study showed that stigasterol also has a chemotherapy sensitization effect, which can enhance the chemotherapy sensitivity of endometrial cancer cells to cisplatin by inhibiting the Nrf2 signaling pathway[11].On the sterol, kaempferol,luteolin, a number of studies have shown that breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, stomach cancer, cervical cancer and leukemia and other tumor cells have inhibitory effects[12-14].In addition,studies in recent years have also found that baicalin and baicalein can regulate the key signaling pathways of tumors, thus inhibiting tumors[15, 16].The results of the active ingredient-target network also showed that the common active components of these Chinese herbs could act on multiple targets, suggesting that quercetin,glutamol, kaempferol and other common components contained in ATXF are of great significance for its anti-liver cancer effect, and may be an important pharmacodynamic material basis.In order to further study the key protein targets of Uantongxiaogranules in the treatment of liver cancer, the predicted potential targets were analyzed by PPI analysis network.Genes such as AKT1, IL6, TP53,MAPK3, TNF, JUN, CASP3, MAPK1, MYC, PTGS2 and MMP9 had a high Degree in the network.Under normal conditions, the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway is abnormally activated in liver cancer tissues, so it is particularly important to develop inhibitors of this pathway [17].IL-6 can be used as a multipotent cytokine to participate in the proliferation, migration, invasion, angiogenesis and apoptosis of hepatoma cells through abnormal activation of IL-6/JAK/STAT signaling pathway[18].In addition, abnormal inactivation of p53 and overexpression of negative regulatory factor MDM2 are another major feature in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Due to the abnormality of this key pathway to maintain cell gene homeostasis,intracellular genes become unstable, and oxidative stress, energy metabolism conversion, and anti-cancer gene abnormalities occur, which eventually lead to liver cancer cells becoming liver cancer cells[19].As an important tumor suppressor gene, the core mechanism of p53 is to induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.When cells are stimulated by DNA damage or other carcinogenic stress,they can be activated by phosphorylation to initiate the transcription of a series of downstream proteins involved in cell cycle arrest, cell senescence and apoptosis[20].As key protein kinases in the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway, ERK1 and ERK2 are involved in regulating many biological processes such as apoptosis, proliferation,immune response and RNA synthesis of tumor cells.Therefore,this pathway is also one of the most important signaling pathways in the occurrence and development of liver cancer[21].Therefore,some studies have pointed out that the development of universal or combined inhibitors targeting RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK, PI3K-AKTmTOR and p53 signaling pathways will provide a new means for the treatment of liver cancer [22].
The results of the “drug-disease” intersection gene KEGG enrichment pathway showed that the core targets of ATXF for prevention and treatment of liver cancer were mainly enriched in hepatitis B virus, TNF signaling, The interleukin pathway and Pathways in cancer.Studies have shown that the 2-hydroxy-3-methylanthraquinone compounds, β-sitosterol, stigmosterol, arbutol and p-hydroxycoumaric acid in ethanol extract of Hedyodyma alba can inhibit HBV antigen to varying degrees[23].Another study showed that both water decoction and alcohol extract had certain inhibitory effect on HBV antigen[24], indicating that ATXF has certain effect on HBV virus infection in the prevention and treatment of HBV-related liver cancer.The specific antiviral active ingredients and their mechanism of action and whether other prescriptions also contain anti-HBV activities need to be further studied.TNF-α and IL-6, as key effector molecules in tumor microenvironment,are overexpressed in patients with HBV-related liver cancer[25].In addition, studies have shown that inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6 and TGF-β can participate in the occurrence and development of tumors, which are of great significance for the epithelial mesenchymal transformation (EMT) of tumor cells,angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis[26].KEGG results showed that the core targets of ATXF enriched the key inflammatory factors in the above key tumor microenvironment, suggesting that ATXF may have a certain effect on the microenvironment of liver cancer.Although some studies have found that ATXF have immunomodulatory effects, they can regulate intracellular T lymphocyte immune factors and serum IL-12 and IFN-γ[4,27], the correlation between IL-6 and TNF-α and Huatongxiao granules in the prevention and treatment of liver cancer needs to be confirmed by experiments.Abnormal intracellular metabolism and signal transduction, resulting in abnormal cell proliferation and apoptosis, are the main mechanisms of cell carcinogenesis.Targeted regulation of these key signal molecules can effectively reverse,delay or even block the occurrence and development of cancer[28].Combined with the core target screening results of PPI network, it is not difficult to find that ATXF can target phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)/Protein kinase B (PI3K).Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mammalian target of rapamycin, the mTOR pathway,Extracellular signal-related kinase (EKR) pathway, p53 pathway and other signal pathway core proteins further reveal the molecular mechanism of HCC prevention and treatment.However, the material basis of “clearing heat and detoxifying”, “dissipating blood stasis and dispersing Jie” and “activating qi and relieving pain” of ATXF,the functional characteristics of monarch medicine and minister medicine and the relationship between them still need in-depth and systematic research.Preliminary results of this study showed that Uhtongxiao granules had regulatory effects on the expression and activation of AKT, ERK and p53 in transplanted rat tumors,suggesting that the above molecules and their related signaling pathways played an important role in the anti-liver cancer effects of Uhtongxiao granules.However, the specific substance composition and how to play the regulatory role need to be further systematically studied.
In summary, the potential targets for preventing and treating liver cancer with TAXF were obtained by network pharmacological analysis and screening in this study, and some core targets were verified by rat tumor transplantation experiments.The results of this study indicate that the PI3K/AKT, p53 and ERK1/2 pathways play an important role in the tumor inhibition of Huatongxiao granules,while the internal relationship between the effective targets and the specific signal transduction mechanism need to be further studied.This study provides a reference for the material basis and specific mechanism of the prevention and treatment of liver cancer, and also has certain guiding significance for the subsequent research.
Authors’ contribution
Liu Huan, Wei Yanfei, Liu Xian: Experimental design, paper writing and animal modeling; Jin Lijie, Liu Shasha: Experiment and data analysis
Conflict of interest
All authors of this article declare no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Assessment of gastric cancer prognosis, immune infiltration based on cuproptosis-related LncRNAs and prediction of traditional Chinese medicine
- The effect and mechanism of stilbene glycosides on improving neuronal injury in Alzheimer's disease rats by regulating ASK/MKK7/JNK pathway
- Meta-analysis of the acupoint application therapy for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Preparation of adhesive resveratrol micelles and determination of drug content
- BMSCs transplantation inhibits neuronal apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats through activation of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway-mediated autophagy
- Research progress of necroptosis and ferroptosis in knee osteoarthritis
