Preparation of adhesive resveratrol micelles and determination of drug content
2024-01-22HUXueYUJiaqiGANLuWANGJiayaoWANGShunfengLIUYanGAOYanan
HU Xue, YU Jia-qi, GAN Lu, WANG Jia-yao, WANG Shun-feng, LIU Yan✉ , GAO Ya-nan✉
1.Key Laboratory of Tropical Translational Medicine Ministry of Education/ Key Laboratory of Tropical Medicinal Plant Development, Hainan Province/ Pharmaceutical Institute of Hainan Medical College, Haikou 571199, China
2.The First Clinical College of Hainan Medical College, Haikou 571199, China)
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1.Introduction
Resveratrol (RES) is a polyphenolic stilbene compound, a fatsoluble compound that is almost insoluble in water.It was first isolated from Platycodon grandiflorum by Takaoka in 1939[1].RES has two structures (cis and trans).In nature, it mainly exists in trans conformation (type).The structure is shown in Fig.1.Trans resveratrol is easily converted into cis configuration under light[2].RES is mainly distributed in grapes, mulberry, blueberry,peanuts and other plants[3-5].It has a variety of pharmacological activities and has been widely studied in aging, cancer,inflammation, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and improvement of neurodegenerative diseases[6-8].RES has high safety.Rats were orally administered at a dose of 200 mg·kg-1·d-1, and beagles were orally administered at a concentration of 600 mg·kg-1·d-1for 90 d.No adverse effects were found[9-12].The water solubility and stability of RES are poor, and the liver metabolism is faster, which makes the bioavailability of the drug itself in the human body lower[13,14].Therefore, it is of great theoretical and practical significance to design a drug delivery system with high drug loading, good stability and high bioavailability to improve its druggability.
Polymeric micelles are a nanoscale drug delivery system.Polymers exist in the form of single molecules in the solution, and can be automatically assembled into micelles when the critical micelle concentration (CMC) is above.The internal lipophilic region can carry hydrophobic drugs, and the external is a hydrophilic corona shell, which can isolate the drug from the external medium[15].
The external hydrophilic structure of the micelles can be functionalized by different groups, such as grafted folic acid(FOL), monoclonal antibody (mAb) and monosaccharides(mannose, glucose, fructose), mitochondria and hormones, to achieve active targeting or pH / temperature / light response of the formulation[16,17].Compared with micelles made of low molecular weight surfactants, polymer micelles have lower CMC and higher stability, which can load drugs with lower stability and increase the stability of drugs.The size of the polymeric micelles is between 10~200 nm, which can prevent the premature exclusion of drugs through glomerular filtration, and can enter the blood vessels and increase the cellular uptake of drugs[18].The hydrophilicity and stability of polymer micelles can improve the bioavailability of drugs, improve the in vivo distribution of drugs, and reduce toxic and side effects[19].
Under certain circumstances, such as subcutaneous implant administration, vaginal administration, wound repair smear administration, tissue engineering injection administration, etc.,increasing the adhesion of the preparation can increase the drug retention at the lesion site, prolong the drug action time, continue to play a therapeutic role and improve bioavailability.The pH-sensitive/ membrane-viscosity polymer micelles prepared by Hu Wenxiao have good adhesion.Through the dual effects of pH sensitivity and intestinal mucosal adhesion, the controlled release of drugs is achieved and the residence time of micelles in vivo is increased[20].The micelles prepared by Mahmood et al.can adhere to the vaginal mucosa, and the adhesion degree is 56.1 times higher than that of the adhesive micelles[21].The high viscosity liposomes prepared by Mao et al.greatly increased the residence time of the preparation at the flap[22].Therefore, the design of polymer micelles with good tissue adhesion has certain application value.
The bioadhesion performance of catechol structure is better.Researchers often use catechol structure to modify polymers to improve their adhesion.Mao et al.prepared liposomes using dopamine-modified DSPE-PEG ( DSPE-PEG-DOPA ) with good adhesion[23]; moreira et al.prepared a film agent using dopaminemodified hyaluronic acid with high adhesion and rigidity[21];pinnaratip et al.modified silicon nanoparticles by PEG-DOPA also had good adhesion[24].In addition, it has been reported that monoglyceride-modified polymer-lipid nanoparticles can increase their hydrophilicity.By changing the amount of monoglycerides, a single regulation of the surface hydrophobicity of nanoparticles can be achieved, thereby increasing their tissue adhesion[23].
In this experiment, the main micellar excipients for preparing RES micelles were screened by investigating the adhesion of pluronic F127, polyether P123 and polyether F68, and then the excipients with better adhesion were optimized by modifying DSPE-PEGDOPA or glyceryl monolinoleate.Finally, RES polymer micelles(RES-M) with better adhesion properties were obtained, and the methodology of content determination of the optimal preparation was investigated.
2.Instruments and reagents
2.1 Instruments
UltiMate 3 000 High Performance Liquid Chromatograph( Symmer Fisher Technology Co., Ltd.), XPS Fluorescence Microplate Reader ( Meigu Molecular Instruments Co., Ltd.), GB/ T23111 Analytical Balance ( METTLER TOLEDO Instruments Shanghai Co., Ltd.), SB-1300 Rotary Evaporator ( Tokyo, Japan ),SHI-DIII Circulating Water Multi-purpose Vacuum Pump ( Shanghai Lichen Bangxi Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.), DLSB-5L / 40 Low Temperature Cooling Liquid Circulation Pump ( Gongyi Yuhua Instrument Co., Ltd.).DZF-6053 vacuum drying box (Shanghai Yiheng Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.), KQ5200 DE numerical control ultrasonic cleaner (Kunshan Ultrasonic Instrument Co., Ltd.).
2.2 Test drug
Polyether L65 (molecular weight 3 600 ~ 3 700, Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.); polyethylene glycol-blockpolypropylene glycol-block-polyethylene glycol P123 (molecular weight ~ 5 800, Annage Chemical); pluronic F127 (SIGMA);glycerol monolinoleate (GML, Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); dSPE-PEG 2K-DOPA ( Xi ‘an Ruixi Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.); resveratrol (Shanghai Yien Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.),methanol (chromatographic grade, TEDIA, USA), TritonX-100 (BioFroxx GmbH).
2.3 Method
2.3.1 Preparation of polymeric micelles
RES-M was prepared by thin film dispersion method.Adhesive excipients (DSPE-PEG-DOPA, glyceryl monolinoleate) and RES were added to the micelle excipients (F127, P123, L65), and were accurately weighed and placed in an eggplant-shaped bottle.Methanol was added to dissolve.Methanol was removed by vacuum evaporation using a rotary evaporator (rotation speed of 60 rpm,temperature of 45 ℃, time of 30 min).And placed in a vacuum drying oven to remove the organic solvent (temperature of 45 ℃, time of 2 h) to obtain a transparent semi-solid film.10 mL of ultrapure water was added to the film-forming eggplant-shaped bottle, and the water was continuously hydrated at atmospheric pressure with a rotary evaporator (rotation speed of 60 rpm,temperature of 45 ℃, time of 45 min).The obtained liquid was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter membrane and loaded into a Xilin bottle to obtain RES-M.In the adhesion test, RES was replaced with coumarin-6, and the micelles were prepared according to the above method.
2.3.2 Screening of adhesive micellar excipients
The polylysine orifice plate experiment was used to screen the micellar excipients with good adhesion.Coumarin-6-loaded micelles were prepared by F127, P123 and L65, respectively.Each 500 μL was added to a polylysine-coated 24-well plate and placed in the dark for 30 min.After discarding the micelles in the orifice plate, PBS was washed three times to remove the non-adherent fluorescent micelles.Subsequently, 1 mL of methanol was added to the orifice plate to dissolve the fluorescent micelles adhered to the polylysine orifice plate.The fluorescence value (excitation light 470 nm, emission light 513 nm) was measured by XPS fluorescence microplate reader after shaking in dark for 10 min.
2.3.3 Screening of excipients for enhancing micelle adhesion
According to the references, DSPE-PEG-DOPA and glyceryl monolinoleate were selected as adhesion-enhancing excipients to prepare micelles[23, 26, 27].The amount of adhesion-enhancing excipients added in the preparation of fluorescent micelles was 3.5% of F127, and the other preparation steps were the same as ‘1.3.1 Preparation of polymer micelles‘.Similarly, the polylysine orifice plate experiment was also used to screen the micelle adhesion enhancement excipients with better effect.The experimental steps were the same as ‘1.3.2 Adhesion into the screening of micelle excipients’.
2.3.4 Myocardial tissue adhesion experiment
Due to the biological adhesion characteristics of dopamine structure in a large number of literatures, the accuracy of the above results was confirmed by increasing the adhesion experiment of myocardial tissue.Rabbits were killed by ear vein injection of air, and the heart was removed by thoracotomy.The myocardial tissue was cut into small pieces with an area of about 0.8 ~ 0.9 cm2and a weight of about 3.3 g, and placed in normal saline.The myocardial tissue was placed in a 24-well plate, added with F127 micelles or F127 +DSPE-PEG-DOPA micelles, and placed in closed light for 30 min and 60 min.The tissue was removed and PBS gently washed the surface of the non-adherent micelles.The fluorescence intensity was measured in a small animal imager (emission wavelength of 520 nm,excitation wavelength of 470 nm).
2.3.5 Establishment of a method for the determination of RES micelle content
1) Chromatographic conditions
Chromatographic column: Shiseido SPOLAR C18 column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm); mobile phase: methanol-water (42: 58, v:v); flow rate: 1.0 mL·min-1; detection wavelength: 305 nm; column temperature: 35 ℃; injection volume: 10 μL.
2) Preparation of solution
(1) Preparation of reference solution
RES 0.0360 g was accurately weighed, placed in a 10 mL volumetric flask, and dissolved in 80 % methanol aqueous solution.The 0.2 mL of the above solution was accurately removed and placed in a 10 mL volumetric flask, and the constant volume was obtained to obtain the reference solution.
(2) Preparation of the sample solution
The RES micelle solution 0.2 mL was placed in a volumetric flask, 7 ~ 8 mL of 80 % methanol aqueous solution was added, and the ultrasonic time was 10 min (160 W, 40 Hz).After being placed at room temperature and constant volume, the test solution was obtained.
2.3.6 Specificity experiment
The three solutions prepared under 3.3.2 were filtered with 0.22 μm microporous membrane, and 10 μL was injected into HPLC.According to the chromatographic conditions of ‘1.3.5’, the chromatograms of RES reference substance, RES-M and blank micelle solution were obtained, and the influence of excipients on the determination of RES content was investigated.
2.3.7 Investigation of linear relationship
0.0250 g of RES was accurately weighed and placed in a 25 mL volumetric flask.It was dissolved in 80 % methanol aqueous solution and diluted to a constant volume.After shaking well, it was used as a stock solution (1 mg/mL).The stock solution 2 mL,1.5 mL, 1 mL, 0.5 mL, 0.25 mL, and 0.1 mL were placed in a 10 mL volumetric flask, and diluted with 80 % methanol aqueous solution to obtain solutions with RES concentrations of 200 μg/mL, 150 μg/ mL, 100 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, 25 μg/mL, and 10 μg/mL.Filtered by 0.22 μm filter membrane, the samples were injected in turn according to the chromatographic conditions of 1.3.5, and the peak area was measured.The peak area (A) was used as the ordinate and the sample concentration (C) was used as the abscissa for linear regression to obtain the regression equation.
2.3.8 Precision test
RES stock solution 0.25 mL, 1 mL, 1.5 mL were placed in a 10 mL volumetric flask, and constant volume with 80 % methanol aqueous solution to prepare low, medium and high (25 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL,150 μg/mL) three concentrations of RES solution.The RES solution was measured every two hours within one day, three times a day,and three days in a row.The relative standard deviation (RSD) was calculated, and the intra-day and inter-day precisions were obtained.
2.3.9 Recovery test
The reference stock solution (1 mg/mL) of 2.88 mL, 3.60 mL and 4.32 mL were accurately drawn and placed in a 10 mL volumetric flask (3 parts per concentration).1 mL blank micelle solution was added to 10 mL, and the appropriate amount was diluted with 80 %methanol aqueous solution.The filtrate was filtered by 0.22 μm filter membrane and the filtrate was taken into HPLC.The recovery rate(%) was calculated according to the peak area.
2.3.10 Stability test
An appropriate amount of test solution was accurately absorbed and placed in a cool and dark place.The above solutions were determined by HPLC at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24 h, respectively.The peak area was recorded and the RSD value was calculated to investigate the stability of the test solution within the day.
2.3.11 Determination of sample content Three batches of micelle samples were taken and the test solution was prepared according to the method under ‘1.3.5’.The test solution was determined according to the established chromatographic conditions, the peak area was recorded and the drug content in the sample was calculated.
3.Results
3.1 Screening of adhesive RES-M
In the previous work of the research group, F127, P123 and L65 were selected as micelle excipients with good encapsulation efficiency and drug loading of RES 27.The polylysine orifice plate adhesion screening test results of fluorescent micelles prepared with F127, P123, and L65 as micellar excipients are shown in Figure 1.It can be seen from the results that the micelle adhesion prepared with F127 as an excipient is relatively good, so F127 is selected for subsequent experimental research.F127, P23 and L65 are all amphoteric triblock polymers formed by ethoxy-propoxy groups with molecular weights of about 12 000, 5 800 and 3 500.The size of adhesion may be related to the molecular weight of the material,and the excipients with larger molecular weight have better adhesion.Generally speaking, surfactants with similar structure and small molecular weight have strong surface activity, strong lubricity and poor adhesion.
The experimental results of screening excipients for enhancing the adhesion of micelles are shown in Figure 1.It can be seen from the results that the addition of DSPE-PEG-DOPA or GML will reduce the adhesion of the preparation.Dopamine (DOPA) is a common bioadhesive substance[24, 25, 27].The decrease in micelle adhesion may be due to the DSPE-PEG segment in the DSPE-PEG-DOPA structural formula.The average molecular weight of the DSPEPEG segment is about 2 750, which is much lower than the average molecular weight of F127, which is consistent with the law that the adhesion obtained under ‘2.1’ decreases with the decrease of molecular weight.GML improves the adhesion by increasing the hydrophobicity of the particle surface[23].In this experiment, GML did not play a role in improving the adhesion of the particles, which may be due to the fact that the main hydrophobic segment of GML was wrapped in the micelle core and could not contact with the tissue or mucosa.

Fig 1 Screening of micellar excipients
3.2 Myocardial tissue adhesion experiment
The results of myocardial tissue adhesion experiment are shown in Figure 2.It can be seen from the experimental results that the fluorescence intensity of F127 micelles on tissues was higher than that of F127 + DSPE-PEG-DOPA micelles, indicating that the addition of DSP-PEG-DOPA did not improve the adhesion of micelles, which was consistent with the results of the above polylysine pore plate experiment.Therefore, this experiment finally determined to use F127 as an auxiliary material to prepare micelles for subsequent research.
3.3 Specificity experiment
The peak time of RES was about 4.5 min.Under this chromatographic condition, the excipients had no effect on determination of RES, and the method had good specificity.The results are shown in Figure 3.
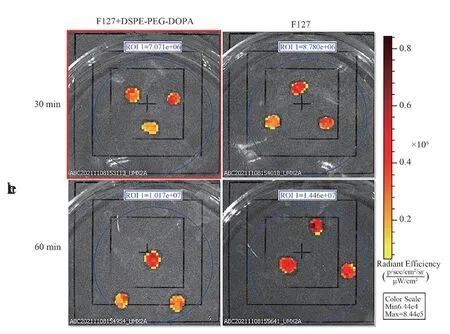
Fig 2 Experimental results of tissue adhesion of F127 micelles and F127 +DSPE-PEG-DOPA micelles
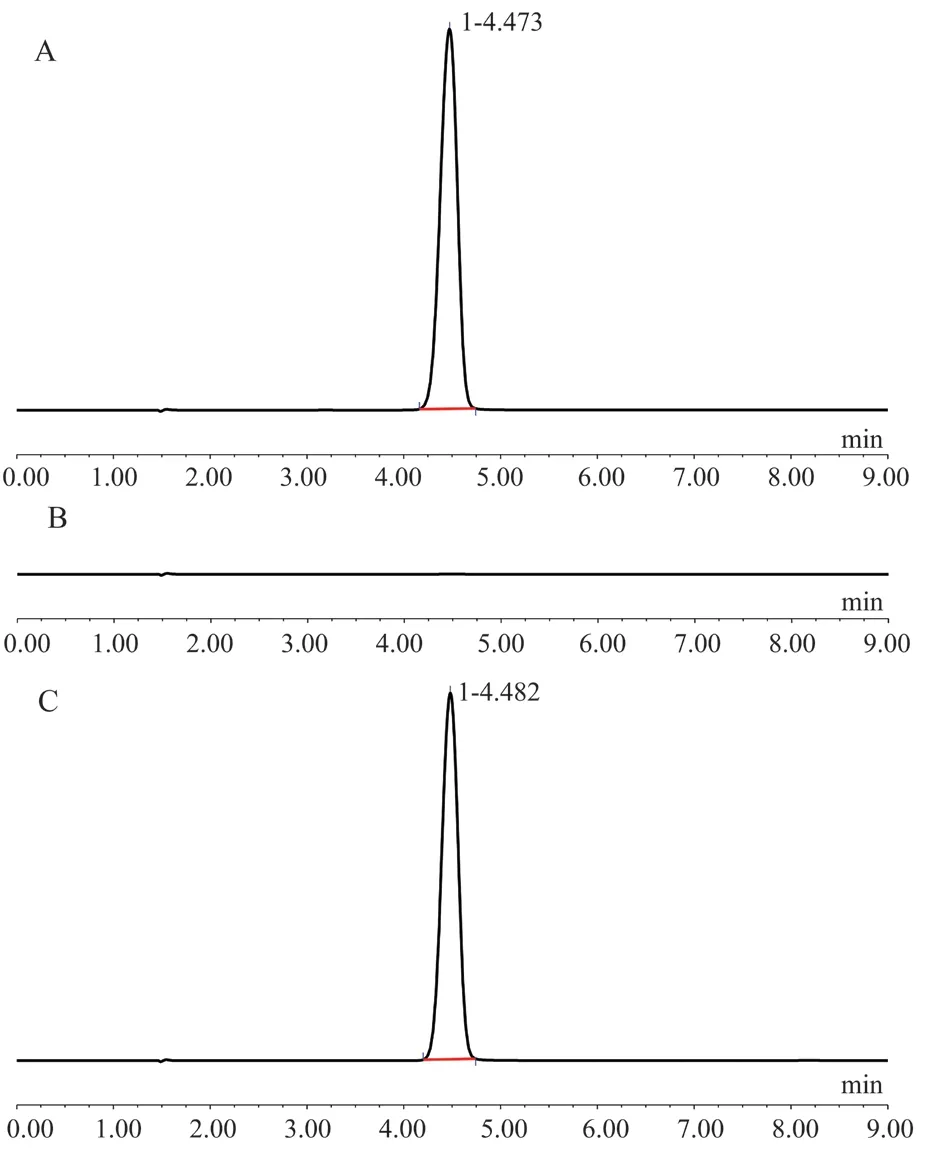
Fig 3 HPLC specific chromatogram
3.4 Investigation of linear relationship
According to the chromatographic conditions of 1.3.5, the peak area was measured.The linear regression was performed with the peak area (A) as the ordinate and the sample concentration (C) as the abscissa.The regression equation was A = 1.2999C-0.773, and the correlation coefficient r = 0.9996, indicating that the peak area and concentration of RES had a good linear relationship in the concentration range of 10 μg/mL~200 μg/mL.
3.5 Precision test
The results of intra-day and inter-day precision are shown in Table 1.The intra-day precision and inter-day precision of RES solution with low, medium and high concentrations were less than 2 %, which met the requirements of the content determination and analysis method.
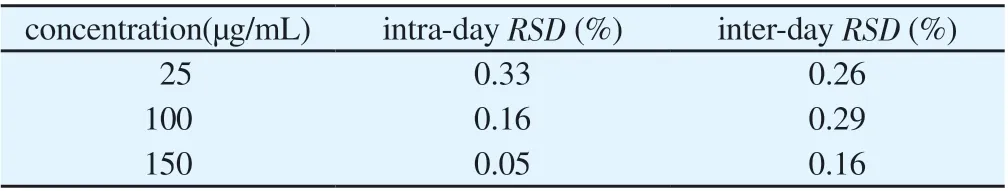
Tab 1 Intra-day precision and inter-day precision test results
3.6 Recovery test
The average recovery of low, medium and high concentrations of drug solution was 100.03 %, and RSD was 0.81 % (n=9).The results show that the established method has high accuracy and meets the requirements of RES content determination.
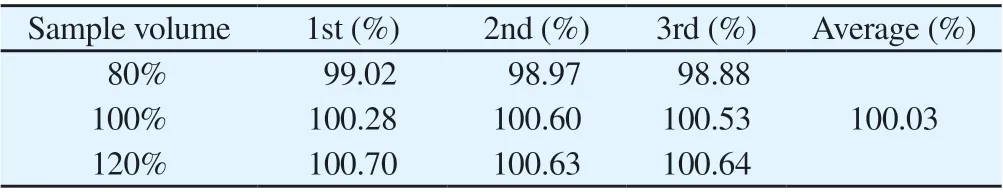
Tab 2 Sample recovery test results
3.7 Stability test
The peak area of the samples at each time point was shown in Table 3, and the RSD was 0.72 % (n=7).The results showed that the RES solution was stable within 24 h.

Tab 3 Stability test results
3.8 Determination of sample content
The drug loading concentration of RES-M was (3.55 ± 0.08) mg·mL-1.The method was accurate and simple, and the results are shown in Table 4.
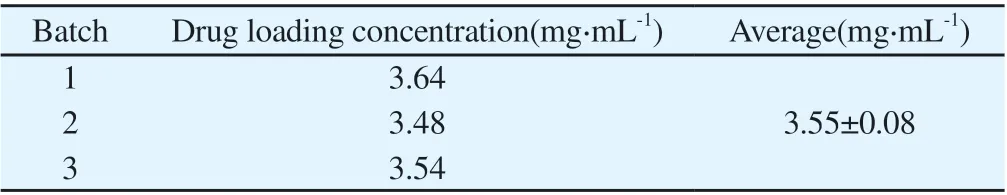
Tab 4 Sample content determination results
4.Discussions
4.1 Selection of micelle excipients and adhesion enhancement excipients
In the preliminary preparation work, F127, P123 and L65 were selected to have higher encapsulation efficiency and drug loading of RES[27].Therefore, the adhesion of RES-M prepared by these three micellar excipients was evaluated.The size of the adhesion may be related to the molecular weight of the substance.The molecular weight of F127, P23 and L65 decreased in turn, and the corresponding micelle adhesion size also decreased in turn.Finally, F127 was selected as a micellar excipient for subsequent experiments.Subsequently, DSPE-PEG-DOPA and GML were screened to investigate the ability of micelle adhesion enhancement.Studies have shown that both DSPE-PEG-DOPA and GML can increase the adhesion of organisms[23,24], but the experimental results show that after adding DSPE-PEG-DOPA or GML, the adhesion of micelles did not increase.The reason may be that the molecular weight of F127 is larger.DSPE-PEG-DOPA and GML are wrapped inside the micelles and cannot exert adhesion.Therefore, F127 is finally determined as a micelle excipient for RES.
4.2 Screening of chromatographic conditions
According to the references, methanol-water system and acetonitrile-water system were selected.The results showed that both methanol-water system and acetonitrile-water system could quickly elute RES.In order to save costs, a cheaper methanol-water system was selected.The peaks of RES in different ratios of organic phase and aqueous phase (60:40,45:55,35:65,40:60,42:58) were investigated.The results showed that when the ratio of methanol to water was 42:58, the peak time was suitable (about 4.5 min) and the peak type was better.
4.3 Investigation of demulsifier
The demulsification effects of methanol, 80 % methanol aqueous solution, 70 % methanol aqueous solution, 60 % methanol aqueous solution, 50 % methanol aqueous solution, 42 % methanol aqueous solution and 42 % methanol aqueous solution containing 0.2 %TritonX-100 were investigated.The results show that with methanol as demulsifier, the peak front is more serious and the symmetry is poor.Using the other several demulsifiers, the RES peak type is good.In order to make RES-M fully demulsify, and the operation is simple, cost savings, the final choice of 80 % methanol aqueous solution as demulsifier.
In this study, RES-M with excellent adhesion properties was successfully screened by polylysine pore plate experiment and small animal imaging experiment, which was expected to prolong the residence time of drugs in specific tissue areas.The HPLC method was successfully established to determine the content of drugs in RES-M.The method is rapid, accurate, specific and precise,which can provide a reliable means for the quality control of the preparation.
Statement: All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Assessment of gastric cancer prognosis, immune infiltration based on cuproptosis-related LncRNAs and prediction of traditional Chinese medicine
- Mechanism of AiTongXiao granule in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma based on network pharmacology and rat transplanted liver cancer model
- The effect and mechanism of stilbene glycosides on improving neuronal injury in Alzheimer's disease rats by regulating ASK/MKK7/JNK pathway
- Meta-analysis of the acupoint application therapy for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- BMSCs transplantation inhibits neuronal apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats through activation of AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway-mediated autophagy
- Research progress of necroptosis and ferroptosis in knee osteoarthritis
