Chemical basis of pregnane X receptor activators in the herbal supplement Gancao (licorice)☆
2023-01-09AnqiChengSifeiLeiJunjieZhuJieLuMryPineWenXieXiocho
Anqi Cheng ,Sifei Lei ,Junjie Zhu ,Jie Lu ,Mry F.Pine ,Wen Xie ,Xiocho M ,*
a Center for Pharmacogenetics,Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences,School of Pharmacy,University of Pittsburgh,Pittsburgh,PA,USA
b Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences,College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences,Washington State University,Spokane,WA,USA
Keywords:Gancao Licorice Glabridin Pregnane X receptor (PXR)Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4)Herb-drug interactions
ABSTRACT Background and aims: The herbal supplement Gancao,also known as licorice,belongs to the genus Glycyrrhiza and has been used worldwide for its hepatoprotective effect.Recent studies have raised concerns about potential herb-drug interactions associated with Gancao via pregnane X receptor (PXR)-mediated induction of hepatic cytochrome P450 3A4(CYP3A4).The current work aimed to determine the phytochemicals in Gancao that activate PXR and induce CYP3A4.Methods: DPX2 cells were used for cell-based PXR reporter assays.The phytochemicals in Gancao extract were identified using a metabolomics approach.The effects of PXR activators identified from in vitro studies were further investigated in PXR-and CYP3A4-humanized mouse models.Results: Gancao was verified to be a PXR-activating herb.Two major phytochemicals in Gancao,glycyrrhizin (GZ) and glycyrrhetinic acid (GA),did not activate PXR in the cell-based reporter assays.However,glabridin was shown to activate PXR in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo studies confirmed that GZ is not a PXR activator and glabridin is a weak PXR activator.Although GA did not active PXR in vitro,it induced CYP3A4 expression in a PXR-dependent manner in the PXR-and CYP3A4-humanized mice.Conclusions: GZ is not a PXR activator.GA could not activate PXR in cell-based reporter assays but it could activate PXR in vivo.Glabridin is a weak PXR activator.This work provides novel insights into the underlying mechanisms of Gancao-related herb-drug interactions via PXR.
1.Introduction
Gancao is a herbal supplement used worldwide as a flavoring agent and for its pharmacological effects.1,2Gancao has been used in Asian countries for thousands of years and is a component of approximately 80% of traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions.3People typically immerse dried Gancao root (with or without other herbs) into water,boil the mixture,and then consume the mixture for its purported hepatoprotective,anti-inflammatory,antioxidant,anti-viral,and anti-cancer properties.4-7In Western countries,Gancao extract,as well as the active phytochemicals glycyrrhizin (GZ) and glycyrrhetinic acid (GA),are components of manufactured foods,beverages,snacks,flavorings,and dietary supplements.2,8-10In addition,derivatives of GZ and GA have been developed for pharmacological purposes.11-13
Despite of the widespread use of Gancao products,the regulation for their safe usage is limited,raising concern for potential herb-drug interactions associated with Gancao.Pregnane X receptor(PXR),a ligand-dependent nuclear receptor,mediates many herb-drug interactions and adverse drug reactions by regulating the expression of Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4),a prominent enzyme involved in drug metabolism.14-17In vitrostudies have shown that Gancao extract activated PXR and induced CYP3A4 expression.18,19GZ and GA in Gancao have been considered as PXR activators based onin vitrodata.20-23However,the data from these previous reports are equivocal due to the lack of demonstration of dose-response in PXR activation,lack ofin vivovalidation,and inconsistencies among different research groups.21-23
The current work aimed to identify the phytochemicals in Gancao that activate PXR.Because of the well-known species differences in PXR with respect to its ligands,15,24we focused on human pregnane X receptor (hPXR) by using cell-based hPXR reporter assays and PXR-humanized mouse models.A metabolomics approach was used to profile the phytochemicals in Gancao extract to screen for PXR activators.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Ethical approval
All experiments were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Pittsburgh.
2.2.Chemicals and materials
Rifampicin (RIF),liquiritin,liquiritin apioside,and GZ were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis,MO,USA).GA,isoliquiritigenin,glabridin,isoliquiritin,and liquiritigenin were purchased from Cayman Chemical Company (Ann Arbor,MI,USA).Isoliquiritin apioside,glabrol,licochalcone B,and echinatin were obtained from MedChemExpress (Monmouth Junction,NJ,USA).Aqueous extract of Gancao (Glycyrrhiza glabra) was purchased from Horbaach(Ronkonkoma,NY,USA).Midazolam(MDZ)and its primary metabolite 1′-hydroxymidazolam (1′-OHMDZ) were obtained from Akorn Pharmaceuticals (Lake Forest,IL,USA) and Toronto Research Chemicals (Toronto,Ontario,Canada),respectively.
2.3.Cell-based reporter assays of hPXR
DPX2 cells (Puracyp,Inc;Carlsbad,CA,USA) were used for screening PXR activators,which were derived from HepG2 cells and stably transfected with hPXR and a luciferase-linked CYP3A4 promoter.25The assays were conducted using a previously reported method with minor revisions.26In brief,DPX2 cells were cultured in 96-well plates(5×105cells/mL)for 24 h.Varying concentrations of Gancao extract or phytochemicals were prepared in a dosing medium and incubated with DPX2 cells for another 24 h.RIF was used as a positive control for hPXR activation.All incubations were conducted in triplicate.
2.4.Metabolite analysis
Ultra-performance liquid chromatography and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOFMS) (Waters Corporation,Milford,MA,USA) were used for the analysis of chemical components in Gancao extract.A 100 mm×2.1 mm UPLC BEH C-18 column (Acquity 1.7 μm) together with a gradient of aqueous acetonitrile with 0.1% of formic acid were used for chemical separation.QTOFMS was conducted in a negative mode with electrospray ionization.The data were collected by MassLynx 4.1(Waters Corporation,Milford,MS,USA) and further analyzed by SIMCA-P(Umetrics,Kinnelon,NJ,USA).
2.5.Animal treatments
PXR-and CYP3A4-humanized mice (TgCYP3A4/hPXR) and CYP3A4-humanized mice deficient inPxr(TgCYP3A4/Pxr-/-) were used to validate the effects of chemicals from Gancao extract on PXR activation and CYP3A4 induction.These mice have been described in previous reports.27,28The mice (male,6-week-old)were treated with GZ,GA,or glabridin(100 mg/kg,p.o.)once daily for 4 days.The mice were sacrificed 24 h after the last dose.The liver samples were collected for analyses of CYP3A4 expression and activity.
2.6.CYP3A4 expression in the liver
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was used to measure CYP3A4 mRNA using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix(Thermo Fisher Scientific;Warrington,UK).The primers were 5′-GTCTTTGGGGCCTACAGCAT-3’ (forward) and 5′-GGGATGAGGAATGGAAAGACTGTT-3’ (reverse) for human CYP3A4 and 5′-GGAGATGGCACAGGAGGAA-3’ (forward) and 5′-GGCCGTAGTGCTTCAGCTT-3’ (reverse) for mouse cyclophilin.S9 fractions of mouse liver were prepared to measure CYP3A4 protein by Western blot.The primary antibodies used for CYP3A4 and GAPDH were purchased from Fizgerald Industries International (North Acton,MA,USA)and MilliporeSigma (Burlington,MA,USA),respectively.
2.7.CYP3A4 activity assays
MDZ was used as a probe of CYP3A4,which was conversed to 1′-OHMDZ.The incubation system included the liver S9 fraction(1 μg/μL),MDZ (30 μmol/L),and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH,1 mmol/L) in a total volume of 100 μL.The mixture was incubated at 37°C for 15 min.Afterward,100 μL of methanol and acetonitrile mixture(1:1 ratio)was used to stop the reaction.The reaction was initiated by the addition of NADPH and allowed to proceed at 37°C for 15 min.Methanol and acetonitrile(1:1 ratio,100 μL)were used to stop the reaction.The mixture was vortexed and then centrifuged at 15,800 ×gfor 10 min.The supernatant was collected to measure 1′-OHMDZ using UPLCQTOFMS.
2.8.Cell-based reporter assays of constitutive androstane receptor(CAR) and glucocorticoid receptor (GR)
The assays were conducted using the same methods as previously described.29,30Briefly,293T cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium with 10% of fetal bovine serum and 5% of penicillin-streptomycin.CAR and GR were transfected into 293T cells and cultured in a 96-well plate for 24 h.Afterward,the testing drugs including GA and positive controls (TCPOBOP for CAR and dexamethasone for GR were added to the cells and incubated for another 24 h.
2.9.Data analysis
All quantified data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 9.4.1.Student'st-test or one-way analysis of variance (One-way ANOVA) was used to determine the differences among groups.Significance was accepted whenP<0.05.
3.Results
3.1.Gancao extract activates hPXR in vitro
A previous report showed that both aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Gancao can activate hPXR.18The current work investigated the effects of the aqueous Gancao extract on hPXR using a cellbased reporter assay.We found that Gancao extract can strongly activate hPXR at the dilution of 1:100,which is similar to RIF(10 μmol/L),the positive control for hPXR activation (Fig.1A).In addition,Gancao extract dose-dependently activated hPXR(Fig.1B),indicating that Gancao is a PXR-activating herb.

Fig.1.Gancao extract activates hPXR.Cell-based hPXR reporter assays were conducted using DPX2 cells.(A) Effect of Gancao extract on hPXR activation.Gancao extract was diluted 100-fold.RIF(10 μmol/L)was used as a positive control for hPXR activation.(B)A dose-dependent hPXR activation by Gancao extract(100-to 1000-fold dilution).The data in control groups were set as 1.All data are expressed as means±SEM(n=3).**P<0.01,***P<0.001,****P<0.0001 vs.control.Abbreviations:hPXR,human pregnane X receptor;RIF,rifampicin;SEM,standard error of the mean.
3.2.Identifications of components in Gancao extract
To facilitate the screening of PXR activators from Gancao,we explored the chemical components in Gancao extract by using a metabolomic approach.The score plot showed significant differences between the control and Gancao extract groups(Fig.2A).The loading S-plot illustrated the variance of each ion between the two groups (Fig.2B).Identifications were completed by comparing the retention time (RT),m/z,and MS/MS fragments of the observed compounds in Gancao extract with chemical standards.The topranking compounds were determined as liquiritin apioside,GZ,and liquiritin (Table 1,Fig.2B-D,Supplemental Figs.1-4).Other identified components from Gancao extract included GA,liquiritigenin,isoliquiritin,isoliquiritigenin,glabridin,licochalcone B,glabrol,and esculetin (Table 1,Supplemental Figs.1-4).

Table 1Identification of phytoconstituents in Gancao extract via metabolomics analysis.Gancao extract was analyzed by UPLC-QTOFMS.
3.3.Screening of PXR activators from Gancao extract
All the identified chemicals from Gancao extract were screened for their effects on hPXR using cell-based reporter assays.Both GZ and GA,the major components in Gancao,have been considered as hPXR activators in previous reports.20-23However,neither GZ nor GA can activate hPXR in our screening assays(Fig.3A).Interestingly,we observed that glabridin can activate hPXR (Fig.3A).To further investigate the effects of GZ,GA,and glabridin on hPXR,a doseresponse assay was conducted,which confirmed that both GA and GZ cannot directly activate hPXR (Fig.3B).Glabridin could dose-dependently activate hPXR(Fig.3B),but the effect was much weaker compared with that of RIF,a well-known hPXR activator.31
3.4.Effects of individual chemicals on hPXR in TgCYP3A4/hPXR mice
Based on thein vitroscreening results(Fig.3),we next validated the effects of GZ,GA,and glabridin on PXR activation using PXRhumanized mice.CYP3A4 expression and activity in the liver of TgCYP3A4/hPXR mice were used as biomarkers of PXR activation.As expected,glabridin moderately upregulated the expression and activity of CYP3A4 in the liver of TgCYP3A4/hPXR mice (Fig.4),indicating that glabridin is an hPXR activator.Consistent with thein vitrodata (Fig.3),treatment with GZ had no impact on the expression and activity of CYP3A4 in the liver of TgCYP3A4/hPXR mice (Fig.4),indicating that GZ is not an hPXR activator.Surprisingly,although GA did not activate hPXR in thein vitroassays(Fig.3),treatment with GA significantly increased the expression of CYP3A4 in the liver of TgCYP3A4/hPXR mice (Fig.4).
3.5.Mechanisms of GA in CYP3A4 regulation
In addition to PXR,CAR and GR also regulate CYP3A4 expression.32,33We therefore asked whether GA is an activator of CAR and/or GR.Using cell-based reporter assays,we found that neither CAR nor GR can be activated by GA (Fig.5A and B).We next refocused on PXR and tested whether GA-mediated CYP3A4 induction in TgCYP3A4/hPXR mice is PXR-dependent.We found that GA cannot upregulate CYP3A4 expression in TgCYP3A4/Pxr-/-mice(Fig.5C),indicating that GA-mediated CYP3A4 inductionin vivois PXR-dependent.
4.Discussion
Using the genetically engineered hPXR cell lines and mouse models,the current work investigated the effects of Gancao,a popular herbal supplement,on hPXR activation and CYP3A4 induction.We confirm that Gancao is a PXR-activating herb.Regarding the components in Gancao that activate PXR,our work demonstrated that: (i) GZ is not a PXR activator;(ii) GA could not activate PXR in cell-based reporter assays but it could activate PXRin vivo;and (iii) glabridin is a weak PXR activator.
GZ,one of the most abundant and active components in Gancao,is approximately 50 times as sweet as sucrose and it has been approved for use as a flavor and aroma in manufactured foods and dietary supplements in the US.34Previous studies suggested that GZ is a PXR activator and potentially leads to CYP3A4-mediated herb-drug interactions.21-23However,our cell-based PXR reporter assays showed that GZ cannot activate hPXR.Ourin vitrofinding on GZ was validated in PXR-humanized mice,which further confirmed that GZ is not a PXR activator.However,GZ can be hydrolyzed by intestinal bacteria-mediated to produce GA,35,36and GA was proven to be a PXR activatorin vivo(Figs.3-5).Therefore,long-term use of GZ at a high dose may still activate PXR via its metabolite GA and lead to PXR-mediated herb-drug interactions.

Fig.2.Metabolomic profiling of Gancao phytoconstituents.Gancao extract was analyzed by UPLC-QTOFMS.(A) Score plot showing the metabolome difference between the control and Gancao extract groups.(B)Loading S-plot indicating the compounds in Gancao extract.(C)Chromatogram of glycyrrhizin(GZ).(D)MS/MS fragmentation of GZ.Major fragment ions were interpreted in the inlaid structural diagram.Abbreviations:MS,mass spectrometry;UPLC-QTOFMS,ultra-performance liquid chromatography and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
GA is an active component in Gancao that has shown anticancer,anti-oxidative stress,anti-microbial,anti-viral,and antiinflammatory activities.37-44In addition,GA derivatives have been developed to improve the pharmacological profile of GA including bioavailability,selectivity,and potency.45-47Our current work found that GA cannot activate PXR in the cell-based reporter assays(Fig.3).However,GA upregulated CYP3A4 expression in the liver in a PXR-dependent manner (Fig.5).It is possible that the metabolite(s) of GA are hPXR activators,and/or GA disrupts the metabolism of endobiotics and leads to the accumulation of endogenous hPXR activators in the liver.Further studies are needed to determine how GA activates hPXRin vivo.
Glabridin is another bioactive compound in Gancao that suppresses inflammation by inhibiting cyclooxygenase.48,49Glabridin also protects against cardiovascular diseases.50A recentin vitrowork suggested that glabridin is a PXR activator.51Our work confirmed the previous finding and further validated the effect of glabridin on PXR activation and CYP3A4 induction using PXR-and CYP3A4-humanized mice.Our data revealed that glabridin is a weak hPXR activator,especially when compared with the prototypic hPXR activator RIF (Figs.3 and 4).Considering the effects of Gancao extract on hPXR activation,which is similar to RIF (Fig.1),we speculate there are still unidentified constituents in Gancao that can activate hPXR.Additional phytochemicals in Gancao extract need to be tested for their effects on PXR activation and CYP3A4 induction.

Fig.3.Screening of Gancao phytoconstituents for PXR activators.DPX2 cells were used for hPXR reporter assays.(A)Effects of the identified compounds(10 μmol/L each)from Gancao extract on hPXR activation.RIF(10 μmol/L)was used as a positive control.All data are expressed as means±SEM(n=3).**P<0.01,****P<0.0001 vs.control(set as 1).(B)Dose responses of GZ,GA,and glabridin on hPXR activation.The data in RIF group at 100 μmol/L were set as 1.All data are expressed as means (n=3).Abbreviations: GA,glycyrrhetinic acid;GZ,glycyrrhizin;hPXR,human pregnane X receptor;RIF,rifampicin;SEM,standard error of the mean.
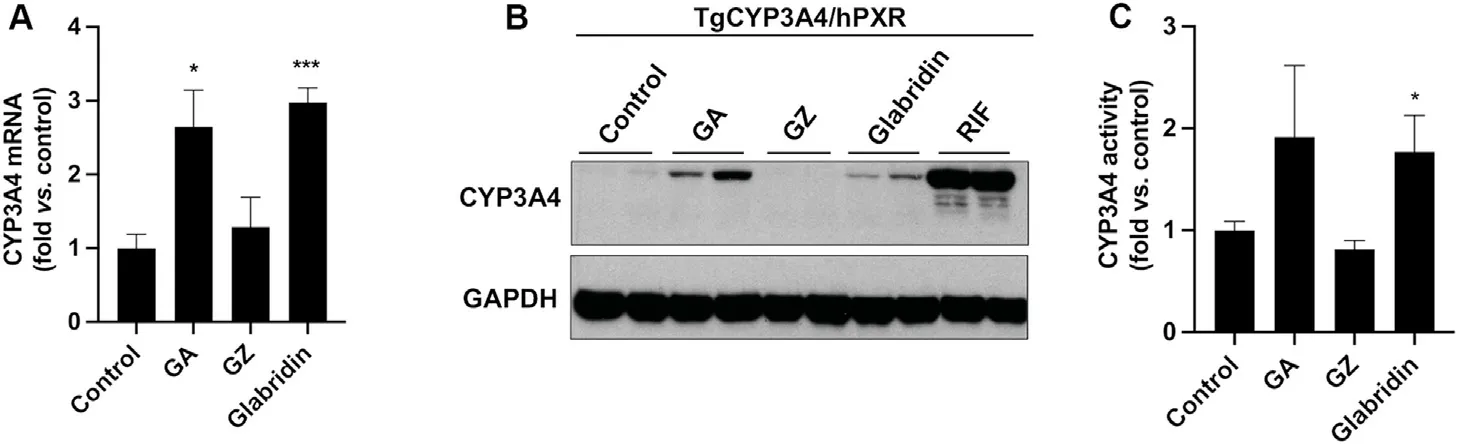
Fig.4.Effects of individual phytochemicals from Gancao on CYP3A4 expression and activity in the livers of TgCYP3A4/hPXR mice.TgCYP3A4/hPXR mice were administered 100 mg/kg of GZ,GA,or glabridin orally(once daily for 4 days).RIF(50 mg/kg)was used as a positive control.(A)qPCR analysis of CYP3A4 mRNA expression in the liver.(B)Western blot of CYP3A4 protein in the liver.GAPDH was used as a loading control.(C) CYP3A4 activity (midazolam 1′-hydroxylation) in the liver S9 fractions.The quantified data are expressed as means±SEM(n=3-4).The data in control groups were set as 1.*P<0.05,***P<0.001 vs.control.Abbreviations:CYP3A4,cytochrome P450 3A4;GA,glycyrrhetinic acid;GZ,glycyrrhizin;hPXR,human pregnane X receptor;qPCR,quantitative polymerase chain reaction;RIF,rifampicin;SEM,standard error of the mean.
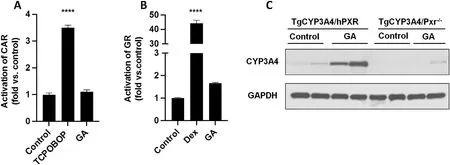
Fig.5.Mechanisms of GA-mediated CYP3A4 induction.(A)Cell-based CAR reporter assays of GA(10 μmol/L).TCPOBOP(250 nmol/L)was used as a positive control for CAR activation.(B)Cell-based GR reporter assays of GA(10 μmol/L).Dexamethasone(Dex,10 nmol/L)was used as a positive control for GR activation.All data are expressed as means±SEM(n=3).****P<0.0001 vs.control.The data in control groups were set as 1.(C)Effects of GA on CYP3A4 expression in the liver of TgCYP3A4/hPXR and TgCYP3A4/Pxr-/-mice.The mice were treated with 100 mg/kg of GA once daily for 4 days.CYP3A4 expression in the liver was determined by Western blotting.GAPDH was used as a loading control.Abbreviations: CAR,constitutive androstane receptor;CYP3A4,cytochrome P450 3A4;GA,glycyrrhetinic acid;GR,glucocorticoid receptor;hPXR,human pregnane X receptor;SEM,standard error of the mean.
In summary,the current work profiled hPXR activators in Gancao,a hepatoprotective herb.We demonstrated that GZ is not an hPXR activator,whereas glabridin is a weak hPXR activator.Our work also revealed that GA could activate hPXRin vivovia unknown mechanisms.The results from this work can be used to guide the safe use of Gancao products by targeting PXR-mediated herb-drug interactions.
Authors' contributions
A.Cheng and X.Ma conceived the project and wrote the manuscript.A.Cheng,S.Lei,J.Zhu,and J.Lu conducted experiments and performed data analysis.A.Cheng,M.F.Paine,W.Xie and X.Ma contributed to the scientific discussion and experimental design.All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the USA National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health Grant R21AT011088 (to X.Ma)and in part by Grant U54AT008909 (to M.F.Paine),and in part by the USA National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Grant R01AI131983 (to X.Ma) and National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Grant R01DK126875 (to X.Ma).
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livres.2022.11.007.
杂志排行
Liver Research的其它文章
- Pathogenesis of fatty liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma☆
- Prevalence,diagnosis,treatment,and associated factors of hepatitis C in the United States from 1999 to 2018: A population-based crosssectional study☆
- Effects of apical sodium-bile acid transporter inhibitor and obeticholic acid co-treatment in experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis☆
- Prediction of effective percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A multi-central retrospective study☆
- MUTYH is a potential prognostic biomarker and correlates with immune infiltrates in hepatocellular carcinoma☆
- Hepatic transcriptome profiling reveals early signatures associated with disease transition from non-alcoholic steatosis to steatohepatitis☆
