基于压缩感知的低复杂度广义空移键控信号检测算法
2024-01-09张新贺谭浩然吕文博
张新贺,谭浩然,吕文博
基于压缩感知的低复杂度广义空移键控信号检测算法
张新贺*,谭浩然,吕文博
(辽宁科技大学 电子与信息工程学院,辽宁 鞍山 114051)(∗通信作者电子邮箱527075114@qq.com)
广义空移键控(GSSK)作为空间调制(SM)的一种简化形式,被广泛应用于大规模多输入多输出(MIMO)系统,以更好地解决传统MIMO技术中的信道间干扰(ICI)、天线间同步(IAS)和多射频(RF)链路等问题。针对GSSK系统最大似然(ML)检测算法计算复杂度高的问题,结合压缩感知(CS)中的子空间追踪(SP)算法和ML检测算法,并结合阈值的设置,提出一种基于CS理论的低复杂度GSSK信号检测算法。首先,用改进的SP算法获得部分发送天线组合(TAC);其次,删除部分天线组合,缩小搜索天线组合的集合;最后,利用ML算法和预设的门限估计发送天线组合。仿真实验结果表明,所提算法的计算复杂度明显低于ML检测算法,同时误比特率(BER)性能逼近ML检测算法,验证了所提算法的有效性。
广义空移键控;多输入多输出;压缩感知;子空间追踪;最大似然检测
0 引言
空间调制(Spatial Modulation, SM)技术[1-6]是一种全新的多天线传输技术,它同时利用空间星座图和信号星座图传递信息,且在每一传输时隙只激活一根发送天线,解决了传统多输入多输出(Multiple-Input Multiple-Output, MIMO)系统存在的信道间干扰(Inter-Channel Interference, ICI)、天线间同步(Inter-Antenna Synchronization, IAS)和多射频(Radio Frequency, RF)链路等问题。为了进一步充分利用信道的空间资源,文献[7-9]中提出了只利用空间星座图传递信息的空移键控(Space Shift Keying, SSK)技术,有效地降低了接收端的检测复杂度。广义SM(Generalized SM, GSM)技术[10-11]和广义SSK(Generalized SSK, GSSK)技术[12-15]打破了SM和SSK技术每一传输时隙只激活一根发送天线的限制,提高了传输速率。对于GSSK技术,最大似然(Maximum Likelihood, ML)检测算法是最优检测算法,它需要遍历所有的发送天线组合[16],缺点是复杂度会随发送天线组合(Transmit Antenna Combination, TAC)数呈指数增长,在大规模传输中的计算复杂度较高甚至无法实现。
为了进一步提高算法的检测性能,本文提出了一种基于CS理论的低复杂度的检测算法,记作SP-ML算法。首先SP算法通过迭代确定最有可能的一些天线序号,并仅保留一半天线;其次从所有天线组合中选择包含这一半天线的组合;最后在这些组合中进行ML检测并结合阈值的设置,恢复原始信号。
本文的主要工作如下:1)使用改进的SP算法选择最可能的发送天线序号;2)通过缩小发送天线序号集合,降低算法的计算复杂度;3)通过预设门限值和ML检测,在误比特率(Bit Error Rate, BER)性能和计算复杂度间进行折中。
1 GSSK系统模型及CS原理
1.1 GSSK系统模型
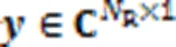
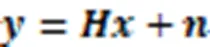
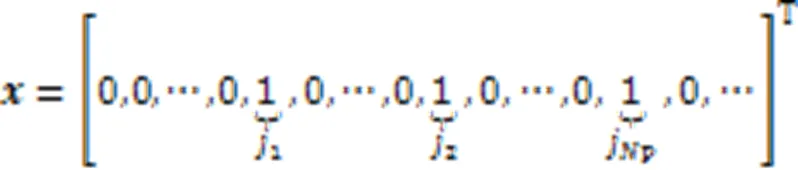
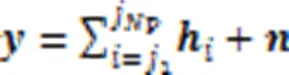
1.2 CS理论
由于GSSK系统中发送信号矢量具有稀疏特性,因此可以用CS理论解决接收端信号的重构问题。
CS理论的示意图如图1所示。
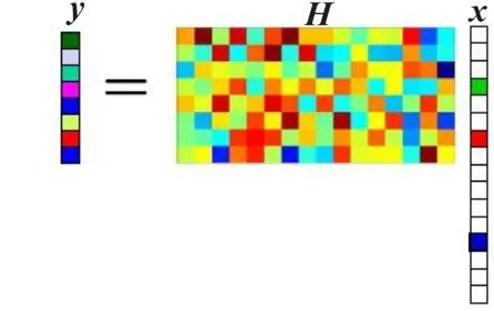
图1 CS理论的示意图
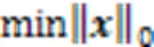
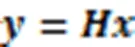
由于实际中存在一定的误差,因此可将该优化问题转换成一种近似形式进行求解:
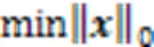
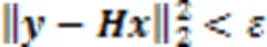
2 GSSK检测算法
本章介绍几种主要的GSSK系统的信号检测算法。
2.1 ML算法
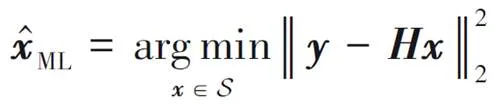
由于ML算法需要遍历所有可能的天线组合,该算法的计算复杂度随着天线组合数的增多而增大,特别是在大天线场景下,算法的计算复杂度就非常高。实际上,在接收端仅需检测发送天线的序号,因此ML算法可简化为:
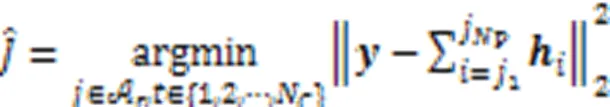
2.2 NCS算法
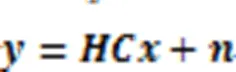
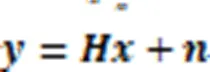
将式(9)实数化处理,得到:
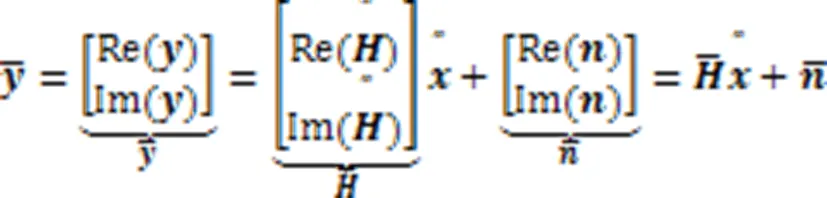
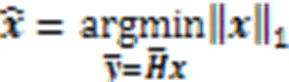
算法1为NCS算法恢复发送信号矢量的伪代码。
算法1 NCS算法。
3) end for
10) end for
2.3 SP算法
与NCS算法相比,SP算法[12]在每次迭代时保留的原子数多于1个。更重要地,SP算法引入了原子删除策略,可以在每次迭代时删除一部分原子。相较于NCS算法,SP算法不仅可以降低计算复杂度,同时还可以改善误比特率性能。SP算法的伪代码如算法2所示。
算法2 SP算法。
3) end for
14) end for
3 基于CS理论的低复杂度检测算法
相较于NCS算法,SP算法的检测性能有一定的提升,但是在计算复杂度和BER性能方面仍需要进行改进。本文提出一种基于CS理论的低复杂度检测算法,即SP算法和ML算法结合的SP-ML算法。
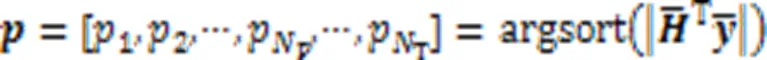
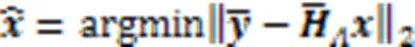
更新的残差可以通过式(14)获得:
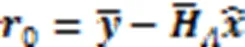
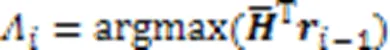
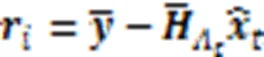
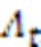
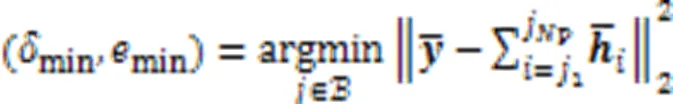
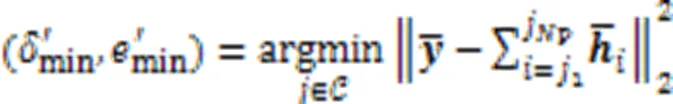
SP-ML算法可以使误比特率性能和复杂度之间达到一个良好的折中。SP-ML算法的伪代码如算法3所示。
算法3 SP-ML算法。
3) end for
16) end for
22) else
24) end if
27) else
29) end if
4 实验与结果分析
为了验证SP-ML算法的误比特率性能和计算复杂度,进行了一系列仿真实验。比较ML算法、NCS算法、SP算法和SP-ML算法的误比特率性能和计算复杂度。在理想信道状态信息的假设下,对误比特率性能和计算复杂度进行了仿真。
4.1 误比特率性能分析

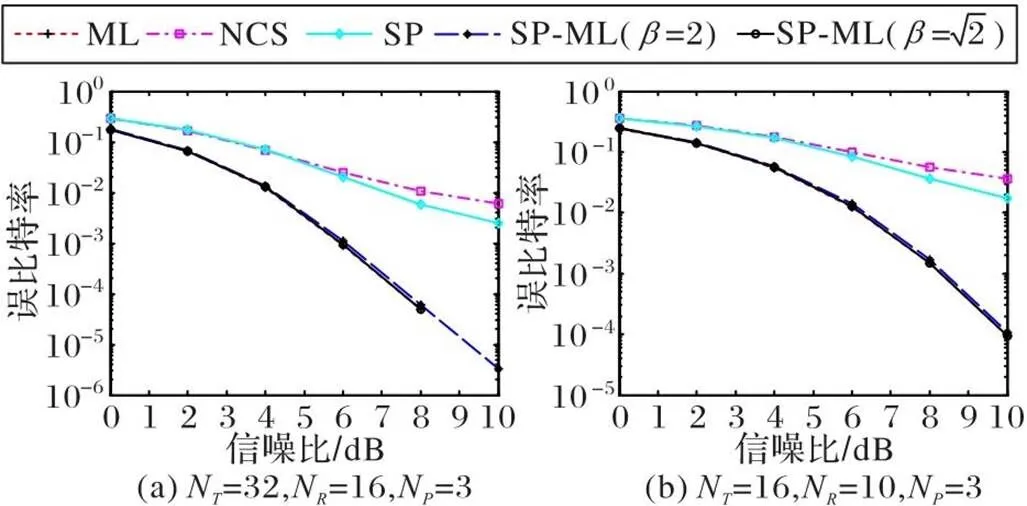
图2 SP-ML与ML、NCS算法的BER性能比较
4.2 计算复杂度分析
4.2.1ML算法
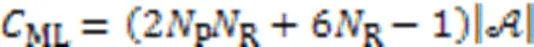
4.2.2NCS算法
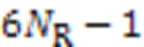
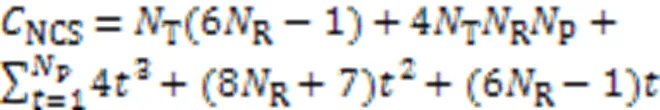
4.2.3SP算法
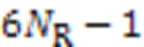
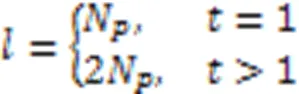

4.2.4SP-ML算法
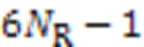
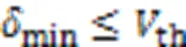
综上所述,SP-ML算法的复杂度可以表示为:
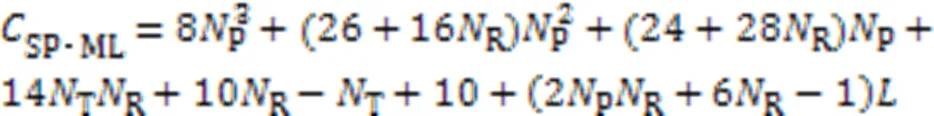
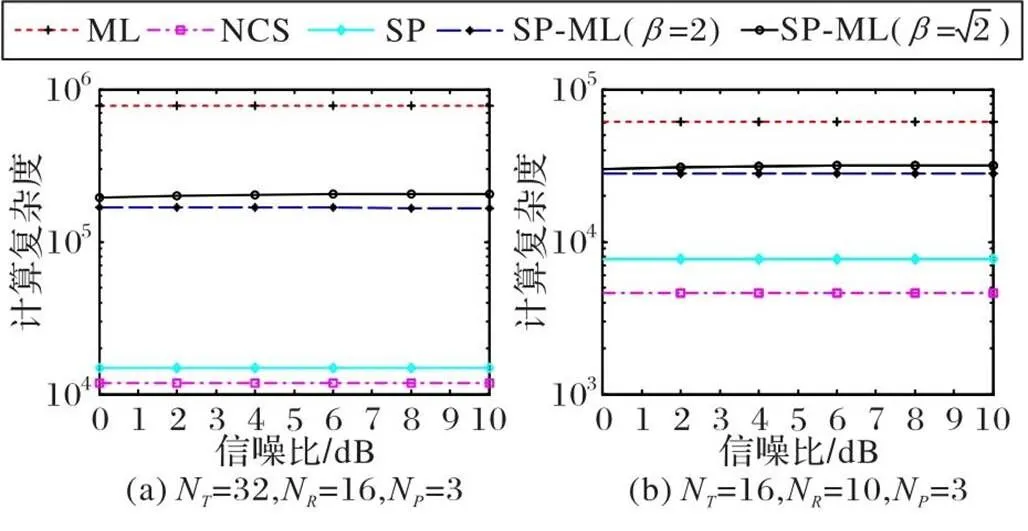
图3 SP-ML与ML、NCS算法的计算复杂度性能比较
5 结语
GSSK系统能够有效解决大规模MIMO中信道间干扰、天线间同步和多射频链路等问题,对大规模MIMO的实际应用和理论研究具有十分重要的意义。本文结合SP算法和ML算法,提出了一种基于CS理论的低复杂度的检测算法。该算法的误比特率性能明显优于SP算法和NCS算法。仿真结果表明,该算法能够在误比特率性能和复杂度之间取得较好的折中,可以实现与ML算法几乎相同的误比特率性能,而复杂度远低于ML算法。本文是基于CS理论的信号检测算法,并与几种常见的GSSK信号的CS算法进行了比较。作者将继续探索基于CS理论的GSSK信号检测算法,并与自适应检测等算法进行比较,并积极探索在复杂信道条件下的信号检测算法。
[1] MESLEH R Y, HAAS H, SINANOVIC S, et al. Spatial modulation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2008, 57(4): 2228-2241.
[2] JEGANATHAN J, GHRAYEB A, SZCZECINSKI L. Spatial modulation: optimal detection and performance analysis [J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2008, 12(8): 545-547.
[3] RENZO M D, HAAS H, GRANT P M. Spatial modulation for multiple-antenna wireless systems: a survey [J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2012, 49(12): 182-191.
[4] CHEN H, XIAO Y, FANG S, et al. Low-complexity transmit antenna selection for offset spatial modulation [J]. Science China: Information Sciences, 2022, 65(9): 249-262.
[5] YANG Y, BAI Z, PANG K, et al. Design and analysis of spatial modulation based orthogonal time frequency space system [J]. China Communications, 2021, 18(8): 209-223.
[6] LI Q, YU X, XIE M, et al. Performance analysis of uplink massive spatial modulation MIMO systems in transmit-correlated Rayleigh channels [J]. China Communications, 2021, 18(2): 27-39.
[7] JEGANATHAN J, GHRAYEB A, SZCZECINSKI L, et al. Space shift keying modulation for MIMO channels [J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2009, 8(7): 3692-3703.
[8] RENZO M D, HAAS H. Improving the performance of Space Shift Keying (SSK) modulation via opportunistic power allocation [J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2010, 14(6): 500-502.
[9] RENZO M D,HAAS H. A general framework for performance analysis of Space Shift Keying (SSK) modulation for MISO correlated Nakagami-fading channels [J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2010, 58(9): 2590-2603.
[10] RENZO M D, HAAS H, GHRAYEB A, et al. Spatial modulation for generalized MIMO: challenges, opportunities, and implementation [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2014, 102(1): 56-103.
[11] YANG P, RENZO M D, XIAO Y, et al. Design guideline for spatial modulation [J]. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2014, 17(1): 6-26.
[12] NTONTIN K, RENZO M D, PEREZ-NEIRA A, et al. Adaptive generalized space shift keying [J]. EURASIP Journal of Wireless Communications and Networking, 2013, 2013(1): 1-15.
[13] NTONTIN K, RENZO M D, PEREZ-NEIRA A, et al. Adaptive Generalized Space Shift Keying (GSSK) modulation for MISO channels: a new method for high diversity and coding gains [C]// Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall). Piscataway : IEEE, 2012: 3-6.
[14] LIU W, GU Z, JIN M L. Penalty function based detector for generalized space shift keying massive MIMO systems [J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(4): 664-667.
[15] ZHANG L, ZHU S, ZHANG L, et al. Low-complexity sparse detector for generalized space shift keying [J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(5): 268-270.
[16] JEGANATHAN J, GHRAYEB A, SZCZECINSKI L. Generalized space shift keying modulation for MIMO channels [C]// Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications. Piscataway: IEEE, 2008: 15-18.
[17] CHANG R Y, CHUNG W-H, LIN S-J. Detection of space shift keying signal in large MIMO systems [C]// Proceedings of the 2012 8th International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference. Piscataway: IEEE, 2012: 27-31.
[18] TROPP J A, GILBERT A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit [J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12): 4655-4666.
[19] YU C-M, HSIEH S-H, LIANG H-W, et al. Compressed sensing detector design for space shift keying in MIMO systems [J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2012, 16(10): 1556-1559.
[20] WANG J, KWON S, SHIM B. Generalized orthogonal matching pursuit [J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(12): 6202-6216.
[21] NEEDELL D, VERSHYNIN R. Signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements via regularized orthogonal matching pursuit [J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2): 310-316.
[22] NEEDELL D, TROPP J A. CoSaMP: iterative signal recovery form incomplete and inaccurate samples [J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2008, 26(3): 301-321.
[23] DAI W, MILENKOVIC Q. Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction [J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(5): 2230-2249.
[24] ZHANG X, TAN H, LV W. A low-complexity detection algorithm for generalized space shift keying systems [J]. IAENG International Journal of Computer Science, 2022, 49(2): 364-368.
[25] DOHONO D L. Compressed sensing [J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289-1306.
[26] CANDES E J, WALKIN M B. An introduction to compressive sampling [J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21-30.
[27] CANDES E J, ROMBERG J, TAO T. Robust uncertainty principle: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information [J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2): 489-509.
[28] 刘飞峰,刘鸿杰,缪颖杰,等.基于无网格压缩感知的通信一体化系统目标参数估计方法研究[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(11): 2076-2086.(LIU F F, LIU H J, MIAO Y J, et al. Research on target parameter estimation method of radar communication integrated system based on grid-less compression sensing [J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(11): 2076-2086.)
[29] XIAO L, YANG P, XIAO Y, et al. Efficient compressive sensing detectors for generalized spatial modulation systems [J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(2): 1284-1298.
Low-complexity generalized space shift keying signal detection algorithm based on compressed sensing
ZHANG Xinhe*, TAN Haoran, LYU Wenbo
(,,114051,)
As a simplified version of Spatial Modulation (SM), Generalized Space Shift Keying (GSSK) has been widely used in massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems. It can better solve the problems such as Inter-Channel Interference (ICI), Inter-Antenna Synchronization (IAS), and multiple Radio Frequency (RF) links in traditional MIMO technology. To solve the problem of high computational complexity of the Maximum Likelihood (ML) detection algorithm for GSSK systems, a low-complexity GSSK signal detection algorithm based on Compressed Sensing (CS) theory was proposed by combining Subspace Tracking (SP) and ML detection algorithms in CS, and presetting the threshold. First, the improved SP algorithm was used to obtain partial Transmit Antenna Combinations (TACs). Secondly, the set of search antennas was shrunk by deleting partial antenna combinations. Finally, the ML algorithm and the preset threshold were used to estimate the TACs. The results of simulation experiments show that the computational complexity of the proposed algorithm is significantly lower than that of ML detection algorithm, and the Bit Error Rate (BER) performance is almost the same as that of ML detection algorithm, which verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
Generalized Space Shift Keying (GSSK); Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO); Compressed Sensing (CS); Subspace Pursuit (SP); Maximum Likelihood (ML) detection
This work is partially supported by Higher Education Research Project of Liaoning Provincial Department (LJKZ0292).
ZHANG Xinhe, born in 1980, Ph. D., associate professor. His research interests include signal detection, compressed sensing.
TAN Haoran, born in 1997, M. S. candidate. Her research interests include wireless communication, compressed sensing.
LYU Wenbo, born in 1997, M. S. candidate. His research interests include signal detection, compressed sensing.
TN914
A
1001-9081(2023)12-3890-06
10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022121808
2022⁃12⁃18;
2023⁃03⁃28;
2023⁃03⁃29。
辽宁省教育厅高等学校科研项目(LJKZ0292)。
张新贺(1980—),男,河北承德人,副教授,博士,主要研究方向:无线通信、压缩感知;谭浩然(1997—),女,辽宁辽阳人,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:信号检测、压缩感知;吕文博(1997—),男,湖北荆门人,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:信号检测、压缩感知。
