Antiurolithiatic activity of Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam a Siddha polyherbal formulation on ethylene glycol-induced urolithiasis in Wister albino rats
2022-11-04HarishanbuselvanVenkatesanArthiGurumurthyRathinamJayarajLakshmanakumarVenkatachalam
Harishanbuselvan Venkatesan ,Arthi Gurumurthy ,Rathinam Jayaraj ,Lakshmanakumar Venkatachalam
1Resident Medical Officer,National Institute of Siddha,Chennai 600047,Tamil Nadu,India.2Sai Siddha Clinic,Salem 636354,Tamil Nadu,India.3Govt upgraded Primary Health Centre,Eriayamangalam,Namakkal 637210,Tamil Nadu,India.4All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS),Raipur 492099,Chattishgarh,India.
Abstract Background:Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam (ABC) is a Siddha polyherbal formulation containing ten medicinal plants that have been used in the Siddha system of medicine,practiced in the Southern part of Tamil Nadu,India for the management of urolithiasis.Objective: The study is carried out to scientifically validate the traditional formulation and to study the mechanism of ABC.Methods: In the present study,the antiurolithiatic activity of ABC was evaluated in Wister albino rats by using ethylene glycol through drinking water.Group I acted as the standard control group and was given unlimited access to conventional rat food and water.Group II-V was given ethylene glycol (0.75%) in water to induce renal calculi for 28 days.Group III got the typical anti-urolithiatic medication,Cystone (750 mg/kg),from the 15th day to the 28th day,whereas Group II functioned as the lithiatic control group and received the vehicle.Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam (200 mg/kg) was administered to Group IV from the 15th to the 28th day as a curative regimen.From the first day to the 28th day,Group V received Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam (200 mg/kg),which was administered as a preventative regimen.All groups'urine samples were taken,and using accepted techniques,their calcium,magnesium,oxalate,inorganic phosphate,protein,and creatinine levels were determined.ABC treatment promotes diuresis which leads to flushing of the renal stones and maintains the alkaline condition in the urinary system which probably mediates the antilithiatic activity.Conclusion: ABC provides structural and functional protection to the kidneys by enhancing its physiological function against stone formation and validates its clinical use.
Keywords: Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam;ethylene glycol;kalladaippu;Siddha drug;urolithiasis
Backgroud
Since the beginning of time,kidney stone illness has plagued people,causing major health issues that last the entirety of the patient's life.Due to dietary choices and lifestyle changes,urolithiasis,also known as kalladaippu in the Siddha system of medicine,is a prevalent condition that affects people of all ages.This has led to a surge in new cases across the world.Renal calculus,often known as urolithiasis or nephrolithiasis,is one of the most prevalent kidney illnesses.Males are more likely to develop it than females but occur in children rarely.A body like a stone made of urine salts is called urinary calculus.Calculus varies in shape and frequency between climates and races.Worldwide 10% of the population was affected by urinary tract stone disease.Calcium oxalates stones are most commonly urate stones,usually in the upper urinary tract,associated with urinary tract infections [1].The prevalence and incidence of nephrolithiasis are reported to be increasing across the world.The body of evidence suggests that the incidence and prevalence of kidney stones are increasing globally [2].Epidemiology of nephrolithiasis varies according to geographical areas and socio-economic conditions.Among Indians,renal tubular acidosis is the main cause of the high incidence of renal calculi.In India,roughly 12 percent of men and 5 percentages of women suffer from kidney stones around the age group between 45 and 50 [3].Urolithiasis is synonymously called“Kalladaippu Noi” in Siddha texts.According to Siddhar Yugi,in his bookyugivaithya cinthamani,he classified the disease kalladaippu into four types:
(1) Vatha kalladaippu
(2) Pittha kalladaippu
(3) Kabha kalladaippu
(4) Mukkutra kalladaippu
Symptoms of kalladaippu include colicky pain radiating from the costal arch obliquely to the lower abdomen,loin to groin and testes,burning micturition,fever,nausea,or vomiting.
In the Siddha system,many herbal and herbo-mineral formulations are mentioned in the texts for kalladaippu diseases.The trial drug Aavarai Bhavana Chooranam is so far not evaluated for urolithiasis.In this study,trial medicine has been evaluated for kallaidaippu(urolithiasis) and its symptoms through pharmacological activities on the animal model.
The imbalance between the factors that promote and inhibit renal calculi results in a multifaceted process that can ultimately lead to kidney failure.Crystals of calcium oxalate make up around 75% of kidney stones.α-1-blockers and calcium channel blockers are common modern drugs,and methods like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy and percutaneous irrigation hemolysis offer successful treatment.Adverse medication reactions include bleeding,hematuria,tubular necrosis,and ensuing renal fibrosis are also noted at the same time.
Indian Traditional medicines,mainly Siddha medicines are becoming more and more popular as alternative and supplementary remedies over recent years because of their low cost and nontoxic nature.Over centuries,a large number of herbal and herbo-mineral preparations have been used in traditional systems of medicine and elsewhere which claims an effective cure for urinary stones.These preparations are gaining importance in controlling hyperoxaluria and subsequent stone formation because of their minimal side effects.Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam (ABC),a formulation prepared by combining ten herbals namely,seeds ofCassia auriculataLinn.,Juices of the following herbsFicus glomerataroxb.,Musa paradisia,Terminalia arjuna,Tribulus terestris,Phyllanthus emblica,Tinospora cordifolia,Asparagus racemosus,Michelia champaka,andAloe barbadensisis used to treat urolithiasis in Siddha system of medicine practiced in South India.The individual herbs have both scientific and traditional effects for their diuretic,and calculus restraining properties,there is no scientific data available for the anti urolithiatic property of ABC formulation.Several models for inducing urolithiasis are available,to determine the drug response but they have some disadvantages such as hematuria,and mortality.In the present study,a modified induction methodology was adopted to induce urolithiasis using ethylene glycol and sodium oxalate to produce renal stones efficiently.Therefore,in the present study,the antilithiatic potential of ABC was scientifically evaluated against experimentally induced urolithiasis in rats using ethylene glycol.
Materials and methods
Material and preparation of trial drug
Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam was taken as a trial drug from the Siddha literature “Mega nivarana bodhini ennum nirizhivu maruthuvam”,Author: Hakeem.P.M.Abdullah sahib.
Ingredients: [4]
(1) Seeds ofCassia auriculata
(2) Bark Juice ofFicus racemosa
(3) Bark Juice ofTerminalia arjuna
(4) Fruit Juice ofPhyllanthus emblica
(5) Tuber Juice ofAsparagus racemosus
(6) Tuber Juice ofMusa paradisiaca
(7) Root Juice ofTribulus terestris
(8) Stem bark Juice ofTinospora cordifolia
(9) Flower Juice ofMichelia champaca
(10) Root Juice ofAloe barbadensis
Fresh plant materials were procured from Thanjavur,Tamil Nadu.Some drugs were procured from raw drug shops in a country drug store,in Chennai.The Botanist,Department of Gunapadam,National Institute of Siddha,identified and verified each plant.The drugs are purified as per the mentioned Siddha literature.The seeds of Cassia auriculata were cleaned well from dust and impurities.The bark ofFicus racemosaandTerminalia arjunawere first cleaned with a cloth and then purified by gently removing the outer skin of these bark with a knife.Fruits ofPhyllanthus emblicawere purified by removing the seed and the flesh was obtained.The roots ofTribulus terrestriswere washed in running tap water to remove the soil and impurities.A tuber ofAsparagus racemosuswas washed thoroughly and the outer skin was peeled off also the center part was removed flowers ofMichelia champacawere cleaned by removing its stalk,sepals,and stamens.Only flowers were used.The root ofAloe barbadensiswas purified by cleaning it in running water [5].The seeds ofCassia auriculatawere soaked and dried each day in juices of 2 to 10 respectively.The seeds were then dried in the shade until all of the moisture had evaporated.It was finely powdered and purified byPittaviyalmuraiand then kept in an airtight container.It was labeled as Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam [6].
Experimental animals
Healthy adult male Wister albino rats weighing about 150-200 gm were included in the study.The animals came from TANUVAS's animal shelter in Madhavaram,Chennai.The animals were maintained at well-ventilated room temperature with a natural 12 +12 hours light/dark cycle in the polypropylene cages.The animals were fed a balanced diet which is a standard rodent pellet diet from Sai Meera foods Pvt Ltd.,Bangalore,and water ad libitum.The animals were housed for 1 week prior to the experiment to acclimatize to the laboratory conditions.Approval for the research work and ethical clearance is obtained from the Institutional Animal Committee of the National Institute of Siddha,Chennai (IAEC approved number:1248/AC/09/CPCSEA-9/DEC-2013/11)
Animal grouping
Wistar albino male rats of body weight ranging from 150-200 gm were used as experimental animals.They were divided into five groups (6 per group) as follows:
● Group I: Control
● Group II: Lithiatic control
● Group III: Standard drug
● Group IV: Curative regimen
● Group V: Preventive regimen
Pharmacological screening for anti-urolithiatic activity
Group I acted as the standard control and was given regular rat feed and water at their discretion.Ethylene glycol (0.75%) in drinking water was fed to Group II-V for induction of renal calculi till the 28th day.Group II served as lithiatic control and received the vehicle,Group III received the standard anti-urolithiatic drug,cystone (750 mg/kg) from the 15th day to the 28th day.Group IV received Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam (200 mg/kg) from the 15th day to the 28th day and served as a curative regimen.Group V received Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam(200 mg/kg) from the 1st day till the 28th day and served as a preventive regimen.All drugs were given once daily by oral route using the gastric tube.On day 28 animals of all the groups were kept in metabolic cages and urine samples were collected for 24 hrs and analyzed for calcium [7],magnesium [8],oxalate [9],inorganic phosphate,protein,and creatinine using standard methods.The serum creatinine levels and urine output volumes of each group were also recorded.
Estimation of urine output
A circular frame made of stainless steel supports a metabolic cage.A lid,a wire mesh bottom,and a funnel are included in the upper piece,which is also used to collect urine.Stainless steel sieves were placed in the funnel to retain the feces,allowing only urine to flow down for collection and measurement.The whole structure is fixed to a metal frame,which keeps the frame in an upright position [10].A conical flask is kept to collect the urine,at the bottom exit of the funnel for a period of 24 hours.Urine volume is expressed as mL/kg.The room temperature is maintained at 27-29 ℃.
Statistical analysis
The results were expressed as Mean ± SD.Analysis of variance(ANOVA) test for multiple comparisons was used for statistical analysis,followed by Dunnett's test,andP<0.05 was considered significant.
Results
The urinary output of the control and experimental rats on day 28 is shown in Figure 1.The urinary volume of normal rats was 5.62 ±0.12 mL/day/rat whereas in the ethylene glycol alone treated rats it was statistically reduced (P<0.01) by 3.46 ± 0.11 mL/day/rat.However,in the extract-treated curative and preventive regimen groups,the urinary outputs increased significantly (P<0.01) to 5.03± 0.13 and 5.07 ± 0.04 mL/day/rat respectively.The chronic administration of 0.75% v/v ethylene glycol aqueous solution to male rats resulted in hyperoxaluria.And the calcium,Oxalate,phosphate,and protein excretion were grossly increased.However,supplementation with Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam significantly (P<0.01) lowered the elevated levels of calcium,oxalate,phosphate,and protein excretion in the urine of curative and preventive regimen groups.Contrary to this,in lithiatic control group,the magnesium excretion was gradually decreased following ethylene glycol treatment as shown in Figure 2.Subsequent administration of the Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam enhanced the magnesium excretion significantly(P<0.01) in both regimens (Table 1).The creatinine clearance of lithiatic control rats was decreased,but it was improved significantly(P<0.01) in standard and Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam treated groups as shown in Figure 3.The data on serum analysis showed a significant increase (P<0.01) in creatinine levels in lithiatic control rats compared to normal rats.After being treated with Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam,serum creatinine levels were restored to normal limits (Table 2).The urinary output of control rats was nearly equivalent to the treated and preventive groups indicated as shown in Table 3.
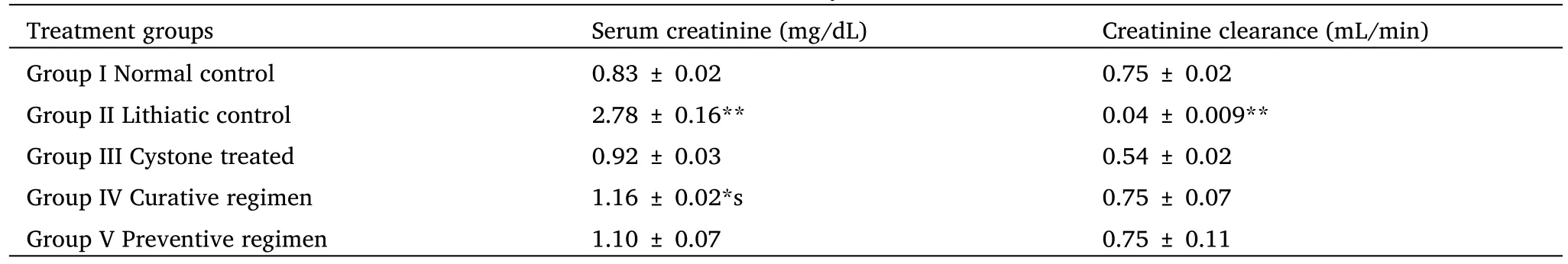
Table 2 Effect of Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranamon urinary and serum creatinine levels of urolithiatic rats

Table 3 Effect of Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam on urinary output
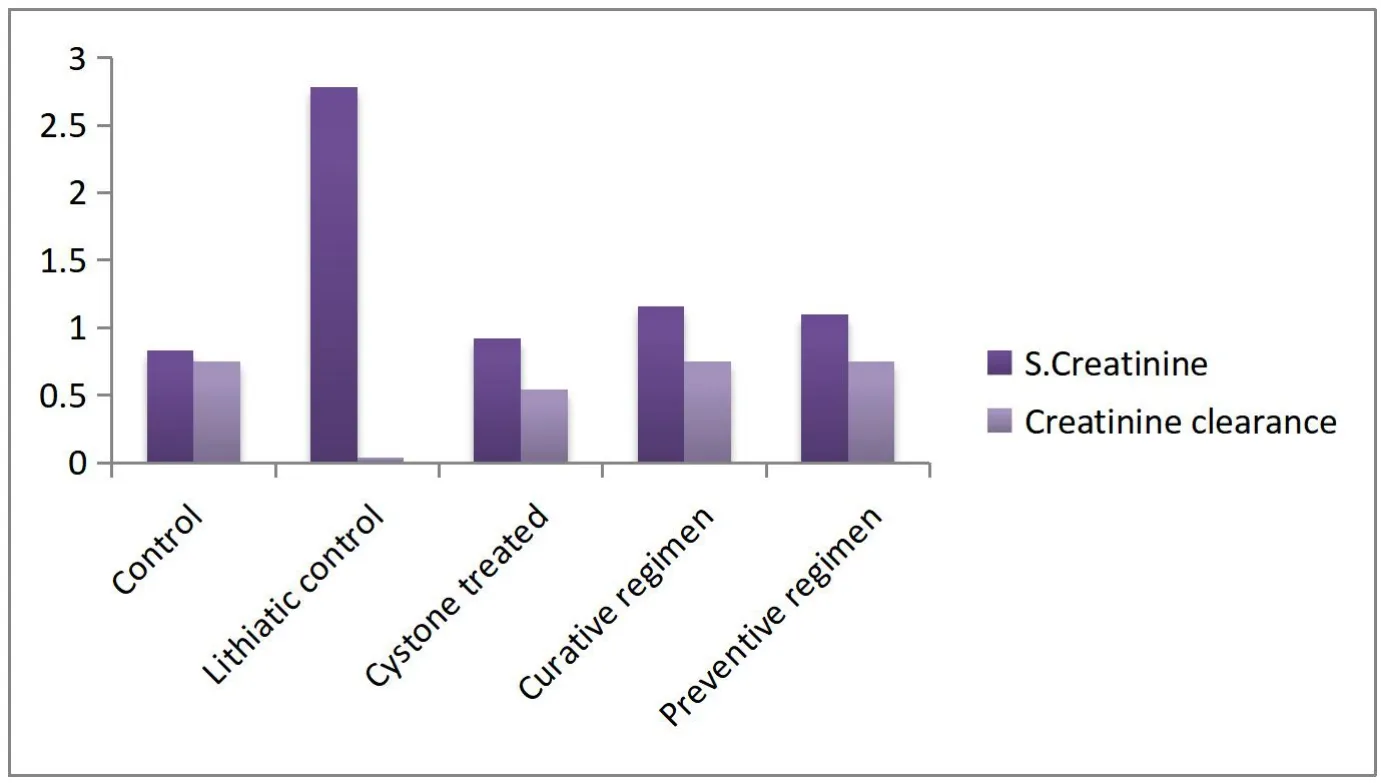
Figure 3 Effect of Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranamon urinary and serum creatinine levels of urolithiatic rats

Table 1 Effect of aqueous extract of Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam on urinary biochemical parameters of urolithiatic rats
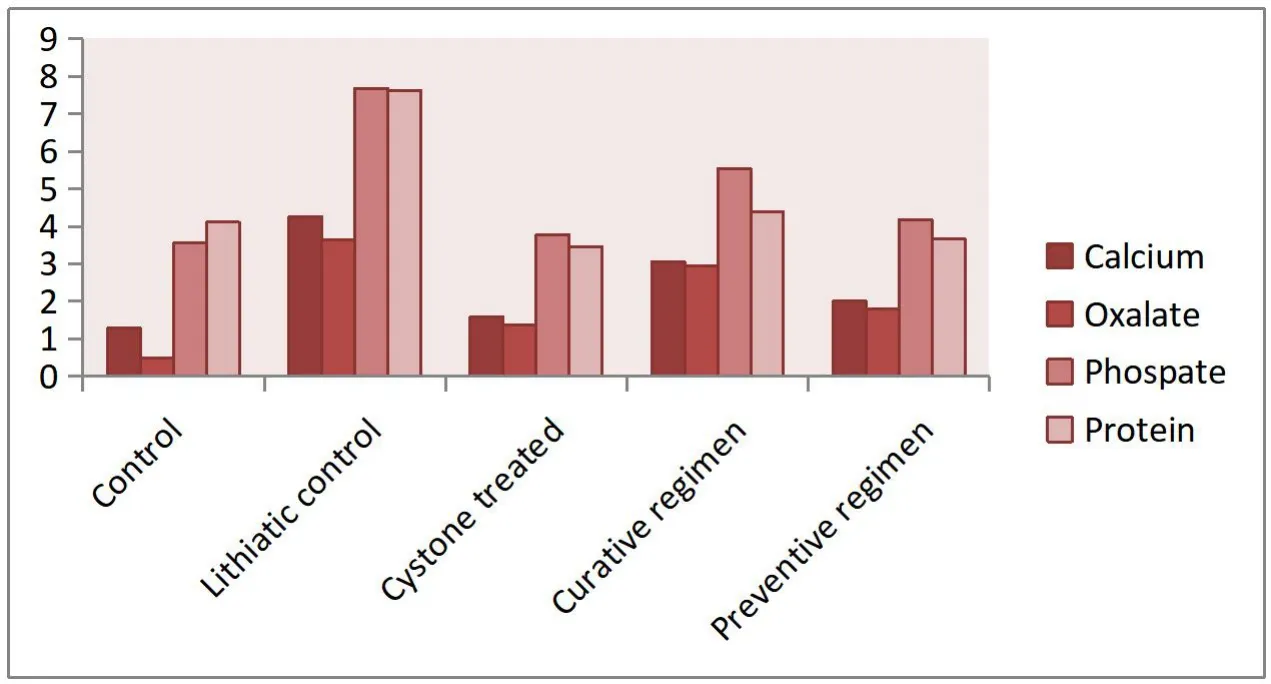
Figure 1 Urinary biochemical parameters of urolithiatic rats
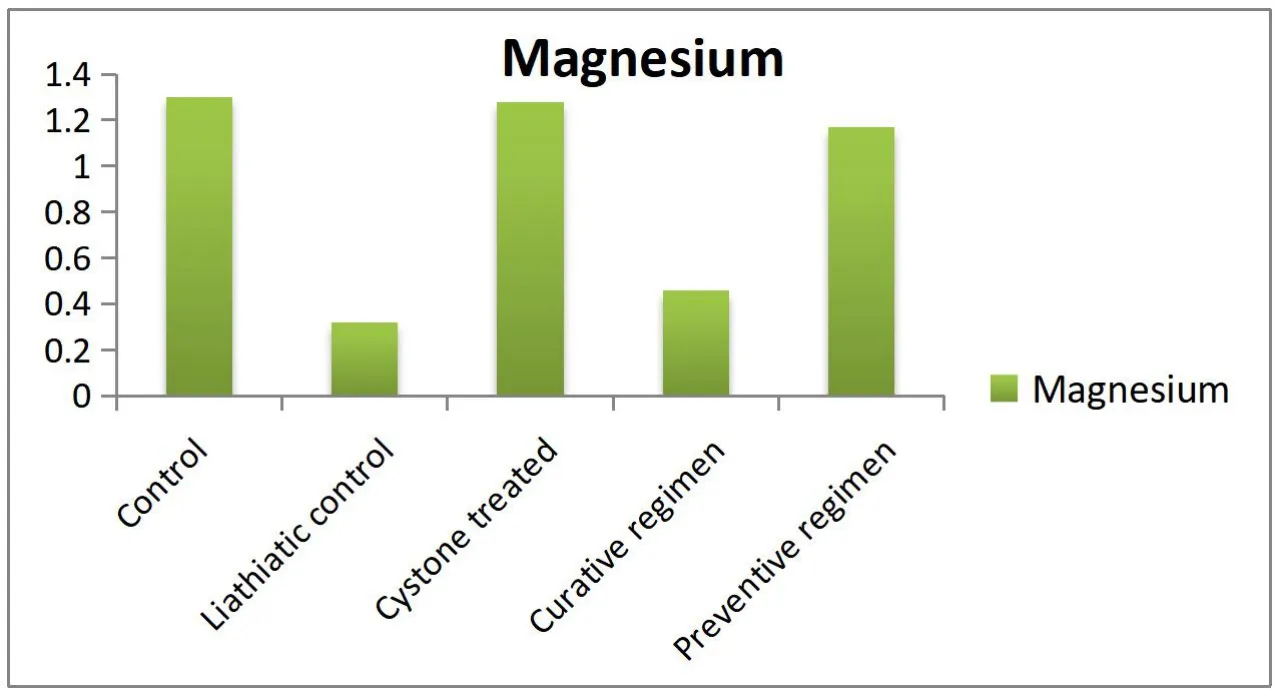
Figure 2 Magnesium level in urine
Conclusion
The study revealed that the administration of Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam showed significant anti-urolithiatic activity indicated by urinary biochemical parameters.The exact mechanism of action is not established but is attributed to the putative mechanism mediated by various phytochemicals interacting toward synergism.It is concluded that the drug Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam can be used in the management of kallaidaippu (uroliathiasis).Further phytochemical exploration is required to establish the exact mechanism of action.
杂志排行
Drug Combination Therapy的其它文章
- Progress in the study of antiplatelet and antithrombotic effects of salvia polyphenolic acid for injection
- Current and emerging trends in antimalarial drugs:a comprehensive review
- Publicly thanks to peer-reviewers 2022
- Theory exploration of ginseng-jujube-licorice group in the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus