Progress in the study of antiplatelet and antithrombotic effects of salvia polyphenolic acid for injection
2022-11-04LeiFanDuHongXieYanZhouBoXuanZhaoXiaoYingHanDeKunLiAiChunJuXinYuZhangWenZheWangChangXiaoLiuWenYuanGao
Lei Fan ,Du-Hong Xie ,Yan Zhou ,Bo-Xuan Zhao ,Xiao-Ying Han ,De-Kun Li ,Ai-Chun Ju,Xin-Yu Zhang,Wen-Zhe Wang,Chang-Xiao Liu,Wen-Yuan Gao*
1School of International Education,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China.2Changsha Health Vocational College,Changsha 410100,China.3School of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China.4Tasly Pride Pharmaceutical Company Limited,Tianjin 300410,China.5Tianjin Pharmaceutical Research Institute,Tianjin 300072,China.
Abstract Salvia polyphenolic acid for injection is a new generation of Chinese medicine injectable,which is developed by extracting and separating the water-soluble phenolic acid active ingredients of Salvia divinorum by using modern advanced technology as raw material.Pharmacological research shows that salvia polyphenolic acid has anti-inflammatory,anti-oxidative stress,neurotrophic,regenerative and protective effects on ischemic brain injury and can reduce myocardial ischemic injury.In clinical practice,it is mainly used in the treatment of stroke (mild to moderate cerebral infarction) in the recovery period of fetish blood obstruction.In recent years,it has also been gradually extended to treating acute cerebral infarction and respiratory syndrome.Since its launch,the pharmacological effects and clinical applications of Danshen polyphenolic acid for injection are reviewed to provide research clues for further essential trials and reference basis for clinical promotion and application.
Keywords: salvia polyphenolic acid for injection;oxidative stress;cardiomyopathy;thrombosis;anti-inflammator;apoptosis
Background
Thrombosis contributes to the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases such as unstable angina,myocardial infarction,transient ischemic attack and atherosclerosis.Platelets play an essential role in thrombosis at damaged vascular sites,especially arterial thrombosis and microvascular thrombosis,which are the leading causes of cardiovascular disease.Clinical meta-analysis has shown that antiplatelet therapy is effective in preventing a severe vascular crisis,arterial occlusion,and venous embolism in patients with high-risk vascular occlusive events.Thus,substances with antiplatelet and antithrombotic effects have the potential to treat a wide range of circulatory disorders [1-3].
Many types of antiplatelet drugs are used in clinical practice,mainly: aspirin,clopidogrel,abciximab and so on.Although these drugs can effectively inhibit platelet aggregation caused by a specific signaling pathway within platelets,there are more adverse reactions(allergic reactions,gastric mucosal injury,severe bleeding,hematopoietic dysfunction,etc.).At the same time,because most drugs have a single mechanism of action after a patient takes a particular class of drugs to inhibit platelet activity,the body can still cause platelet activation through other signaling pathways.Thus,the therapeutic effect is weakened,and the occurrence of recurrent ischemic events and the resulting mortality remains high.In some populations,aspirin and clopidogrel are resistant or unresponsive,and some patients are resistant to both drugs [4-7].For this reason,the search for antiplatelet agents with high efficacy and safety remains a priority for researchers in various countries.
Salvia miltiorrhizais the dried root or rhizome ofSalvia miltiorrhiza,a plant of the family Labiatae.Clinical use shows that various Salvia preparations can effectively prevent and treat cardiovascular diseases,hyperlipidemia and cerebrovascular diseases.Salvianolic acid is a water-soluble phenolic acid compound inSalvia miltiorrhiza,which vigorously protects cell membranes against oxidative stress damage.Modern pharmacological studies have shown that salvianolic acid has a wide range of pharmacological activities,which can scavenge oxygen free radicals to counteract oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial damage in rat heart and liver,effectively preventing ischemic damage in brain tissue and reducing ischemic damage myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.These substances can be involved in the pathological response of the body through different mechanisms.For example,they can bind to platelet surface-related receptors,recruit more platelets in the bloodstream to reach the site of vascular injury,adhere to each other,form platelet aggregates,and eventually initiate the clotting process,exerting a hemostatic effect,or form thrombi,causing thromboembolic disease.
Mechanism of platelet activation
Under normal physiological conditions,a healthy blood system releases inhibitory signals that place platelets in a resting state,in traditional forms such as round and heathered.Activation of platelets by vascular injury,inflammation,smoking,excessive alcohol consumption,diabetes,hypertension,hyperlipidemia,and certain cardiovascular diseases produces reactions such as aggregation,deformation,adhesion,and release of granule contents [8].The granule contents released by platelets include substances such as platelet-activating factor,arachidonic acid,adenosine diphosphate(ADP),thrombin,epinephrine,and 5-hydroxytryptamine [9].
The role of platelet G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)signaling pathway in thrombosis
GPCRs are 7-transmembrane proteins that are regulated in a similar manner;GPCRs are activated by extracellular ligands,resulting in conformational changes that trigger downstream signaling pathways that regulate physiological processes through,for example,second messengers.GPCR downstream binding proteins are mainly G proteins,but there are also non-G protein-dependent signaling pathways that can bind directly to G-protein-coupled receptor kinase(GRK) and repressor proteins.
Studies have shown that Salvianolic acids for injection (SAFI) could increase the influx of Ca2+in cardiomyocytes in heart failure.Although the intracellular Ca2+effect of SAFI on platelets may be different from that on cardiomyocytes,this SAFI effect on Ca2+might also be related to the weaker effect of SAFI on ADP-induced platelet aggregation.Platelet aggregation is a complex process involving a series of signal transduction mechanisms within platelets.Under the action of agonists,specific receptors on the membrane bind to ligands,undergo conformational changes,activate critical enzymatic reactions in platelets,generate or release some intracellular signal molecules,and undergo a series of biochemical reactions,leading to adsorption and aggregation.Platelet membrane surface receptors are mainly GPCRs,and all known soluble platelet agonists bind to platelet surface GPCRs [10-13].After vascular injury,many active substances are released from endothelial cells,chemotactic platelets adhere to the damaged site,and bind to the corresponding surface receptors to activate platelets [14].Activated platelets release stored substances,such as ADP,serotonin,platelet-activating factor,arachidonic acid-induced thromboxane A2,etc.,to initiate and promote platelet aggregation [15].A common pathway for inducing platelet aggregation was the activation of glycoproteins on platelet membranes by causing an increase in intracellular Ca2+concentration(Figure 1).
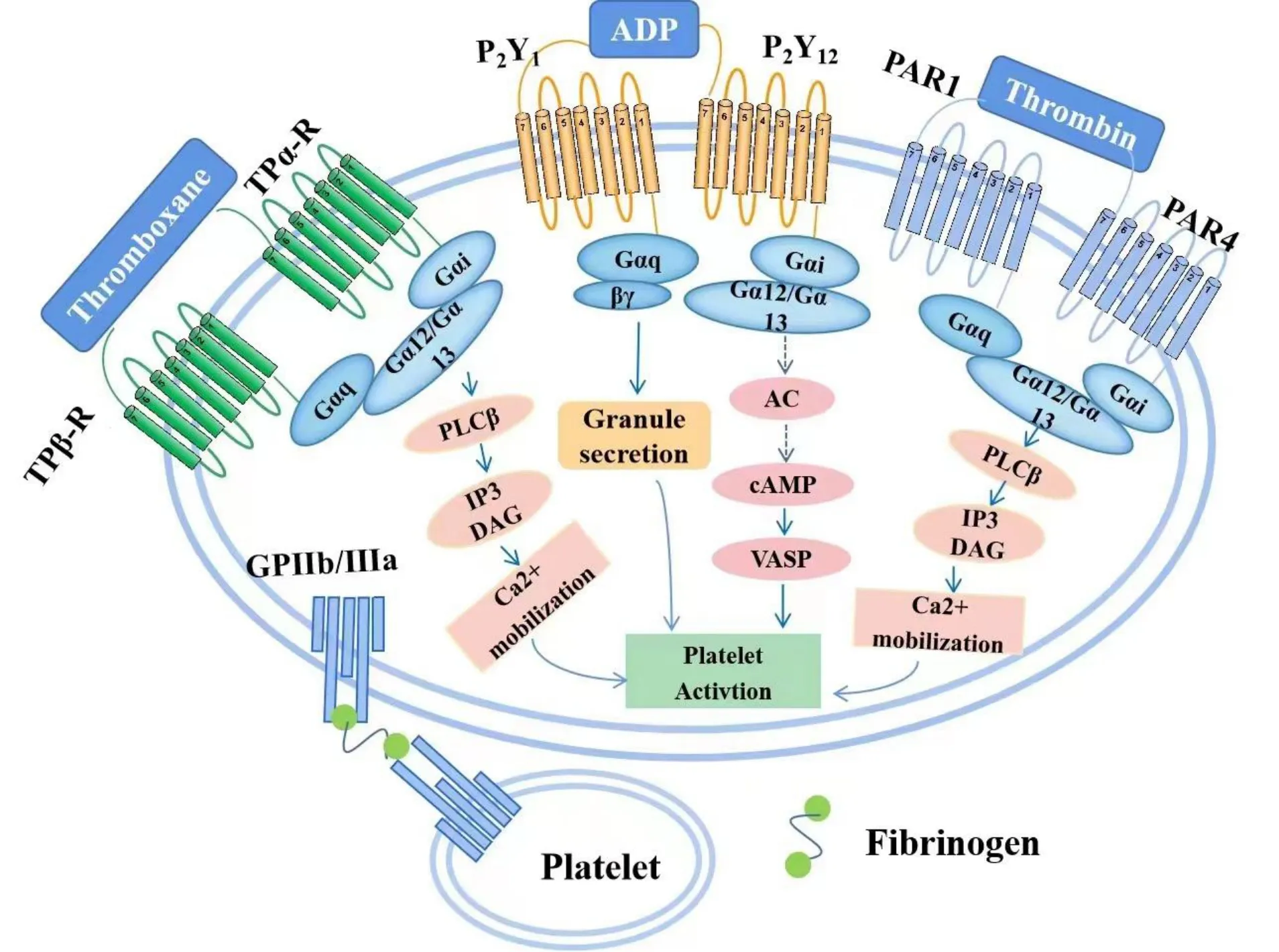
Figure 1 Mechanisms of platelet aggregation induced by various inducers
ADP is the first signaling molecule that stimulates platelet aggregation,exists in dense platelet granules,and is a critical platelet activation mediator.ADP-induced platelet morphological changes,aggregation,intracellular calcium mobilization and decreased cAMP content [16-19].ADP-induced platelet aggregation requires the participation of fibrinogen and Ca2+[20].Low concentrations of ADP caused reversible platelet aggregation,while high concentrations of ADP caused biphasic aggregation [21].The first phase of aggregation is primary aggregation,which occurs by the direct action of ADP on platelets [22].The second phase is secondary aggregation,caused by the release of endogenous ADP from platelets due to the addition of ADP.
Thrombin is the most potent known platelet agonist,and different concentrations of thrombin can produce reversible or irreversible platelet aggregation [23-26].In the absence of Ca2+,thrombin can cause release but not aggregation.The arachidonic acid metabolite thromboxane A2 is a potent agonist in platelet aggregation.Thrombin and thromboxane A2 bind to the corresponding receptors,activate phospholipase C (PLC) through the transmembrane transduction of G protein,increase inositol phosphate (IP) production,and increase cytoplasmic Ca2+concentration.Activated Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of protein kinase C (PKC) results in the expression of GPIIb-IIIa on the platelet surface,which further causes platelet aggregation [27].
Study on the chemical composition of Salvianolic acids for injection
SAFI is based onSalvia miltiorrhiza,of which the main component is salvia polyphenolic acid.Most of the salvia polyphenolic acids are based on Danshensu and caffeic acid as structural units.The compounds are classified into monomers and polymers reckoning on the amount of benzol rings in their structures,where polymers include dimers,trimers and tetramers[28].Monomers include tannins,caffeic acid,protocatechuic organic compounds,and protocatechuic acid.Dimers embrace rosmarinic acid,rosmarinic acid methylcool,salvianolic acid F,salvianolic acid G,salvianolic acid D,and protocatechuic acid.Trimers include salvianolic acid A,salvianolic acid C,salvianolic acid H,salvianolic acid J,salvianolic acid I,purslaneic acid and its esterified derivatives,etc.The tetramers include salvianolic acid B and its salts and esterified derivatives,salvianolic acid E,salvianolic acid Y,etc.Information about each component is presented in Table 1.
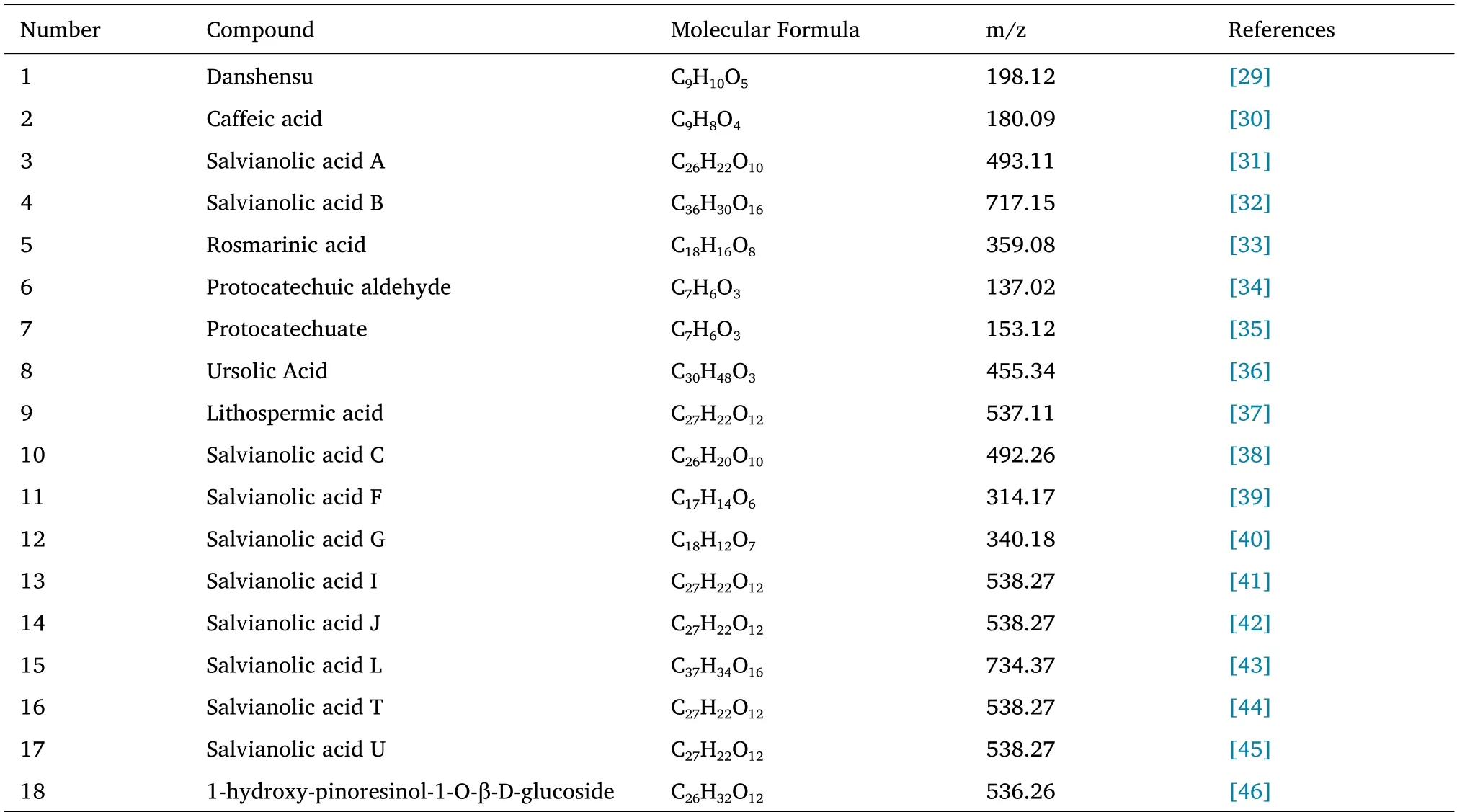
Table 1 Water-soluble phenolic acids of Salvia miltiorrhiza
Pharmacological effects of Salvianolic acids for injection
SAFI is a modern Chinese medicine compound preparation with multi-target,multi-link and holistic regulation of the body.It is used in the recovery period of stasis and blood obstruction in the central meridians of stroke disease (mild to moderate cerebral infarction),which is characterized by hemiplegia,slanting of the mouth and tongue,strong tongue and speech and numbness of the partial body.At present,domestic and foreign research is mainly concentrated on pharmacological effects,composition analysis,mechanism of action and clinical application.Studies on the pharmacological effects of Salvianolic acids for injection have been abundant.Now we summarize the pharmacological effects of Salvianolic acids for injection in recent years in order to better guide the clinical use and secondary development.
Anti-inflammatory effect
After the ischemic injury,inflammatory cells within the blood rapidly migrate to the ischemic infarct area after exudation,releasing plenty of inflammatory factors,such as tumor necrosis factor,interleukin(IL)-1β and IL-6.These can increase the expression of integrin proteins,P-selectin,E-selectin and other substances on endothelial cells.Then damage cerebrovascular endothelial cells,resulting in neuronal cell necrosis and apoptosis and aggravating ischemic brain injury[47].However,some studies have shown that the role of IL-6 in stroke pathogenesis is two-sided,protecting and damaging brain tissue.Its mechanism of injury is mainly achieved through overexpression in infarct foci [48].Some studies experimentally confirmed that SAFI could directly inhibit the expression of post-stroke inflammatory factors [49-51].Further in vitro studies exposed that in glyoxylation-deprived and reoxygenated cortical neuronal culture systems (simulating ischemia-reperfusion injuryinvitro).SAFI dose-relatedly inhibited the expression level of Toll-like receptor 4 and downstream proteins,including the myeloid differentiation molecule MyD88,nuclear factor-kB,and TNF receptor-associated factor 6,along with a significant decrease in pro-inflammatory factor levels[52,53].
By binding to amino acid 207 of STAT3,ryanodine inhibited Ang II-induced STAT3 nuclear translocation,and by binding to amino acids 635/637,it inhibited Ang II-induced STAT3 phosphorylation.Through the“double attack”on STAT3,ryanodine down-regulated the expression ofpro-hypertrophic fibrosis-relatedgenes controlled by STAT3.Finally,it achieved the drug effect of alleviating ventricular remodeling and protecting cardiac function (Figure 2).
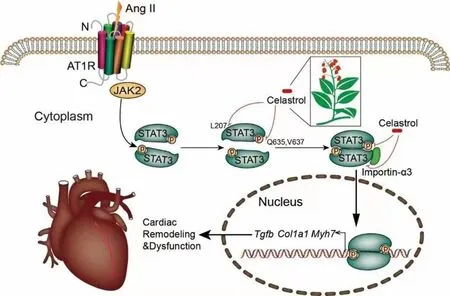
Figure 2 Attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling by targeting STAT3
Inhibition of neural apoptosis
Apoptosis is a programmed cell death regulated by genes,and there are two major pathways that regulate apoptosis: the mitochondrial pathway and the death receptor pathway.SAFI inhibits apoptosis in neuronal cells mainly by regulating the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.Mitochondria are responsible for cellular energy production.When mitochondria undergo oxidative phosphorylation is disturbed,it leads to an enhanced rate of reactive oxygen species(ROS)generation.This process not only reduces cellular energy production but also leads to an increased propensity for ROS production [54].When the blood supply to the ischemic organ is restored,the influx of oxygen exacerbates the creation of ROS,which affects the normal working of the respiratory chain in the mitochondria and damages DNA,proteins and lipids in the membrane components.Ultimately resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction,causing cell and tissue dysfunction and thus cell death[55].
Early in ischemic stroke,microglia and astrocytes are activated and recruit large amounts of adhesion factors,chemokines,and cytokines from the blood to induce an inflammatory cascade[56].Microglia are targets of inflammatory intermediator action and are concerned with regulating the inflammatory response.Wang et al.used a co-culture system of neurons and microglia found that the cytoprotective effect of SAFI was not due to its protection of neurons from inflammatory mediator damage,but to its ability to inhibit inflammatory factors discharged by microglia.Astrocytes are vital to the blood-brain barrier and have neuroregenerative and reparative effects under normal conditions [57].Ischemic damage is exacerbated by decreased astrocyte viability and increased intercellular excitatory glutamate concentrations after cerebral ischemia.Study observed the expression of astrocyte-specific protein glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein in different parts of ischemic rat brain tissue and found that SAFI intravenous injection of 21 mg/kg 3d could significantly inhibit the expression of glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein in the ischemic semi-dark zone and improve the viability of astrocytes [58].Thus decreasing the penetrability of the blood-brain barrier.Therefore,microglia and astroglial fine activation regulation during cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury is of great significance in neuroinflammation.
Inhibition of oxidative stress
Oxidative stress is a negative impact created by free radicals within the body and is considered a crucial factor contributing to aging and disease.The accumulation of excessive ROS regulates a series of intracellular signaling pathways,such as the activated mitogenic protein kinases pathway or the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) pathway,inducing cell death [59,60].In vivo animal experiments have shown that SAFI has potent antioxidant effects in vivo.In vitro culture of oxidized low-density-lipoprotein-induced umbilical veinology endothelial cells also revealed that SAFI could scavenge free radicals and defend against oxidative stress-induced epithelium cell damage [61].The above findings suggest that the antioxidant effects of SAFI in vitro and in vivo alleviate ischemic stroke greatly.
Conclusion
In conclusion,salvianolic acid is the most critical water-soluble active component ofSalvia miltiorrhiza,family Labiatae,which exerts antiplatelet aggregation and antithrombotic effects from multiple perspectives by affecting multiple targets and multiple pathways,providing a theoretical basis for the rational clinical application and drug development of salvianolic acid.Although there are many studies on the effects of salvianolic acid on ischemic cardiomyopathy,they are mainly focused on the treatment of myocardial infarction and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.In contrast,the studies related to the effects and mechanisms of action of salvianolic acid on ischemic cardiomyopathy such as ischemic heart failure and angina pectoris are still limited and need further in-depth study.At present,the actual drug action targets of salvianolic acid have not been identified and confirmed,which is the biggest challenge and the greatest hope in this field.
杂志排行
Drug Combination Therapy的其它文章
- Current and emerging trends in antimalarial drugs:a comprehensive review
- Publicly thanks to peer-reviewers 2022
- Antiurolithiatic activity of Aavarai Bhavanai Chooranam a Siddha polyherbal formulation on ethylene glycol-induced urolithiasis in Wister albino rats
- Theory exploration of ginseng-jujube-licorice group in the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus