Mapping the global research landscape on insulin resistance:Visualization and bibliometric analysis
2022-09-16SaedZyoudMunaShakhshirAmerKoniAmaniAbushanabMoyadShahwanAmmarAbdulrahmanJairounRandAlSubuAdhamAbuTahaSamahAlJabi
INTRODUCTION
During the last two decades, the global prevalence of diabetes has increased dramatically. Diabetes is increasing worldwide, both in terms of prevalence and the number of affected[1]. For more than half a century, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes have been associated. Insulin resistance is not only a powerful predictor of future type 2 diabetes development but is also a therapeutic target in the presence of hyperglycemia[2]. Insulin resistance is defined as a reduced physiological response to insulin stimulation of target tissues, especially adipose tissue, liver, and muscle. Insulin resistance limits glucose disposal, leading to a compensatory increase in beta cell insulin synthesis and hyperinsulinemia[3]. More than 30 years ago, hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance were hypothesized to be key contributors to hypertension, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, hyperuricemia, visceral adiposity, elevated inflammatory markers, prothrombic state, and endothelial dysfunction related to obesity and the metabolic syndrome[4].
Several bibliometric studies have been conducted in diabetes research[5-9] or in depression and insulin research[10]. However, no bibliometric study has been conducted on insulin resistance research.As a scientific evaluation approach, bibliometrics can assess the research impact of organizations and individuals[11]. Similarly, bibliometrics provide evidence to promote the formation of future research hotspots[12,13]. As a result, this research aims to examine the scientific development in insulin resistance thoroughly. Therefore, this bibliometric analysis was designed to examine the research trend related to insulin resistance and identify future research hotspots. Furthermore, the study offers some important information by providing references and ideas for future studies on insulin resistance pathophysiology and clinical applications.
He had first seen her not much more than a year ago, as she rode up an escalator in a department store downtown, one gray November Saturday while he was buying ties
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data acquisition
The documents in the current study were obtained and downloaded from the Scopus database on January 29, 2022 to prevent bias caused by the database’s daily updates. With more than 36000 titles from around 11678 publishers, of which 34346 were peer-reviewed journals, Scopus is one of the most extensive and authoritative databases for collecting academic information[14,15]. Unfortunately, only one database may be utilized in bibliometric analyses because data from many databases cannot be integrated and analyzed. On the other hand, systematic reviews use multiple databases to retrieve a large number of documents for further analysis[16]. Furthermore, only one database was chosen on the topic and objective coverage, and past research has shown that Web of Science and PubMed are included in the Scopus database. Based on previous studies and findings, it was recommended to use Scopus (Elsevier database) because it was the most comprehensive database on the subject, offering all the data needed for quantitative analysis[17,18].
Search strategy
Keywords used in the Scopus engine to achieve the aim of this study were chosen from previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses on insulin resistance[19-21]. “Insulin resistance” or “insulin sensitivity” was used as a search expression in the title search in the Scopus database over the last two decades (January 2002 to December 2021). This study used the keywords “insulin resistance” or “insulin sensitivity” because we are more interested in these terms than related terminology. Therefore,keywords were used instead of a title/abstract search in the title search. Consequently, the search for the title will provide the fewest false positive documents, making it a trustworthy strategy[22-26]. A title/abstract search, on the other hand, will provide numerous false positives in which the main focus is not on insulin resistance per se.
Bibliometric analysis
As described in previous studies, the bibliometric technique was applied[27-30]. The following bibliometric indicators were generated when the refined findings were exported to Microsoft Excel: (1)Growth pattern; (2) Type of publications; (3) Core countries; (4) Core institutions; (5) Core funding agencies; (6) Prolific authors; (7) Core journals with their impact factors (IF); and (8) Top 10 cited articles. The Impact Index per article for the top 10 highly-cited papers collected from
, https://www.referencecitationanalysis.com, was presented.
is an open, multidisciplinary citation analysis database owned by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.(Pleasanton, CA 94566, United States)[31].
Visualized analysis
VOSviewer 1.6.18 was used to perform a co-occurrence analysis and visualize the collaborative networks of the countries to determine a worldwide scientific cooperation network across countries/regions and keywords in the titles and/or abstracts to determine hotspots and research trends. VOSviewer maps have nodes or frames that are colored and scaled differently. The node or the frame size is proportional to the number of times it appears. The node’s or the frame’s color indicates its link to other nodes with similar colors[32].
RESULTS
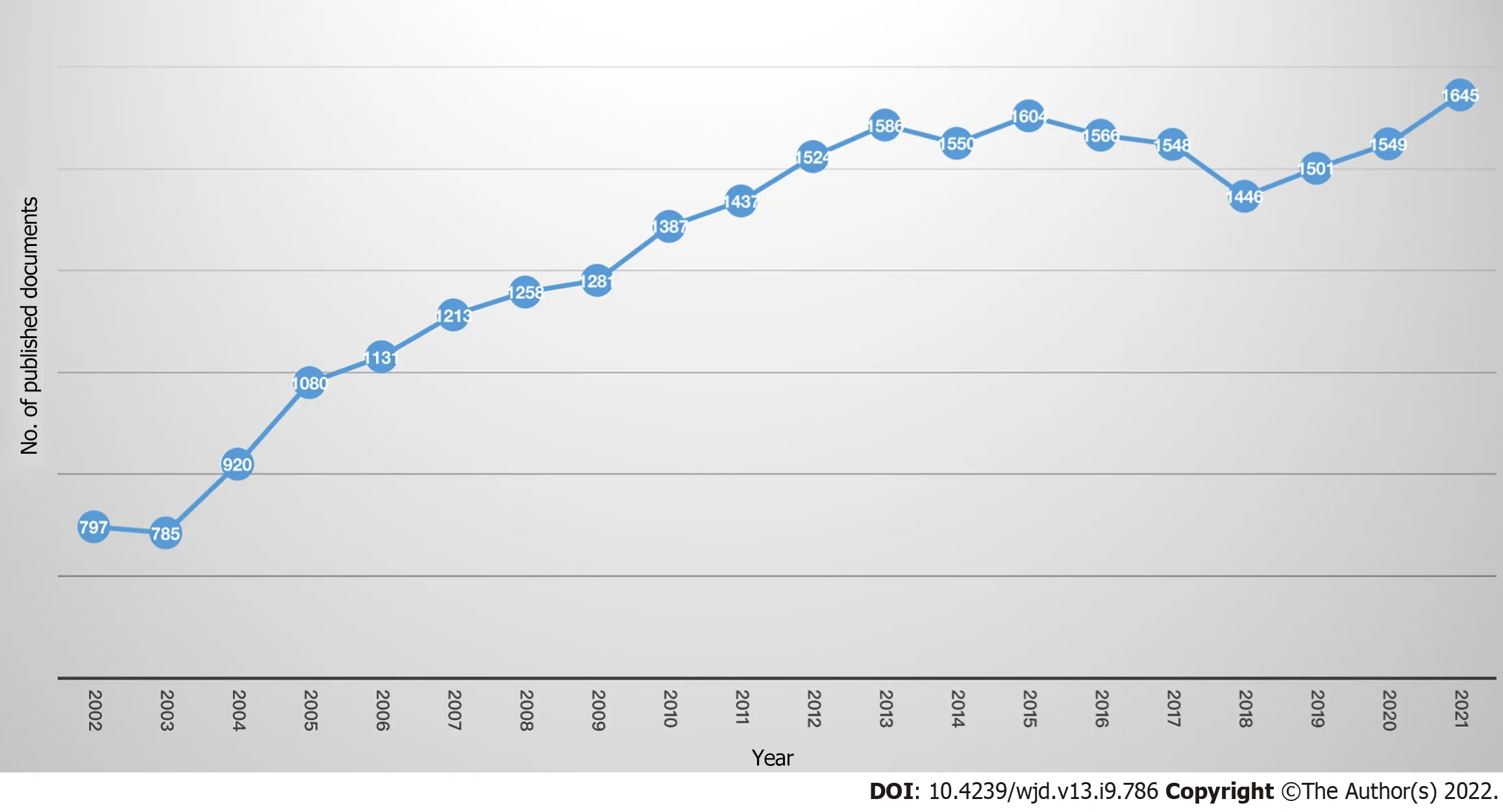
Current status and annual trend
A total of 26808 articles on insulin resistance were included in the Scopus database. The articles included research articles (
= 21918; 81.76%), review articles (
= 2641; 9.85%), and letters (
= 653;2.44%). After 2003, as shown in Figure 1, the number of publications on insulin resistance studies increased rapidly. In 2021, 1645 papers were published, the highest amount in two decades.
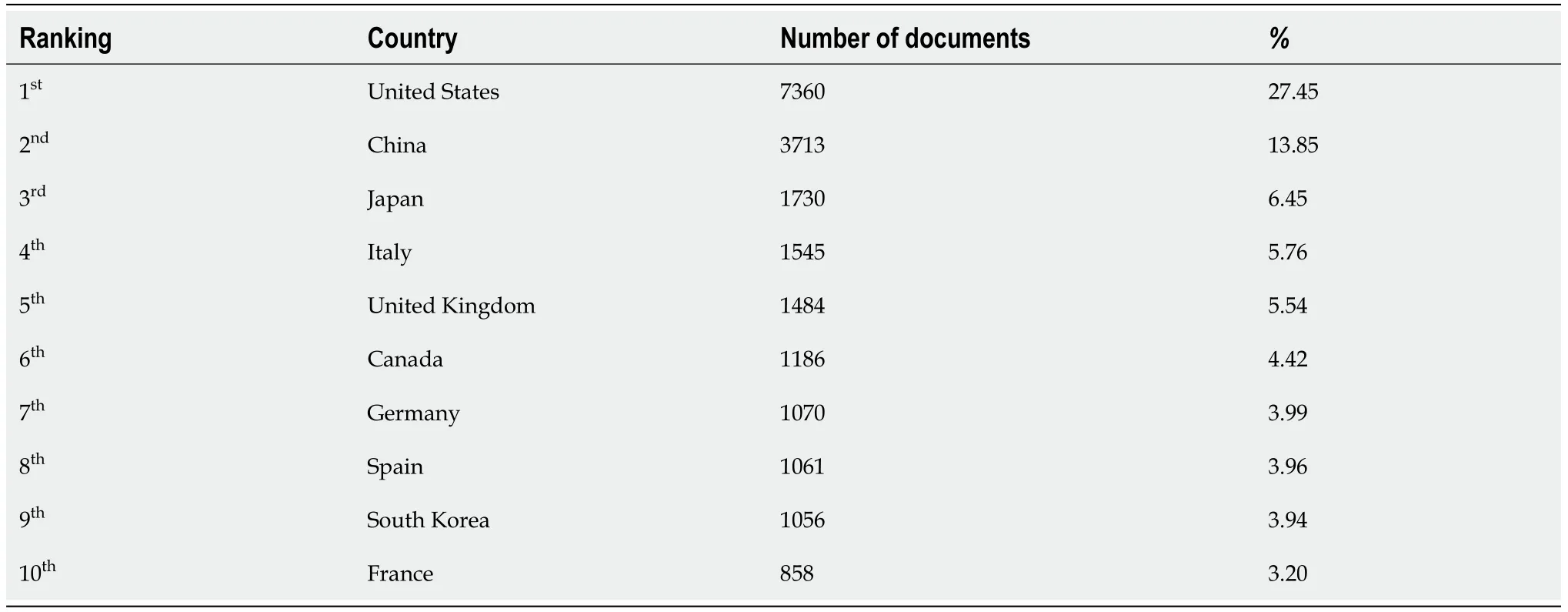
Analysis of countries
Furthermore, the increase in insulin resistance publications can be attributed to the fact that numerous hot topics were published during this period[33-37], exposing novel hypotheses and establishing new research fields such as “inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance”and “mechanisms linking obesity and insulin resistance”. Several studies have shown that inflammation is a critical mediator in obesity-induced insulin resistance. Most of these investigations examined the links between adipose tissue in obesity and the regulation of inflammation and insulin resistance[46-49]and the mechanisms by which dietary anti-inflammatory components/functional nutrients may be helpful[50-52].
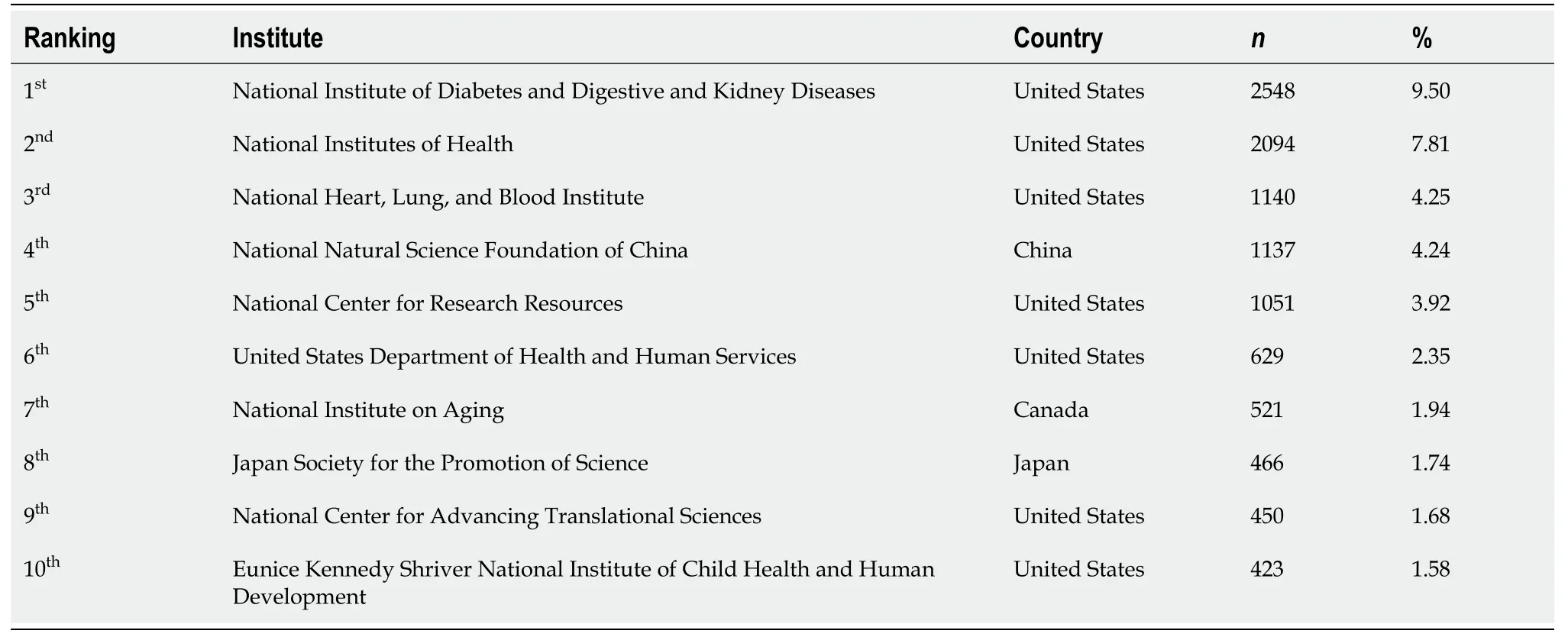
Analysis of institutions
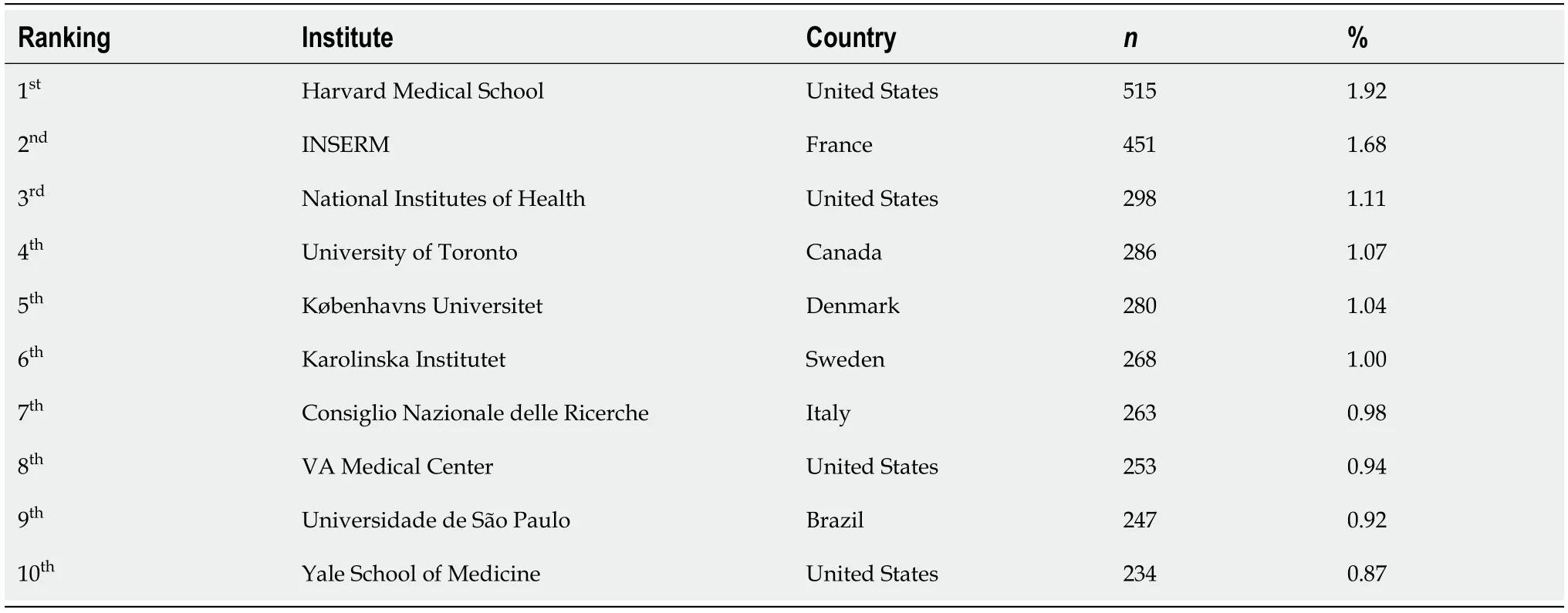
The top 10 active institutions are listed in Table 2. Harvard Medical School was first with 515 (1.92%)articles, followed by INSERM with 451 (1.68%) articles and the National Institutes of Health with 298(1.11%). The top 10 active institutions were mainly based in the United States.
The chances of No. 9 hitting a home-run ball to Row 9, Seat 9 in right field on May 9, the only day I ever visited the ballpark, are almost infinitely17 remote. I can only explain it by saying it s magic-something that happens every so often between a fan and his hero. Something wonderful.
Analysis of funding agencies
Table 3 lists the top 10 funding agencies with the highest output. Seven funding agencies are from the United States, and one each is from Japan, China, and Canada. These countries contributed 10459(39.01%) documents. The three most productive funding agencies were the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (
= 2548; 9.50%), the National Institutes of Health (
=2094, 7.81%), and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
1140, 4.25%).
34. A regular blow-out: Blow-out is a colloquialism97 from the UK meaning An excessive spree of drinking, eating, spending or sex (Duckworth 2003). Andrew Lang considers phrase this to be an example of Hansel s vulgarity in a footnote to the story in The Blue Fairy Book.
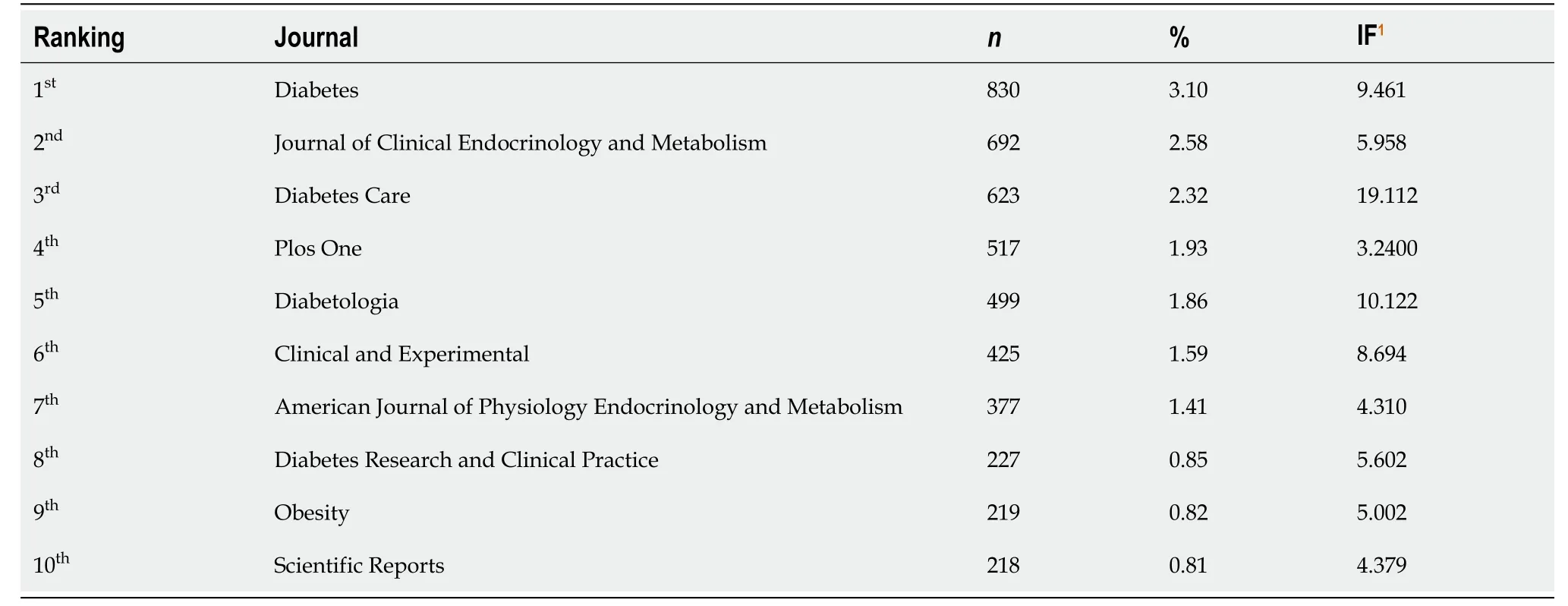
Analysis of journals
Table 4 shows the top 10 most active journals. Diabetes Journal was first (
= 830; 3.10%), followed by Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (
= 692, 2.58%) and Diabetes Care (
= 623; 2.32%). Four of the journals on the active list were on the subject of diabetes. All the journals on the active list have a relatively high impact factor.
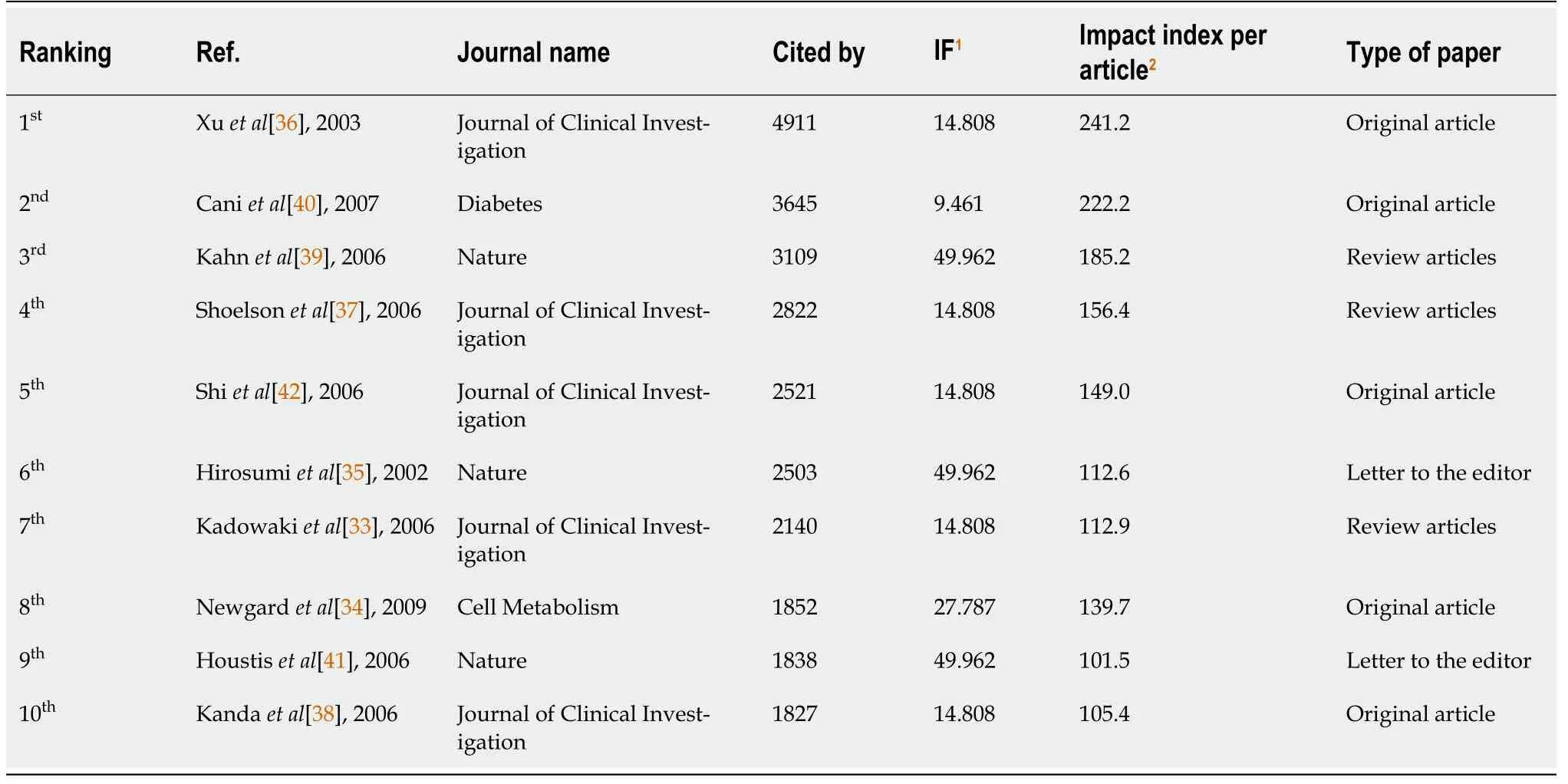
Analysis of citations
Table 5 lists the top 10 articles that were the most cited in research related to insulin resistance from 2002to 2021. The 10 highest citations ranged from 4911 to 1827[33-42]. Furthermore, the 10 most cited articles have an impact index per article of 101.5 to 241.2 (Table 5).
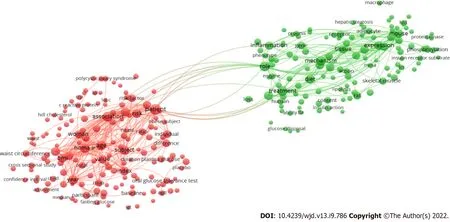
Term co-occurrence cluster analysis of research hotspots
The term co-occurrence analysis provided a complete summary of hot topics discussed in insulin resistance research. VOSviewer detected 456 keywords that appeared a minimum of 300 times in the titles and abstracts of the included articles by analyzing the contents of the titles and abstracts. All terms were sorted into clusters on the VOSviewer keyword co-occurrence visualization map, and various clusters were colored differently (Figure 3). There are two clusters: (1) Cluster #1, shown by green dots,contained phrases typically found in publications relating to “inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance”; and (2) Cluster #2, shown by red dots, contained phrases typically found in publications relating to “mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance”. Hotspots in the field of insulin resistance were revealed
an overlay visualization map scaled by occurrence. The colored terms differ depending on when they appeared in the literature. The blue keywords were first shown, followed by the yellow keywords. After 2013, the most popular terms were related to inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance (Figure 4).

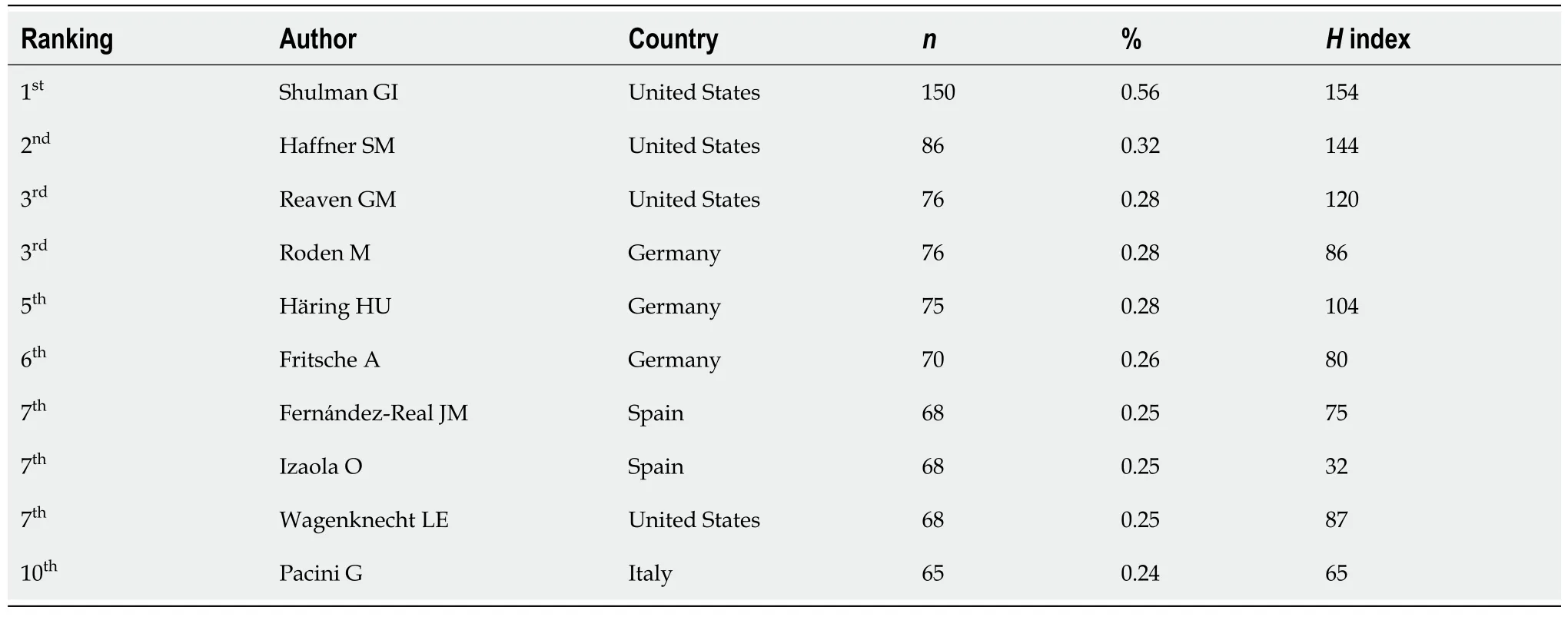
Analysis of authorship
The total number of authors who participated in the publication of the retrieved documents was 80932,a mean of 3.1 authors per document. The list of the top 10 active authors in insulin resistance research,ranked by the total number of publications in the last two decades (2002-2021), is shown in Table 6. The top 10 list included four from the United States, three from Germany, two from Spain, and one from Italy.
DISCUSSION
Several bibliometric studies have been carried out on the subject of diabetic investigation. However, no bibliometric study has been done on research into insulin resistance.
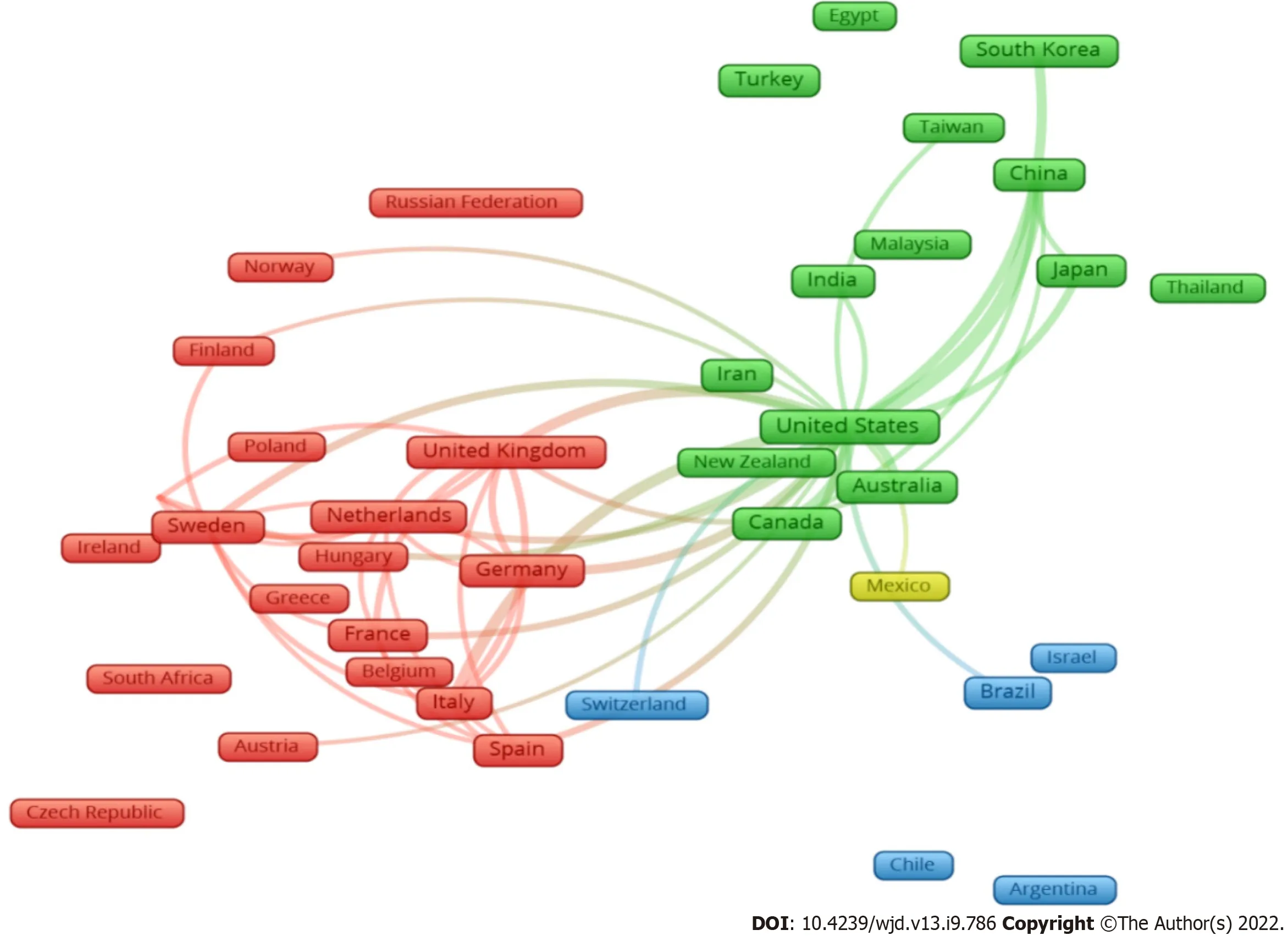
Another important reason for the contribution of different world regions is the high level of international collaboration, as evident from the thick lines coming out from most countries in the visualization map. This collaboration was initiated because different regions of the research groups in different regions of the world were involved in different aspects of insulin resistance research or different complications of insulin resistance. Another area of relevance for the current study with regard to scientific publications on insulin resistance is the quality of research papers. It is worth noting that nine of the top 10 cited articles were published in journals with an IF larger than 10, implying that they have a large impact in medicine: Journal of Clinical Investigation, Cell Metabolism, and Nature. As shown,articles related to insulin resistance have been published both in endocrinology and non-endocrinologysubject areas, such as medicine, biochemistry, genetics, and molecular biology, nursing, pharmacology,toxicology, and pharmaceutics, agricultural and biological sciences, neuroscience, and immunology and microbiology journals, revealing the contribution and collaboration of many researchers from different subject areas. Previous research has confirmed that[43-45]. The findings of this study confirm the close association between IF and citations and the fact that the most cited articles are frequently published in journals at the top of the IF list, which helps these journals maintain their high IF.
and went on eating, without putting themselves about. Hansel, who thoroughly27 appreciated the roof, tore down a big bit of it, while Gretel pushed out a whole round window-pane, and sat down the better to enjoy it. Suddenly the door opened, and an ancient dame28 leaning on a staff37 hobbled out. Hansel and Gretel were so terrified that they let what they had in their hands fall. But the old woman shook her head and said: Oh, ho! you dear children, who led you here? Just come in and stay with me, no ill shall befall you. 38 She took them both by the hand and let them into the house, and laid a most sumptuous29 dinner before them--milk and sugared pancakes, with apples and nuts. After they had finished, two beautiful little white beds were prepared for them, and when Hansel and Gretel lay down in them they felt as if they had got into heaven.
After school, the girls invited me to join them in front of the school. I was thrilled to be a member of the club, however tentative. We waited. For what, I didn’t yet know. Oh, how I wish I had gone home, but I had a lesson to learn.
During the study period, 136 countries contributed to research on insulin resistance. The highest number of articles was from the United States (
= 7360; 27.45%), followed by China (
= 3713; 13.85%),Japan (
= 1730, 6.45%), Italy (
= 1545; 5.54%), and the United Kingdom (
= 1484; 5.54%) (Table 1). The country network map included 42 frames (Figure 2). The top three countries in terms of centrality were the United States, China, and the United Kingdom. The centrality proved that they had close relationships and substantial intellectual effects on other countries.
Publications with the highest citation frequencies have the greatest academic effect[53,54]. For example, the study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation in 2003 by Xu
[36] was ranked first. It was revealed that macrophages in white adipose tissue are involved in morbid obesity and that macrophage-associated inflammatory activities may contribute to the pathophysiology of obesityinduced insulin resistance[36]. The article ranked second was published in Diabetes by Cani
[40].Metabolic endotoxemia was found to alter the inflammatory tone of the body, causing weight gain and diabetes[40].
Strengths and limitations
This is the first bibliometric and visual analysis study to investigate research trends and hotspots in insulin resistance from 2002 to 2021. The current study reviewed linked papers on this issue from numerous perspectives, demonstrated a comprehensive view of understanding in this field during the last few years, and gave direction for future investigations. New researchers in this discipline may simply access meaningful and relevant material with the aid of this bibliometric study. However, certain limitations apply to the generalizability of these findings. First, bibliometric analyses solely used published material from the Scopus database. This may underestimate the amount of research done in South America, China, the Middle East, and other regions of the globe with non-English and unindexed publications. Second, because bibliometric data changes over time, indexing delays may have caused a slight (but not significant) in the number of documents or other metrics. Third, to avoid selection bias,the current study only searched the title for terms such as “insulin resistance” or “insulin sensitivity”.As a result, the possibility of false positive or false negative results should always be considered. Fourth,Scopus’s results reflect the type and content of Scopus’s database. As a result, if prolific authors have two or more Scopus profiles, their research output is likely to be dispersed, and their names may not appear in the active list. The same is true when alternative spellings of an institution’s name are used in published documents. As a result, interpreting data about the most active authors, institutions, and nations should be limited to the Scopus findings produced using the described technique.
CONCLUSION
But when he got back to the dragon he discovered that not only had the cup been chipped but it had a crack he had not seen. What little water there was had drained out while he was climbing. He approached the dragon and said, I m sorry. I meant to help you, I really did. But the cup is empty.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
The Scopus database and
were used to compile the literature on insulin resistance. In addition, VOSviewer software was used to visually assess data collected from relevant publications.
Research motivation
Bibliometric analysis of insulin resistance publications in the last 20 years revealed that the number of articles published has gradually increased in recent years, indicating that more and more researchers are becoming involved in insulin resistance research. To our knowledge, this is the first bibliometric study that comprehensively examined worldwide trends in insulin resistance research over the last 20 years.The current study showed that research activity on insulin resistance was worldwide and involved countries in different world regions. The United States and China had a noticeable edge on this topic,probably due to a greater economy and investment in the scientific field. The research output from these countries may be related to a diverse spectrum of researchers interested in this topic and strong financial support for researchers.
Research objectives
This bibliometric study aimed to identify and assess the current state and trends in insulin resistance research production worldwide and visually analyze research hotspots on this subject.
Research methods
Insulin resistance is a condition in which muscle cells take up and store glucose and triglycerides,resulting in elevated amounts of glucose and triglycerides circulating in the bloodstream.
Research results
This is the first bibliometric analysis of trends in insulin resistance. The number of publications on insulin resistance has increased in the last decade. Our results indicated that the “inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance” and “mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance” will remain research hotspots in the future.
This paper contributes essential information by providing references and suggestions for future research on pathophysiology and clinical uses of insulin resistance. This approach may aid researchers in identifying new topics of inquiry and identifying research hotspots and frontiers. Perhaps in the future,high-quality clinical evidence will be collected.
Research conclusions
Our findings indicate that interest in insulin resistance has gradually increased among researchers, as shown by the increasing number of citations and annual publications. Moreover, publications in this field have increased significantly in the last decade, while low-income countries with higher burdens continue to produce fewer publications.
Research perspectives
We both have nothing! The rich widow over the way in the basementhas made advances to me; she will make me rich, but you are in myheart; what do you advise me to do?
FOOTNOTES
Zyoud SH developed the concept for the manuscript, reviewed the literature, designed the study, collected the data, analyzed the data, made significant contributions to the existing literature search and interpretation of the manuscript, and wrote the manuscript; Shakhshir M, Koni A, Abushanab AS, Jairoun AA,Shahwan WM, Al Subu R, Abu Taha A, and Al-Jabi SW participated in interpretation of the data and made revisions to the initial draft; and all authors provided critical review and approved the final manuscript before submission.
To our knowledge, this was the first study to conduct a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of insulin resistance publications from 2002 to 2021, covering the publication year, the number of citations, and current hot topics and trends projected from them. Our data showed that insulin resistance has steadily gained interest from researchers, as evidenced by the number of citations and yearly publications. So far, the United States has been the undisputed leader in this topic, which cannot be divorced from adequate funding sources. Publications have grown significantly in the last decade, while low-income countries with greater burdens continue to produce fewer publications in this field. “Inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance” and “mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance” were hotspots for insulin resistance research in the past 20 years. This approach might assist researchers in choosing new research areas and recognizing research hotspots and frontiers. In the future, perhaps high-quality clinical evidence will be acquired.
All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
The authors have read the PRISMA 2009 Checklist, and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the PRISMA 2009 Checklist.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
9. Cry: Bettelheim writes that There is no greater threat in life than that we will be deserted74, left all alone (Bettelheim p. 145). By continuing to let his brothers cry, Little Thumb is once again letting his muteness stand in place of his cleverness; thus far, all of his work has been internal. The challenges that come after this point are-even more terrifyingly-contained in the external, harder-to-control world. Return to place in story.
She exclaimed pointing to something afar, “Look, Venus in rising!” I looked up and saw nothing but a lamp round the bend in a mountain path. I beamed and said pointing to a tiny lamplight on the opposite mountain, “It’s Jupiter over there!”
Palestine
Sa’ed H Zyoud 0000-0002-7369-2058; Muna Shakhshir 0000-0002-6213-8457; Amani S Abushanab 0000-0001-6290-787X; Moyad Shahwan 0000-0001-8367-4841; Ammar Abdulrahman Jairoun 0000-0002-4471-0878; Rand Al Subu 0000-0002-9624-7467; Adham Abu Taha 0000-0002-2889-1138; Samah W Al-Jabi 0000-0002-4414-9427.
Wang JJ
Filipodia
Today, I keep that key in my dresser drawer and treasure it. Whenever I hold it in my hand, I am reminded of all the wonderful things Dad has done for me over the years. I realize that, although he is now 68 and I am 40, I still look to him for wisdom, guidance and reassurance15. Most of all, I marvel16 at the fact that his thoughtful gesture of making the extra key may have saved my life. And I understand how a simple act of love can make extraordinary things happen.
ChenYX
1 World Health Organization. Diabetes. [cited 5 February 2022]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/factsheets/detail/diabetes
2 Taylor R. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
2012; 61: 778-779 [PMID: 22442298 DOI: 10.2337/db12-0073]
3 Freeman AM, Pennings N. Insulin Resistance. 2022 Jul 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan- [PMID: 29939616]
4 da Silva AA, do Carmo JM, Li X, Wang Z, Mouton AJ, Hall JE. Role of Hyperinsulinemia and Insulin Resistance in Hypertension: Metabolic Syndrome Revisited.
2020; 36: 671-682 [PMID: 32389340 DOI:10.1016/j.cjca.2020.02.066]
5 Song Y, Zhao F. Bibliometric analysis of metabolic surgery for type 2 diabetes: current status and future prospects.
2022; 74: 697-707 [PMID: 35094308 DOI: 10.1007/s13304-021-01201-5]
6 Chen L, Ma S, Hu D, Lin H, Zhu Y, Chen K, Chen L, Zheng C, Liu J, Liao Y. Bibliometric Study of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Research.
2020; 11: 561494 [PMID: 33041801 DOI:10.3389/fphar.2020.561494]
7 Lin X, Chen P, Lin F. Mapping global research trends in diabetes and COVID-19 outbreak in the past year: a bibliometric analysis.
2022; 11: 1241-1252 [PMID: 34806394 DOI: 10.21037/apm-21-2636]
8 Dong Y, Liu Y, Yu J, Qi S, Liu H. Mapping research trends in diabetic retinopathy from 2010 to 2019: A bibliometric analysis.
2021; 100: e23981 [PMID: 33545985 DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023981]
9 Hosseinkhani S, Aazami H, Hashemi E, Dehghanbanadaki H, Adibi-Motlagh B, Razi F. The trend in application of omics in type 2 diabetes researches; A bibliometric study.
2021; 15: 102250 [PMID: 34419857 DOI:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102250]
10 Zou X, Sun Y. Bibliometrics Analysis of the Research Status and Trends of the Association Between Depression and Insulin From 2010 to 2020.
2021; 12: 683474 [PMID: 34366917 DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.683474]
11 Bornmann L. Measuring impact in research evaluations: a thorough discussion of methods for, effects of and problems with impact measurements.
2017; 73: 775-787 [DOI: 10.1007/s10734-016-9995-x]
12 Gu D, Li J, Li X, Liang C. Visualizing the knowledge structure and evolution of big data research in healthcare informatics.
2017; 98: 22-32 [PMID: 28034409 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2016.11.006]
13 Wang X, Guo J, Gu D, Yang Y, Yang X, Zhu K. Tracking knowledge evolution, hotspots and future directions of emerging technologies in cancers research: a bibliometrics review.
2019; 10: 2643-2653 [PMID: 31258772 DOI:10.7150/jca.32739]
14 Sweileh WM. Substandard and falsified medical products: bibliometric analysis and mapping of scientific research.
2021; 17: 114 [PMID: 34556126 DOI: 10.1186/s12992-021-00766-5]
15 Sweileh WM. Global research activity on mathematical modeling of transmission and control of 23 selected infectious disease outbreak.
2022; 18: 4 [PMID: 35062966 DOI: 10.1186/s12992-022-00803-x]
16 Sweileh WM. A bibliometric analysis of health-related literature on natural disasters from 1900 to 2017.
2019; 17: 18 [PMID: 30744641 DOI: 10.1186/s12961-019-0418-1]
17 Cebrino J, Portero de la Cruz S. A worldwide bibliometric analysis of published literature on workplace violence in healthcare personnel.
2020; 15: e0242781 [PMID: 33227018 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242781]
18 Sweileh WM. Bibliometric analysis of global scientific literature on vaccine hesitancy in peer-reviewed journals (1990-2019).
2020; 20: 1252 [PMID: 32807154 DOI: 10.1186/s12889-020-09368-z]
19 Su KZ, Li YR, Zhang D, Yuan JH, Zhang CS, Liu Y, Song LM, Lin Q, Li MW, Dong J. Relation of Circulating Resistin to Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
2019; 10: 1399[PMID: 31803062 DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01399]
20 Sampath Kumar A, Maiya AG, Shastry BA, Vaishali K, Ravishankar N, Hazari A, Gundmi S, Jadhav R. Exercise and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
2019; 62: 98-103 [PMID: 30553010 DOI: 10.1016/j.rehab.2018.11.001]
21 Shoshtari-Yeganeh B, Zarean M, Mansourian M, Riahi R, Poursafa P, Teiri H, Rafiei N, Dehdashti B, Kelishadi R.Systematic review and meta-analysis on the association between phthalates exposure and insulin resistance.
2019; 26: 9435-9442 [PMID: 30734259 DOI: 10.1007/s11356-019-04373-1]
22 Sweileh WM. Global research activity on antimicrobial resistance in food-producing animals.
2021;79: 49 [PMID: 33849636 DOI: 10.1186/s13690-021-00572-w]
23 Sweileh WM. Bibliometric analysis of peer-reviewed literature on antimicrobial stewardship from 1990 to 2019.
2021; 17: 1 [PMID: 33397377 DOI: 10.1186/s12992-020-00651-7]
24 Sweileh WM. Health-related publications on people living in fragile states in the alert zone: a bibliometric analysis.
2020; 14: 70 [PMID: 32868982 DOI: 10.1186/s13033-020-00402-6]
25 Sweileh WM. Global research publications on systemic use of off-label and unlicensed drugs: A bibliometric analysis(1990-2020).
2022; 33: 77-89 [PMID: 34275912 DOI: 10.3233/JRS-210012]
26 Sweileh WM. Global Research Activity on Elder Abuse: A Bibliometric Analysis (1950-2017).
2021; 23: 79-87 [PMID: 32488667 DOI: 10.1007/s10903-020-01034-1]
27 Abushamma F, Barqawi A, Al-Jabi SW, Akkawi M, Maree M, Zyoud SH. Global Analysis of Research Trends on Kidney Function After Nephron-Sparing Surgery: A Bibliometric and Visualised Study.
2021; 13: 7479-7487[PMID: 34611441 DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S324284]
28 Zyoud SH, Smale S, Waring WS, Sweileh W, Al-Jabi SW. Global research trends in the microbiome related to irritable bowel syndrome: A bibliometric and visualized study.
2021; 27: 1341-1353 [PMID: 33833487 DOI:10.3748/wjg.v27.i13.1341]
29 Barqawi A, Abushamma FA, Akkawi M, Al-Jabi SW, Shahwan MJ, Jairoun AA, Zyoud SH. Global trends in research related to sleeve gastrectomy: A bibliometric and visualized study.
2021; 13: 1509-1522 [PMID:34950437 DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i11.1509]
30 Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW. Mapping the situation of research on coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): a preliminary bibliometric analysis during the early stage of the outbreak.
2020; 20: 561 [PMID: 32738881 DOI:10.1186/s12879-020-05293-z]
31 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. Reference Citation Analysis. [cited 2 February 2022]. Available from:https://www.referencecitationanalysis.com
32 van Eck NJ, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping.
2010; 84: 523-538 [PMID: 20585380 DOI: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3]
33 Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K, Ueki K, Tobe K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome.
2006; 116: 1784-1792 [PMID: 16823476 DOI:10.1172/JCI29126]
34 Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Stevens RD, Lien LF, Haqq AM, Shah SH, Arlotto M, Slentz CA, Rochon J,Gallup D, Ilkayeva O, Wenner BR, Yancy WS Jr, Eisenson H, Musante G, Surwit RS, Millington DS, Butler MD, Svetkey LP. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance.
2009; 9: 311-326 [PMID: 19356713 DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.02.002]
35 Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, Görgün CZ, Uysal KT, Maeda K, Karin M, Hotamisligil GS. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance.
2002; 420: 333-336 [PMID: 12447443 DOI: 10.1038/nature01137]
36 Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA, Chen H. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance.
2003; 112:1821-1830 [PMID: 14679177 DOI: 10.1172/JCI19451]
37 Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB. Inflammation and insulin resistance.
2006; 116: 1793-1801 [PMID:16823477 DOI: 10.1172/JCI29069]
38 Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K, Hiasa K, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Miyachi H, Maeda S, Egashira K, Kasuga M.MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity.
2006; 116: 1494-1505 [PMID: 16691291 DOI: 10.1172/JCI26498]
39 Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
2006;444: 840-846 [PMID: 17167471 DOI: 10.1038/nature05482]
40 Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Tuohy KM, Chabo C, Waget A,Delmée E, Cousin B, Sulpice T, Chamontin B, Ferrières J, Tanti JF, Gibson GR, Casteilla L, Delzenne NM, Alessi MC,Burcelin R. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance.
2007; 56: 1761-1772 [PMID:17456850 DOI: 10.2337/db06-1491]
41 Houstis N, Rosen ED, Lander ES. Reactive oxygen species have a causal role in multiple forms of insulin resistance.
2006; 440: 944-948 [PMID: 16612386 DOI: 10.1038/nature04634]
42 Shi H, Kokoeva MV, Inouye K, Tzameli I, Yin H, Flier JS. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance.
2006; 116: 3015-3025 [PMID: 17053832 DOI: 10.1172/JCI28898]
43 Tas F. An analysis of the most-cited research papers on oncology: which journals have they been published in?
2014; 35: 4645-4649 [PMID: 24414487 DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-1608-7]
44 Sharma M, Sarin A, Gupta P, Sachdeva S, Desai AV. Journal impact factor: its use, significance and limitations.
2014; 13: 146 [PMID: 25191134 DOI: 10.4103/1450-1147.139151]
45 Saha S, Saint S, Christakis DA. Impact factor: a valid measure of journal quality?
2003; 91: 42-46[PMID: 12572533]
46 Olefsky JM, Glass CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance.
2010; 72: 219-246 [PMID:20148674 DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135846]
47 Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A, Galgani JE, Stadler K, Mynatt RL, Ravussin E, Stephens JM, Dixit VD. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance.
2011; 17: 179-188 [PMID:21217695 DOI: 10.1038/nm.2279]
48 Dandona P, Aljada A, Bandyopadhyay A. Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes.
2004; 25: 4-7 [PMID: 14698276 DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2003.10.013]
49 Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M, Vidal H, Capeau J, Feve B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance.
2006; 17: 4-12 [PMID: 16613757]
50 McArdle MA, Finucane OM, Connaughton RM, McMorrow AM, Roche HM. Mechanisms of obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance: insights into the emerging role of nutritional strategies.
2013; 4: 52 [PMID: 23675368 DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00052]
51 Maeda N, Shimomura I, Kishida K, Nishizawa H, Matsuda M, Nagaretani H, Furuyama N, Kondo H, Takahashi M, Arita Y, Komuro R, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Tochino Y, Okutomi K, Horie M, Takeda S, Aoyama T, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y.Diet-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking adiponectin/ACRP30.
2002; 8: 731-737 [PMID: 12068289 DOI:10.1038/nm724]
52 Vrieze A, Van Nood E, Holleman F, Salojärvi J, Kootte RS, Bartelsman JF, Dallinga-Thie GM, Ackermans MT, Serlie MJ,Oozeer R, Derrien M, Druesne A, Van Hylckama Vlieg JE, Bloks VW, Groen AK, Heilig HG, Zoetendal EG, Stroes ES, de Vos WM, Hoekstra JB, Nieuwdorp M. Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
2012; 143: 913-6.e7 [PMID: 22728514 DOI:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.031]
53 Filion KB, Pless IB. Factors related to the frequency of citation of epidemiologic publications.
2008; 5: 3 [PMID: 18302781 DOI: 10.1186/1742-5573-5-3]
54 Opthof T. Differences in citation frequency of clinical and basic science papers in cardiovascular research.
2011; 49: 613-621 [PMID: 21567267 DOI: 10.1007/s11517-011-0783-6]
杂志排行
World Journal of Diabetes的其它文章
- Different nutrient compositions in diet and taking hypoglycemic drugs can modulate gut microbial flora
- Role of insulin in pancreatic microcirculatory oxygen profile and bioenergetics
- Relationship between age of pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and mode of delivery and neonatal Apgar score
- Hyperglycemia and reduced adiposity of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice are not alleviated by oral benzylamine supplementation
- Effectiveness and safety of COVID-19 vaccines in patients with diabetes as a factor for vaccine hesitancy
- COVID-19 associated diabetes mellitus: A review
