Regulatory Effects of Zuogui Pill on Apoptosis of Follicles in Rats Injured by 60Co-γ Rays Based on PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
2022-11-28FenqinZHAOMingxiaANXiaonanDINGJieyingLIUYanZHAOZhihuiXIEShupingLI
Fenqin ZHAO, Mingxia AN, Xiaonan DING, Jieying LIU, Yan ZHAO, Zhihui XIE, Shuping LI
1. Gansu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, China; 2. Gansu Provincial People’s Hospital, Lanzhou 730000, China
Abstract [Objectives] To explore the protective effects of Zuogui Pill on 60Co-γ-ray-induced premature aging of rats based on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) signaling pathway. [Methods] Sixty sexually mature female SD rats were irradiated with 60Co-γ-ray (6.0 Gy, LD40) for 24 h at one time. These rats were randomly divided into model group, Progynova group [0.18 (g·kg)/d], Progynova [0.09 (g·kg)/d] + Zuogui Pill high dose [23.625 (g·kg)/d)] group, Zuogui Pill high dose [23.625 (g·kg)/d)] group, Zuogui Pill medium dose [9.45 (g· kg)/d)] group and Zuogui Pill low dose [4.725 (g·kg)/d] group. The administration (once a day) lasted 21 d. The rat serum [follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH) and estradiol (E2)] were detected by Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The morphological changes of ovary were observed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. The apoptosis rate of granulosa cells was detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL). The protein expression of phosphorylated (p)-PI3K, p-Akt, p-mTOR, B-cell lymphoma-2(Bcl-2), and Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) in ovarian tissues were detected by Western blot. [Results] Compared with the normal group, the model group showed significant increase in the serum FSH (P<0.01), significant decrease in serum E2 (P<0.05), and decrease in the number of early follicles and luteum in the ovary (P<0.01). Besides, the apoptosis rate of granulosa cells increased significantly (P<0.01); the expression of p-PI3K, p-Akt, p-mTOR and Bcl-2 in ovarian tissue decreased significantly, while the expression of Bax increased significantly (P<0.01). Compared with the model group, the number of early follicles in the ovary increased and the apoptosis rate of granulosa cells decreased after intervention in each administration group. In addition, the protein expressions of p-PI3K, p-Akt, p-mTOR and Bcl-2 increased, while the expression of Bax decreased, especially in Progynova+Zuogui Pill high dose group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05, P<0.01). [Conclusions] Zuogui Pill may protect the radiation-injured ovary through activating the expression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR protein in ovarian tissue, increasing the amount of Bcl-2 protein and inhibiting the expression of Bax protein.
Key words Radiation injury, Premature ovarian failure (POF), Zuogui Pill, Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL), Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) signaling pathway, B-cell lymphoma-2, Bcl-2-associated X protein
1 Introduction
The radiotherapy induced premature ovarian failure (POF) is mainly caused by follicular atresia caused by oocyte apoptosis[1-2], followed by ovarian atrophy and reduction of primordial follicle reserve. In the short term, POF has effects on reproductive health, and long-term deficiency of estrogen has serious effects on women’s bone mineral density, cardiovascular and neurological systems[3]. It has been proved that 3.2 Gy γ-ray (LD20) radiation dose acting on the ovary can cause changes in ovarian histology and serum hormone levels[4]. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinases/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K/Akt/mTOR) signaling pathway plays an important role in granulosa cell apoptosis and follicle development[5-8]. Abnormal expression of this signaling pathway molecule may trigger rapid follicle apoptosis and lead to the occurrence of POF[9]. Estrogen replacement therapy has become the main treatment for POF, but its high risk of inducing breast and endometrial cancer limits its clinical application.
According to Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) theory, the pathogenesis of ionizing radiation damage is heat-toxin amassment in yin phase, insufficient spleen and kidney transportation and transformation, and qi and blood damage, which is consistent with the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal reactions and bone marrow suppression side effects of modern medical radiotherapy. The damage to reproductive function is manifested as deficiency of kidney qi, lack of sperm motility, spleen failing in transportation, lack of sources for qi and blood engendering transformation, inability to replenish the essence of reproduction, and may also lead to low reproductive function and even infertility. Therefore, it is particularly important to study the molecular mechanism of radiation-induced ovarian damage and the long-term protective effect of traditional Chinese medicine.
Zuogui Pill, first recorded inCompleteWorksofJingyue·NewPrescriptionsofEightCategoriesofFormulasby famous physician Zhang Jingyue in the Ming Dynasty, is a classic kidney-invigorating formula, based on the theory that the kidney governs reproduction and bone marrow, has been clinically used for the treatment of women with menopausal syndrome, premature ovarian failure, osteoporosis and other aging diseases[10]. There have been theoretical studies on the efficacy of Zuogui Pill’s "reinforcing the kidney and promoting the pulse"[11], up-regulating ovarian vascular endothelial growth factor in premature aging rats[12], up-regulating connexins in the ovary of chemotherapy-injured rats and enhancing granulosa cells to oocyte protein information transduction and nutrition[13], up-regulating granulosa cell B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) protein, Smad4 and Cyclin A (Cyclin A), directly or indirectly achieving the effect of stimulating follicle development and treating premature ovarian failure[14]. The TCM-based treatment of radiation injury focuses on nourishing and nourishing yin and promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis[15]. There is no report on whether Zuogui Pill’s effect of nourishing kidney and nourishing yin can play a role in radiation injury ovary and its action mechanism. In view of this situation, we explored the molecular mechanism of radiation injury-induced POF and the protective effect of Zuogui Pill on radiation-injured ovaries, to provide a theoretical basis for the long-term clinical management of radiation-injured POF.
2 Materials
2.1 AnimalsWe selected 70 female SPF 8-week-old SD rats, with a body weight of (220±20) g, and the experimental animal certificate number of SYXK (Gan) 2015-0005. The experiment was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Gansu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (approval number 2020-255). All rats have free access to feeds, the room temperature was controlled at (22±3) ℃, the indoor relative humidity was maintained at 35%-45%, and the 12-h light time was guaranteed (lighting at 8:00-20:00; no light at 20:00-8:00).
2.2 Drugs and reagentsZuogui Pill formula granules consist of 24 g of Rehmanniae Radix Praeparata (batch No.1031263), 12 g of Dioscoreae rhizoma (batch No.1032993), 12 g of Corni Fructus (batch No.1030033), 12 g of Lycii Fructus (batch No.1010423), 12 g of Cuscutae Semen (1012053), 9 g of Cyathulae Radix (batch No.1035963), the above formula granules were purchased from Guangdong Yifang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; 12 g of Testudinis Carapacis Et Plastri Colla (batch No.1908003) purchased from Zhengxing Longxi Pharmaceutical Industry Co., Ltd.; 12 g of Cervi Cornus Colla (batch No.02180515) purchased from Gansu Herun Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. All medicinal materials were provided by the pharmacy of the Affiliated Hospital of Gansu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and identified by the chief expert of the Department of Pharmacy, Yang Xicang, chief Chinese pharmacist, meeting the relevant requirements of theChinesePharmacopoeia(2020 Edition). Progynova (estradiol valerate, Guangzhou Branch of Bayer Medical Care Inc., batch No.J20171038, 1 mg/tablet).
PVDF membrane, ECL luminescent solution (Millipore, USA, batch No.IRVH00010, P36599), Glycine Tris, Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS), RIPA Lysis Solution, Tween-20, SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) gel preparation kit, BCA protein quantification kit, Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining kit (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd., batch No.of G8200, T8060, S8010, R0010, 20150702, P1200, PC0020, and G1120), PI3 kinase p110 beta antibody, Akt (phospho Ser473) antibody, mTOR antibody, Bcl-2 antibody, Bax antibody, β-actin (β-actin) (GeneTex, USA, batch No.of GTX111173, GTX128414, GTX101557, GTX100064, GTX109683, and bs-0061R), goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG), horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled streptavidin, DAB color development kit (Beijing Zhong Shan -Golden Bridge Biological Technology Co., Ltd., batch No.of SP-9002, SP-9001 and ZLI-9018), HRP goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) (Immunoway, USA, batch No.RS0001), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and estradiol (E2) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits (Jiangsu Feiya Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch No.of MM-0624R1, MM-0566R1, and MM-0575R1).
2.3 InstrumentONCOR Impression Plut type high-energy linear accelerator (Siemens, Germany); X21FS1 inverted microscope (Olympusc, Japan); DYCZ-40G Western blot membrane transfer instrument; DYCZ-25D electrophoresis apparatus (Beijing Liuyi Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); iMark microplate reader (Bio Rad, USA); 5424R high-speed refrigerated centrifuge (Eppendorf, Germany); MiniChemi 610 chemiluminescence imaging system (Beijing Sage Creation Science Co., Ltd.); BSA224s analytical balance (Sartorius Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd.).
3 Methods
3.1 Animal model preparation and groupingThe whole body of rats was irradiated with60Co-γ rays at a time of 6.0 Gy, the dose rate was 3 Gy/min, 6 mV, and the irradiation source skin distance (SSD) was 100 cm. In a 10 cm×10 cm special lead mold, the size of the irradiation field was 2.0 cm×2.0 cm, and the irradiation time was 2.2 min (Department of Radiotherapy, Gansu Provincial People’s Hospital, High Energy Linear Accelerator). At 24 h after irradiation, multiple leukocytes and a small number of nucleated keratinocytes were observed through vaginal exfoliation, indicating that the model was successful. Rats were randomly divided into radiation model group, Progynova (2 mg) group, Progynova (1 mg)+Zuogui Pill high dose group, Zuogui Pill high, medium and low dose groups and normal group (without irradiation).
3.2 Drug treatmentThe next day after the successful building of model, oral administration was given. The dose of Zuogui Pill was converted to the dose of rats[9.45 (g·kg)/d] according to the adult human dose[105 (g·70 kg)/d]. Dissolved the Zuogui Pill formula granules in heated sterilized purified water to prepare Zuogui Pill concentration decoction of 1.89 g crude drug/mL. Low dose[4.725 (g·kg)/d], medium dose [9.45 (g·kg)/d] and high dose [23.625 (g·kg)/d]. Progynova group[calculated based on a 70 kg adult taking 2 mg of Progynova per day, rat dose: [0.18 (g·kg)/d]. Progynova+Zuogui Pill high dose group was Progynova 0.09 (g·kg)/d +Zuogui Pill 23.625 (g·kg)/d. The rats in the normal group and the model group were given the same volume of normal saline by gavage for 21 d.
3.3 Detection indicators and methods
3.3.1Detection of serum sex hormone levels in rats by ELISA. After the treatment, took the blood of 1.5 mL from the heart, centrifuged at 3 000 r/min for 10 min at 4 ℃ (centrifugation radius 8 cm), pipetted upper serum into the EP tube, and detected the contents of serum FSH, E2and LH by ELISA kit. The steps were strictly in accordance with the instructions of the kit.
3.3.2Observation of histopathological changes of ovarian tissue by HE staining. After completion of the treatment, the rats were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. One side of the ovarian tissue was taken for 4 μm section, HE stained, and the number of follicles was calculated. The ovarian tissue was serially sectioned, and every other section was counted. Only follicles with definite oocyte nuclei stained can be counted, and the follicle counting method can be found in reference[18].
3.3.3Detection of Bcl-2 and Bax expression by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Paraffin sections of ovarian tissue were deparaffinized and hydrated, incubated with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 15 min, washed with PBS for 5 min ×3 times, added goat serum to block, incubated at 37 ℃ for 30 min, added primary antibody (Bcl-2 1∶100, Bax 1∶100) dropwise, overnight at 4 ℃, recovered at 37 ℃ for 35 min, washed with PBS for 5 min×3 times; added the secondary antibody (biotin-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG working solution 1∶50) dropwise, incubated at 37 ℃ for 30 min, and washed with PBS for 5 min×3 times; added tertiary antibody (HRP-labeled streptavidin working solution 1∶50) dropwise, incubate at 37 ℃ for 30 min, and washed with PBS for 5 min×3 times; DAB color developed (1∶20) for 3 min, observed under microscope, terminated the reaction when it showed brownish yellow color. Counterstained with hematoxylin, dehydrated with graded alcohol, and mounted with neutral gum.
3.3.4Detection of ovarian cell apoptosis by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) method. Took out the paraffin-embedded ovarian tissue section on the other side, soaked it in xylene for 5 min, deparaffinized, and washed with graded ethanol (90%, 80%, and 70%) for 3 min each time. For each sample, added 100 μL of Proteinase K working solution (PBS diluted Proteinase K, final concentration 20 mg/L) dropwise to submerge the tissue and incubated at 37 ℃ for 30 min. Added 100 μL of 1×Equilibration Buffer solution to submerge the tissue, incubated at 37 ℃ for 30 min, washed off most of the tissue with absorbent paper, added 50 μL of TdT buffer, incubated at 37 ℃ for 60 min in the dark, removed the coverglass, and incubated with PBS solution for 5 min three times. Washed three times with PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100 and 5 g/L BSA for 5 min each time. Immersed the slides in DAPI solution (2 mg/L) for 5 min in the dark, and washed with deionized water for 5 min three times. Mounted the slide with anti-fluorescence decay mounting medium, and observed the green particles under a fluorescence microscope at (520±20) nm. Blue particles were observed at 460 nm. The images were analyzed by Image-Pro Plus software. Under the optical microscope, the nuclei of positive cells (apoptotic cells) were uneven brown and located on the granulosa cells and oocytes. Randomly selected 3 sections from each specimen, combined with staining, selected 5 fields for each section under a high-power field (×200), and then calculated the apoptosis of granulosa cells and the total number of cells in the 5 fields. Apoptosis index (AI)=Positive cells/Total number of cells×100%.
3.3.5Detection of expression of PI3K, Akt, m-TOR, Bcl-2 and Bax in ovarian tissue by Western blot. Took 200 mg of ovaries, followed the kit instructions, added PI3K, AKT, mTOR, Bcl-2 and Bax primary antibodies (1∶1 000), used β-actin antibody (1∶5 000) as an internal reference, and incubated at 4 ℃ overnight. After washing the membrane, added the secondary antibody (HRP Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (diluted 1∶5 000) for 2 h, washed the membrane with TBST for 6 min at room temperature and shook for 5 times. Added ECL luminescent solution (mixing of Reagent A and Reagent B at 1∶1) dropwise to the PVDF membrane and reacted for 5 min. Exposed and developed for observation. Then, used Image J to analyze and quantify the gray value of the band.

4 Results and analysis
4.1 Effects on the changes of serum FSH, LH and E2levels in irradiated ratsBoth the model group and drug administration groups had rat deaths. Compared with the normal group, the serum FSH in the model group was significantly increased (P<0.01), and the E2content was significantly decreased (P<0.05) after irradiation. Compared with the model group, each administration group could alleviate the radiation induced ovarian hypofunction state, and the serum FSH showed a decreasing trend. The FSH in the Progynova group was significantly decreased (P<0.05), and the FSH in the Progynova+Zuogui Pill high-dose group was significantly decreased (P<0.01). The serum LH level decreased and the E2level increased, and there was no significant difference between the groups, which may be related to the apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells caused by radiation and the reduction of the ability to synthesize and secrete estrogen (Table 1).
4.2 Effects on ovarian follicles of radiation-injured ratsIn the normal group, follicles at all levels were visible, and the mature follicles were larger in size and more follicular fluid. Compared with the normal group, the ovary of the model group was atrophied, with multiple small follicles and occasional mature follicles, oocytes and granulosa cells pyknosis, and the number of primary follicles and corpus luteum decreased significantly (P<0.01). Compared with the model group, the number of primary follicles in each administration group increased (P<0.05,P<0.01). Secondary follicles and mature follicles showed an increasing trend, but the difference was not statistically significant. There were still some granulosa cells apoptotic around the follicles, and the difference in the number of ovarian follicles between the groups was not significant, indicating that Zuogui Pill has no obvious advantage in improving the number and structure of ovarian follicles (Table 2 and Fig.1).

Table 1 Effects of Zuogui Pill on serum FSH, LH and E2 levels in irradiated rats of each group

Table 2 Effects of Zuogui Pill on the number of different levels of follicles in each group of rats

Note: A. normal group; B. model group; C. Progynova group; D-F. Zuogui Pill high, medium and low dose groups; G. Progynova+Zuogui Pill high dose group.
4.3 Effect on apoptosis of ovarian tissue in irradiated rats
Our study results showed that the apoptosis of ovarian tissue in the normal group was mainly in the oocytes and granulosa cells of the follicles, and the nucleus was stained inhomogeneous brown with clear boundaries. Fluorescence shows apoptotic cells were green granules. Compared with the normal group, the fluorescence of the model group was enhanced, the area was increased, and the AI was significantly increased (P<0.01). Compared with the model group, the fluorescence of each administration group was weakened, the area was reduced, and the AI of ovarian tissue was decreased. The AI of Progynova group and Zuogui+Zuogui Pill high dose group was significantly decreased in (P<0.05), as shown in Table 3 and Fig.2.

Fig.2 Effects of Zuogui Pill on ovarian apoptosis of rats in each group (TUNEL, ×200)
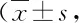
Table 3 Effects of Zuogui Pill on ovarian apoptosis of rats in each group %)
4.4 Effects on the expressions of p-PI3K, p-Akt, m-TOR, Bcl-2 and Bax proteins in the ovaries of irradiated ratsCompared with the normal group, the expressions of p-PI3K, p-Akt, p-mTOR and Bcl-2 proteins in the ovaries of rats the model group were significantly decreased, and the expression of Bax protein was significantly increased (P<0.01). Compared with the model group, the expressions of p-PI3K, p-mTOR and Bcl-2 proteins in the Progynova or (and) Zuogui Pill (high, medium, and low) dose groups were significantly increased (P<0.05,P<0.01), and the expression of Bax protein was decreased (P<0.05,P<0.01). In particular, the Progynova+Zuogui Pill high dose group showed the most significant effect (Table 4, Fig.3-5).

Table 4 Effects of Zuogui Pill groups on the protein levels of PI3K, p-Akt, p-mTOR, Bax and Bcl-2 in rat ovarian tissue

Fig.3 Electrophoresis of PI3K, p-Akt, p-mTOR, Bax and Bcl-2 proteins in ovarian tissue of rats in each group

Fig.4 Effects of Zuogui Pill on the expression of Bcl-2 protein in ovarian tissue of rats in each group (IHC,×400)

Fig.5 Effects of Zuogui Pill on the expression of Bax protein in ovarian tissue of rats in each group (IHC, ×400)
5 Discussion
The apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells andoocytes is the central link of POF. Ionizing radiation and activation of various gene factors can induce cell apoptosis. The regulation of follicle apoptosis depends on the interaction of related hormones and cytokines in the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis. According to the TCM theory, the radiation belongs to the fire pathogen, and it damages the viscera and bowels, consumes blood and damages the essence, leading to deficiency of essential qi. The theory of "kidney storing essence" and "kidney governing the reproduction" has the same effect as modern medicine "hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian axis". Studies have shown that kidney-tonifying Chinese medicines inhibit the apoptosis of granulosa cells by up-regulating p-mTOR, thereby promoting the secretion of E2and progesterone (P) in granulosa cells[16]. Zuogui Pill has functions of enriching the kidney and replenishing yin, filling in the essence to benefit marrow, harmonization of fire and water, and treating yang for yin. Whether it also plays a protective effect on radiation-injured ovaries by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway is to be studied.
The results of the study showed that the number of primary follicles in the ovary of rats after irradiation decreased, the tissue necrosis and hemorrhage were more, and the follicle atresia was obvious, which was related to the apoptosis of granulosa cells in the ovary[17-18]. Besides, there was apoptosis of granulosa cells and the ability to synthesize estrogen was reduced, resulting in a significant decrease in serum E2levels, and positive feedback stimulated the pituitary to release a large amount of FSH and LH. Western blot verification showed that the expressions of phosphorylated PI3K, Akt and mTOR proteins in the ovary were significantly decreased, which was mainly related to the increase in the apoptosis of ovarian cells caused by radiation, and the low or even non-expression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway proteins involved in cell growth and proliferation. Radiation led to POF. On the one hand, ovarian granulosa cells apoptotic estrogen levels decreased, and feedback stimulation of pituitary to secrete a large amount of FSH rapidly increased the phosphorylation of Akt in the ovary for a short time, activated PI3K/Akt[19-20], and promoted the atresia of residual primordial follicle apoptosis. On the other hand, radiation led to bone marrow function suppression, insufficient blood supply to ovarian tissue, resulting in follicular atresia. In addition, the expression of classical apoptotic proteins showed that the pro-apoptotic Bax protein was highly expressed in ovarian tissue, while the apoptosis-inhibiting Bcl-2 protein was low. Estradiol valerate is a classic drug for hormone replacement therapy for POF, so we selected it as a positive control drug in this experiment[21]. After administration of Zuogui Pill, we found that each administration group showed an increase in the serum E2level, decrease in the FSH level, increase in the number of primary follicles and secondary follicles, and decrease in the number of atretic follicles in radiation-injured rats. The main mechanism may be that Zuogui Pill stimulated the growth of granulosa cells and promoted the development of primordial follicles by activating the expression of phosphorylated PI3K protein in ovarian tissue and activating downstream Akt phosphorylation and mTOR protein through cascade reactions[22-24]. The follicles developed gradually, and the level of serum estrogen increased, which feedback the secretion of pituitary FSH and LH[13, 25-26]. At the same time, in the case of low or lack of estrogen, the combination of estrogen receptor (ER) and PI3K would also activate the PI3K/Akt pathway, which regulates each other[27]and promotes the recovery of ovarian function. This is related to the fact that tonifying the kidney can up-regulate the protein expression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to promote follicular development[28], and also related to the fact that kidney-tonifying drugs regulate apoptosis or autophagy through mTOR pathway[16], and promoting the high expression of Bcl-2 protein and the low expression of Bax protein in the ovarian tissue of rats in the model group. Furthermore, based on the theory of "kidney generating marrow and brain being the sea of marrow", it is believed that sufficient kidney essence and marrow can promote the power of hypothalamus and pituitary functional activities. Studies have shown that Zuogui Pill can increase the content of acetylcholine (Ach) in the hippocampus of rats[29], improve the mitochondrial damage in chronic ischemic oxidative stress brain tissue[30], and promote the repair of brain nerve tissue. Therefore, we consider that the effects of Zuogui Pill of tonifying the kidney and nourishing the marrow can promote the ischemia and hypoxia of the hypothalamus and pituitary caused by radiation, restore the function of the HPO axis, and further assist the recovery of ovarian functions.
In summary, the protective effects of Zuogui Pill on radiated ovary is to activate the expression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal protein in ovarian tissue, transform qi and blood, replenish healthy qi, nourish viscera and bowels, promote the proliferation of oocytes and granulosa cells, promote the development of residual follicles, and restore damaged ovaries. But the specific mechanism of action remains to be further studied. Radiation damage to the ovary is related to its radiation dose, and this damage is irreversible[3]. Therefore, taking radiation protection measures and exposing to radiation as low as possible may be an effective way to protect ovarian function.
杂志排行
Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Establishment of Quality Standard for Freeze-dried Tablets of Polygonatum sibiricum and Study on Anti-tumor Activity of Diosgenin
- Herbal Textual Research of Inulae Flos in Chinese Classic Prescription
- Quality Standard of Zijinbiao
- Quality Standard of Yi Medicinal Material Anaphalis margaritacea
- Serum Metabolomic Characteristics of Primary Dysmenorrhea Rat Model Induced by Estradiol Benzoate Combined with Oxytocin
- Prescription Design and Preparation Process of Paeonol Bead Popping Gum with Hypoglycemic Effect
