Finite-Horizon l2–l∞State Estimation for Networked Systems Under Mixed Protocols
2023-03-27JiyueGuoYuanlongYueBaoyeSongandZhongyiZhao
Jiyue Guo, Yuanlong Yue, Baoye Song, and Zhongyi Zhao
Dear Editor,
This letter is concerned with the finite-horizonl2–l∞state estimation (SE) problem for a class of networked time-delay systems where the measurements are transmitted through two individual communication channels.With the aim of preventing the transmitted data from conflicts, the signal transmissions over such the communication channels are scheduled by different communication protocols,namely the stochastic communication protocol (SCP) and Round-Robin protocol (RRP).A mixed scheduling model is proposed to describe the transmission behaviors subject to such two protocols.The objective of this letter is to design an estimator such that the estimation error achieves the desired finite-horizonl2–l∞performance in the mean square.By using the Lyapunov stability theory, a sufficient condition is proposed to guarantee the existence of the desired estimator.An illustrative simulation example is given to verify the effectiveness and correctness of the proposed design scheme.
In the past decades, the SE problem has become a hot research topic in the field of signal processing and control leading to a great number of excellent results published in the literature, see e.g., [1]and [2].At the same time, a lot of SE techniques have been reported such as the set-membership SE [3],l2–l∞SE [4] and variance-constrained SE [5].Among others, thel2–l∞SE method has been found suitable to deal with square-summable noises.Note that due to various reasons such as temperature fluctuations and component ageing[6], almost all practical systems contain certain time-varying parameters.In such a case, the traditionall2–l∞SE technique that is implemented over an infinite-horizon is no longer suitable.Accordingly, it makes practical sense to study thel2–l∞SE problem over a finitehorizon.





Fig.1.State trajectories of z(s) and zˆ(s) under mixed protocols.
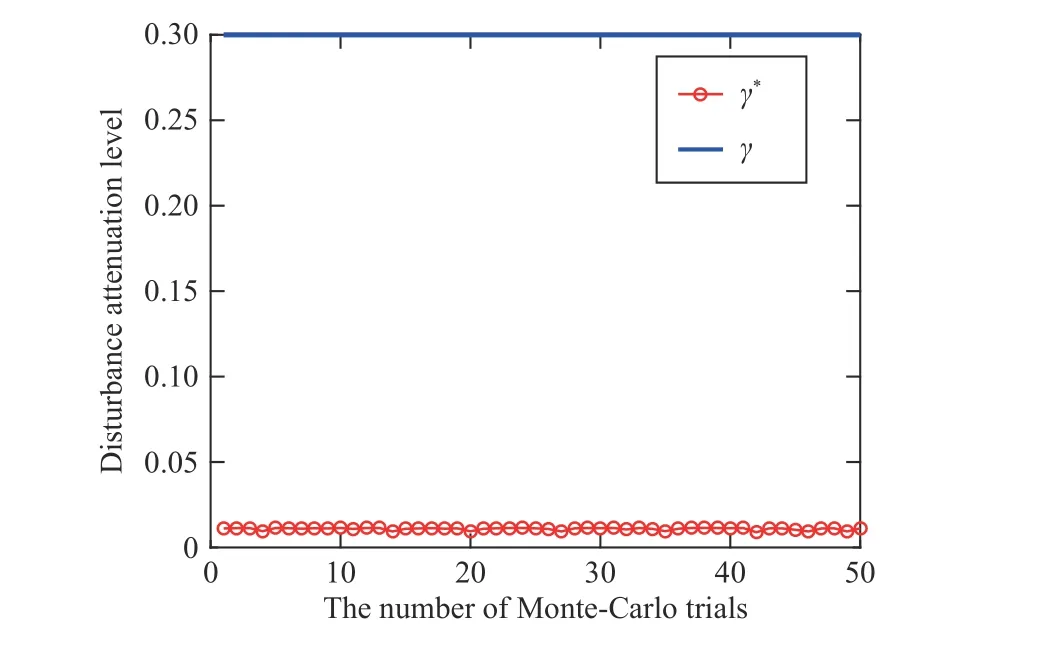
Fig.2.γ∗and the disturbance attenuation level.
杂志排行
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica的其它文章
- Current-Aided Multiple-AUV Cooperative Localization and Target Tracking in Anchor-Free Environments
- Event-Triggered Asymmetric Bipartite Consensus Tracking for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems Based on Model-Free Adaptive Control
- UltraStar: A Lightweight Simulator of Ultra-Dense LEO Satellite Constellation Networking for 6G
- Multi-AUV Inspection for Process Monitoring of Underwater Oil Transportation
- Process Monitoring Based on Temporal Feature Agglomeration and Enhancement
- Parallel Learning: Overview and Perspective for Computational Learning Across Syn2Real and Sim2Real
