Small Amplicons Mutation Library for Vaccine Screening by Error-Prone Polymerase Chain Reaction
2023-05-18CHENGManman程曼曼ZHANGYunlong张云龙CHENTingZHANGMinmin张敏敏LUChangrui陆昌瑞
CHENG Manman(程曼曼), ZHANG Yunlong(张云龙), CHEN Ting(陈 婷), ZHANG Minmin(张敏敏), LU Changrui(陆昌瑞)
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
Abstract:Library construction is a common method used to screen target genes in molecular biology. Most library constructions are not suitable for a small DNA library (<100 base pair(bp)) and low RNA library output. To maximize the library’s complexity, error-prone polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to increase the base mutation rate. After introducing the DNA fragments into the competent cell, the library complexity could reach 109. Library mutation rate increased exponentially with the dilution and amplification of error-prone PCR. The error-prone PCR conditions were optimized including deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) concentration, Mn2+ concentration, Mg2+ concentration, PCR cycle number, and primer length. Then, a RNA library with high complexity can be obtained by in vitro transcription to meet most molecular biological screening requirements, and can also be used for mRNA vaccine screening.
Key words:error-prone polymerase chain reaction; in vitro transcription; DNA library; RNA library
Introduction
Error-prone polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a preferred method for introducing random mutations and often used in synthetic biology and directed evolution[1]. Compared with normal PCR, error-prone PCR takes advantage of the low fidelity of DNA polymerase[2].TaqDNA polymerase isolated from thermophiles[3]has good thermal stability, and low error with approximately one nucleotide every 105due to its fidelity[4]. Error-prone PCR improves the mismatch rate by changing the conditions of the reaction system based on normal PCR[5]. To form random DNA library mutation[6], the following aspects are usually considered. (1)TaqDNA polymerase is a natural DNA polymerase with a high mutation rate due to the lack of correction effect of 3′ to 5′ exonuclease[7]. (2) Adding Mn2+or Mg2+into the PCR reaction buffer can improve the mutation activity ofTaqDNA polymerase[8]. (3) The mismatch rate ofTaqpolymerase can be increased to some extent by changing different deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate(dNTP) concentrations[9]. (4)The PCR products of the previous round can be used as the template for the next round[10]. (5) The size of the library can be adjusted according to the length of the reverse primer[11]. (6) The cycle number of error-prone PCR can be increased[12]. All the PCR results were tested by agarose gel electrophoresis[13].
DNA library[14]is an important technology to discover the expression mode of genes or explore their splicing form[15]. And they can be used to screen other gene products of protein, DNA or antibody interactions[16]. At present, the construction of DNA library is generally extracted mRNA from a certain biological tissue, and then reverse transcription to obtain cDNA[17], but this method is only applicable to RNA with high and stable expression[18]. In addition to the instability of many transcripts and the complex of RNA secondary structures or other factors, reverse transcriptase is often interrupted, and then a large number of truncated cDNA clones often appeared in cDNA library[19]. A new method was adopted to construct DNA library in this research, which was amplified by error-prone PCR, and then randomly mutated DNA fragment[20]. This method is not affected by RNA stability, or the insufficient of library size due to the loss of low-expression fragments caused by differences in DNA expression levels[21]. The size of DNA library can be continuously expanded according to experimental requirements[22]. At last we usedinvitrotranscription method to transcribe the synthesized DNA library, and all the RNA fragments collection formed RNA library.
1 Experiments
1.1 Templates preparation
The template synthesized by Sangon Biotech was TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAGCCCGGATAGCTCAGTCGGTAGAGCAGCGGCCGATATCCGCGGGTCCAGGGTTCAA, ligated with T-vector, 100 μL of competent DH5αcells were placed on ice at 4 ℃, and 1 μL of template plasmid was added to the competent cells, heat shock 90 s at 42 ℃ after half an hour on ice. Then the competent cells were incubated at 37 ℃ for 30 min, centrifuged at 4 000 r/min for 3 min. The supernatant was removed and the cells were coated on the plate. Single clone were selected for culture. Plasmid with concentration of 200 ng/μL were extracted by plasmid extraction kit (Sangon Biotech Shanghai China).
1.2 Error-prone PCR
Error-prone reaction mixture including 1 mmol/L forward primers, 1 mmol/L reverse primers, 3 mmol/L dNTP, 1.25 mmol/L MgCl2, and 10 μL PCR buffer were added to 1.5 mL tubes. We took 10 μL PCR tubes and labeled them Nos.1-10, the No.1 PCR tube with 93 μL of the mixture, and the remaining tubes with 84 μL mixture. Add 1 μL template into tube No.1 and place it on Thermocycler (Bio-RAD T100 Shanghai China) for amplification. The procedure was as follows: pre-denaturation at 94 ℃ for 5 min, denaturation at 94 ℃ for 30 s, annealing at 60 ℃ for 30 s, extension at 72 ℃ for 1 min, final extension at 72 ℃ for 10 min, and retention at 4 ℃. When the temperature reached the first annealing temperature, 5 μmol/L of freshly prepared MnCl2and 1 μL 5 U/μLTaqDNA polymerase were added, the number of per PCR cycles was 10. Then 10 μL of PCR product was transferred to the next tube and the process was repeated. After the PCR procedure finished, the products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. (1) When the concentrations of deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) &deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP) and deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) &deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP) was 0.2 mmol/L and 1 mmol/L, respectively, the mutation rate reached the maximum, but there was no target band under this condition. The concentration series of dNTP was set as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 mmol/L. (2) The circle was set as 5, 10, 20, 30, and 40. (3) The concentration of Mn2+was set at 5, 15, 25, 35, and 45 μmol/L. (4) The concentration of Mg2+was set at 0.25, 0.75, 1.25, 1.75, and 2.25 mmol/L. (5) The length of reverse primers was set to 25 bp, 30 bp, and 35 bp.
1.3 Preparation of DNA library
The PCR product from error-prone PCR was ligated with T-vector for transformation using T-vector Kit (Sangon Biotech Shanghai China). The following components were added to a PCR tube: 1 μL of PCR product, 1 μL of T-vector, 5 μL of ligation buffer, and 1 μL of 50% polyethylene glycol (PEG)4000, 1 μL of T4 DNA ligase, 1 μL of ddH2O, and the reagent mix was incubated at 16 ℃ for 12 h. Top10 competent cells were thawed on ice for 30 min, and 10 μL PCR ligation system was added into the cells. After the cells were gently mixed and placed on ice for 30 min, heat shock 90 s at 42 ℃, and then placed on ice again for 5 min, incubation at 37 ℃ for 1 h. Centrifuging at 4 000 r/min for 3 min, the supernatant was discarded and pellet coated on 20 μL isopropyl bata-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) and 100 μL X-gal ammonia benzyl late[23]. After incubation at 37 ℃ for 1 h and overnight culture for 12 h, 10 single clones were selected for sequencing, and the clones were then washed and sequenced from the plate.
1.4 Preparation of RNA library
All PCR products were mixed together forinvitrotranscription. Mix 1 mL sample with 5 mL reaction system, and the reaction system includes 6 mmol/L NTPs, 30 mmol/L Tris-HCl, 25 mmol/L MgCl2, 10 mmol/L DTT, 2 mmol/L spermidine, 1%Triton X-100 50 μL, and 500 μL of T7 RNA polymerase prepared by lab. After another 2 h, transcription products were centrifuged at 4 ℃, 6 000 r/min, 30 min, and then the supernatant in the reaction system was collected and heated at 65 ℃ for 15 min. The transcription products were slowly added to 12% urea polyacrylamide gel. The filtrate was concentrated by a 3 kDa ultrafiltration tube to obtain RNA library, the RNA library was finally stored at -80 ℃.
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 RNA fold getting a stem-loop structure with high variability
A 79 bp sequence containing T7 and tRNA was designed by SnapGene[24]. RNA fold software[25]was used to analyze the stem-loop structure of RNA with strong flexibility. Different conformational changes can occur at different concentrations of Mg2+. The template was obtained by plasmid miniprep shown in Fig. 1.
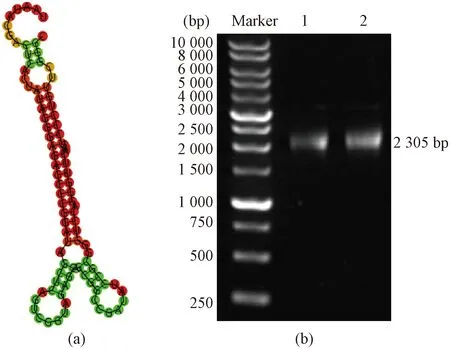
Fig. 1 Template preparation: (a) secondary structure prediction of the template using RNA fold; (b) DNA agarose gel electrophoresis for the template
2.2 Optimal conditions of error-prone PCR obtained by optimization
The optimal conditions for error-prone PCR include dNTP concentration, Mn2+concentration, Mg2+concentration, PCR cycle number, and primer length. When conducting error-prone PCR,TaqDNA polymerase with a high mutation rate was selected as the enzyme for polymerizing various dNTP in PCR. On this basis, the above five variables are optimized. As expected, error-prone PCR prefers higher dNTP concentration, but the growth rate is slow after 3 mmol/L shown in Fig. 2 (a). The PCR result suggests that as the number of cycles increased, the non-specificity of the product was enhanced, so the number of cycles was selected as 10 shown in Fig. 2(b). And the concentration of Mn2+with 25 μmol/L can yield more PCR products shown in Fig. 2(c). And the concentration of Mg2+with 1.25 mmol/L, the number of PCR products reached the maximum, shown in Fig. 2(d). The length of the primers was optimized, and the library quality would be different depending on the size of the primers. PCR yield reached the maximum when the primer length was 25 bp as shown in Fig. 2(e). Due to the interaction of various factors, response surface analysis was adopted, and the three factors with the greatest influence above, Mn2+and Mg2+concentrations, and primer length were selected for response surface hybridization, and the optimal conditions for error-prone PCR were selected for response surface hybridization shown in Fig. 2(f), and the optimal conditions for error-prone PCR were obtained as follows: dNTP concentration was 3 mmol/L, the number of cycles was 10, Mn2+concentration was 25 μmol/L, Mg2+concentration was 1.25 mmol/L, and primer length was 25 bp.
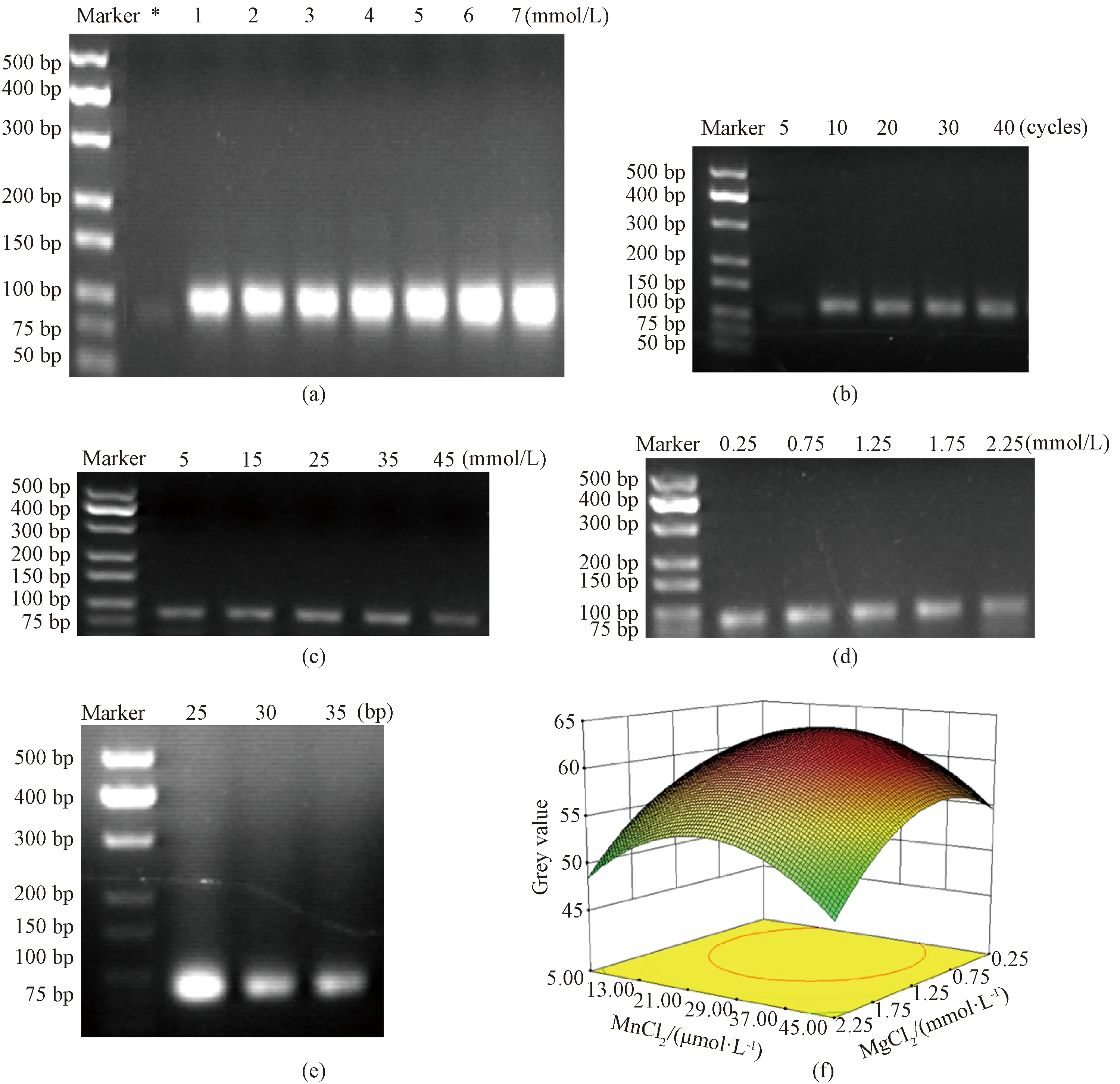
* — dATP&dGTP 0.2 mmol/L and dTTP&dCTP 1 mmol/L.
2.3 Sequencing to get high mutated DNA library
We use the PCR products as template of the next PCR to achieve the dilution and amplification effect. It could be seen that non-specific target bands appeared in the subsequent DNA gel, and this phenomenon are more obvious as the increasing of dilution as shown in Fig. 3. In Fig.3, the numbers represent the number of lanes.
After sequencing, no mutation was found in the 23 bases of the forward primer, and the bases of template have different degrees of mutation. Based on the differences of base mutation shown in Fig. 4(c), the overlapping peaks in first-generation sequencing showed that there was no mutation in the forward primers, but the other bases were mutated to varying degrees. We can find from Fig. 4 that the mutation rate of the four bases A, T, C, and G in the middle can be reached 425. The library size can be estimated as 109shown in Fig. 4(b). The results of first-generation sequencing also confirmed the existence of insertion sequences in PCR resulting in larger template fragments and there are different degrees of mutation in the middle of the unchanged primers before and after shown in Fig. 4(c), which is consistent with the results obtained by PCR.

Fig. 3 DNA library construction: (a) using the last PCR product as the next PCR template; (b)-(d) agarose gel diagram obtained by using 3 mmol/L agarose gel and tris acetate edta (TAE)

Fig. 4 DNA library sequencing: (a) template and primer diagram designed by Snapgene; (b) sequencing peak diagram; (c) comparison diagram between partial sequences obtained by Mega sequencing and template
2.4 In vitro transcribed as RNA library
DNA was transcribed into RNA byinvitrotranscription and RNA library was obtained by 12 mmol/L polyacrylamide gel and purification. The xylene blue in Fig.5(a) was the indicator band and the target band was obtained by purification with concentrations of 536 ng/μL. Moreover, the library contains fragments of different size.Invitrotranscription shown in Fig. 5(b), no extra strips was produced and the purified RNA was of high quality. In Fig.5(b), nt means nucleartide. Therefore, the concentration of library is large, and this library can be used for subsequent experimental screening, shown in Fig. 5.
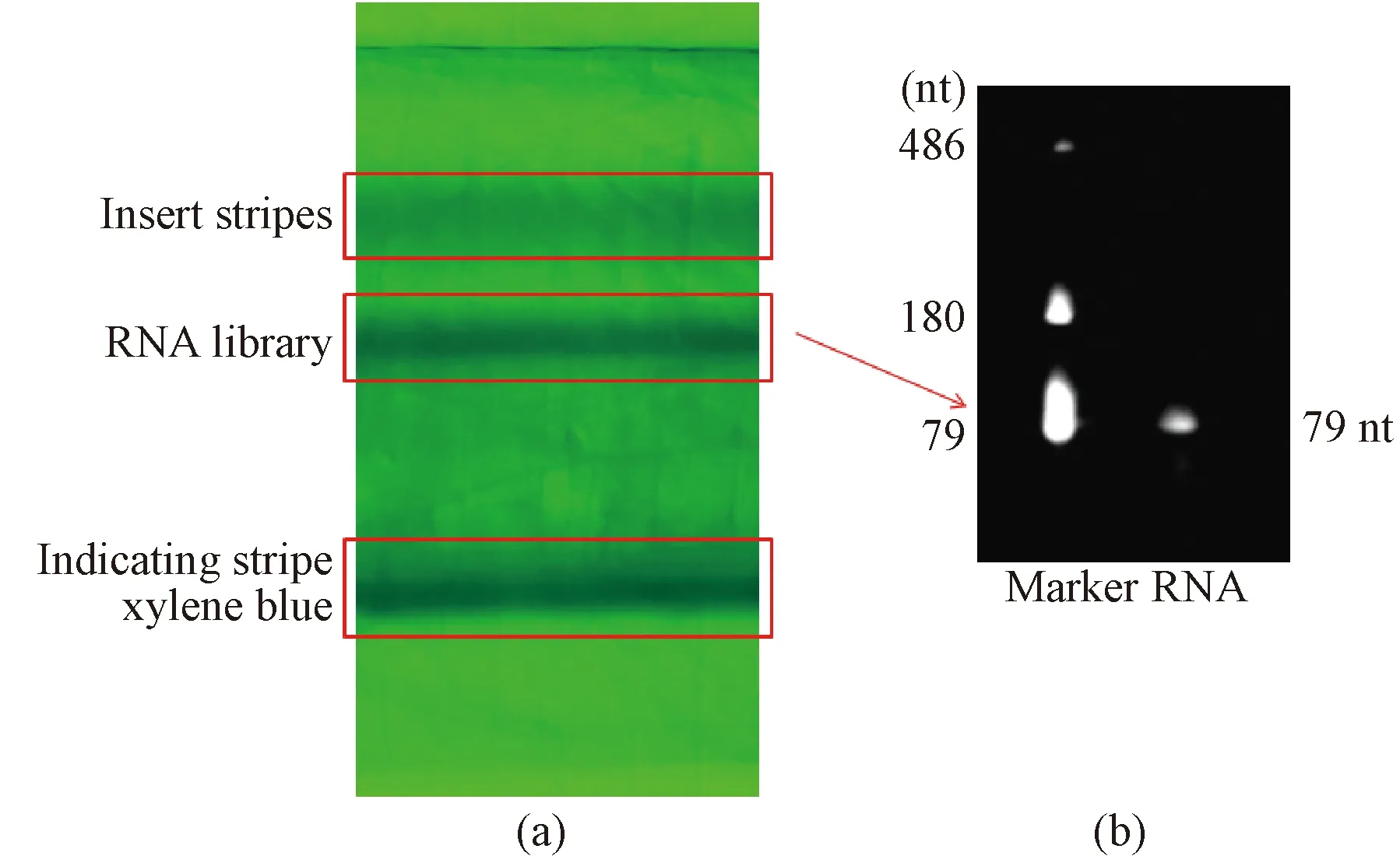
Fig. 5 RNA library construction: (a) in vitro transfer image obtained with 12% polyacrylamide gel; (b) purified RNA library
3 Conclusions
An optimized error-prone PCR situation was adopted to construct a DNA library. The optimal conditions of error-prone PCR were as follows: dNTP concentration was 3 mmol/L, PCR cycle number was 10, Mn2+concentration was 25 μmol/L, Mg2+concentration was 1.25 mmol/L, and primer length was 25 bp. PCR products after each cycle were used as the template of the next PCR to achieve dilution effect. A DNA library was obtained by mixing the PCR products amplified above, and then an RNA library was obtained byinvitrotranscription. And the RNA library can meet the needs of many molecular biology screening, including RNA vaccine.
杂志排行
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Simultaneous Morphologies and Luminescence Control of NaYF4∶Yb/Er Nanophosphors by Surfactants for Cancer Cell Imaging
- Porous Graphene-Based Electrodes for Fiber-Shaped Supercapacitors with Good Electrical Conductivity
- Fabrication of High-Efficiency Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofiber Membranes for Air Filtration Based on Principle of Stable Electrospinning
- Construction of Oriented Structure in Inner Surface of Small-Diameter Artificial Blood Vessels: A Review
- Auto-Generation Method of Child Basic Block Structure
- Proportion Integration Differentiation (PID) Control Strategy of Belt Sander Based on Fuzzy Algorithm
