Determination of Harmful Elements and Analysis of Pollution Level in Lysimachia christinae
2022-11-28LiWANYaGUOQinXIANGQiXIAOWenwuYANG
Li WAN, Ya GUO, Qin XIANG, Qi XIAO, Wenwu YANG
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Development and Utilization of Genuine Medicinal Materials in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, Wanzhou Institute for Food and Drug Control, Chongqing 404000, China
Abstract [Objectives] To detect content of Pb,Cd,Hg,As,Cu,Zn,and Cr in Lysimachia christinae,and to analyze the pollution level. [Methods] Seven kinds of elements in L. christinae were determined by Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and analyzed by single index and comprehensive index. [Results] The seven heavy metal elements showed good linearity in their respective concentration ranges. The recoveries of the samples were 84.5%-109.5%,and the RSD values were 2.30%-5.10%. Comparing the measured results of heavy metal elements with the limit values stipulated in the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and other standards, the Cr element in 19 batches of samples exceeded the standard, and the Zn element in 7 batches of samples exceeded the standard. The exceeding rates were 100.0% and 36.8%, respectively; the content of other heavy metal elements did not exceed the standard. The order of individual index from large to small was Cr, Zn, Cd, Hg, Cu, As, and Pb, and the average comprehensive pollution level was mild pollution and above. [Conclusions] L. christinae was mainly polluted by Cr, followed by Zn; this study can provide basic data for drafting of the limit standard for heavy metal elements in L. christinae.
Key words Lysimachia christinae, Heavy metals elements, Harmful elements, ICP-MS, Microwave digestion, Single factor index method, Comprehensive index method, Pollution level analysis, Quality control
1 Introduction
Lysimachiachristinaeis the whole plant of Primulaceae perennial herb, and it has the functions of preventing and treating stones, treating kidney injury, protecting nerves, resisting oxidation, treating gallbladder-related diseases and resisting inflammation[1-2]. Currently, there have been a large number of literature reports on the active components and pharmacological effects ofL.christinae, but there are relatively few reports on the risks caused by the residues of exogenous harmful substances. At present, exogenous harmful substances, such as heavy metal elements, still exceed the standard in soil, food and medicine. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is widely used in the analysis of heavy metals in various industries because of its simple operation, wide range of analysis and low detection limit[3-5]. At present, 7 elements in 19 batches ofL.christinaewere detected by ICP-MS, and the pollution was evaluated by single index method and comprehensive index method, in order to provide an experimental basis for quality and safety control.
2 Instruments and drug testing
ICAP-Q Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer (Thermo Fisher, USA) and MultiwavePRO microwave digestion instrument (Anton Paar, Austria). Samples ofL.christinae[The samples were collected from Chongqing, Sichuan, Anhui, Jiangxi and other provinces, numbered as JQC1-JQC19 (Chongqing Kangwanjia Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd., Chengdu Qilong Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd., Chongqing Tonghechun Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Sichuan Zining Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd., Chongqing Zhongmiao Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Sichuan Yunbotang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chongqing Jinshangdao Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chongqing Kangjia Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chengdu Renjihong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Hebei Chufeng Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd., Chongqing Wanli Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Sichuan Zining Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd., Chongqing Kangjia Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Ximei Chongqing Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Sichuan Jingcheng Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd., Anguo Juyaotang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.), identified as the dry whole grass ofL.christinaeHance by Li Jieyu, Associate Professor of Chongqing Three Gorges Medical College, and crushed into coarse powder; Pb, Cd, Hg, As, Cu, Zn, Cr, In, Ge, Bi, Au standard solution (TMRM, the concentration of 1 mg/mL, batch No.:B21050065, B21040027, B2101079, B21050215, B2103467, B2104097, B2103030, B21040100, B21050151, B2103482, B2103369).
3 Methods and results
3.1 Preparation of solutionThe standard solution of each single element was diluted with 10% HNO3solution, and finally a series of mixed solutions containing Pb, Cr, As, Cd (1.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0, 40.0 ng/mL), Cu, Zn (10.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 500.0 ng/mL), Hg (0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 ng/mL) were prepared. The sample solution was prepared by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) in the Four General Rules (2321) in the 2020 edition ofChinesePharmacopoeia[1]. The microwave digestion instrument adopted programmed temperature (from room temperature to 120 ℃ in 0-15 min, lasting 15-20 min; then to 150 ℃ at 4.5 ℃/min, lasting 7 min; then to 180 ℃ at 4.5 ℃/min, lasting 15 min). According to the literature method, the contents of 7 elements in the samples were determined[4].
3.2 Test of linear range and sample recovery rateThe blank solution and the prepared mixed standard solution of a series of concentrations were injected and analyzed respectively. It can be seen from Table 1 thatrwas 0.999 0-0.999 9. Six samples ofL.christinaewith a known content of about 0.25 g were weighed precisely, then mixed with proper amount of reference solution respectively, and the test solution was prepared according to the preceding method. The average recovery rate of each element was 84.5%-109.5%, andRSDwas 2.30%-5.10%, which indicated that the linear relationship of the method used was good and the accuracy was high, which met the requirements of analysis and determination.

Table 1 Linear relationship and sample recovery rate (n=6)
3.3 Test of precision and repeatabilityThe third mixed standard solution was determined continuously for 6 times, and theRSDof the measured values of Pb, Cd, Hg, As, Cu, Zn and Cr were 1.40%, 1.90%, 1.50%, 1.80%, 2.70%, 1.10% and 1.00%, respectively, indicating that the precision of the instrument was good. Six samples of the sameL.christinaewere precisely weighed and prepared for determination according to the method ofPharmacopoeia. TheRSDof Pb, Cd, Hg, As, Cu, Zn and Cr was calculated to be 2.30%, 2.50%, 2.90%, 3.10%, 3.30%, 1.90%, 1.80%, respectively, indicating good repeatability.
3.4 Determination of samplesIt can be seen from Table 2 that the content of Pb, Cd, As, Hg, Cu, Zn and Cr in 19 batches ofL.christinaewas 1.053-3.360, 0.052-0.519, 0.170-0.820, 0.013-0.160, 5.005-10.500, 17.200-30.350, 2.690-39.254 mg/kg, respectively, and the average content was Zn > Cr > Cu > Pb > As > Cd > Hg. When taking the maximum limits for harmful elements (Pb≤5 mg/kg, Cd≤1 mg/kg, As≤2 mg/kg, Hg≤0.2 mg/kg, Cu≤20 mg/kg, Zn≤25 mg/kg, Cr≤2.0 mg/kg) stipulated in the 2020 edition ofChinesePharmacopoeia,GB14963-2011NationalStandardforFoodSafety—Honey, andGB2762-2017NationalStandardforFoodSafetyLimitsofContaminantsinFood, the Cr in 19 batches of samples exceeded the standard, with an over-limit ratio of 100%, and the maximum content was 39.254 mg/kg, which exceeded the national limit standard by 19.6 times. Zn in 7 batches of samples exceeded the standard, and the over-limit ratio was 36.8%. Pb, Hg, As, Cu and Cd in all samples did not exceed the standard.

Table 2 Determination results of harmful elements (mg/kg, n=3)
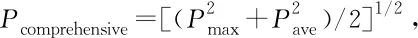
It can be seen from Table 3 that the average pollution index of seven heavy metals and harmful elements inL.christinaewas in the following order: Cr > Zn > Cd > Hg > Cu > Pb > As. It can be seen that Cr was the most harmful element toL.christinae, followed by Zn.

Table 3 Results of pollution levels
4 Discussion
In this paper,L.christinaewas not polluted by five harmful elements (Pb, Hg, As, Cu and Cd), but it was seriously polluted by Cr and Zn, and the highest content of Cr was 19.6 times of the limit. As a result, 19 batches of samples were rated as lightly polluted or above. The soil, atmosphere and water exposed toL.christinaehave a direct or indirect impact on its heavy metal content, and its own genetic characteristics determine its ability to absorb and enrich heavy metals. Therefore, the factors leading to the serious pollution of heavy metals inL.christinaeare diverse and complex, and further research is needed. At the same time, the experiment suggests that when studying the pollution of heavy metal elements, we should not only pay attention to the five elements (Pb, Hg, As, Cu and Cd) stipulated in Chinese Pharmacopoeia, but also analyze other heavy metal elements, such as Cr and Zn. Appropriate amount of Cr is an important element for normal growth and development and regulation of blood sugar, but if excess Cr, especially hexavalent Cr, accumulates in the human body, it will be carcinogenic and cause DNA damage, and is easy to cause adenocarcinoma, lung cancer and other diseases. Zn is essential for the human body and participates in the synthesis of a variety of enzymes in the body. Excessive intake of Zn will cause symptoms of anemia, loss of appetite, and even proteinuria and hematuria, so the control of Cr and Zn inL.christinaeshould be strengthened. The method used in this paper was simple and accurate, and could be used for the determination of Pb, Hg, As, Cu, Cd, Cr, Zn and other elements inL.christinae.
杂志排行
Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Establishment of Quality Standard for Freeze-dried Tablets of Polygonatum sibiricum and Study on Anti-tumor Activity of Diosgenin
- Herbal Textual Research of Inulae Flos in Chinese Classic Prescription
- Quality Standard of Zijinbiao
- Quality Standard of Yi Medicinal Material Anaphalis margaritacea
- Serum Metabolomic Characteristics of Primary Dysmenorrhea Rat Model Induced by Estradiol Benzoate Combined with Oxytocin
- Prescription Design and Preparation Process of Paeonol Bead Popping Gum with Hypoglycemic Effect
