Experimental study on the regulation effect of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on cough variant asthma based on airway neurogenic inflammation
2023-09-23HUANGHuisiHANChaoSHIYanhongQIChunliXIONGAihuaZHANGQiulingLIANGHuiling
HUANG Hui-si, HAN Chao, SHI Yan-hong✉, QI Chun-li, XIONG Ai-hua, ZHANG Qiuling, LIANG Hui-ling
1.The Affiliated TCM Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510000 Guangdong, China
2.Jinan University, Guangzhou 510000 Guangdong, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the mechanism of regulation of airway neurogenic inflammation by Qiaoqin Qingfei agent in rats with cough variant asthma (CVA).Methods: 48 SD rats were randomly divided into blank group, model group, montelukast sodium group (1.05 mg/kg) and high, medium and low dose groups (26,13,6.5 g/kg), with 8 rats in each group.The rat CVA model was established by the method of ovalbumin (OVA) combined with aluminum hydroxide(Al(OH)3) sensitization and repeated stimulation.From the second day of sensitization, the rat CVA model was given by gavage for 28 days.The pathological changes of lung tissue were observed under microscope by HE staining.The content changes of nerve growth factor (NGF)and substance P (SP) in alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were determined by double-antibody sandwich ABC-ELISA, and the protein expression levels of NGF and SP in lung tissue were detected by immunohistochemistry.Results: Pathological findings showed significant inflammatory manifestations in the model group, and the inflammatory infiltration in the highdose, medium-dose and low-dose groups of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent and montelukast sodium groups were alleviated to varying degrees.Compared with blank group, the protein expression levels of NGF and SP in lung tissue of model group were significantly increased (P < 0.01).Compared with model group, the protein expression levels of NGF and SP in lung tissue and the contents of NGF and SP in alveolar lavage fluid in high-dose, medium-dose and low-dose groups and montelukast sodium group were significantly decreased (P <0.05).Conclusion:Qiaoqin Qingfei agent may reduce airway inflammation and relieve cough variant asthma by regulating the protein expression levels of NGF and SP in airway neurogenic inflammation.
1.Introduction
Cough variant asthma (CVA), also known as latent asthma,is a specific type of asthma with chronic dry cough as the only or important symptom, and is the preliminary state of typical asthma[1-3].At present, the treatment of CVA in Western medicine mainly includes inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators and leukotriene receptor antagonists[4],but most patients feel the burden of long-term use of glucocorticoids, and the control level is not ideal, and some patients still develop into typical asthma[5].Qiaoqin Qingfei agent made in our hospital is a modified traditional Chinese medicine concentrated tea bag according to the clinical application for many years.Through more than 20 years of clinical application,it has been found that it has good curative effect in the prevention and treatment of acute and chronic bronchitis and asthma.Current studies have found that airway neurogenic inflammation is closely related to the occurrence and development of CVA.Therefore,this study intends to observe the prevention and treatment effect of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on CVA by ovalbumin (OVA) induced rat model of CVA, and preliminarily explore its mechanism of action and its association with airway neurogenic inflammation, as reported below.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Animals
A total of 48 specific pathogen free (SPF) SD rats, half male and half female, with an average body weight of about (150-180) g,were purchased from Beijing Huafukang Biotechnology Co., LTD.(certificate number: SCXK (Beijing) 2019-0008).The animals were bred in the Laboratory Animal Management Center of Jinan University (SYXK (Guangdong) 2017-0174).The relative humidity was 40%-70%, the temperature was (22±2) ℃, and the light-dark cycle was 12 h.This experiment was approved by the Experimental Animal Welfare Ethics Committee of Jinan University (approval number: IACAC-20210824-08).
2.2 Drugs and reagents
Ovalbumin (sigma, Lot#SLCH2414); Aluminum hydroxide(Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory, batch number:20210104); Sodium chloride injection (Chenxin Pharmaceutical Co., LTD., batch number: 2106250721); Montelukast sodium chewable tablets (Shijiazhuang Shiyao Group Ouyi Pharmaceutical Co., LTD., Sinopharm approval number H20203047); Qiaoqin Qingfei agent (Supply from the preparation room of the Affiliated TCM Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, 2.5 kg crude drug dosage /L); Rat nerve growth factor ELISA kit (Bosted, product number: EK0471); Rat substance P ELISA kit (Huamei, product number: CSB-E08358r); Rabbit anti-NGF Polyclonal Antibody(SAB Biotech Co., LTD., product number: 41239); Rabbit anti-Sp1 Antibody (SAB Biotech Co., LTD., product number: 37251); SABC immunohistochemical kit (Bosted, product number: SA1020); DAB kit (Bosted, Accession number: AR1027).
2.3 Primary instrument
Haier compressed-type medical atomizer (Anhui instrument injection standard 20192080049, model: YS-06), analytical balance(Guangdong Huayunyi Biological Engineering Co., LTD., model:BSA2202S), micro sample automatic five classification animal blood analyzer (DREW Scientific, USA, model: HEMAVET 950FS),microplate reader (Shanghai Thermo Fisher Instruments Co., LTD.,model: Multiskan Mk3).
2.4 Model building
Animal models were established based on literature reports and previous research work[6-9].After 10 days of adaptive feeding in a quiet, dry and ventilated environment, SD rats were sensitized with ovalbumin (OVA) combined with aluminum hydroxide(Al(OH)3) and repeatedly challenged to establish a rat cough variant asthma (CVA) model.(1) Sensitization stage: On the first, third,fifth, seventh and eleventh days of the experiment, the rats in the intervention group and the model group were intraperitoneally and subcutaneously injected with 10% ovalbumin and aluminum hydroxide suspension 1 mL (0.5 mL intraperitoneally, and the remaining 0.5 mL subcutaneously on the back), and the blank group was intraperitoneally injected with the same amount of normal saline.(2) Challenge stage: on the 15th day, the rats in the intervention group and the model group were placed in an organic closed glass box and aerosolized with 1% OVA solution for 30 min,once a day for 2 weeks to induce asthma.The rats in the blank group were aerosolized with the same amount and equal time of normal saline.The success of the model was determined by abdominal muscle contraction, shortness of breath, cough, and the percentage of eosinophils in the blood of the model group was significantly higher than that of the blank group (P<0.05).
2.5 Grouping, administration and sampling
Forty-eight SD rats were randomly divided into 6 groups: blank group, model group, montelukast sodium group and Qiaoqin Qingfei agent high, medium and low dose groups, with 8 rats in each group.From the second day of sensitization, the Qiaoqin Qingfei agent high, medium and low dose groups were given Qiaoqin Qingfei agent 26, 13 and 6.5 g/kg by gavage, respectively, the montelukast sodium group was given montelukast sodium suspension 1.05 mg/kg by gavage, and the blank group and the model group were given the equal volume of distilled water by gavage, once a day for 28 days.After 4 weeks of continuous treatment, the animals were fasted for 12 h before euthanasia, and the corresponding test objects were given again for 40 min in the next morning.Then the rats were weighed and anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital(45 mg/kg).Normal saline 3 mL was injected into the trachea, and repeated aspiration was performed to extract the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF).The BALF was centrifuged at 4 ℃ and 4000 r/min for 10 min, and then the supernatant was taken and stored at -80℃ until testing.The right lung was quickly dissected, and the right lung tissue was fixed in 10% formaldehyde solution for hematoxylineosin (HE) staining and immunohistochemical detection.
2.6 HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of lung tissue
The right upper lobe of the lung was fixed with 10% formaldehyde solution, dehydrated, transparent, embedded in paraffin, sectioned,and stained with HE.The pathological changes of lung tissue were observed under light microscope.
2.7 The contents of NGF and SP in alveolar lavage fluid were determined by ELISA
Double antibody sandwich ABC-ELISA method was used to detect the results according to the instructions of NGF and SP kits.After the reaction, the optical density (OD) value of each well was measured by microplate reader at the wavelength of 450 nm.The concentration of standard substance and the corresponding OD value were used to draw a standard curve, and then the corresponding contents of rat NGF and SP were calculated on the curve according to the OD value of the sample.
2.8 The protein expression levels of NGF and SP in lung tissue were detected by immunohistochemistry
Tissue sections of the right middle lobe of the rat lung were removed and deparaffinized to water.After antigen repair and blocking, the primary antibody was incubated at 37 ℃ for 1 h.The secondary antibody was incubated for 30 min, followed by DAB color development, hematoxylin counterstain and dehydration sealing, and then observed and photographed under a light microscope.The brown yellow was considered positive staining.Five regions of each slice were selected and photographed, and the pathological images were analyzed by Image-Pro Plus v6.0.The OD value of the immunopositive products in each group was measured,and then the average value was taken to obtain the expression levels of NGF and SP in the lung tissue of the animal.
2.9 Statistical treatment methods
SPSS 26.0 statistical software was used to analyze the data.Continuous data were expressed as (mean ± standard deviation).The data obeys normal distribution were analyzed by t test, and the data disobeys normal distribution were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test.In terms of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the number and percentage of blood eosinophils in cough variant asthma model rats
As shown in Table 1, compared with the blank group, the number and percentage of blood eosinophils in the model group increased,and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.01).Compared with the model group, montelukast sodium significantly reduced the number and percentage of blood eosinophils (P<0.05), and the middle and low dose Qiaoqin Qingfei agent groups also reduced the number and percentage of eosinophils (P<0.05).In conclusion,the model group showed abdominal muscle contraction, shortness of breath, cough, and the percentage of eosinophils in blood was significantly higher than that in the blank group, so the model was successful (P<0.05).
Tab 1 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the number and percentage of blood eosinophils in cough variant asthma model rats (±s , n=8)
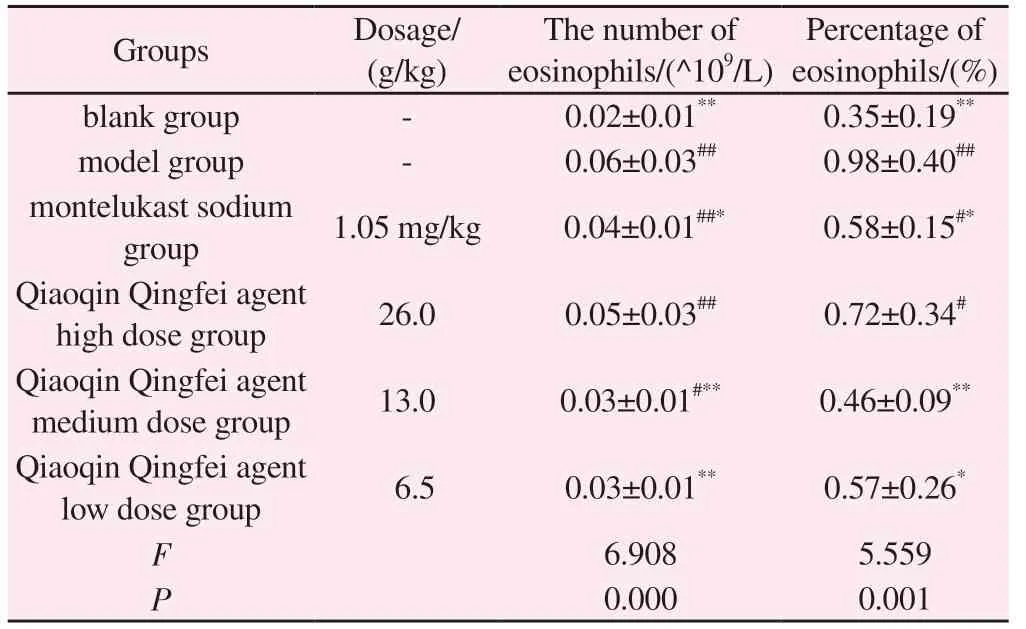
Tab 1 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the number and percentage of blood eosinophils in cough variant asthma model rats (±s , n=8)
Note: Compared with blank group: #P<0.05, ##P<0.01; Compared with model group: *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
Percentage of eosinophils/(%)Groups Dosage/(g/kg)The number of eosinophils/(^109/L)blank group - 0.02±0.01** 0.35±0.19**model group - 0.06±0.03## 0.98±0.40##montelukast sodium group 1.05 mg/kg 0.04±0.01##* 0.58±0.15#*Qiaoqin Qingfei agent high dose group 26.0 0.05±0.03## 0.72±0.34#Qiaoqin Qingfei agent medium dose group 13.0 0.03±0.01#** 0.46±0.09**Qiaoqin Qingfei agent low dose group 6.5 0.03±0.01** 0.57±0.26*F 6.908 5.559 P 0.000 0.001
3.2 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on pathological changes of lung tissue in cough variant asthma model rats
The results are shown in Figures 1 and 2.In the blank group,the lung tracheal epithelial cells were neatly arranged, a small amount of epithelial cells were shed in the lumen, no infiltrated inflammatory cells were observed in the airway wall, no alveolar expansion was observed, no necrosis and exfoliation of epithelial cells and inflammatory cells were observed in the alveoli, no congestion was observed in the pulmonary blood vessels, no obvious inflammatory cell infiltration in the wall, and no thickening of the alveolar wall.Compared with the blank group, the rats in the model group showed a large number of inflammatory cell infiltration around the pulmonary blood vessel wall, loose structure of the blood vessel wall, obvious edema, some thickening of the alveolar wall,inflammatory cell infiltration in the alveolar wall, and necrosis and abscission of the epithelial cells in the lung trachea.In each drug intervention group, montelukast sodium group had some necrotic epithelial cells in the lung trachea, a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration in the airway wall, slight thickening of the alveolar wall, and a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration in the alveolar wall, but there was no obvious expansion of the alveolar,and some slight congestion of the blood vessels.The pathological changes of lung tissue in the Qiaoqin Qingfei agent group were alleviated to varying degrees, the necrosis and shedding of epithelial cells were reduced, and the infiltration of inflammatory cells around the tracheal wall was significantly reduced, and there was no obvious thickening of alveolar wall and no alveolar expansion.Among them,the high-dose Qiaoqin Qingfei agent group had the most significant improvement, followed by the medium-dose and low-dose Qiaoqin Qingfei agent groups.
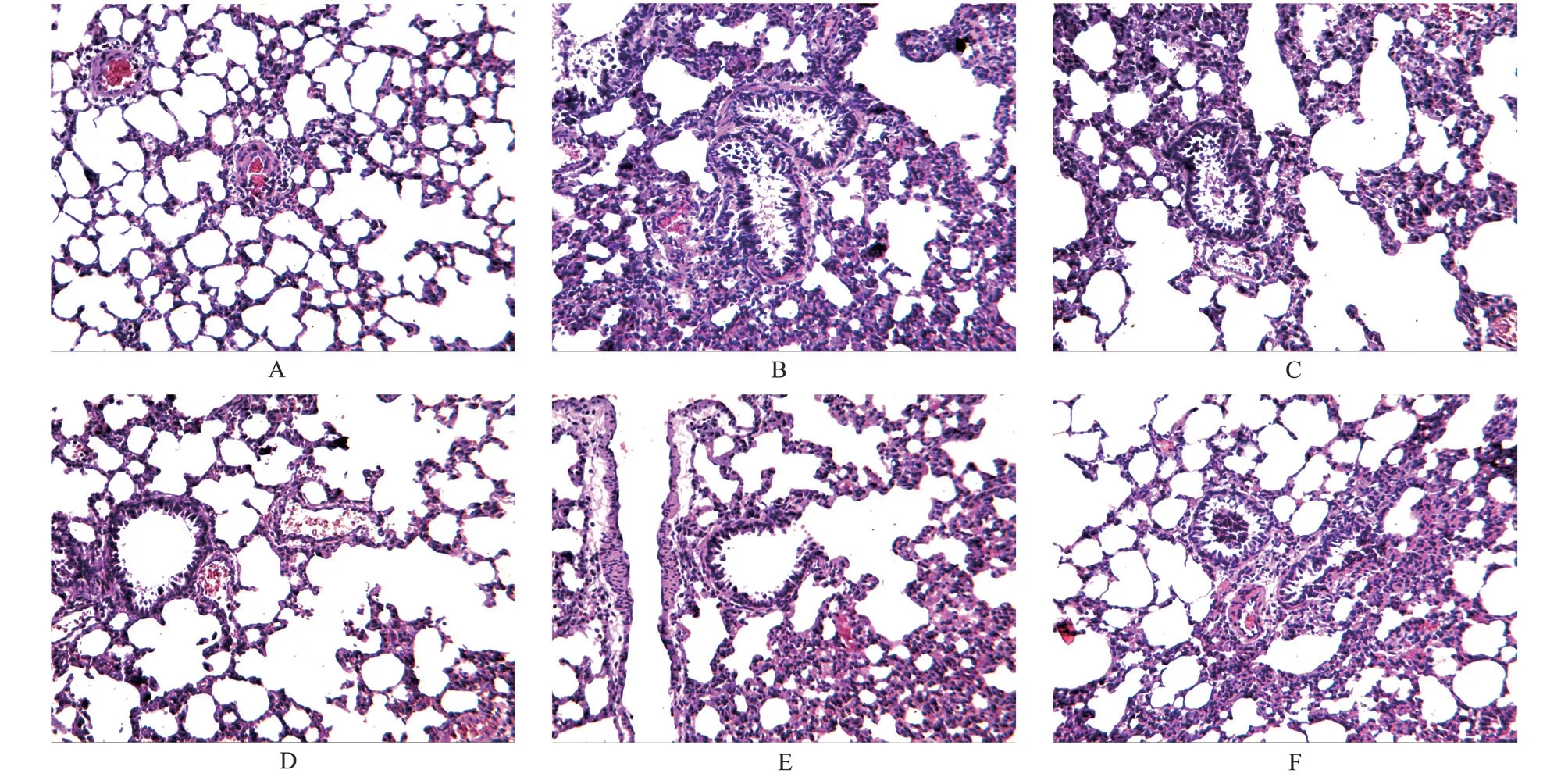
Fig 1 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on pathological changes of lung tissue in cough variant asthma model rats (HE staining, ×100)
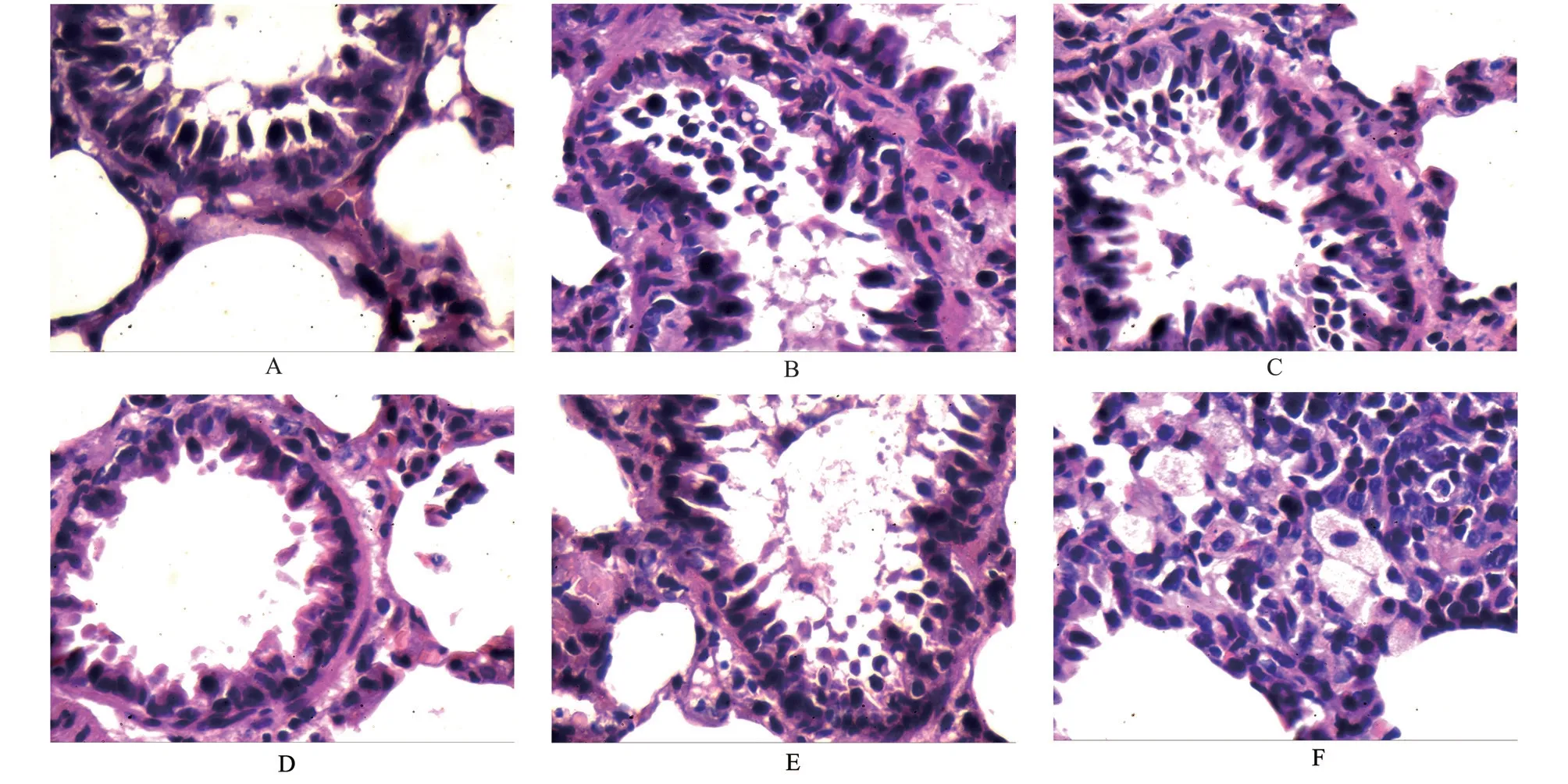
Fig 2 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on pathological changes of lung tissue in cough variant asthma model rats (HE staining, ×400)
3.3 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the contents of NGF and SP in alveolar lavage solution of cough variant asthma rats
The results are shown in Table 2.Compared with the blank group,the contents of NGF and SP in the alveolar lavage fluid of the model group were increased, but the difference was not significant(P>0.05).Compared with the model group, the levels of NGF and SP in the high, medium and low dose Qiaoqin Qingfei agent groups and the montelukast sodium group were significantly decreased(P>0.05).
3.4 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the expression of NGF and SP protein in lung tissue in cough variant asthma model rats
The results are shown in Figures 3, 4, and Table 3.Comparedwith the blank group, the protein expression levels of NGF and SP in the lung tissue of the model group were significantly increased(P<0.01).Compared with the model group, the expression levels of NGF and SP in the lung tissue of the high, medium and low dose Qiaoqin Qingfei agent groups and the montelukast sodium group were significantly decreased (P<0.01).
Tab 2 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the contents of NGF and SP in alveolar lavage solution of cough variant asthma rats (±s ,n=8)
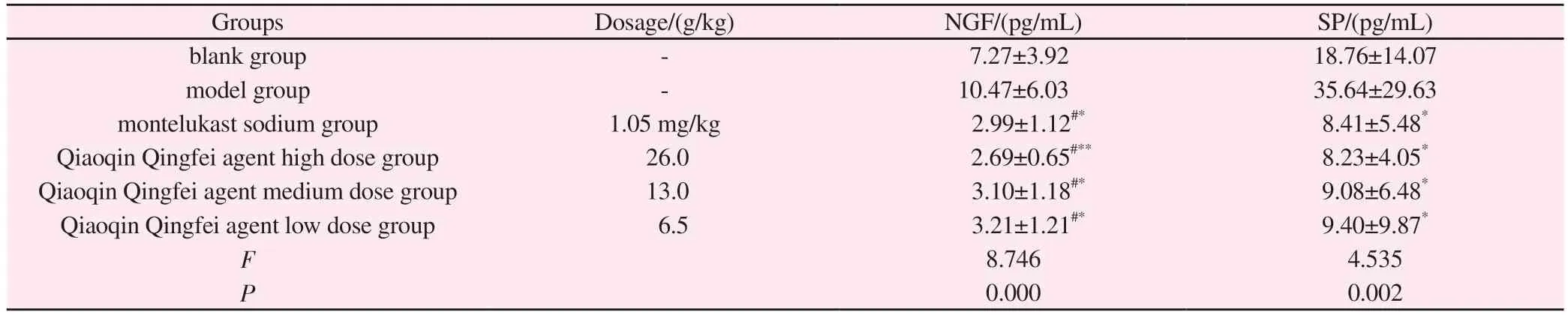
Tab 2 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the contents of NGF and SP in alveolar lavage solution of cough variant asthma rats (±s ,n=8)
Note: Compared with blank group: #P<0.05, ##P<0.01; Compared with model group: *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
Groups Dosage/(g/kg) NGF/(pg/mL) SP/(pg/mL)blank group - 7.27±3.92 18.76±14.07 model group - 10.47±6.03 35.64±29.63 montelukast sodium group 1.05 mg/kg 2.99±1.12#* 8.41±5.48*Qiaoqin Qingfei agent high dose group 26.0 2.69±0.65#** 8.23±4.05*Qiaoqin Qingfei agent medium dose group 13.0 3.10±1.18#* 9.08±6.48*Qiaoqin Qingfei agent low dose group 6.5 3.21±1.21#* 9.40±9.87*F 8.746 4.535 P 0.000 0.002
Tab 3 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the expression of NGF and SP protein in lung tissue in cough variant asthma model rats (±s ,n=8)
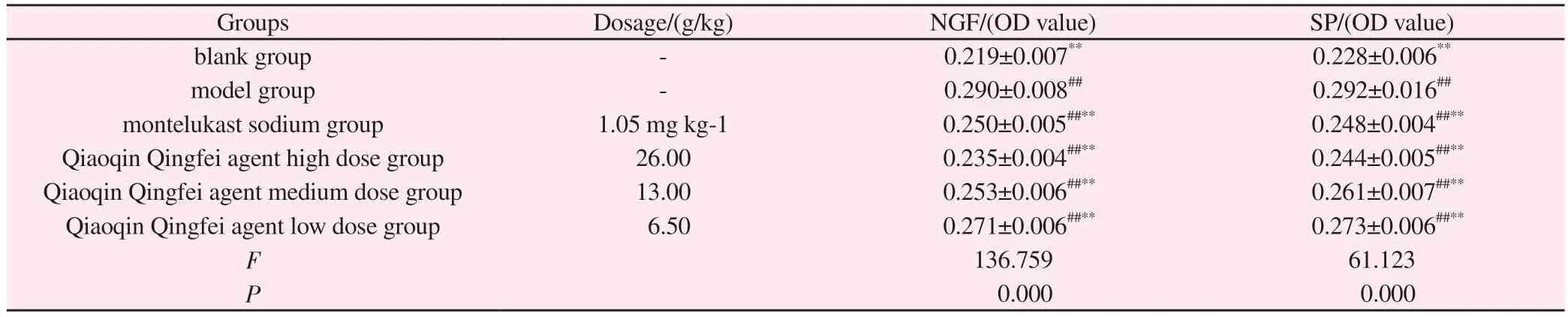
Tab 3 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the expression of NGF and SP protein in lung tissue in cough variant asthma model rats (±s ,n=8)
Note: Compared with blank group: #P<0.05, ##P<0.01; Compared with model group: *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
Groups Dosage/(g/kg) NGF/(OD value) SP/(OD value)blank group - 0.219±0.007** 0.228±0.006**model group - 0.290±0.008## 0.292±0.016##montelukast sodium group 1.05 mg·kg-1 0.250±0.005##** 0.248±0.004##**Qiaoqin Qingfei agent high dose group 26.00 0.235±0.004##** 0.244±0.005##**Qiaoqin Qingfei agent medium dose group 13.00 0.253±0.006##** 0.261±0.007##**Qiaoqin Qingfei agent low dose group 6.50 0.271±0.006##** 0.273±0.006##**F 136.759 61.123 P 0.000 0.000
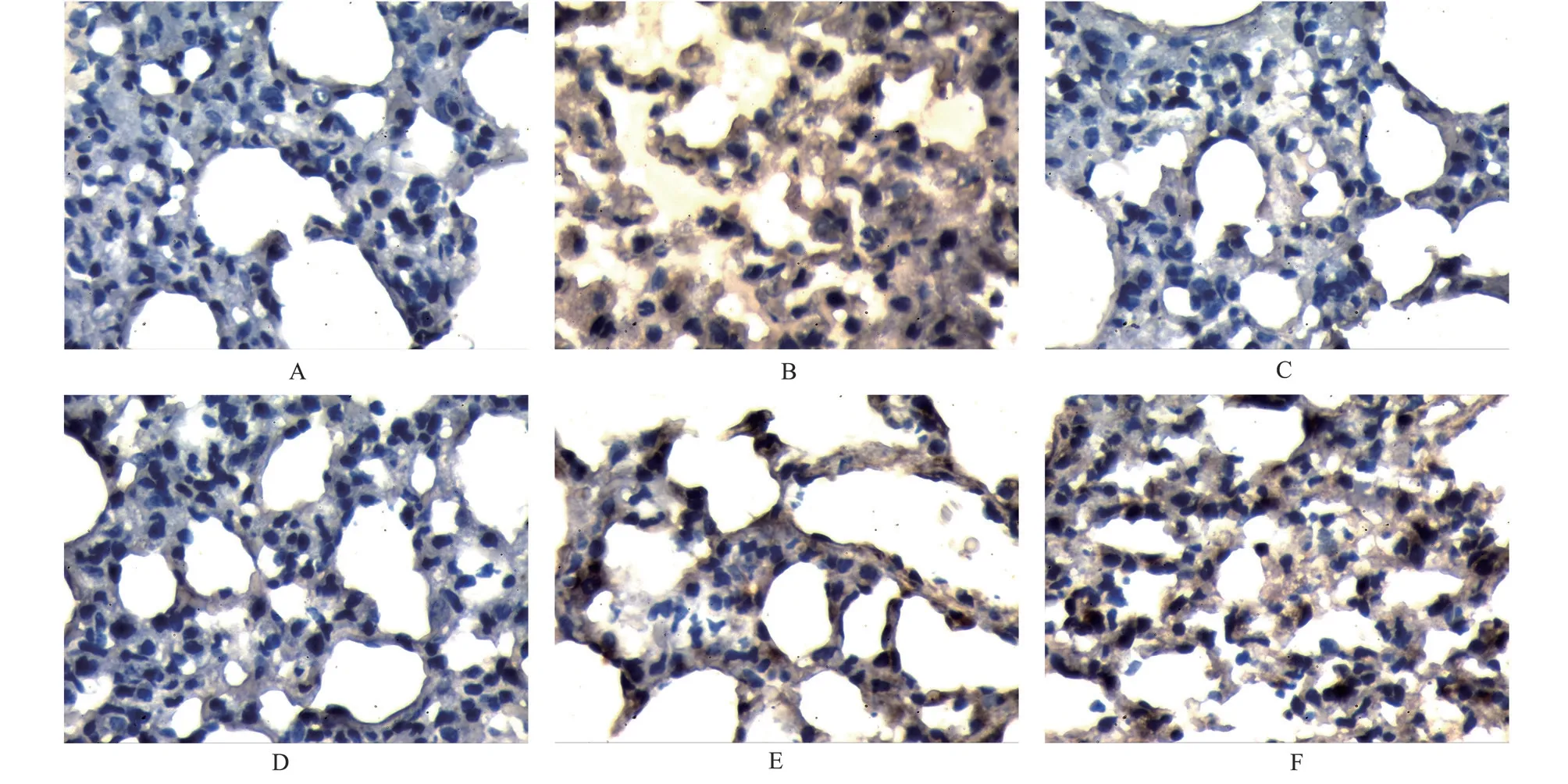
Fig 4 Effects of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on the expression of SP protein in lung tissue in cough variant asthma model rats (IHC, ×400)
4.Discussion
The pathogenesis of CVA is complex, which is the result of the combined influence of immune, environmental, genetic and other factors, including chronic airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness, airway remodeling and genetic factors are the main pathogenesis.In recent years, more and more attention has been paid to airway neurogenic inflammation caused by the regulation of neuropeptides secreted by sensory nerve endings[10].The physiological changes produced by tachykinin secreted by sensory nerve endings, such as increased microvascular permeability,increased mucus secretion, airway smooth muscle contraction,cough, and promotion of leukocyte adhesion, are called “airway neurogenic inflammation”.At present, relevant studies have shown that neurogenic inflammation may be an important pathogenesis of CVA, and the occurrence of airway neurogenic inflammation is also an important reason for increased cough sensitivity and persistent dry cough[11].
NGF is a key cytokine in the regulation of neurogenic inflammation, which can amplify airway inflammation through the nervous and immune system and play an important role in airway neurogenic inflammation[12].Studies have shown that it may be involved in a variety of pathological reactions such as airway smooth muscle contraction and neurogenic inflammation in asthma,and is closely related to the formation and development of airway inflammation, so as to play an important regulatory role in the process of airway chronic inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness and airway remodeling in asthma[13-15].Foreign studies have shown that NGF can promote the secretion of tachykinin in nerve cells,up-regulate the expression of tachykinin receptors, and induce neurogenic inflammation and participate in the pathogenesis of asthma[16].
SP, a kind of tachykinin neurotransmitter, is a sensory neuropeptide released by the non-adrenergic and non-cholinergic nervous system.It can be induced and expressed in airway inflammation and plays an important role in the regulation of neurogenic inflammation[17].SP is widely present in the bronchial and alveolar walls, which is closely related to increased mucus secretion and bronchial smooth muscle contraction.It can increase vascular permeability, plasma exudation,cause tissue edema and other pathological changes, and manifest as airway neurogenic inflammation in CVA[18-21].SP has a powerful pro-inflammatory effect, which can participate in the formation of airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation by inducing inflammatory cell infiltration[22], enhance the permeability of blood vessels, lead to inflammatory exudation, chemotactic neutrophils and monocyte-macrophages, thus aggravating airway inflammation and forming a vicious circle[23-25].
Although there is no disease name corresponding to CVA in traditional Chinese medicine, most experts of traditional Chinese medicine advocate that CVA is similar to asthma in etiology and pathogenesis, which is “caused by the presence of latent sputum”and belongs to the categories of “wheezing cough”, “wind cough”,“persistent cough”, and “spasmic cough”.The traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treatment for this disease is to strengthen the root,eliminate wind and relieve cough.Qiaoqin Qingfei agent is a pure traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation, our hospital has been clinically used for many years, it is composed of forsythia,scutellaria baicalensis, isatidis, radix scrophularia, radix peucedani,peppermint, schizonepeta, platycodon, bitter apricot seed, licorice and other traditional Chinese medicine.The whole formula cleans and reduces the lung heat, and relieves the pharynx and cough.Previous studies of our research group have proved that Qiaoqin Qingfei agent has good preventive and therapeutic effects on asthma[26-27].Therefore, the aim of this study is to further investigate the correlation between airway neurogenic inflammation and CVA by observing the expression of NGF and SP in the lung tissue of CVA rats, and to explore whether Qiaoqin Qingfei agent can prevent and treat CVA by regulating airway neurogenic inflammation, so as to provide laboratory basis for clinical prevention and treatment of CVA.
According to literature reports, NGF and SP are closely related to the pathogenesis of CVA and the occurrence of airway neurogenic inflammation.They can participate in the pathogenesis of CVA by regulating airway neurogenic inflammation.The results of this experiment showed that compared with the blank group, the levels of NGF and SP in the model group were significantly increased,suggesting that the levels of NGF and SP were increased in the state of CVA, which confirmed that NGF and SP were involved in the occurrence and development of CVA, and may aggravate airway inflammation by inducing the release of inflammatory cytokines.After the drug intervention, compared with the model group, the inflammatory response of lung tissue in each group was reduced to varying degrees, and the protein expression levels of NGF and SP and the contents of NGF and SP in alveolar lavage fluid were significantly decreased.
Domestic and foreign studies have shown that MAPK and ERK pathways are important signal transduction pathways in the process of neurogenic inflammation, among which ERK signaling pathway can be activated by NGF[26].In our previous study, it has been confirmed that Qiaoqin Qingfei agent can significantly reduce the protein expression of p38 MAPK and the mRNA expression of ERK1/2 in lung tissue of asthmatic rats, and effectively regulate the transduction of HMGB-MAPK-ERK signaling pathway[26, 27].Therefore, we speculate that Qiaoqin Qingfei agent may mediate and regulate the MAPK and ERK inflammatory pathways by regulating the protein expression levels of NGF and SP in airway neurogenic inflammation, thus reducing airway inflammation and slowing down the development of cough variant asthma.
The pathological results of lung tissue showed that there were obvious inflammatory pathological changes in the lung tissue of the CVA rat model group, and the protein expression levels of NGF and SP were significantly increased, but this change could not be confirmed in the detection of alveolar lavage fluid.This result suggests that CVA is a chronic disease with long-term development,and sometimes the detection methods, detection sites and detection indicators do not necessarily reflect the real situation in the early stage of the disease in time.Therefore, we should pay more attention to the importance of early control of airway neurogenic inflammation, so as to prevent the disease before it occurs, slow down or even block the process of CVA.In order to achieve the purpose of early prevention and treatment of CVA to asthma.
In conclusion, Qiaoqin Qingfei agent can effectively regulate the protein expression levels of NGF and SP in lung tissue, reduce the abnormally elevated levels of NGF and SP in CVA state, thus alleviate a series of waterfall effects of airway inflammation,intervene the occurrence and development of airway inflammation,and effectively relieve cough variant asthma.However, the specific targets remain to be further explored.
The author contribution
Huang Huisi: experimental research, index test, analysis of data and writing papers; Chao Han and Yanhong Shi: experimental design and guidance, funding acquisition, paper review; Qi Chunli and Xiong Aihua: model establishment, material sampling and index detection;Zhang Qiuling, Liang Huiling: indicator detection, funding access.All the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Meta-analysis of Traditional Chinese Medicine combined with Ivabradine in the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure
- Study on the molecular mechanism of rapamycin-induced autophagy in acute T lymphoblastic leukemia cells
- Effect of Huoxue Yiqi recipe on proliferation, migration and tube formation of miR-484 overexpressed umbilical vein endothelial cells
- A study of acupoint specificity and mechanism of electroacupuncture intervention on chronic colitis in rats based on PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Application of ARFI technology to explore the clinical study of Gandou Tang in treating liver fibrosis of wilson's disease with damp-heat accumulation
- Clinical efficacy of dapagliflozin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction
