Analysis of laboratory and imaging examination results of patients with COVID-19 2 years after discharge in Chengdu
2022-11-02ZhaoBenNanDuQingKangJunLiuDafengZhangLingLanLijuanYuanYuan
Zhao Ben-Nan, Du Qing , Kang Jun, Liu Da-feng, Zhang Ling, Lan Li-juan, Yuan Yuan
1. Department of Comprehensive Internal Medicine, Public Health Clinical Center of Chengdu,Chengdu 610061, China
2. Department of Infectious Diseases, the First Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu 610513, China
Keywords:COVID-19 SARS-CoV-2 Follow-up Laboratory test Vaccination
ABSTRACT Objective: To summarize the follow-up results of laboratory examination, echocardiographic and chest CT of patients with COVID-19 at the time of 2 years after discharge in Chengdu. Methods:A total of 29 COVID-19 survivors who have participated in the 1-year follow-up and 2-year follow-up at Public Health Clinical Center of Chengdu were included in our study. Their blood laboratory tests, echocardiography and chest CT results were analyzed in order to evaluate the long-term recovery of COVID-19 survivors. Results: The most common abnormal laboratory test results at the 2-year follow-up were increased serum fibronectin (21 cases, 72.4%) and decreased NK cell counts (19 cases, 65.5%). Compared with laboratory test results at the 1-year follow-up,platelet count, hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase and creatine kinase isoenzyme were decreased(all P<0.05), while serum fibrinogen, triglyceride, insulin and non-specific immunoglobulin A were increased (all P<0.05). Serum specific total SARS-CoV-2 antibody amount in COVID-19 survivors at half a year after COVID-19 vaccine was significantly higher than that before vaccination. More than half of patients (55.2%) had normal echocardiography results at the 2-year follow-up, the main abnormal results of them were valve regurgitation (7 cases, 24.1%) and reduced left ventricular diastolic function (9 cases, 31.0%). Compared with 1-year follow-up, 7 patients had fewer abnormal cardiac ultrasound results. 28 cases underwent chest CT at the 2-year follow-up, the mainly abnormal results were ground glass shadow (17.9%), pulmonary nodules(diameter<6mm) (32.1%) and scattered cable shadow (39.3%). 71.4% (20/28) of them had no significant change between the two chest CT results. Conclusion: The mainly abnormal blood laboratory indicators in COVID-19 survivors at 2-year follow-up after discharge were increased serum fibronectin and decreased NK cell counts. Although echocardiography and chest CT results were no significant change between 1-year follow-up and 2-year follow-up among COVID-19 survivors, there were still some patients whose abnormal results were decreasing. Serum specific total SARS-CoV-2 antibody amount in COVID-19 survivors at half a year after COVID-19 vaccine was still significantly higher than that before vaccination, but the amount of specific antibody had a downward trend with time.
1. Introduction
Infected with SARS-CoV-2 can have long-term effects on multiple organs and systems in patients [1-3], most studies have observed time endpoints of discharge or discharge from hospital 1 year after recovery [4-6]. Recently, the 2-year follow-up results of more than 1,000 patients in Wuhan were published in The Lancet-Respirology[7], mainly reporting the long-term sequelae of patients with new coronavirus pneumonia (referred to as new coronary pneumonia)after recovery. mental health and lung function follow-up results.In view of the fact that there are few reports on the follow-up and follow-up of patients with SARS-CoV-2 for more than one year, we summarize the results of blood laboratory examinations,cardiac color Doppler ultrasound and chest high-resolution CT examinations of COVID-19 survivors in Chengdu two years after discharge, in order to provide reference for the long-term recovery of patients who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Research objects
As of May 2022, 29 COVID-19 survivors who had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the mainland and had participated in the 1-year follow-up and 2-year follow-up at Public Health Clinical Center of Chengdu were included in our study.
2.2 Research methods
The follow-up observational research method was used in our study, we collect the laboratory and imaging examination results of the subjects 1-year follow-up and 2-year follow-up. Laboratory tests include white blood cell count (WBC), lymphocyte count(LYM), red cell count (RBC), platelet count (PLT), and biochemical C Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase(AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, GGT), albumin (albumin, ALB), total bilirubin (total bilirubin,TBIL), serum ferritin (serum ferritin, Fer), serum fibrinogen (serum fibrinogen, FN), urea (Urea), creatinine (creatinine, CR), uric acid(uric acid, UA), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (HBDH), creatine kinase (CK) in myocardial enzymes ), creatine kinase isoenzyme (CK-MB), total cholesterol(CHOL), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol(high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C), insulin (insulin,INS), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), prothrombin time (PT),fibrinogen (FBG), thrombin time (TT) in coagulation routine ,fibrinogen degradation products (fibrinogen degradation, products FDP), D-dimer (D-Dimer), non-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG),immunoglobulin A (IgA), immunoglobulin M (IgM) , complement C3, C4, CD3+T cell count, CD4+T cell count, CD8+T cell count,CD4+/CD8+ ratio, B cell count, NK cell count in lymphocyte subsets, SARS-CoV-2 IgM antibodies, IgG antibodies, total antibodies. Imaging examinations were mainly cardiac color Doppler ultrasound and high-resolution chest CT. SARS-CoV-2 specific IgM and IgG were detected by Mike i3000 automatic chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer, and the total antibody was detected by Wantai Caris200 automatic chemiluminescence immunoassay analyzer. Representation (S value is the detection value of the chemiluminescence reaction signal generated by the luminometer measuring serum samples, CO value is the critical value calculated by the instrument through the luminescence value of the calibrator,that is, the cut-off value), and the unit is COI.
2.3 Statistical analysis
Data were entered using Excel, and SPSS 26.0 software was used for statistical analysis. The measurement data was first tested for normality, and it was expressed as (±s) when it obeyed the normal distribution. The comparison was performed using two independent samples t test or paired samples t test; number) [M(P25, P75)],the comparison was performed using two independent samples nonparametric test or paired Wilcoxon signed rank test. Enumeration data were expressed as the number of cases (%), and Fisher's exact test was used for comparison between groups. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2.4 Clinical trial registration and ethical review
The registration number of the follow-up study of COVID-19 survivors is ChiCTR2000034563 in the China Clinical Trial Registration Center, and the registration unit is Chengdu Public Health Clinical Medical Center. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Chengdu Public Health Clinical Medical Center (approval number: PJ-K2020-06-01), and all patients who returned to the clinic signed an informed consent form, which complied with the regulations of the National Health Commission and the requirements of the Declaration of Helsinki.
3. Results
3.1 Normal information
A total of 29 COVID-19 survivors were included in our study,ranging in age from 23 to 66 years old (average age 45.6 years old),10 males and 19 females; 24 were diagnosed as normal type and 5 were diagnosed as severe/critical type at the time of discharge.There were 14 cases with underlying diseases (including 6 cases of hypertension, 5 cases of diabetes mellitus, 9 cases of fatty liver,and 4 cases of chronic hepatitis B). All the cases with diabetes mellitus used oral hypoglycemic drugs, but not insulin. 23 people were vaccinated with the new coronavirus inactivated vaccine 14 to 17 months after discharge, and the two-dose vaccination was 6 to 7 months away from the 2-year follow-up after discharge.
3.2 laboratory test results
Because metabolism-related laboratory indicators are greatly affected by lifestyle habits such as diet, except for blood lipids,blood uric acid, insulin, and glycosylated hemoglobin, among the abnormal laboratory indicators in the 2-year follow-up, 5 patients had elevated ALT (accounting for 5 patients). 17.2%, including 1 case with hepatitis B and 4 cases with fatty liver), FN increased in 21 cases (72.4%), complement C4 decreased in 8 cases (27.6%),and NK cell count decreased in 19 cases (65.5%). The proportion of men with fatty liver was higher than that of women (60.00% vs.15.79%, P<0.05), and the ratio of RBC, GGT, Fer, Urea, CR, UA,CK, CK-MB and TG in men was higher than that in women, and the difference was statistically significant (Pall <0.05); male HDL-C and nonspecific IgM were lower than females, and the difference was statistically significant (Pall <0.05) (Table 1).Comparison of blood laboratory test results between 2-year followup and 1-year follow-up showed that, PLT, HBDH, and CK-MB were lower than those at 1-year follow-up, and the difference was statistically significant (all P < 0.05); FN, TG, INS, nonspecific Heterosexual IgA was higher than that at 1-year follow-up, and the difference was statistically significant (all P<0.05). There was no statistical significance in the two comparisons of other laboratory indicators (P>0.05) (Table 2).
3.3 Results of SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies in vaccinated COVID-19 survivors
Among the 23 patients who were vaccinated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine1 year after discharge, the paired Wilcoxon signed-rank test showed that the IgG antibody value 2 years after discharge (six months after vaccination) was higher than that of 1 year after discharge, but the difference was not statistically significant (Z=-1.913, P=0.056); the total antibody to 2019-nCoV was significantly higher than 1 year after discharge, and the difference was statistically significant (Z=-3.516, P<0.001) (Table 3).
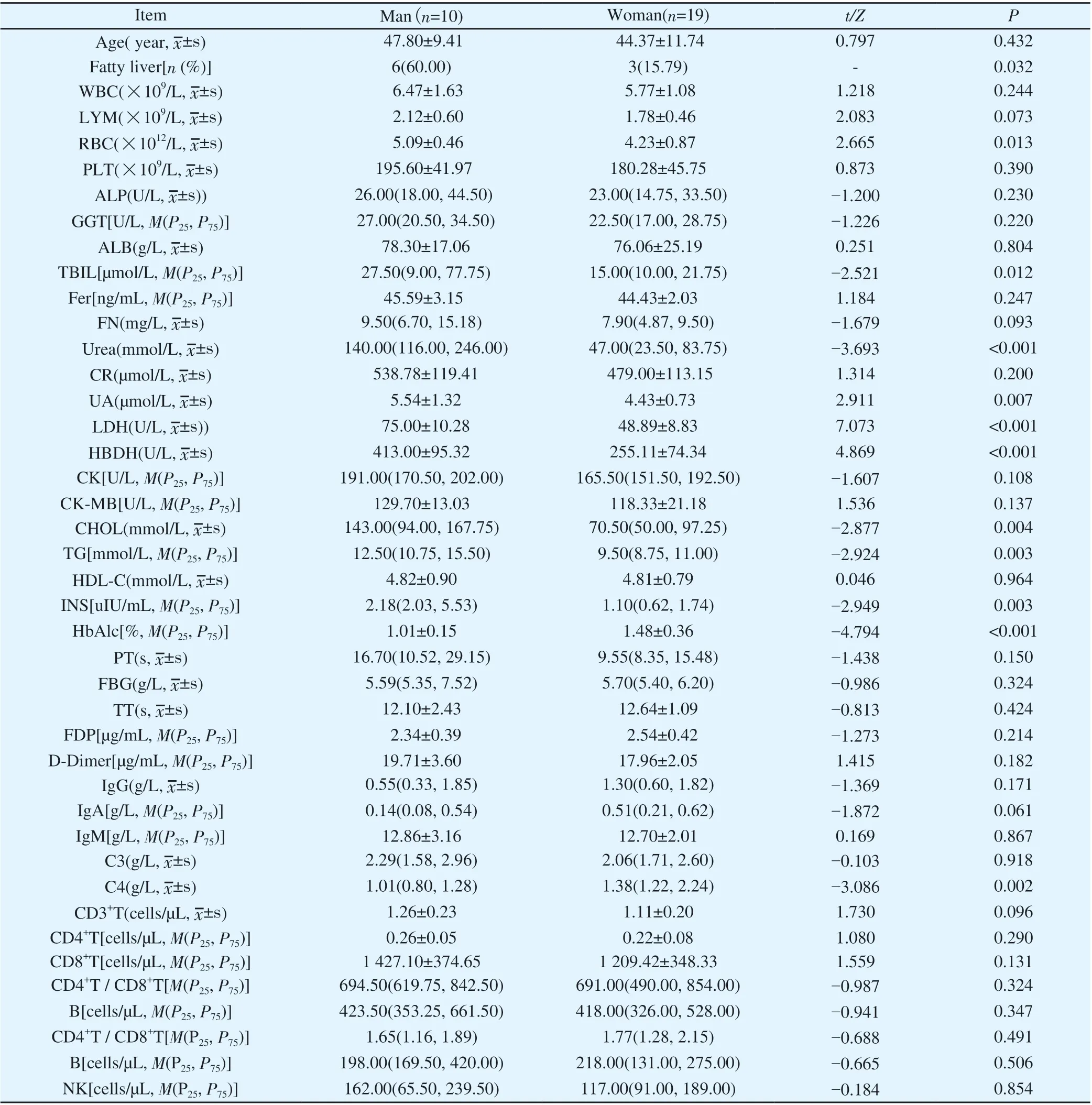
Table1 Differences of laboratory examination results in different genders two years after discharge (n=29)

Table 2 Changes in laboratory test results(n=29)
3.4 Echocardiography results
More than half of the patients (55.2%) had normal echocardiographic results at 2-year follow-up, and the abnormal results mainly included mild valve regurgitation (24.1%) and decreased left ventricular diastolic function (31.0%). The results ofechocardiography 2 years after discharge and 1 year after discharge showed that the results remained unchanged in 18 cases (62.1%),and abnormal results increased in 4 cases (13.8%), including 2 cases of mild valve regurgitation and decreased left ventricular diastolic function. 2 cases), and 7 cases of abnormal results (accounting for 24.1%, of which 4 cases of valvular regurgitation were not reported,2 cases of decreased left ventricular diastolic function were not reported, and 1 case of original pericardial effusion disappeared).A 29-year-old young woman at the time of illness showed a small amount of pericardial effusion at the follow-up visit six months, one year, and one and a half years after discharge. Cardiac MRI showed myocardial edema. The echocardiography result was normal at the follow-up visit 2 years after discharge.

Table 3 Changes of SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies in COVID-19 survivors[n=23,(M(P25,P75)]
3.5 Chest CT results
One patient did not undergo chest CT, and the remaining 28 patients had chest CT results at 2-year follow-up: normal in 7 cases(25.0%), small nodules (diameter < 6 mm) in 9 cases (32.1%), of which 5 were single nodules cases, 4 cases of multiple nodules), 11 cases of spots and streak shadows (39.3%), 5 cases of ground glass shadows (17.9%, including 3 cases of slight ground glass shadows and 2 cases of sheet ground glass shadows), lung Bullae in 3 cases(10.7%), local pleural adhesion in 2 cases (7.1%), bronchiectasis in 1 case, grid shadow in 1 case, and interlobular septal thickening in 1 case. Those with flaky ground-glass opacity, grid opacity, and interlobular septal thickening were all severe/critical cases.
Comparison of chest CT results between 2-year follow-up and 1-year follow-up showed that there was no significant change in the results in 20 cases (71.4%), and the original lesions decreased or disappeared in 6 cases (21.4%, including 3 cases of groundglass opacity, and 3 cases of small lesions). Nodules disappeared in 3 cases, cord shadow slightly decreased in 2 cases), and groundglass opacity slightly increased in 2 cases (accounting for 7.2%, the report suggests that the hypostatic effect may not be excluded). In 1 patient diagnosed as critically ill, the ground-glass opacity gradually absorbed a small amount with the prolongation of recovery time
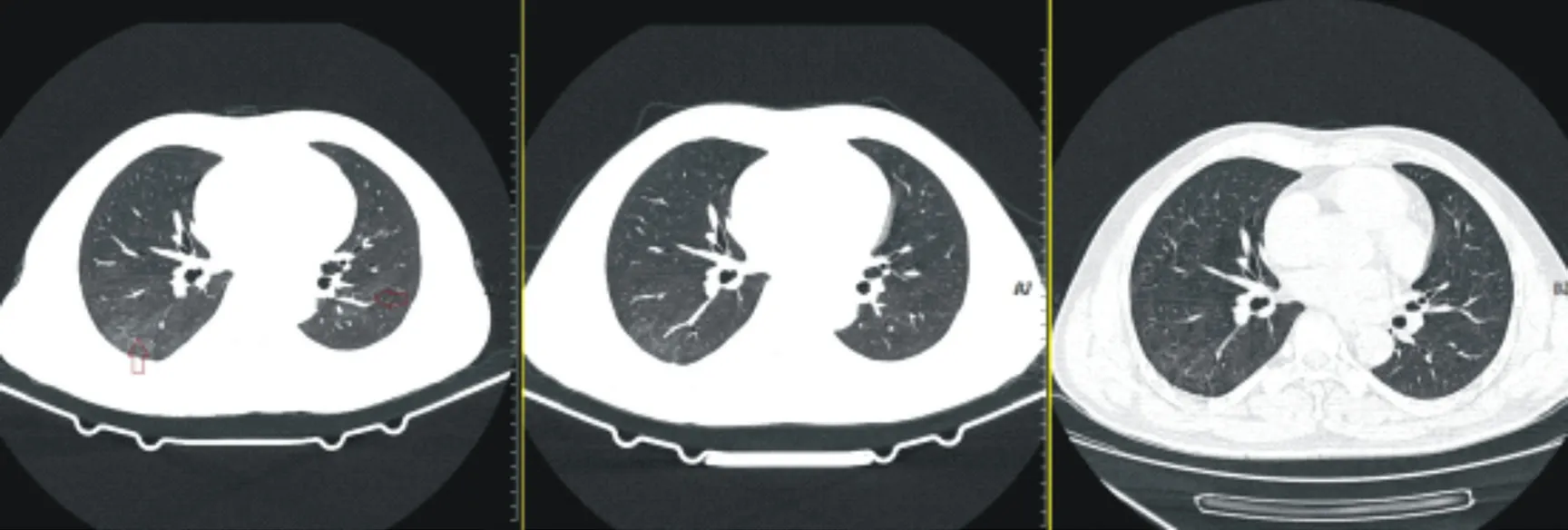
Figure 1 Chest CT images of a critically ill patient six months, one year, and two years after discharge
4 Discussion
Previous studies have shown that SARS virus can enter and destroy pancreatic islets through ACE2, resulting in damage to islet function and increased blood sugar [8]. Therefore, some scholars believe that SARS-CoV-2 may also destroy islet beta cells through this mechanism [9]. Whether the infection of the new coronavirus will cause long-term effects on the pancreatic beta cells of patients is a current research hotspot. This study showed that the insulin levels of patients with new coronary pneumonia 2 years after discharge did not decrease compared to 1 year after discharge.Myocardial injury often occurs in patients with SARS-CoV-2 [10-12], and studies have shown that some patients still have persistent myocardial inflammation after recovery through cardiac MRI [13-14]. In this study, most of the patients (62.1%) had no change in the results of echocardiography at 1 and 2 years after discharge. Among the 4 patients with an increase in abnormal echocardiographic results, 2 were 51 years old, 1 was 52 years old, and 1 was 63 years old. All were middle-aged and elderly, and 3 had hypertension and 2 had diabetes. The increased abnormal results were 2 cases of decreased left ventricular diastolic function, 1 case of mild mitral valve regurgitation, and 1 case of mild tricuspid valve regurgitation.Tissue degeneration or loss of ventricular compliance and elasticity.In addition, 7 patients (24.1%) had fewer abnormal results. Among them, 1 young woman with no underlying disease had multiple follow-up echocardiograms after discharge, all of which showed pericardial effusion, and cardiac MRI showed the presence of myocardial edema, which was excluded after perfecting relevant examinations. Other common causes of pericardial effusion were identified, and echocardiography showed disappearance of pericardial effusion at 2-year follow-up. Blood laboratory examinations also showed that CK-MB and HBDH in myocardial enzymes were lower than that of 1-year follow-up (all P<0.05). The above results suggest that although some patients with SARS-CoV-2 may experience long-term myocardial damage, it may be alleviated or self-healed over time.At 2-year follow-up, most of the laboratory test results except for metabolic indexes were within the normal range, and there were very few cases with abnormal indexes exceeding 4, suggesting that with the prolongation of recovery time, the functions of various organs gradually returned to normal. The results showed that some laboratory indicators of men were higher than those of women 2 years after discharge (P<0.05), which may be because the proportion of men with fatty liver in this study was significantly higher than that of women, and fatty liver patients often combined with metabolism such as blood lipids and uric acid. The indicator is abnormal. In addition, Xu Jing[15] included data from 27 978 physical examinations, showing that the quartiles of serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, blood uric acid, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein in men were higher than those in women,and the quartiles of high-density lipoprotein were lower than those of women. Female (P<0.01), consistent with the results of this study.Furthermore, the normal reference range of CK and hemoglobin in males is higher than that in females, suggesting that these test results themselves are different between males and females. As for male non-specific IgM lower than female, the above-mentioned report has not been found, which may be due to the small sample size of this study.
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 is the most effective way to prevent and control the epidemic. Studies by Liu Yang[16] and others showed that 13-15 days after inoculation with two doses of Kexing inactivated vaccine, the positive rates of specific IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibodies were both 100%. Six months after vaccination, nearly half of the people were still positive for specific IgG antibodies, but the amount of antibodies decreased significantly [17]. At present, there are few reports on the kinetics of specific antibodies in vivo after vaccination in patients with previous COVID-19 infection. The author's previous study[18] showed that 24-78 days after the completion of two doses of inactivated vaccine in previously infected patients, the specific IgG and total antibodies were significantly higher than those before inoculation (all P<0.05).In this study, the specific total antibody was still significantly higher than that before the vaccination half a year after the previous infection (P<0.05), and the specific IgG was also slightly higher than that before the vaccination, but the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). The results may be affected by the small sample size, but it can also reflect that with the extension of the vaccination time, the specific antibodies in the COVID-19 survivors also tend to decline gradually. It should be pointed out that the SARS-CoV-2 total antibody detection in this study included specific IgM, IgG and IgA antibodies produced against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD. Most (79.3%) researchers were vaccinated against the SARS-CoV-2, and The non-specific IgA increased 2 years after discharge compared with 1 year after discharge (P<0.05),suggesting that the specific IgA antibody was mainly increased in the past six months after vaccination with the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine compared with before vaccination, that is, specific IgA antibodies after vaccination The decay of IgA antibodies may be slower than that of IgG antibodies. At present, there is no consensus on whether and when to vaccinate the third dose of the new coronavirus vaccine for previously infected people. Long-term observation of the kinetic changes of specific antibodies in such people can provide a theoretical basis for solving this problem. This study showed that more than half of the patients with previous infection had increased FN (72.4%) and decreased NK cell count (65.5%) 2 years after discharge. Compared with 1 year after discharge, the mean FN increased by about 100 mg/L (P<0.05), and FN was also increased in patients with previous infection who did not have underlying liver diseases. FN in blood is mainly synthesized and secreted by hepatocytes, and its elevation is common in hepatitis, fatty liver,early cirrhosis, liver cancer, diabetes, acute nephritis, thrombosis and other diseases. Basic studies have shown [19] that fibronectin levels are significantly up-regulated in alternately activated macrophages during the healing phase of chronic inflammatory diseases and acute inflammatory responses. Because most researchers have been vaccinated against the new crown virus, it is unclear whether this change is a long-term sequelae of the new crown virus infection or is related to the vaccination.Xu Lingfang's study of 82 patients with SARS-CoV-2 [20] showed that with the prolongation of the recovery period, the ground-glass shadow lesions in the lung gradually absorbed, the consolidation shadow and fibrous cord shadow gradually increased, and the abnormal rate of chest CT increased from 48.78 at the time of discharge. % decreased to 21.95%, 9.76%, and 8.55% at 2, 4, and 6 months after discharge, and 20 patients had pulmonary fibrosis changes 6 months after discharge. This study showed that the main imaging abnormalities left in the lungs 2 years after recovery were small nodules and streak shadows, and some patients could have a little ground-glass shadows. One to two years after recovery, some patients are still absorbing the lung lesions. The study by Huang[7] et al. showed that the most common residual imaging abnormalities on chest CT in Wuhan cases were ground glass shadows and irregular streak shadows 2 years after discharge, which is consistent with the results of this study.
In conclusion, the mainly abnormal blood laboratory indicators in COVID-19 survivors at 2-year follow-up after discharge were increased serum fibronectin and decreased NK cell counts. Although echocardiography and chest CT results were no significant change between 1-year follow-up and 2-year follow-up among COVID-19 survivors, there were still some patients whose abnormal results were decreasing. Serum specific total SARS-CoV-2 antibody amount in COVID-19 survivors at half a year after COVID-19 vaccine was still significantly higher than that before vaccination, but the amount of specific antibody had a downward trend with time.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Advances in BRAF gene mutations in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Research progress on the correlation between lncRNA and the pathogenesis of COPFD
- Efficacy and prognosis of vacuum-assisted excision for benign intraductal papilloma of breast: A meta-analysis
- Clinical efficacy and perioperative safety of simultaneous or staged bilateral total hip arthroplasty:A Meta analysis
- Kaempferol attenuates knee osteoarthritis via inhibiting cartilage apoptosis in mice
- Effect of Acacetin on flagellin induced NLRC4 inflammasome activation in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages
