Meta-analysis of Traditional Chinese Medicine combined with Ivabradine in the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure
2023-09-23OUYANGJiahuiZHANGMiaoDUTianyiGAOZhuyeLILizhi
OUYANG Jia-hui, ZHANG Miao, DU Tian-yi, GAO Zhu-ye, LI Li-zhi
1.Graduate school of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2.School of Chinese Medicine,University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing 100700, China
3.National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Cardiology, Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences, Beijing 100091,China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective:To systemically evaluate clinical efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine(TCM) combined with ivabradine (IVA) in the treatment of chronic heart failure(CHF).Method: We searched China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)datebase, Wanfang datebase , Chinese Scientifific Journal Database(VIP ) datebase, PubMed,Conchrane Library and EMbase database to enroll the random control trials(RCTs) of TCM combined with IVA treating CHF.Meta-analysis was performed by Review Manager 5.3 software.Results: A total of 10 RCTs involving 960 patients were included.The results of Meta-analysis showed that compared with control group, the experimental group could improve the efficiency of cardiac function improvement [RR=1.19,95%CI(1.12,1.27),P<0.000 01], increase left ventricular ejection fraction[MD=4.36,95%CI(2.88,5.83),P<0.000 1]and reduce heart rate[MD=-8.21,95%CI(-12.08,-4.34),P<0.000 01], the incidence of adverse reactions was similar between two groups[RR=1.00,95%CI(0.62,1.61),P=1.00].Conclusion:Traditional Chinese medicine combined with ivabradine has significant efficacy and good safety in improving cardiac function, improving left ventricular ejection fraction and reducing heart rate in the treatment of chronic heart failure.
1.Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is a clinical syndrome with impaired ventricular filling or ejection of blood or both resulting from various cardiac structural or functional abnormalities,and is the terminal stage of various cardiovascular diseases with high disability and lethality rates of[1].With the aging population, the prevalence of heart failure and management costs are increasing, which has become an important public health problem threatening people’s health[2].
Elevated heart rate(HR) is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes and hospitalization in patients with heart failure[3].Ivbradine (IVA) is a specific If channel inhibitor that can simply reduce sinus rhythm without effecting myocardial contractility and blood pressure, and can significantly reduces the risk of deteriorating heart failure, rehospitalization and cardiovascular death, but long-term use of IVA is likely to cause adverse reactions such as bradycardia and visual disturbance[4-5].Traditional Chinese medicine(TCM) has specific and unique advantages in improving cardiac function and stabilizing cardiac rhythm.Some studies have shown that combining TCM treatment on the basis of standard treatment of heart failure can significantly improve clinical efficacy and reduce the risk of adverse events[6-8].In recent years, there has been an increasing number of studies on TCM combined with IVA in the treatment of chronic heart failure(CHF).Therefore, this study aims to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of TCM combined with IVA in the treatment of CHF, in order to provide reference for clinical decision-making.
2.Research data and methods
2.1 Inclusion criteria
(1)Study design: Randomized controlled trial(RCT); (2)Participants: The patients in the original studies were diagnosed as chronic heart failure.Patient gender and age were unlimited; (3)Interventions: The treatment group was given TCM combined with IVA and conventional HF treatment, and the control group was given IVA and conventional HF treatment.Conventional HF treatment refers to the relevant guidelines of the “2018 Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure in China”[9], and the course of treatment is not limited.
2.2 Outcome measures
(1)Efficiency of cardiac function improvement:According to the patient’s symptoms and cardiac function improvement, it is judged as markedly effective, effective, and ineffective.Efficiency of cardiac function improvement= (markedly effectiv cases + effective cases) /total cases × 100%; (2) Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF); (3)Heart rate (HR); (4)Adverse reactions.
2.3 Exclusion criteria
(1)Non-RCT studies such as observational studies, systematic reviews, reviews, etc; (2)Non-Chinese and English studies; (3)Studies with incomplete or missing data; (4)Duplicate published studies.
2.4 Search strategy
The following electronic databases were searched from their inception to August 1, 2021: China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)datebase, Wanfang datebase, Chinese Scientifific Journal Database(VIP ) datebase, PubMed, Conchrane Library and EMbase database to enroll the RCTs of TCM combined with IVA treating CHF.The search strategy used the following general terms individually or combined:”ivabradine””heart failure””heart decompensation””cardiac failure””traditional Chinese medicine””medicine,Chinese traditional”etc.At the same time,manually search the references of the included studies to supplement the acquisition of relevant studies information.
2.5 Studies screening and data extraction
Two researchers independently screened the studies, extracted relevant information and data, and then cross-checked it.If disputes occur, negotiate with a third party.During screening, the title and abstract should be read first.After removing irrelevant studies, the full text should be further read to determine whether to include.Data extraction content includes: basic information of included studies,basic informationof participants, intervention measures, course of treatment, related factors of literature bias risk evaluation, outcomes data, etc.
2.6 Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
According to Cochrane Reviewer’s Handbook evaluation criteria of the quality of RCTs were used, which involved the random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personal, blinding of outcomes assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting and other bias.
2.7 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis were performed using the Review Manager 5.4 software.Dichotomous outcomes were presented risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) to estimate report effffect.Continuous data were used as mean difffference (MD) with 95% CI.Clinical heterogeneity was quantified by χ-squared statistic and I-squared value.If I2≤0% and P>0.10, it indicates that the heterogeneity between studies was small, and the fixed effects model was used for analysis.On the contrary, it shows that the heterogeneity between the studies was large, and the random effects model was used for analysis.Further subgroup analysis or sensitivity analysis was used to look for sources of heterogeneity if there was significant heterogeneity, or performed descriptive analysis only[10].Draw the funnel plots to test the publication biases.
3.Results
3.1 Search process and results
A total of 92 studies documents were obtained for the initial search,and 10 studies[11-20] were finally included after layer by layer screening.Studies screening process and results are shown in Figure 1.
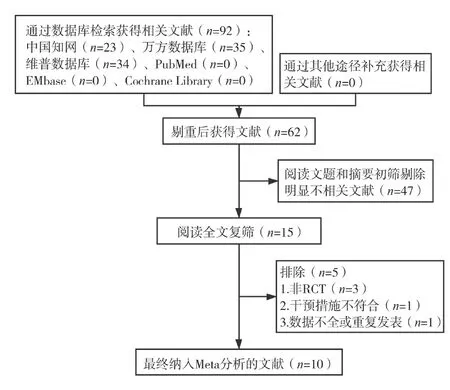
Fig 1 Process of searching and screening studies
3.2 Study Characteristics
Basic characteristics of included studies were presented in Table 1.
Tab 1 Basic characteristics of included studies(±s )

Tab 1 Basic characteristics of included studies(±s )
T:Treatment group;C:Control group;①Efficiency of cardiac function improvement;②Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF);③Heart rate (HR); ④Adverse reactions;NYHA: New York Heart Association classification of cardiac function
Study ID Sample size Average age NYHA Intervention Course Outcomes T C T C Wang Qi 2020[11] 42/42 57.93±5.52 /57.81±5.45 Ⅱ~Ⅳ Shensong Yangxin Capsule 1.2g tid +IVA 5mg bid IVA 5mg bid 2 weeks ①②④LI Kangling 2020[12] 35/35 65.4±2.5 /66.5±3.2 Ⅲ Linggui Zhugan Decoction 1dose qd +IVA 5mg bid IVA 5mg bid 1 week ①③SU Dali 2020[13] 30/30 61.74±7.01 /62.44±7.24 Ⅱ~Ⅳ Zhigancao Decoction 1bag bid + IVA 5mg bid IVA 5mg bid 1 months ①XIA Jiahui 2019[14] 67/67 58±8/ 57±8 Ⅱ~Ⅳ Qiangxin Decoction 200ml bid + IVA 5mg bid IVA 5mg bid 4 weeks ①②ZENG Hui 2019[15] 45/45 62.4±2.5/ 61.2±2.4 Ⅲ~Ⅳ Wenxin Keli 9g tid + IVA2.5mg~5mg bid IVA 2.5mg~5mg bid 3 months ①②③④XU Yanqian 2020[16] 61/61 71.63±6.83/ 72.31±5.48 Ⅱ、Ⅲ Shensong Yangxin Capsule 1.2g tid +IVA 2.5mg~7.5mg bid IVA 2.5mg~7.5mg bid 12 weeks ①②LI Qianyun 2019[17] 64/64 64.6/ 64.5 Ⅲ~Ⅳ Qiliqiangxin Capsule 1.2g tid + IVA 2.5mg~7.5mg bid IVA 2.5mg~7.5mg bid 12 weeks ①③④WANG Jingquan 2019[18] 40/40 63.8±2.9/ 64.5±3.4 Ⅱ~Ⅳ Qiliqiangxin Capsule 4.8g tid + IVA 5mg bid IVA 5mg bid 3 months ①②③④ZHOU Yu 2019[19] 30/30 55.12±7.99/ 54.98±8.07 Ⅱ~Ⅳ Qiliqiangxin Capsule 1.2g tid + IVA 5mg bid IVA 5mg bid 3 months ②③④WANG Yangling 2018[20] 51/51 55.09±7.41/ 54.63±7.92 Ⅱ~Ⅳ Qiliqiangxin Capsule 1.2g tid + IVA 5mg bid IVA 5mg bid 3 months ①③④
3.3 Risk of bias assessment of the included studies
The 10 studies[11-20] included were RCTs, of which 2 studies[16-17]used random number table method for random grouping, 1 study[19]used lottery method for random grouping, and the rest of the studies only mentioned the word “random” without specifying the specific plan.One study[14]reported blinding the assessors of the results.None of the included studies described allocation concealment.None of the included studies report incomplete data.Details were described in Figure 2.

Fig 2 Bias risk assessment diagram of the included studies
3.4 Results of Meta-analysis
3.4.1 Efficiency of cardiac function improvement
A total of 9 studies[11-18,20] included 870 patients compared efficiency of cardiac function improvement.There was no heterogeneity between the studies(P=0.73,I2=0%).The results of fixed-effect model analysis, as displayed in Figure 3, suggest that TCM combined with IVA can significantly improve the efficiency of cardiac function improvement in CHF patients[RR=1.19,95%CI(1.1 2,1.27),P<0.000 01].3.4.2 Left ventricular ejection fraction(LVEF)
A total of 6 studies[11,14-16,18-19] included 570 patients compared LEVF.There was heterogeneity between the studies(P=0.01,I2=67%).The results of random-effect model analysis, as displayed in Figure4,suggest that TCM combined with IVA can significantly improve the LVEF in CHF patients, and the difference is statistically significant[MD=4.36,95%CI(2.88,5.83),P<0.000 01].
In order to find the source of heterogeneity, a sensitivity analysis was carried out by deleting studies one by one, and it was found that after eliminating one study[19] with a sample size of 60 cases, the heterogeneity of LEVF was reduced (P=0.11, I2=47%).The results of the fixed-effect model analysis suggest that TCM combined with IVA can significantly improve the LVEF of CHF patients, and the difference is statistically significant [MD=4.90, 95%CI (4.09, 5.71),P<0.000 01](Figure 5).This indicated that the source of LVEF heterogeneity among studies may be related to the sample size of the included studies.
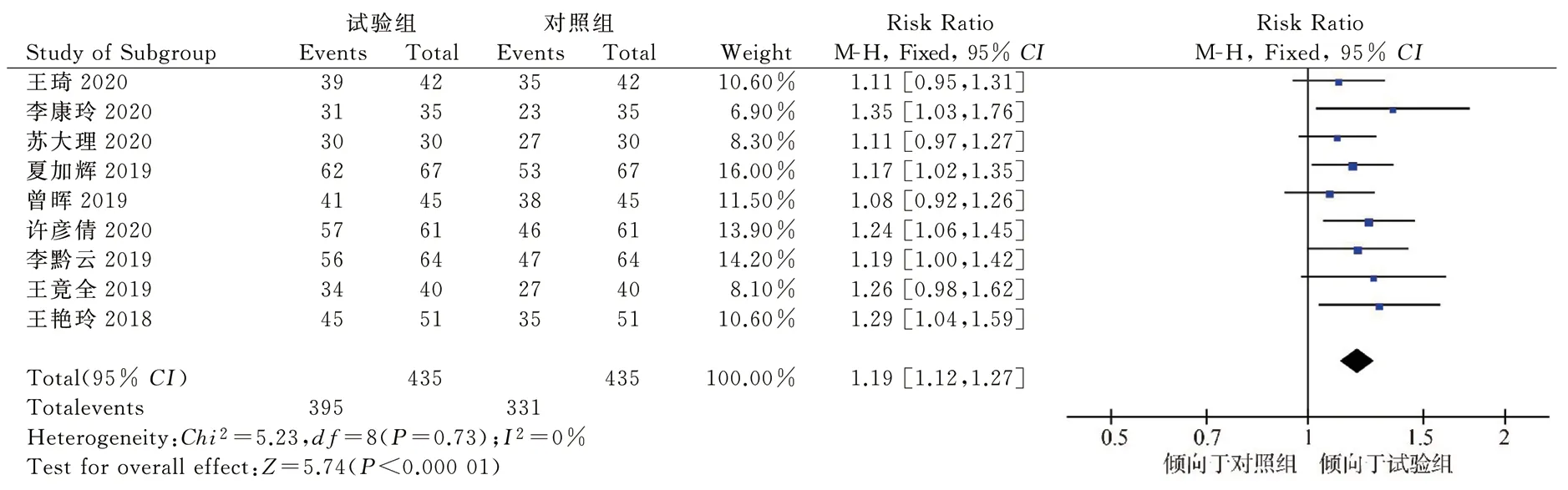
Fig 3 Meta-analysis of efficiency of cardiac function improvement

Fig 4 Meta-analysis of LEVF
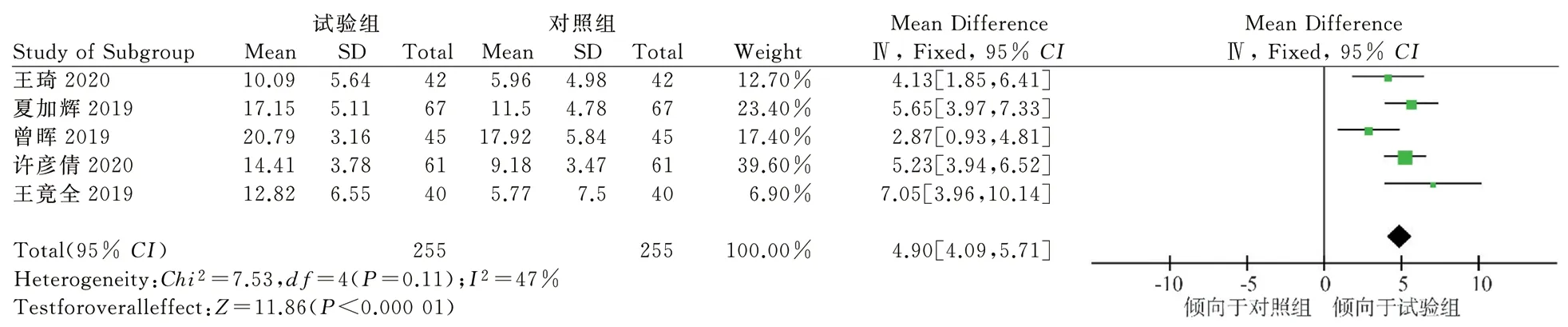
Fig 5 Sensitivity analysis of LEVF
3.4.3 Heart rate (HR)
A total of 6 studies[12,15,17-20] included 530 patients compared HR.There was heterogeneity between the studies(P=0.000 01,I2=94%).The results of random-effect model analysis, as displayed in Figure 6, suggest that TCM combined with IVA can significantly lower the HR in CHF patients, and the difference is statistically significant[MD=-8.21,95%CI(-12.08,-4.34),P<0.000 1].In order to determine the source of the heterogeneity of HR, a subgroup analysis was carried out according to the age of the patient:3 studies[12,17-18] were included in the group with an average age of 63 years, and the results of random effects model analysis suggest that TCM combined with IVA can significantly lower the HR in patients with CHF, and the difference is statistically significant[MD=-12.73,95%CI (-14.80,-10.67),P<0.000 01].A total of 3 studies[15,19-20] were included in the group with an average age of <63 years, the random-effect model analysis results suggest that TCM combined with IVA can significantly lower the HR in CHF patients, and the difference is statistically significant[MD=-3.58,95%CI(-5.79,-1.37),P=0.002].The results of subgroup analysis suggest that patients aged 63 years old have a more significant reduction in HR after Chinese medicine combined with IVA treatment(Figure 7).This indicated that the source of heterogeneity of HR between studies may be related to the age of patients.
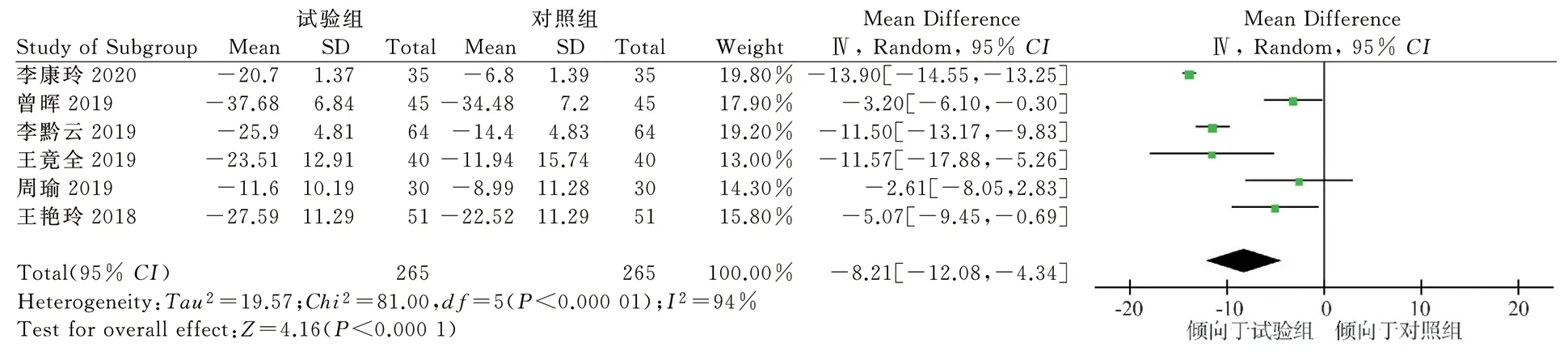
Fig 6 Meta-analysis of heart rate

Fig 7 Subgroup analysis of heart rate
3.4.4 Adverse reactions
A total of 6 studies[11,15,17-20]reported adverse reactions.One study[17] reported that no adverse reactions occurred in both groups during the treatment period, and 5 studies[11,15,18-20] reported the incidence of adverse reactions in the two groups.The adverse reactions of the two groups were mild, and the main adverse reactions were visual disturbance, bradycardia, headache, and dizziness.The results of the fixed-effects model analysis suggest that the incidence of adverse reactions in the two groups is equivalent[RR=1.00,95%CI(0.62,1.61),P=1.00].(Figure 8)
3.4.5 Publication bias
Use funnel plots to test publication bias on the efficiency of cardiac function improvement.The funnel plots is not completely symmetrical, indicating that there was a greater risk of publication bias in various studies.(Figure 9).

Fig 8 Meta-analysis of adverse reactions
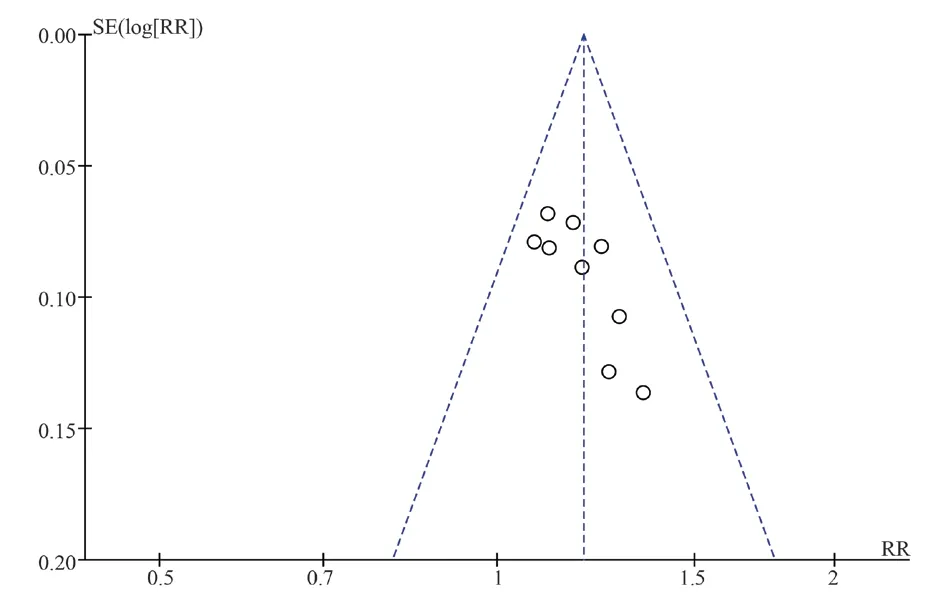
Fig 9 Funnel plot of efficiency of cardiac function improvement
4.Discussion
Heart failure can cause discomfort such as exertional dyspnea,paroxysmal dyspnea at night, orthopnoea , limitation of physical activity,and peripheral edema, which seriously affect the quality of life of patients[21].Heart failure can cause significant hospitalization and mortality.The 1-year hospitalization rate of CHF patients was 31.9%, and the 1-year mortality rate was as high as[21].The current standard treatments for HF are mainly Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) antagonists, β-receptor blockers,diuretics,etc[9,22].Although the existing drug treatment and surgical treatment can slow the development of HF, improve heart function, but the prognosis for the terminal stage of CHF is still poor[9,22].Multi-center study had shown that the readmission rate and mortality of patients with HF are positively correlated with their heart rate, so heart rate management is one of the keys to the treatment of HF[23].Large-scale SHIFT studies confirmed that:IVA simply reduced the heart rate, could effectively improve the symptoms and heart function of HF patients, and reduce the risk of re-hospitalization and cardiovascular death from worsening HF[24].
Traditional Chinese medicine had its unique insights on the syndrome differentiation and treatment of heart failure[25].According to the symptoms and signs of HF, it was classified as “zheng”,“asthma certificate” and “edema”[26].HF is a deficiency disease,the deficiency are mainly Qi deficiency, Yang deficiency, and the evils are mainly blood stasis, drinking water, and turbid phlegm.Therefore, the treatment takes “ Yi Qi, warm Yang, promote blood circulation and diuresis” as the common method, and takes into account the individual differences of patients, each focusing on the syndrome differentiation treatment[27].
In recent years, more and more studies had reported the clinical efficacy and mechanism of TCM for CHF.Wang Dingcang et al[28]found that yiqi and blood circulation method can significantly improve cardiac function and effectively inhibit ventricular reconstruction in CHF patients.Weng Huiyuan et al[29] found that Self-made Wenyang Lishui Tongluo Decoction can slow down myocardial fibrosis, reduce the level of inflammatory reaction.Song Tingting et al[30] found that Yiqi Qiangxin Yin can interfere with apoptosis of cardiomyocytes in the CHF model, and then slow the progression of CHF.The treatment of integrated TCM and western medicine with CHF, can fully mobilize the advantages of integrated TCM and western medicine, andbetter realize the comprehensive management of CHF.
The results of Meta analysis in this study suggested that the clinical efficacy of TCM combined with IVA for CHF was significant and superior to IVA alone in improving cardiac function and regulating HR, to improve LVEF.Sensitivity analysis found that the source of heterogeneity of LVEF may be related to the sample size included in the studies.Through subgroup analysis of HR, it was found that CHF patients aged 63 years old have a more significant decrease in HR after receiving TCM combined with IVA treatment.The degrees of adverse reactions were mild and the incidence of adverse reactions was comparable, indicating the good clinical safety of TCM and IVA for CHF.
There are some limitations in this study: In the included studies,only a small part of the studies mentioned specific randomization methods and realization of blinding, and most of them failed to mention random methods, the implementation of blinding methods and allocation concealment, so that the overall methodological quality of the studies were low; The intervention measures included in the studies were relatively broad, only limited to TCM, and not limited to specific prescriptions and drug formulations; The etiology and course of the included patients and the course of drug intervention and treatment were not the same, which might increase the heterogeneity between the studies; This study only included Chinese and English documents, which increase lead to a certain selection bias.
In conclusion, according to the results of the current Meta analysis,TCM combined with IVA has significant efficacy and good safety in improving cardiac function, improving left ventricular ejection fraction and reducing heart rate in the treatment of chronic heart failure, and it is worthy of clinical application.Due to the general quality of the included studies, it is hoped that more large-sample,high-quality randomized controlled trials will provide a more reliable evidence-based basis for the treatment of CHF with TCM combined with IVA.
Author contributions
First author: Ouyang Jiahui: Responsible for studies search and screening, data extraction and collection, chart drawing,paper writing and modification, etc.Zhang Miao:Responsible for studiessearch and screening, data extraction and collection,etc.;Du Tianyi:Responsible for proofreading and revising the article;Corresponding author Li Lizhi, Gao Zhuye: Responsible for the article topic selection and the review of the article.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Study on the molecular mechanism of rapamycin-induced autophagy in acute T lymphoblastic leukemia cells
- Effect of Huoxue Yiqi recipe on proliferation, migration and tube formation of miR-484 overexpressed umbilical vein endothelial cells
- Experimental study on the regulation effect of Qiaoqin Qingfei agent on cough variant asthma based on airway neurogenic inflammation
- A study of acupoint specificity and mechanism of electroacupuncture intervention on chronic colitis in rats based on PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Application of ARFI technology to explore the clinical study of Gandou Tang in treating liver fibrosis of wilson's disease with damp-heat accumulation
- Clinical efficacy of dapagliflozin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction
