Potential role of hydrogen sulfide in central nervous system tumors:a narrative review
2022-09-10WeiPengMengLingZhangJianZhangGangChen
Wei Peng,Meng-Ling Zhang,Jian Zhang,Gang Chen
Department of Neurosurgery &Brain and Nerve Research Laboratory,The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University,Suzhou,Jiangsu Province,China
Abstract Central nervous system tumors are classified as diseases of special clinical significance with high disability and high mortality.In addition to cerebrovascular diseases and craniocerebral injuries,tumors are the most common diseases of the central nervous system.Hydrogen sulfide,the third endogenous gas signaling molecule discovered in humans besides nitric oxide and carbon monoxide,plays an important role in the pathophysiology of human diseases.It is reported that hydrogen sulfide not only exerts a wide range of biological effects,but also develops a certain relationship with tumor development and neovascularization.A variety of studies have shown that hydrogen sulfide acts as a vasodilator and angiogenetic factor to facilitate growth,proliferation,migration and invasion of cancer cells.In this review,the pathological mechanisms and the effect of hydrogen sulfide on the central nervous system tumors are introduced.
Key words:central nervous system;clinical research;experimental research;glioblastoma multiforme;hydrogen sulfide;hypoxia inducible factor-1α;p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase;pituitary tumor;therapeutic implications
INTRODUCTION
Central nervous system (CNS) tumors are classified as nervous system diseases characterized by high disability and mortality.1They are the most common diseases of the CNS except for cerebrovascular diseases and craniocerebral injuries,including meningiomas,gliomas,pituitary tumors and so on.2Among them,glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most malignant brain tumor,with a strong ability to spread and invade the surrounding parenchyma.The number of treatment options is increasing;however,the prognosis is still poor.3,4Pituitary tumors are a group of tumors originated from the residual cells of anterior and posterior pituitary and craniopharyngeal epithelium,accounting for 10–20% of intracranial tumors,most of which are benign.5,6
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is usually considered an environmental pollutant with its smell of rotten eggs.However,with continuously furthering research in recent years,H2S has been discovered as a gaseous chemical messenger with regulatory roles in neurotransmission,cardiovascular regulation,cell metabolism and other physiological processes in mammalians.7-9Recently,it has been reported that H2S plays a role in a wide range of physiological and pathophysiological properties on cancer progress.10,11Previous results have evidenced that H2S may act as a vascular relaxant and angiogenetic factor to promote the growth,proliferation,migration and invasion of cancer cells.12,13H2S is extremely fat-soluble,can freely pass through cell membranes,widely presenting in various parts of the human body,with a variety of production and transformation methods.14Generally speaking,on the one hand,H2S can be synthesized by cystathionine β-synthetase and cystathionine c-lyase extracted with sulfur-containing amino acids as substrates,in pyridoxal-50-phosphate-(PLP-)-dependent reactions.15-17On the other hand,it can produce through nonenzymatic reduction of elemental sulfur in the blood using reduction equivalents provided by glycolysis,or in the form of sodium bisulfide.18Changes in H2S metabolism and/or signal transduction are closely related to human diseases,especially cancer.An increasing number of studies have reported that cystathionine β-synthetase,cystathionine c-lyase and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase are overexpressed in tumor cell lines and tumor tissues,with colorectal cancer,ovarian cancer,breast cancer,and glioma involved.11,16,19-21In this review,the potential role of endogenous and exogenous H2S in CNS tumors is described and the implications of H2S on future treatment strategies are discussed.
EXPERIMENTAL FINDING ABOUT THE ROLES OF HYDROGEN SULFIDE IN CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS
The mechanisms underlying the roles of H2S in the CNS tumors have not been fully elucidated.As is known to all,a therapeutic method must be verified by a large amount of basic experiments before being applied to clinic.However,not all studies can reach the same result.We collected several experiments related to CNS tumors and H2S and summarized the outcomes (Table 1),in which the researchers detected the effects of H2S on brain tumors and explored the potential mechanisms by which this gas can promotes tumor cells growth.
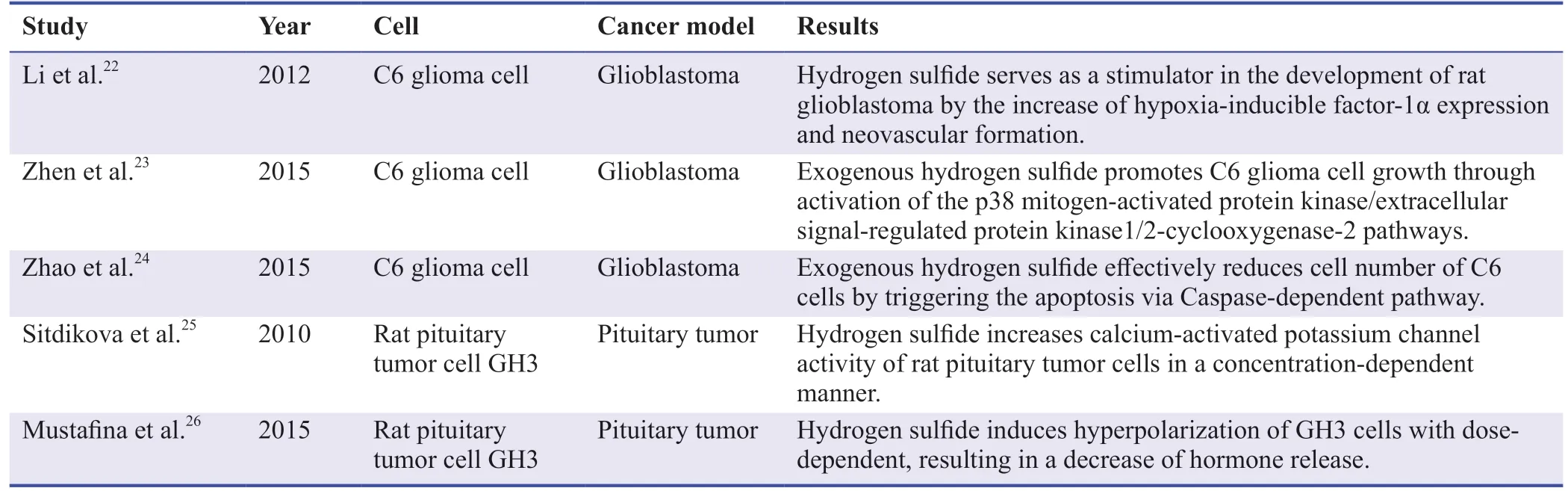
Table 1:Experimental studies regarding hydrogen sulfide in brain tumor
Li et al.22reported that H2S serves as a stimulator in the development of rat glioblastoma and exogenous H2S strongly promotes the tumor growth.It was observed that the H2S content in the tumor group was significantly higher than that in the control group.Compared with normal rats,endogenous H2S production in the brain of tumor-bearing mice increased,and with the growth of tumors,endogenous H2S production further increased.Furthermore,exogenous H2S promoted the expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in GBM tissues,while increased HIF-1α further stimulates tumor growth.HIF-1α can be activated in a variety of factors (including hypoxia,inflammation,adenosine triphosphate levels,and isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation status),as well as in gliomas and immune cell infiltrating tumors.27HIF-1α increases the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in cancer cells,which impairs the recruitment of tumor immune cells and produces immunosuppression.28Similarly,HIF-1α’s increased activity promotes the production of vascular endothelial growth produced by endothelial cells,which can modulate chemotactic properties of immune cell-mediated tumor infiltration.29Vascular endothelial growth factor binds to its receptor neuropilin-1 to attract regulatory T cells to the tumor site,and malignant cells secrete transforming growth factor-β to attract regulatory T cells to GBM,preventing the killing of cancer cells.27,30There is increasing evidence that IDH1,closely related to the carcinogenesis mediated by HIF-1α,is the most common mutated gene in GBM.31-33The mutated IDH1 increases its level by protecting HIF-1α from degradation.In the midst of IDH1 mutant gliomas,the transcriptional activity of HIF-1α increases,intensifying the growth of gliomas.34,35Besides,under normal oxygen conditions,the degradation of HIF-1α is promoted by prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing proteins with its transcriptional activity being inhibited by HIF-1α inhibitor protein (encoded by Hif-1α).36,37A typical feature of HIF-1α-dependent signaling is hypoxia,a condition in which tissue oxygen supply is in reduction.37,38Since hypoxic conditions are characteristic of the tumor microenvironment,the effects of both are inhibited.Therefore,HIF-1α is often upregulated in solid malignant tumors (such as GBM).38Lactic acid accumulation caused by hypoxia can lead to an acidic tumor microenvironment and induction local inflammation.Lactic acid can promote the polarization of macrophages’ expression of immunosuppressive arginase 1 through HIF-1α-mediated mechanism and promotion of tumor growth.27,39In addition,the tumor-specific T cell effector functions can be impacted by HIF-1α via an increase of glycolysis and promotion of T cell differentiation.40,41This study provides evidence for the angiogenic effect of H2S mediated by promoting and stabilizing HIF-1α protein expression under hypoxic conditions.
In 2015,Zhen et al.23found that H2S induced C6 glioma cell proliferation through utilizing its two-fold cytoprotective and anti-apoptosis functions via decrease of the expression of caspase-3.Within the range of physiological dose of H2S (0.2–1 mM),different doses of NaHS (100–1600 μM) promoted cell proliferation.The optimal concentration of NaHS for inducing maximum proliferation and markedly diminished cell apoptosis was 400 μM.On the other hand,Zhao et al.24reported NaHS failed to act as a mitogen to promote proliferation of C6 cells but succeeded in functioning as a stimulus to activate the apoptosis of C6 cells.They showed that the application of NaHS significantly increased the phospho-p38/p38 protein expression rate in C6 cells,indicating that p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation is linked to NaHS-mediated apoptosis of C6 cells.Different research results are related to different conditions,such as time and concentration of cell treatment.The latter treated C6 cells with NaHS (100–1000 μM) for 48 hours.MAPK,a serine threonine protein kinase,evolutionarily conserved in all eucaryotes that can be activated by different extracellular stimuli,such as cytokines,neurotransmitters,hormones,cell stress and cell adhesion,42-44and plays significant roles in gene expression regulation and cytoplasmic function activities.Moreover,MAPK takes part in the regulation of many important cell physiology/pathology processes such as cell growth and proliferation,differentiation,adaption to the environment,and inflammation response.45Researches have founded that MAPKs (p38 MAPK and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2) also activate cyclooxygenase-2 signal pathway and other signaling cascades in various tumor cell types.46-49Cyclooxygenase-2 is a kind of inducible enzyme whose expression is enhanced under the conditions of tissue damage and inflammation,closely related to the growth of tumor as an important molecule in the process of tumor proliferation,angiogenesis,anti-apoptosis and invasion.50-53Besides,previous studies have emphasized that the activation of cyclooxygenase-2 in the glioma depends on the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 pathway.54-56p38 MAPK and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 pathway can be activated by NaHS to induce proliferation and anti-apoptosis.23
In addition,some studies have discovered the potential role of H2S in pituitary tumor cells.The one major discover of these studies is that the NaHS induces a dose-dependent hyperpolarization and truncation of spontaneous action potentials in rat pituitary GH3 cells via activating of adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels as H2S donor,resulting in decrease of secretion.26NaHS increases the magnitude of adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium currents,as well as whether in GH3 cells at rest or in a depolarization reaction,NaHS can reduce the exocytosis of secreted particles.26This effect is exerted in a dose-dependent manner.26Sitdikova et al.25found H2S promotes the activation of calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels in rat pituitary tumor (GH3) cells,which is probably related to the reduction of sulfhydryl groups of the channel protein.BK channels mediates or regulates many physiological functions and pathophysiological conditions.57As is known to all,the activity of BK channels in the channels protein is regulated by the redox state of the key sulfhydryl group,with the exchange of free mercaptan and disulfide involved.58,59Under oxidation conditions,activity of BK channels is enhanced in both reduction and inhibition.60H2S as a reducing agent may increase the channel open probability by redox regulation of cysteine or other residues of channel protein.25
It is concluded that H2S is fully involved in the pathological process of CNS tumors,especially in that of gliomas and pituitary tumors,indicating that the clinical application of H2S has great prospects,which can be further examined as a potential neuroprotective gas for CNS tumors,according to experimental results above.
CLINICAL FINDINGS ABOUT THE ROLES OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS
Currently,research on H2S in CNS tumors is still at the cells experimental stage and has not yet been applied clinically.However,there is ample evidence to show thatin vivo,H2S is produced mainly by two key enzymes,cystathionine β-synthetase and cystathionine c-lyase,which are primarily present in the CNS.Although there is no direct evidence indicating that H2S has neuroprotective effect in clinical trials,the close touch with brain injury caused by CNS tumors is no doubt,which needs us to make great efforts to the study.
PERSPECTIVES
According to the data of the current research,H2S plays a role in promoting growth of brain tumors.Although some studies have found that the role of H2S is somewhat inconsistent with those mentioned above,which may be caused by differences in dose,mode of action,and type of disease.Although we have not fully understood its mechanism,we will continue to do a lot of research in the future.Finally,we believe that H2S will open up a new path into the treatment of the CNS tumors.
Author contributions
WP and MLZ were responsible for writing the manuscript.JZ was responsible for its revision.JZ and GC were responsible for its drafting and revision.All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript for publication.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Financial support
None.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement
This is an open access journal,and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License,which allows others to remix,tweak,and build upon the work non-commercially,as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
杂志排行
Medical Gas Research的其它文章
- Effects of nitrous oxide on end-tidal carbon dioxide measurements in spontaneously breathing patients under general anesthesia
- A special oropharyngeal oxygenation device to facilitate apneic oxygenation in comparison to high flow oxygenation devices
- Xenon as a transdermal enhancer for niacinamide in Strat-MTM membranes
- Effect of an ionic antineoplastic agent Cytoreg on blood chemistry in a Wistar rat model
- Comparing the effect of xenon and sevoflurane anesthesia on postoperative neural injury biomarkers:a randomized controlled trial
- Role of hyperbaric oxygen in glioma:a narrative review
