高温影响拟南芥减数分裂染色质上5-甲基胞嘧啶的分布
2023-01-05刘虹杨珂宁莹洁马月平宋粲杨杰峰
刘虹,杨珂,宁莹洁,马月平,宋粲,杨杰峰*
(1中南民族大学 生命科学学院&武陵山区特色资源植物种质保护与利用湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430074;2三峡大学 生物与制药学院,宜昌 443002;3湖北生态工程职业技术学院,武汉 430200)
Meiotic recombination(MR)drives reciprocal exchange of genetic materials through formation of crossovers(COs),which is vital for genomic diversity and meanwhile safeguards balanced segregation of homologous chromosomes. MR is initiated by programmed generation of DNA double-strand breaks(DSBs),with plants defective for DSB formation exhibiting failed homolog synapsis and impaired MR[1].At early stages of MR,large number of DSBs are generated,however,only a minor proportion of them are processed into crossovers(COs)[2].DSBs and COs are not evenly distributed on the chromosomes,which,however,are shaped by both MR regulators and/or epigenetic modifications on the chromatin[2-3].Generally,DSBs and COs tend to localize at chromosome regions with lower nucleosome density and DNA methylation levels[4].
Many aspects of plant development are prone to be impacted by variations of environmental conditions including light,temperature,and nutrition.Especially,male reproductive development is hypersensitive to extremetemperaturestresses[5].Indifferentplantspecies,low temperatures have been found to predominantly affect meiotic cytokinesis,which consequently causes meiotic restitution and unreduced gametes[6-7].In contrast,increased environmental temperatures induce a broader impact on multiple meiosis processes,including MR rate shift,chromosome segregation,and microtubule-based phragmoplast formation[8-12].These facts indicate that male meiosis and recombination are more instable under a higher temperature condition.Considering that male meiosis is crucial for plant male fertility and seed set,and has an important role in influencing genomic diversity and stability over generations,environmental temperatures thus may affect genome evolution of plants by manipulating one or more meiosis programs.
Heat stress alters CO distribution,and/or suppresses CO by inhibiting DSB formation in Arabidopsis[8,12].DNA methylation is a feature that shapes DSB and/or CO landscape,and is also sensitive to temperature variations[13],so increased temperature may influence distribution of DSBs and/or COs by modulating DNA methylation status on the chromatin.In this study,immunostaining of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) on prophase I-staged chromosomes in wild-type Columbia-0 (Col-0)Arabidopsis plants was performed under both control and high temperature conditions.Changes of 5mC signals at both heterochromatin and euchromatin chromosome regions suggest that elevation of environmental temperatures affect DNA methylation status and distribution during MRin Arabidopsis.
1 Material and Methods
1.1 Plant materials and growth conditions
Arabidopsis thalianaColumbia-0(Col-0)plants were cultivated in growth chambers with a 16 h day/8 h night,20℃,and 50%humidity condition.For temperature stress treatment,young flowering plants were transferred to a humid chamber with a 16 h day/8 h night and at 32 and 36-38℃conditions for 24 h,respectively.Meiosis-staged flower buds were fixed by Carnoy's Fluid(ethanol:acetic acid=3∶1)upon the finish of treatment.
1.2 Immunolocalization of 5mC
Immunolocalization assay was performed by referring to[14].Antibody against 5-Methylcytosine(Invitrogen,ondary Antibody Alexa Fluor 555(Invitrogen)was diluted by 1∶400.
1.3 Microscopy
Fluorescence images were recorded using an Olympus IX83 inverted fluorescence microscope with a X-Cite lamp and a Prime BSI camera.Bifluorescent images and Z-stacks were processed using Image J.Brightness and contrast setting of pictures were adjusted using PowerPoint 2016.
2 Results
The landscape of both DSBs and CO highly correlates with methylation status of chromatin[2-4,15].To test whether affected distribution of DSBs and/or CO under increased temperature is caused by variation in DNA methylation landscape[8],immunolocalization of methylated cytosines in wild-type Col-0 plants was performed using an anti-5-methylcytosine(5mC)antibody.Under control temperature,5mC foci were found to be enriched at heterochromatin regions on leptotene,zygotene and pachytene chromosomes(Fig.1),which was in line with the previous report[16].Under 32℃,however,5mC signal showed increased or decreased enrichment at some euchromatin or heterochromatin regions on the prophase chromosomes,respectively[Fig.2(a)-(d),see white arrows].Similar alterations were observed in plants stressed by 36-38℃[Fig.3(a)-(d),see white arrows].These observations suggest that the increase of temperature has an impact on the occurrence and/or distribution of DNA methylation on chromatin during MR in Arabidopsis.
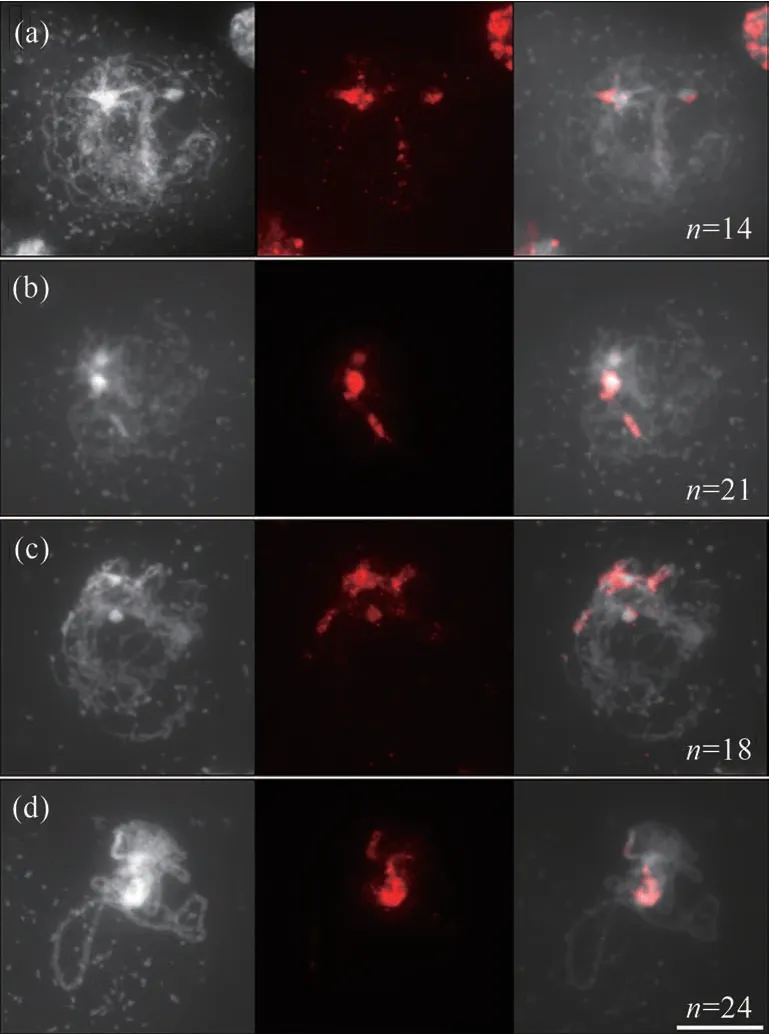
Fig.1 Immunolocalization of 5mCin wild-type Col-0 plants incubated at 20℃图1 免疫荧光技术检查野生型Col-0在20℃时染色体上5mC的分布
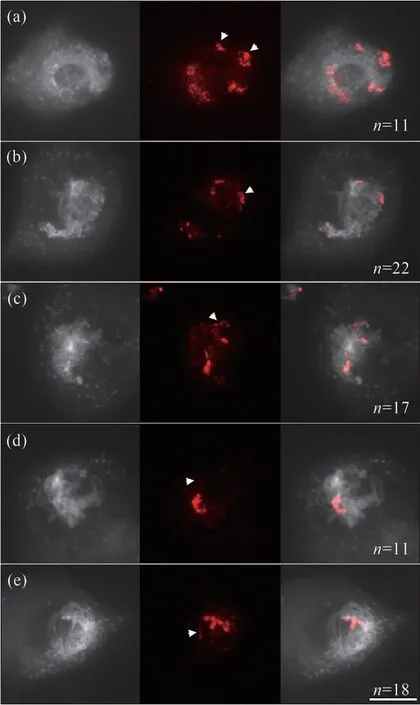
Fig.2 Immunolocalization of 5mCin wild-type Col-0 plants incubated at 32℃图2 免疫荧光技术检查野生型Col-0植株在32℃时染色体上5mC的分布
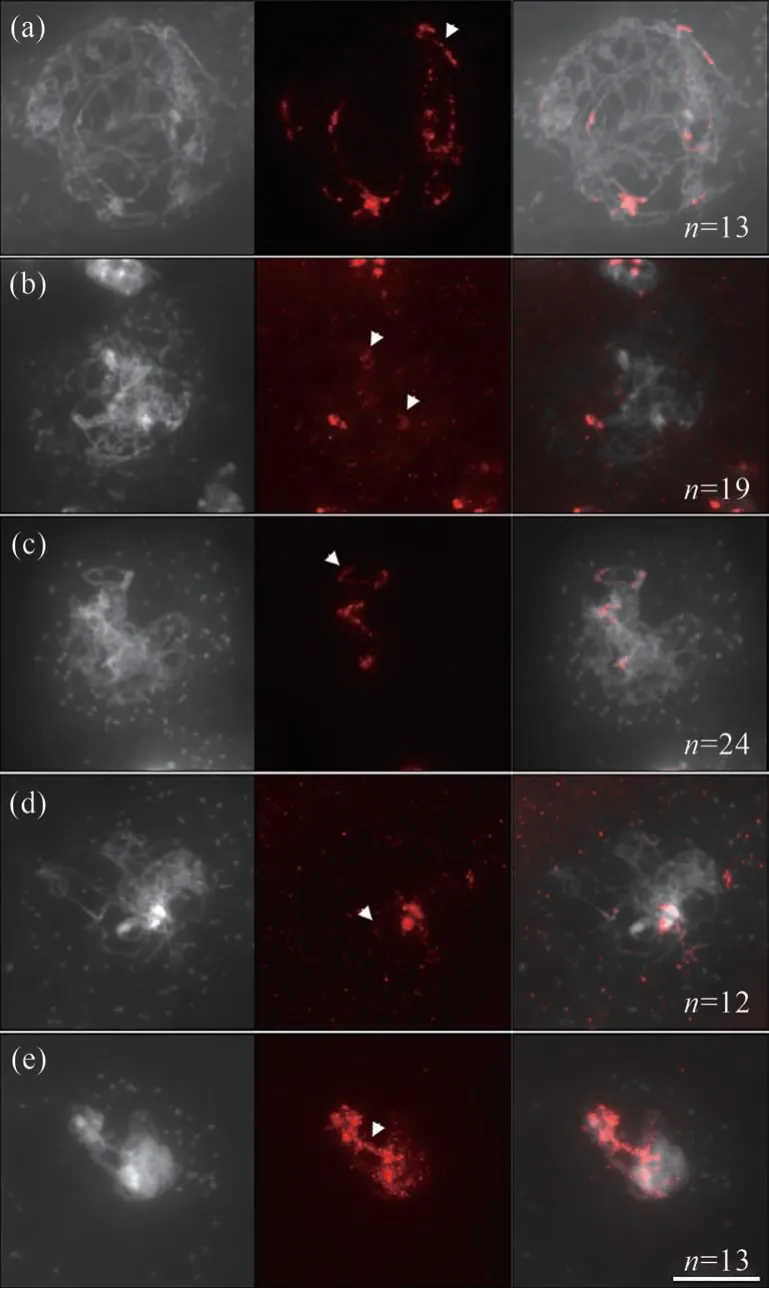
Fig.3 Immunolocalization of 5mCin wild-type Col-0 plants incubated at 36-38℃图3 免疫荧光技术检查野生型Col-0在36~38℃时染色体上5mC的分布
3 Discussion
In multiple species,environmental temperatures have been shown to influence the landscape of DSBs and/or CO during meiotic recombination[8-10].The landscape of both DSBs and COare shaped by genomic features including epigenetic modification status/patterns of DNA and histone proteins[2,4,15,17],which are targets of temperature stimulus[13].The effects of heat stress on plant growth and development are accompanied by epigenetic modification.Heat stress affected the DNA methylation level of plants to a certain extent.Some studies have found through highthroughput sequencing technology that certain genes are involved in heat stress response inArabidopsis thalianaunder heat stress,which reduces DNA methylation level[18].The study showed that the DNA methylationstatusateuchromatinand/orheterochromatin regions of chromatin changed upon the elevation of temperature.The heat-induced reshape of DSB and/or COlandscape hence could at least partially be owing to the variations of DNA methylation distribution on the chromatin.Meanwhile,the distribution of CO on the chromosomes is also sensitive to variations of DSB abundance[19].The affected DSB formation at higher temperature conditions(e.g.32℃)thus may also contributetothealtered landscapeof CO[8].Examination the landscape of DSBs and/or CO in heat-stressed mutants defective forde novoand/or maintenance of DNA methylation;e.g.drm1 drm2 cmt3andmet1[20]would contribute to the understanding the association of DNA methylation and MR in response to environmental temperature alterations.
