The Systematic Regulation of "Impossible Trinity"for Cryptocurrency under the Theory of Risk Society*
2023-12-21ChengXuejun
Cheng Xuejun
(Law School, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China)
Abstract: Driven by the double drive of credit carriers and advanced technology, the currency has evolved from ancient commodity currency to past metal currency and further developed into legal currency and digital currency nowadays. Blockchain technology has rapidly emerged and driven the diversified development of digital currencies to break the regulatory failure of traditional legal currencies. Unlike legal digital currency backed by legal credit, non-legal digital currencies are referred to as cryptocurrencies due to their use of encryption technology and lack of legal credit.They can be further divided into private and stable digital currencies. Granted, the cryptocurrency driven by blockchain technology undoubtedly exhibits innovative enhancements. However, as an innovative financial product in an intelligent society, the cryptocurrency under the risk society theory also derives the "impossible trinity" risk. This implies that cryptocurrency cannot simultaneously achieve the goal of stable currency value, credit carrier, and decentralized supply, triggering legal, financial and technical risks. From modern financial regulation especially "twin peaks regulation" theory, implementing systematic regulation of cryptocurrency risks is the inevitable requirement for improving legal norms, the inherent requirement for preventing financial risks, and the objective requirement for protecting consumer rights. By conditionally drawing on the risk regulation experience of cryptocurrencies from developed countries outside the region and starting from legal, financial, and technical regulation levels, the systematic regulation of the risk of cryptocurrencies in China is comprehensively constructed.
Keywords: blockchain technology; cryptocurrency; impossible trinity; system risk; regulation system
1 Introduction
With the development of the credit system and advanced technology, the currency has been evolving in terms of credit carrier and technology. Currency develops its credit from individual credit (commodity currency) to enterprise credit (institutional currency) and further develops its credit from national credit (legal tender) to social consensus(cryptocurrency). In the aspect of carrier evolution, currency changes its technology from commodity currency to metal currency (smelting technology), paper currency (paper making technology) and cryptocurrency (digital technology). To prevent the financial risk caused by "subprime crisis", Satoshi Nakamoto (2008) put forward an electronic cash system,theoretically promoting cryptocurrency innovation by blockchain technology[1]. However, due to the relatively short development time of cryptocurrencies, there is currently no unified concept definition at present.
The European Central Bank (ECB) was the one of the first regulatory institutions to acknowledge cryptocurrency and classifying it as a virtual currency in its 2012 research report. The EBC believes that it is an unregulated cryptocurrency typically issued and controlled by developers, accepted and used by specific virtual community members[2]. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) defined cryptocurrency as a virtual currency based on distributed technology and decentralized payment institutions in its 2015 research report, and constructed "the money flower" classification according to the characteristics of issuance, manifestation, access permissions, and transmission characteristics[3]. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) believes that virtual currencies are digital expressions of value, including cryptocurrencies, certain asset backed currencies, and even airline miles[4]. Cryptocurrency is a virtual currency issued and traded by decentralized institutions through the use of encryption technology[5]. At the academic level, certain scholars(2013) regarded cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin as a "complementary currency"[6]. Furthermore, other scholars (2015)conducted in-depth analysis of cryptocurrencies in China examining various aspects of basic principles, currency characteristics and disputes, development and evolution, payment innovation, and legal governance[7]. Moreover, some scholars believe that cryptocurrency is not a true currency[8], and some scholars have analyzed the legal risks and regulatory challenges of stable digital currencies (Diem) from the perspective of legal regulation. While others discussed how regulatory authorities can respond to the development of stable digital currencies and elaborated on the regulatory path from blockchain, stable currency and regulatory sandbox[9]. It is evident that still some various definitions of cryptocurrency currently, but it is generally accepted that cryptocurrency refers to a type of digital currency, rather than physical currency such as paper currency and coins. It undertakes functions similar to physical currency and can support instant transactions and ownership transfer without geographical restrictions. From a conceptual perspective, digital currencies are divided into non-legal and legal cryptocurrencies based on national credit support, that is, whether they have national credit by legal factors. Among them, cryptocurrencies can be divided into two categories: ordinary cryptocurrencies represented by Bitcoin (BTC), Bitcoin Cash (BCH), and stable cryptocurrencies represented by USDT and Diem; legal cryptocurrencies can be divided into wholesale central bank digital currencies (Jasper project in Canada) and retail central bank digital currencies (e-CNY project in China) based on their intended use. This paper focuses on the controversial non-legal cryptocurrencies.
In terms of cryptocurrency risks, some scholars analyzed its risks from the cryptocurrency formation mechanism at the macro perspective, including price bubbles, financial crimes, and value fluctuations[10]. In contrast, others analyzed its risks from the cryptocurrency structure at the micro view, including platform risk[11], money laundering risk[12], data risk, and liquidity risk[13]. Still, they generally lack structural and correlation study to cryptocurrency risks. Admittedly,cryptocurrency brings so many related risks that it should reconstruct the financial regulation system[14]. Therefore,Some scholars demonstrate regulatory necessity from the legal requirements of cryptocurrency[15]; others believe that the direct regulation of a package of prohibitions on cryptocurrency may lead to regulation failure, they suggest cryptocurrency can adopt indirect regulation[16], regulatory sandbox[17]and so on. Nowadays, different countries have adopted a differentiated risk regulatory path for cryptocurrencies on the basis of blockchain technology application and risk prevention ability. The United Kingdom, the United States and South Korea has separately adopted laissez-faire regulation mode, risk prevention mode[18]and control mode. Therefore, by examining the system risk of cryptocurrency under the theory of risk society, this paper draws on the risk regulation experience in other developed law system countries,so as to explore the systematic regulation system of cryptocurrency in China from legal, financial and technical risk.
2 Risk Exploration: The "Impossible Trinity" Risk of Cryptocurrency in the Risk Society
2.1 Blockchain Technology Changes the Era of Risk Society
As the industrial revolution progresses, human society has transitioned from an agricultural society to an industrial society, consequently the natural risk of traditional agricultural society has also changed to the social risk of industrial society. Due to the change in social development and risk types, the mode of social regulation has shifted from emphasizing human regulation (rule by men) to legal regulation (rule of law). The main reason is that industrialized production emphasizes standardized order and rules, and legal regulation is the epitome of standardized order and rules.However, as Ulrich Beck said, today's society is on the volcano of civilization, and the theory of risk society is based on the discussion of capitalist industrial society. Based on blockchain and artificial intelligence, society has gradually transferred to an intelligent society, humans will connect and create through various technological means. The intelligent society that maps and interacts with real society may have a digital living space of a new social system. Its main social characteristics will evolve from industrial production to intelligent development, and its primary currency type will shift from traditional legal currency (paper currency, coins) to cryptocurrency. With the rapid growth and deep embedding of cryptocurrencies into various industries of the social economy, the risk types of intelligent society will break through the limitations of traditional social "natural risk-social risk", and its risk structure may evolve from a single dimensional natural risk (social risk) to a complex dimensional systemic risk.
In short, the risks faced by an intelligent society are the risks inherent in modernization, which are magnified on a large scale and systematically exacerbated by gloonal risk regulation model not based on information technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence may be difficult to predict the complicated dimensions of system risks in the intelligent society. Therefore, the theoretical basis of risk society is still applicable in blockchain and artificial intelligence technology and it needs to explore a model of systematic regulation (legal, technical, and financial regulation,etc.) from the blockchain technology and cryptocurrency (table 1).
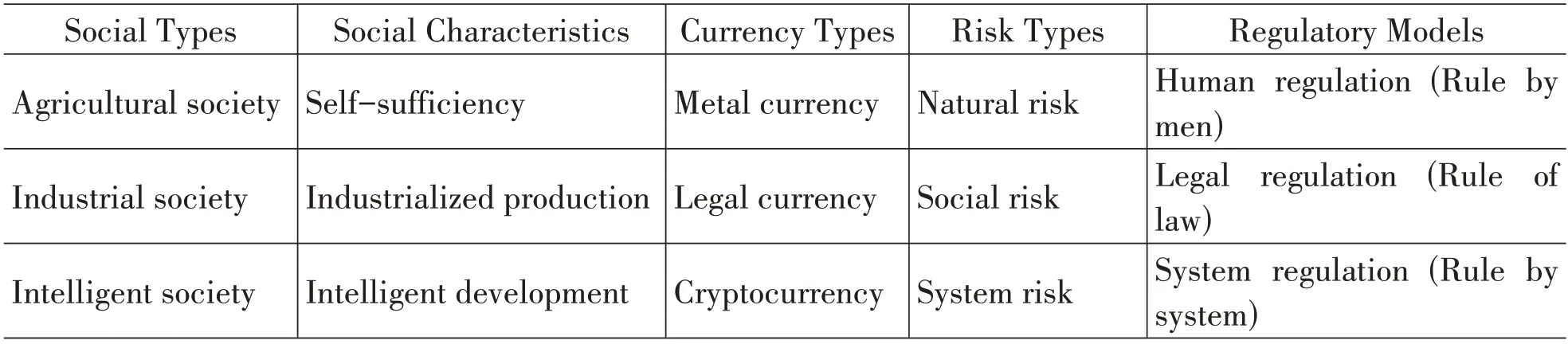
Table 1 Risk Types and Regulatory Models under Different Social Types
2.2 The Impossible Trinity Risk of Cryptocurrency under the Era of Risk Society
In the risk society, the impact of the currency game is that the central bank monopolizes the monetary power, but quantitative easing (QE) policies under the central bank's regulation failure lead to inflation and debt crisis, resulting in the national credit crisis for traditional legal tender. To solve the financial crisis, blockchain has been driving the cryptocurrency development, but a new challenge has emerged known as currency's "impossible trinity" (table 2),which means cryptocurrency cannot simultaneously accomplish currency stability, credit carrier and decentralized supply. It can achieve two goals at most for one country, if one country hopes to achieve currency stability and credit carrier, it will be difficult to accomplish decentralization; If one country hopes to achieve credit carrier and decentralization,it will be difficult to maintain currency stability; If one country hopes to achieve currency stability and decentralization,it will be difficult to accomplish credit carrier[19].
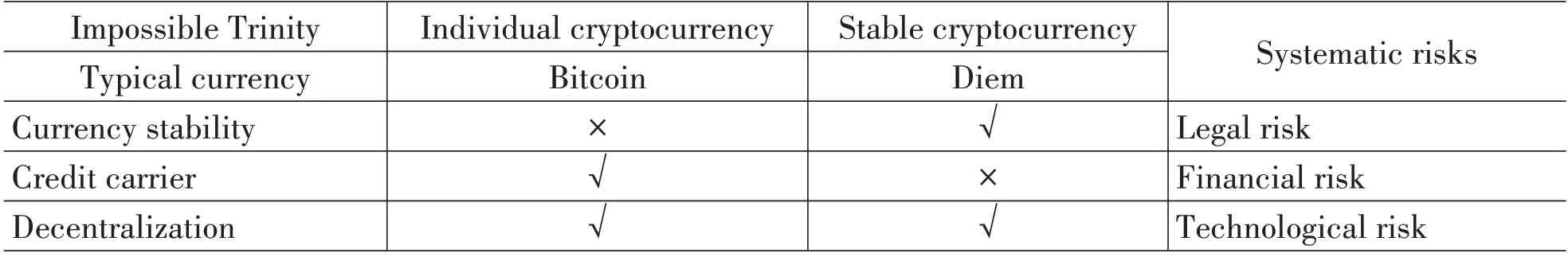
Table 2 The "Impossible Trinity" Risk of Cryptocurrency
Firstly, Blockchain is the technological foundation of cryptocurrencies, which is not the traditional currency. On the one hand, cryptocurrency is based on decentralized blockchain technology, and its essence is machine credit rather than national credit, which leads to poor currency stability. On the other hand, the lack of control and issuance of cryptocurrency by central institutions such as the central bank can impact its credibility, so that many cryptocurrencies (including Bitcoin, and Litecoin) exhibit significant price volatility. The price of Bitcoin has increased from 0 US dollars per coin in 2013 to 34650.60 US dollars per coin in October 2023, highlighting the inherent volatility of cryptocurrencies and the challenges they face in becoming a stable accounting unit. In addition, there is little correlation between the exchange rate of cryptocurrencies and legal tenders (such as US dollars, Euros and other foreign currencies), and there is little correlation between cryptocurrency's exchange rate and precious metals (such as gold and silver). Therefore, it becomes challenging for cryptocurrency to realize currency hedging, and it will bring some legal risk because it is not real currency based on national credit and guarantee.
Secondly, by applying blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies can construct credit carriers. Different from traditional currencies that assume the value scale, circulation means, payment means, and value storage, the credit carrier of cryptocurrency is not national credit but machine credit, so it will cause financial risk. Financial recession leads to financial products with a high rate of return for many investors. However, cryptocurrency can meet the needs of investors, so it is regarded as one of the important investment vehicles by most investors. For example, some e-commerce giant overseas accept Litecoin as an payment, but this acceptance is limited in some economies where Litecoin payment is accepted, and its payment function has not yet fully achieved. Furthermore, Litecoin has not demonstrated strong performance as a reliable measure of value and store of value. The primary reason for business operators and consumers to accept cryptocurrencies is that its charges are lower than the fee of credit card. Therefore, it is very necessary to strengthen the regulation of financial risks caused by cryptocurrency credit carriers.
Finally, cryptocurrencies have the characteristics of technological decentralization, because they adopt the monetary mechanism built by blockchain technology. Cryptocurrency is highly dependent on the algorithm and blockchain technology, it can be divided into traditional cryptocurrency, public cryptocurrency, stable cryptocurrency and managed cryptocurrency[20]. However, as an emerging technology with a relatively short history of development, blockchain technology still has many defects such as technical agnosticism, structural opacity, information asymmetry, spatial completeness, and management decentralization, so that cryptocurrency based on the decentralized blockchain has a lot of technological risk.
3 Theoretical Reflection: Why Implement Systematic Regulation of Cryptocurrency Risks
With the increasingly risky nature of modern digital society, risk regulation has become increasingly prominent,aiming to maintain financial market stability and protect financial consumers' rights. Since the 1990s, the financial liberalization theory has developed rapidly under "financial repression" and "financial deepening". It has been criticized due to the 1997, 2001, and 2007 financial crisis. Michael Taylor has proposed "twin peaks regulation", which focuses on strengthening the systemic financial risks prevention and the consumer rights protection, this regulation has increasingly become the direction of financial regulatory reform. Cryptocurrency can derive system risks because of its imperfect legal norms, high financial risks, and inadequate consumer rights protection. Based on modern financial regulatory theory, particularly the "twin peaks regulation" theory. The implementation of systematic regulation of cryptocurrency risk is deemed necessary. This is imperative as it fulfills the requirement for improving legal norms, the inherent requirement for preventing financial risk and the objective requirement for protecting consumer rights.
3.1 The Inevitable Requirement for Improving Legal Norms
Legal norms are the infrastructure for the stable operation of the financial system. The legal norms of cryptocurrency can be divided into horizontal transaction and vertical regulation relations. The former has a specific legal norms basis and can refer to civil and commercial law, includingthe Civil Code and Company Law of China. However, the latter has a severe problem of inadequate regulation norms, so it cannot effectively adjust the legal regulation relationship.Therefore, It is an inevitable requirement for improving legal norms to regulate cryptocurrency. Nowadays, China is still at the initial period in terms of the legal regulation of cryptocurrency and that the countries with written law systems have complex legislative procedures, relatively slow in the enactment of laws, with a specific time lag, the legal regulations of cryptocurrency is often at a loss due to the lack of rules.
At present, China adopts a cautious regulation to cryptocurrency and has enacted some legal norms. The Notice on Preventing Risks of Bitcoin has made clear legal provisions in five aspects: Correctly understanding the attributes of Bitcoin (Bitcoin is not currency but virtual commodity which cannot be circulated in the currency market, because it does not have the attributes of legal compensation and mandatory monetary). Financial institutions and payment institutions are not allowed to conduct business related to Bitcoin. Strengthening the management of Bitcoin internet websites. Preventing potential money laundering risks arising from Bitcoin. Strengthening education on public currency knowledge and investment risk warning. However, China defines Bitcoin trading as commodity trading, which affirms that natural persons and legal institutions can participate in Bitcoin trading autonomously according to their will. With the increasing trend of preventing financial risks and strengthening financial regulation, State financial regulatory agencies regards initial coin offerings (ICO) as illegal financing behaviour so that China stopped ICO. However, different from the regulation of non-legal cryptocurrency, China encourages the development of legal cryptocurrency, and has begun to steadily promote the pilot work of Local central bank digital currency (e-CNY), trying to effectively promote the digitalization, intelligence and internationalization of CNY. In conclusion, It is the inevitable requirement for improving legal norms so that China needs to implement systematic regulation.
3.2 The Inherent Requirement for Preventing Financial Risk
After the "subprime crisis" in 2008, more and more economies have realized the limitations of traditional "separate regulation" on modern financial innovation in the background of digital finance, and they have shifted from traditional financial technology to modern financial regulation, especially "twin peaks regulation", which was firstly proposed by Michael Taylor in the bank of England. He believed that financial regulation cannot accomplish triple goals at the same time, it can achieve two goals at most for financial regulation, so that the best solution is by twin peaks regulation to achieve two goals. The first goal is the system protection goal. Using macro and micro-prudential regulation,will separately prevent systemic financial risks and promote financial institutions' stable operation[21]. The second goal is the consumer protection goal, which includes prudential regulation of small and medium-sized institutions, operation behavior, and market behavior regulation. It will be helpful for correcting financial institutions' opportunism and protecting financial consumers by preventing unfair financial transactions in some economies.
Under the background of blockchain technology, why has China changed financial regulatory framework from the original "one central bank and three regulatory commissions" before 2013 to "one central bank, one state administration for financial regulation, and one regulatory commission" in 2023? Because China has begun to adopt "twin peaks regulation" (figure 1): One peak is central bank (The People's Bank of China), which is responsible for macro-prudential regulation, including systemic financial risk prevention and cryptocurrency issuance rights. The other peak is State Administration for Financial Regulation (SAFR) and China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), taking charge in micro-prudential regulation and consumer rights protection, including cryptocurrency operation rights. In 2023, the State Administration for Financial Regulation (SAFR) has established a unified system based on the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC), to take charge of financial regulation except for the security industry and strengthened institutional regulation, functional regulation, penetrating regulation and continuous regulation. The People's Bank of China's daily regulatory and consumer protection responsibilities for financial holding companies and other financial groups and the consumer protection responsibilities of CSRC are transferred to the SAFR. By establishing the SAFR, the institutional responsibilities in the field of financial regulation can be optimized and adjusted, which is very important for strengthening modern financial regulation and solving long-standing prominent contradictions and problems in the financial field. It is very good for regulating cryptocurrency.
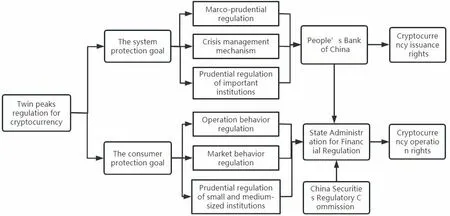
Figure 1 Twin Peaks Regulation for Cryptocurrency in Chinese Financial Regulatory Framework
3.3 The Objective Requirement for Protecting Consumer Rights
Unlike traditional digital currencies, cryptocurrencies have some innovative technical characteristics, including decentralization, anonymity, and tamper-resistance. Admittedly, cryptocurrency plays a constructive role in stimulating the digitalization of traditional currency. However, cryptocurrencies also bring some destructive effects, resulting in monetary and financial risks. On the one hand, the cryptocurrency plays a constructive role. Based on the innovative attributes of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies attempt to transform the traditional monetary and financial industry through technology, providing monetary and financial services through the use of smart contracts running based on distributed ledger technology (DLT), aiming to replace the traditional centralized financial intermediary through a peerto-peer relationship, to realize the democratization of finance. On the other hand, cryptocurrency plays a "disruptive innovation" role[22], posing some challenges to traditional currency and breeding lots of financial risks, including risks of trading platforms, inadequate operation facilities, and technical loopholes. These risks will seriously affect the fair competition and stable currency market development .
Cryptocurrency can bring many potential benefits, such as faster transaction efficiency, more reliable security mechanisms, lower transaction costs, and better user experience. However, the existing legal regulations lack a clear legal positioning for cryptocurrencies and do not apply to traditional financial regulatory systems, which can easily infringe on the legitimate rights and interests of financial consumers and disrupt the market order of cryptocurrencies. Firstly, cryptocurrencies have a typical feature of technological decentralization, so all kinds of technical hackers can steal digital currencies of financial consumers through Trojan programs, platform vulnerabilities, and other means,seriously damaging the legitimate rights and interests of financial consumers and causing significant economic losses.For example, cryptocurrency trading platforms such as Mt. Gox and Flexcoin lost a large number of cryptocurrencies after technological hacking attacks, leading to the bankruptcy of trading platforms and financial consumers. Moreover,the high-tech hacking methods have brought significant difficulties to the police's reconnaissance and evidence collection, making it difficult for the police to effectively lock in technical hackers and recover economic losses from financial consumers through public remedies. Secondly, driven by blockchain, the power difference between cryptocurrency operators and consumers is increasingly widening. Due to limitations such as technological level, asset strength, and financial experience, financial consumers are often in a more vulnerable position compared to operators of cryptocurrencies, making it difficult to ensure the effective realization of their legitimate rights and interests. Therefore, from the perspective of the modern rule of law concept of economic freedom, economic democracy and economic justice, various economies must strengthen the systematic regulation of cryptocurrency and provide preferential protection for consumers of cryptocurrency. In conclusion, driven by blockchain technology, cryptocurrency is a new kind of financial innovation, which still belongs to the finance industry. The risk regulation of cryptocurrencies can still be applied to "twin peaks regulation" to accomplish twin goals, including the system protection goal and the consumer protection goal. As for the consumer protection goal, financial regulation authorities can use behaviour regulation, such as operation and market behaviour regulation, so as to protect cryptocurrency operation rights.
4 Regulatory Construction: How to Build the Systematic Regulation of Cryptocurrency Risks in China
In the context of blockchain technology, the risk regulation of cryptocurrencies is a systematic and complex project rather than just a one-dimensional legal or financial regulatory engineering issue. To ensure that China's cryptocurrency layout can be transformed into a national competitive advantage and to prevent the risks corresponding to the"impossible trinity" of cryptocurrency, namely the legal risks corresponding to currency stability, the financial risks corresponding to credit carriers, and the technical risks corresponding to technological decentralization. Based on the development of Chinese localized cryptocurrency and international regulatory experience, this paper constructs a systematic regulatory system for the steady growth of Chinese cryptocurrency from law, finance, and technology regulation perspectives. To be specific, China should not be limited to the concept of traditional currency to define cryptocurrency but should start from the "impossible trinity" principle of cryptocurrency, fully absorb modern financial regulatory theory and international regulatory experience, and comprehensively construct a systematic regulatory system for cryptocurrency risks in China: strengthen legal regulation and strictly regulate market access mechanisms; establish a diversified financial regulation system to prevent financial risks; construct the "smart regulation" model to protect consumer rights.
4.1 Strengthen Legal Regulation and Strictly Regulate Market Access Mechanisms
From the perspective of technical principles, Cryptocurrencies have inherent functional drawbacks, which prevent them functioning as legal tender. On the one hand, cryptocurrency cannot reach social consensus so that it won't be a world currency and have value storage. On the other hand, cryptocurrency cannot be an exchange medium and accounting unit. However, in some markets of cryptocurrency, especially in some developing countries with unstable financial systems, cryptocurrency may have much higher comparative advantages than standard currency, it can provide an alternative way to traditional currency and provide a cost-effective remittance system. Most scholars believe cryptocurrency is not real currency because it lacks national credit support , and its inherent defects will cause some security issues.However, the decentralization of cryptocurrency also has advantages over the monetary system controlled by authoritative institutions. Take bitcoin as an example, the total amount of bitcoin will be at most 21 million because of its technical characteristics,so it is very difficult to be controlled for single person or institution. However, legal tender (paper currency and mints) are easily manipulated by politicians or monopolies in circulation, resulting in inflation or deflation. Despite the significant technical deficiencies and risks associated with cryptocurrencies, with the increasing level of technology and currency acceptance, the volatility of cryptocurrencies will also decrease and. Therefore, the larger the user base of cryptocurrency, the smaller the impact of a single user on its value, and the more stable the currency value.
Nowadays, different countries have adopted different regulatory approaches to the risks of cryptocurrencies in a risk society. The United States has adopted a positive regulation idea for cryptocurrency. It recognizes its legitimacy in circulation: Firstly, In terms of the legal status and attributes of cryptocurrency, some states, including California, Arizona, Florida, and Delaware have carried out some legal regulations on cryptocurrencies. New York State defines cryptocurrency as a financial asset, but the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) defines cryptocurrency as a medium of exchange circulated in the currency market to some extent, but cryptocurrency does not have all the attributes of legal tender. Secondly, In terms of cryptocurrency license and elements of legal procedure, there are four kinds of license, including cryptocurrency, currency transfer, trust, and money services business (MSB) license. The element of legal procedure for a cryptocurrency license should include substantive review, administrative license, and regular inspection; the element of legal procedure for a currency transfer license needs to include substantive review and administrative licensing; the element of legal procedure for a trust license should include strict substantive review and licensing; the element of legal procedure for money services business (MSB) needs to register (no restriction on substance examination). Lastly, Regarding monetary regulation institutions and the basis of legal regulation. Take New York state as an example, the cryptocurrency license regulation institution is the New York State Department of Financial Services (NYSDFS), abiding by uniform regulation of the Virtual Currency Business Act; the currency transfer license regulation institution is also NYSDFS, abiding by money transmission laws; the trust licenses regulation institution is NYSDFS, abiding financial services law and commercial bank law; the money services business regulation institution is FinCEN, abiding uniform money services act and bank secrecy act. In Asia, Japan has given cryptocurrency(such as Bitcoin, etc.) a high legal status, which is relatively rare in the all over the world. Japan amended the Capital Settlement Law in 2016, integrating cryptocurrency into the regulation system. Since then, cryptocurrency has been regarded as a legal payment means. In Europe, Germany believes that cryptocurrencies (especially bitcoin) are units of account, cryptocurrencies are similar to foreign exchange financial instruments, but according to the German Payment Services Supervision Act, cryptocurrencies are not legal tender which have not national credit support. Cryptocurrency can be used privately as a means of payment in barter transactions or as a substitute currency for contracts in private law. The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK has issued a consumer warning stating that cryptocurrency difference contracts (CFDS) pose a risk of price speculation and that financial consumers should be vigilant.
Therefore, under the background of the risk society, many economies make full use of information technology and inherent endowment of legal tender to promote cryptocurrencies. Many economies are accelerating the research and development experiments of legal digital currencies, such as the Ubin project in Singapore and the e-krona in Sweden,aiming to maximize the technical efficiency of cryptocurrencies, avoid the potential risks of cryptocurrencies, which will be suitable for integrating the technical credit (cryptocurrency) and the national credit (legal cryptocurrencies)[23].Based on the risk characteristics of cryptocurrencies, China adopts a classification and hierarchical regulation approach for cryptocurrencies, that is, strictly regulates non-legal cryptocurrencies, and even introduces legal regulations and adopts prohibition rules to completely ban bitcoin and ICO. On the other hand, China adopts property rules for legal digital currencies (cryptocurrencies), market entities can voluntarily trade statutory cryptocurrencies, and their legal status is equivalent to that of current legal tender. In conclusion, legal digital currencies which obtained the national credit guarantee can solve the inherent risks of cryptocurrencies, which have better transaction legitimacy and stable value. In conclusion, it is necessary to strengthen legal regulation and strictly regulate market access mechanisms in the field of cryptocurrencies for China, to prevent financial risks and protect financial risks.
4.2 Establish a Diversified Financial Regulation System to Prevent Financial Risks
With the continuous development of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency, the United States has implemented federal and state financial regulation systems to prevent financial risks for cryptocurrencies. On the one hand, federal financial regulation authorities include the FinCEN, SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission), IRS (the Internal Revenue Service), CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission), and CFPB (Consumer Financial Protection Bureau), which are in charge of risk regulation of cryptocurrencies. On the other hand, As for state financial regulation,New York State has made the regulatory license (Bitlicense) for cryptocurrencies. The federal government has not enacted unified regulations on "mining" activities of cryptocurrencies. Still, some states (such as South Carolina) have banned "mining" businesses because cryptocurrency is regarded as securities, and it is illegal for institutions to sell it to residents without proper regulation[24]. In Asia, the financial regulation authority of cryptocurrency in Japan is the Financial Services Agency (FSA). Japan has been integrating cryptocurrencies into its regulatory system, recognizing it as a legitimate means of payment. However, it does not consider it a complete legal tender and should be subject to appropriate financial regulation. The Korea Financial Services Commission (FSC) regards ICO as an illegal act. The FSC announced that it would prohibit raising funds and transactions need to be strictly regulated. To better prevent financial risks, China should insist on innovating and establishing a diversified financial regulation system.
Nowadays, cryptocurrency has a short and fast development time. Under the background of blockchain technology, China has reformed the traditional financial regulatory framework to the "central bank, state administration for financial regulation, and regulatory commission" in 2023. Although this financial regulatory system reform reflects a trend from separate regulation to functional regulation, this financial regulation system has not jumped out of the traditional financial regulation framework of "multiple branches and separate regulation" and established a diversified financial regulation system to prevent financial risks: Firstly, It shows a "multiple" regulatory trend for so many financial regulation institutions. In China, The national financial regulation institutions include "one central bank (PBoC), one state administration for financial regulation (SAFR), and one regulatory commission (CSRC)", and the local financial regulation institutions are the local financial regulatory bureaus, which undertake the financial regulation responsibilities. Secondly, financial regulation adopts "separate" rather than functional regulation. The "separate" financial regulation system has some advantages for traditional finance because it is good for increasing high regulation efficiency and clarifying regulation responsibilities. However, under the risk society driven by information technology such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, information technology promotes the deep application and bring challenges to the regulation mechanism, which will give birth to financial regulation loopholes and arbitrage. At that time, the traditional financial regulation mechanism may fail to prevent financial risks and harm consumers' interests. Drawing on the extraterritorial regulation experience of the cryptocurrency innovation, it needs to adopt functional regulations for similar financial businesses to realize the systematic regulation pattern: Strengthening the behaviour regulation and improving the financial regulation system design. Therefore, China's main subject of cryptocurrency regulation needs to change its functions and strengthen its behaviour regulation. China should build a diversified regulatory system with its characteristics, including government regulation, industry self-discipline, corporate autonomy, and social supervision, so that financial activities, including cryptocurrency, are included in the scope of modern financial regulation to prevent financial risks.
4.3 Construct the Smart Regulation Model to Protect Consumer Rights
Cryptocurrency, as the most critical application field of blockchain technology. The openness, transparency and disintermediation of blockchain technology can improve regulatory efficiency and reduce regulatory costs, which will profoundly impact risk regulation. Nowadays, many economies are actively exploring blockchain to solve regulatory problems and promote regulatory digitization and efficiency.
To effectively encourage financial innovation and protect financial consumers, China shall persist in neutrality principle to innovative technologies, pay full attention to risk points, and adopt the smart regulation model of cryptocurrency according to the development scale and time (figure 2). The so-called smart regulation is a progressive and intelligent regulation model carried out according to the development scale of enterprises related to cryptocurrency.Cryptocurrency regulatory agencies must consider different risk factors, enterprise cost factors, and consumer rights factors, with varying priority factors at different stages[25]. (1) During the introduction stage of cryptocurrency-related enterprises, financial regulatory agencies should not prematurely replace the market in making judgments. Still, they should understand the enterprise's innovative business models, organizational structures, and other "flexible" risk factors. Testing and piloting can be adopted to reduce information asymmetry and avoid potential "regulatory excesses" to curb innovation. (2) During the growth stage of cryptocurrency-related enterprises, financial regulatory agencies can first adopt the "regulatory sandbox" model, as it is conducive to expanding the scope of pilot experiments in the early stage and eliminating the inhibitory factors given by regulatory agencies while controlling risks and protecting consumer rights; then, regulatory authorities will determine whether to implement restricted licenses/special charters based on sandbox testing. This allows innovative companies to develop their customers and businesses further. (3) During the maturity stage of cryptocurrency-related enterprises, financial regulatory authorities can issue corresponding full licenses based on their scale and income[26].
In recent years, how to strike a balance between encouraging financial innovation and effectively preventing and controlling financial risks has become an important issue for financial regulators. In 2015, the United Kingdom creatively proposed a "regulatory sandbox" mechanism, forming a complete operational model and institutional system composed of process design, testing tools, access criteria, assessment mechanisms, risk management measures, etc. As for regulatory sandbox mechanism, the FCA in the United Kingdom plays an important role in setting policy goals, issuing supporting policies, and exercising regulatory functions. Based on the research of the UK's "regulatory sandbox"system design, if China implements the "regulatory sandbox" mechanism in the field of cryptocurrencies, it needs to strengthen its regulatory guidance function in terms of target positioning, institutional design, regulatory framework, access conditions, regulatory flexibility, and other aspects. China Securities Regulatory Commission and other departments piloted the "regulatory sandbox" in November 2021. Based on the consideration of preventing financial risk and protecting financial consumers, financial regulatory agencies can adopt moderately innovative financial regulation and gradually promote smart regulation. Firstly, based on the development practice of cryptocurrencies, China combines the innovative "regulatory sandbox" with the traditional "experimental pilot" mechanism. Under the authorization of the central financial regulatory agency, local financial regulatory agencies can carry out the "regulatory sandbox" trial,and pilot the circulation of cryptocurrencies on a small scale in some regions. Secondly, as for the management institution of the "regulatory sandbox", it is proposed that the Financial Working Committee of the CPC Central Committee can serve as the coordinating subject to take charge in coordinating major financial issues. Thirdly, as for the "regulatory sandbox" process design, the Chinese "regulatory sandbox" should include the application stage, assessment stage,test stage, and exit stage and guarantee the time process of each step is operational. Neither because the processing time is too short to operate, the volume of business is too large to lead to the regulatory resources, nor because the processing time is too long to cause the applicant to lack motivation. So that China can gradually improve the regulatory system for cryptocurrencies, filling the "grey regulation" zone caused by the lack of systematic regulation under the premise of controllable risks and consumer rights protection, and promoting the compliant and intelligent development of cryptocurrencies in China.
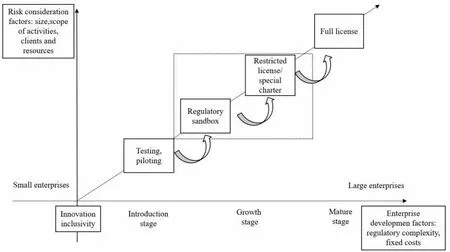
Figure 2 Constructing the Smart Regulation Model of Cryptocurrency in China
5 Conclusion
From traditional agricultural and industrial society to modern intelligent society, currency has evolved from a dual perspective of credit carrier and technology. On the one hand, from the perspective of credit carrier evolution, the currency has evolved from personal credit (commodity currency) to institutional credit (institutional cryptocurrency) and further evolved into national credit (legal tender) and social consensus (cryptocurrency). On the other hand, from the perspective of technology evolution, the currency has evolved from commodity currency (such as shell coin) to metal currency (such as silver coin) and ultimately to paper currency and cryptocurrency. Nowadays, cryptocurrency is a new type of cryptocurrency that has rapidly developed through the deepening of information technology. It uses information technologies such as P2P networks, cryptography, blockchain, consensus algorithms, and so on. Its prominent feature is that cryptocurrency can achieve point-to-point direct financial transactions without relying on specific intermediaries,achieving faster transaction efficiency, more reliable security mechanisms, and lower transaction costs. However, while cryptocurrencies innovate and develop, they may also bring about an "impossible trinity", meaning they cannot achieve currency stability, credit carriers, and decentralized supply in the meantime, and derive corresponding comprehensive legal, financial, and technological risks.
In the context of a risk society, although China has introduced corresponding legal norms to strengthen the risk regulation of cryptocurrencies, existing legal norms lack a clear legal positioning and systematic regulation of cryptocurrencies, making it difficult to achieve good regulatory goals. Therefore, by deeply analyzing the "impossible trinity"and its comprehensive risks of cryptocurrencies in the risk society, this paper focuses on deconstructing the necessity of implementing systematic regulation of cryptocurrencies, effectively combining overseas regulatory experience and localized regulatory practices, China can comprehensively construct a systematic regulation of cryptocurrency risks:Strengthening legal regulation and strictly regulating market access mechanisms, establishing a diversified financial regulation system to prevent financial risks, constructing the smart regulation model to protect consumer rights.
