Menstrual cycle characteristics as an indicator of fertility outcomes:evidence from prospective birth cohort study in China
2022-07-28LIUXipingWUXiaqiuBAOLirongPENGJinKaKitHui
LIU Xiping,WU Xiaqiu,BAO Lirong,PENG Jin,Ka-Kit Hui
LIU Xiping,WU Xiaqiu,School of Public Health,Zhejiang Chinese Medical University,Hangzhou 310053,China
BAO Lirong,Zhejiang Chinese Medical University,Hangzhou 310053,China
PENG Jin,Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine,China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences,Beijing 100700,China
Ka-Kit Hui,Department of Medicine,David Geffen School of Medicine,UCLA,Los Angeles 90024,USA
Abstract OBJECTIVE:To evidently assess the applicability of regulate menstrual cycle (MC) characteristics in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) as an indicator for fertility.METHODS:A community-based prospective cohort study was conducted in China.Between January 2010 and December 2012,women who were willing to conceive within 2 years were enrolled in the study.Other than the MC length pattern,a well-adopted MC characteristic,menstrual blood color and clots were specifically concerned for women enrolled. All participants were followed up in 2 years by trained nurses.Pregnancy rate,fecundability odds ratio (FOR) and risk of miscarriage were assessed as fertility outcomes.RESULTS:A total of 2109 women were effectively included in this cohort for analysis.Results show that women with irregular MC length were less likely to achieve conception (FORirregular=0.59;95% CI=0.45-0.77,P <0.001).Menstrual blood in bright red color was also associated with decline in likelihood of conception(FOR=0.79;95% CI=0.63-0.98,P=0.04).Women with menstrual blood in light red were at higher risk of miscarriage (OR=2.39;95% CI=0.91-6.28,P=0.08).No significant impact was found between menstrual blood clots and fertility outcomes (FOR=1.02,95% CI=0.83-1.25,P=0.88;OR=1.26 95% CI=0.77-2.07,P=0.35).CONCLUSIONS:MC characteristics can be an effective and simple indicator for women’s fertility.Increasing the knowledge of MC characteristics for women in reproductive ages would bring great benefits to their preconception health conditions.
Keywords:menstrual cycle;fertility;odds ratio;abortion,spontaneous;medicine,Chinese traditional;preconception care
1.INTRODUCTION
Menstrual cycles (MC) of women,the consequences of physiological and hormonal changes in women's body,perform in complex but coordinated patterns.A healthy menstrual cycle is generally defined as approximately 28-day per cycle,within 3-5 d menstrual bleeding,bright or dark red color of blood.1,2If any imbalance in body occurs,disorders in MC characteristics may happen as a consequence.For instance,advanced ovarian aging can shorten the length of luteal phase,leading to MC lengths shorter than 28 d.3Later rise in Follicle-stimulating hormone and Luteinizing hormone peaks in follicular phase can cause MC length longer than 31 d.2Disorder of hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis,or extreme lowor over-body weights can increase the risk of anovulation,resulting in irregularities in MC length.4,5Low estrogen levels in the body may cause the unstable of endometrium,which leads to spotting of blood in light red color.6Fibroids in uterine or other tumor microenvironment can result in dark menstrual blood color,also visible blood clots.7
Studies showed that MC length can be a marker of women’s potential to conceive and fertility outcome.Irregularities in MC length may decrease the odds of conceiving in that cycle,8leading to infertility,4or low birth weight.5Both longer and shorter cycles were more likely to be spontaneously aborted after conception,comparing with 30-to 31-day cycles.9However,evidence assessing the association between MC length and fecundability is inconsistent.In one study,women with a MC length of <26 d only have half chance of giving birth,comparing with women with MC length of >34 d.3In another study,longer cycles (>31 d) were associate with decreased fecundability.10Those findings meant that MC length may be not proper as a sole indicator to women’s fertility.
Other than MC length,menstrual blood color and texture may also act as indicators of women’s health.Physiologically,menstrual blood is a blood mixed with secretions from the vagina and uterus,old cellular tissue,red blood cells and mesenchymal stem cells.11The pathologic changes of vagina,uterus or whole body will have effects on the physical status of menstrual blood,which can be visually reflected by color.12The cessation of bleeding relies on an intact endometrial coagulation system to achieve hemostasis.7An overactive fibrinolytic system can interfere with hemostasis and contribute to visible blood clots.However,few studies take menstrual blood color or texture into account as markers of women's health or fertility.
Differed from Western Medicine,Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) practitioners concern more and broader on menstrual cycles in a holistic and integrative manner.As a matter of fact,menstrual blood color,texture,length and frequency are all involved in TCM diagnosis,to assess women’s reproductive status.13Also,improving menstrual cycles is one of the most important core principles in TCM infertility treatment.14A research launched in Australia showed that,15all women with infertility reported menstrual changes after 1-3 months of TCM therapy,including regulations of MC length and changes to blood color and texture.Almost half of them conceived after TCM therapy.As the number of women using TCM for fertility enhancement has increasingly risen,16,17it is urgently needed to deepen the understandings in MC characteristics and fertility of women before TCM diagnosis and treatment.18
By exploring the association between these three MC characteristics and fertility outcomes,the aim of this study was to unravel the potential impacts of menstrual color and clots on women's fertility outcomes.
2.MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1.Study design and population
The prospective cohort study was conducted in Fengtai District of Beijing,China.The cohort was a subset of the population who accepted National Free Pre-pregnancy Checkups20(NFPC) and the routine preconception care service provided by Fengtai family plan committee.Fengtai district is mainly composed by counties and urban-rural fringes,with a predominantly migrant population from different areas of China.Between January 2010 and December 2012,a total of 2265 women who were new married,and held the willing to conceive in 2 years,registered in our database were included in the study.According to the diagnosis standard of NFPC,participants who were diagnosed as:polycystic ovarian disease,pelvic inflammatory disease,endometriosis,pelvic radiation,vaginal inflammation,anemia,viral infections (TORCH,rubella,cytomegalovirus and Herpes),liver,kidney or thyroid dysfunction,were excluded in this study.Participant with self or partner history of infertility were also excluded.Face to face interviews were conducted by trained nurses,all information was collected in the database at the same time.Baseline information includes demographic characteristic (date of birth,date of marriage,educational attainment and current occupation),behavior characteristics (smoking,alcohol drinking,noise,poison materials,radiation,or pet exposure),family history(diabetes,congenital heart disease),personal medical history,age at menarche,abortion history and assessment of menstrual cycle characteristics.
2.2.Assessment of menstrual cycle characteristics
MC characteristics include three aspects:length pattern,menstrual blood color,and blood clots.The MC characteristics of subjects were evaluated by self-report questionnaire involving participants’ symptom happened during the past 3 months,with good reliability(coefficient of stability=0.81) (Table 1).

Table 1 Questionnaire for menstrual cycle characteristics
MC length measures the duration of a menstrual cycle from the first day of menstrual bleeding to the last day before the next bleeding.A normal MC length pattern is between 27 and 32 d,with no more than 3 days’variations among months.21Abnormal length patterns can be classified into three types below:short,long,and irregular length patterns.The short length pattern was defined as a menstrual cycle shorter than 27 d in last three months,while the long length pattern was longer than 32 d.22The irregular length pattern was defined as high variance in MC length over 5 d among different months.If the cycle length varies more than 3 d from month to month continually,it will be considered as irregular pattern,even if some MC length data fell within the 27 to 32 d range.
Blood color was self-judged by participants based on blood color scale.As an example,Figure 1 demonstrates the reference MC color card with three shades of red,from light to dark (i.e.,Light Red,Bright Red,Dark Red).
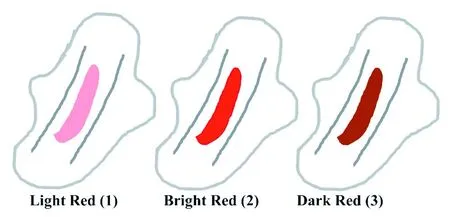
Figure 1 Menstrual blood color scale
2.3.Follow-up
Trained nurses made follow-up telephone interviews.The first follow up was conducted within 12 months after baseline examination.Information about clinical pregnancy was obtained,including the last menstrual period (date),live birth,ongoing birth,or self-report miscarriage.In this study,we defined miscarriage as a pregnancy loss before 20 weeks of gestation.23If the participant was not pregnant at this interview,repeated a 12-month inquiry was made.
2.4.Ethical approval and trial register
The institutional review board at Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine,China academy of Chinese Medical Science,Beijing,approved the protocol and all participants provided informed consent (No.2009NO7).Additionally,the protocol was registered in Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (No.ChiCTR-RCH-13003082).
2.5.Statistical analysis
Statistical tests were conducted through Univariate analysis,χ2tests or Fisher's exact test to evaluate the means and standard deviation,or distribution of demographic data and covariates across categories of study participation and by fertility outcomes.Pregnancy rate (PR) was calculated by the number of women achieved clinical pregnancy during the study divided by the number of women included in final analyses.Fecundability odds ratio (FOR) was also calculated to evaluate probability of conception in last three years(fecundability).
Both fit linear model and multivariable regression model were created to determine the impact of MC characteristics on fecundability.The fit linear model was primarily used to assess the association between MC characteristics and PR.Subsequently,the multivariable regression model was applied to calculate FORs and 95%confidence intervals (95%CI) for each measure relative to its reference category.FOR of less than 1.0 suggests reduced fecundability (likelihood of conception) and Pvalues <0.05 indicate statistical significance.Moreover,a logistic regression model was employed to determine the relationship between MC characteristics and pregnancy outcome (“live birth”,“miscarriage”).To adjust for potential confounders,covariates were added to all models above,including age,education level,age at menarche,and abortion history.
All data were analyzed using R software (version 3.4.2 and version 3.6.1).Using the mean imputation method,the missing data of age and age at menarche were replaced by average value.
3.RESULTS
A total of 2265 women were initially enrolled in this cohort,with 29 women changed to conception control,127 women lost to follow-up.Finally,2109 women were effectively included in this study.Around two-thirds of participants (1394,66.10%) achieved conception during the study,of which 1119 gave live birth,187 were ongoing pregnancy,and 88 ended with miscarriage at the time of follow-up.Study flow diagram of this study was shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 Study flow of women enrollment,follow up and pregnancy diagnosis
Table 2 shows the demographic as well as MC characteristics of the study population from the initial interview.The participants were aged 20-44 years with a mean age of (27.85 ± 2.88) years.Most of women were in a high-education level (84.97% with bachelor’s degree or above).Very few women (less than 0.6%) were smokers or drank alcohol,or were exposed to radiation,noise or poison environments.The mean age at menarche was (13.22 ± 1.36) years.Around three-quarter (73.02%)women reported no abortion history,while 457 (21.67%)and 19 (0.90%) women suffered pregnancy loss 1-2 times and more than 3 times,respectively.Approximately 1 in 4 women (24.47%) reported in normal MC length pattern,but the number of women with light menstrual blood color was much higher(54.24%).More than half women (53.83%) reported sometimes or usually having blood clots during menstrual flow.No statistical significance of distributions of MC characteristics were found among different abortion groups.
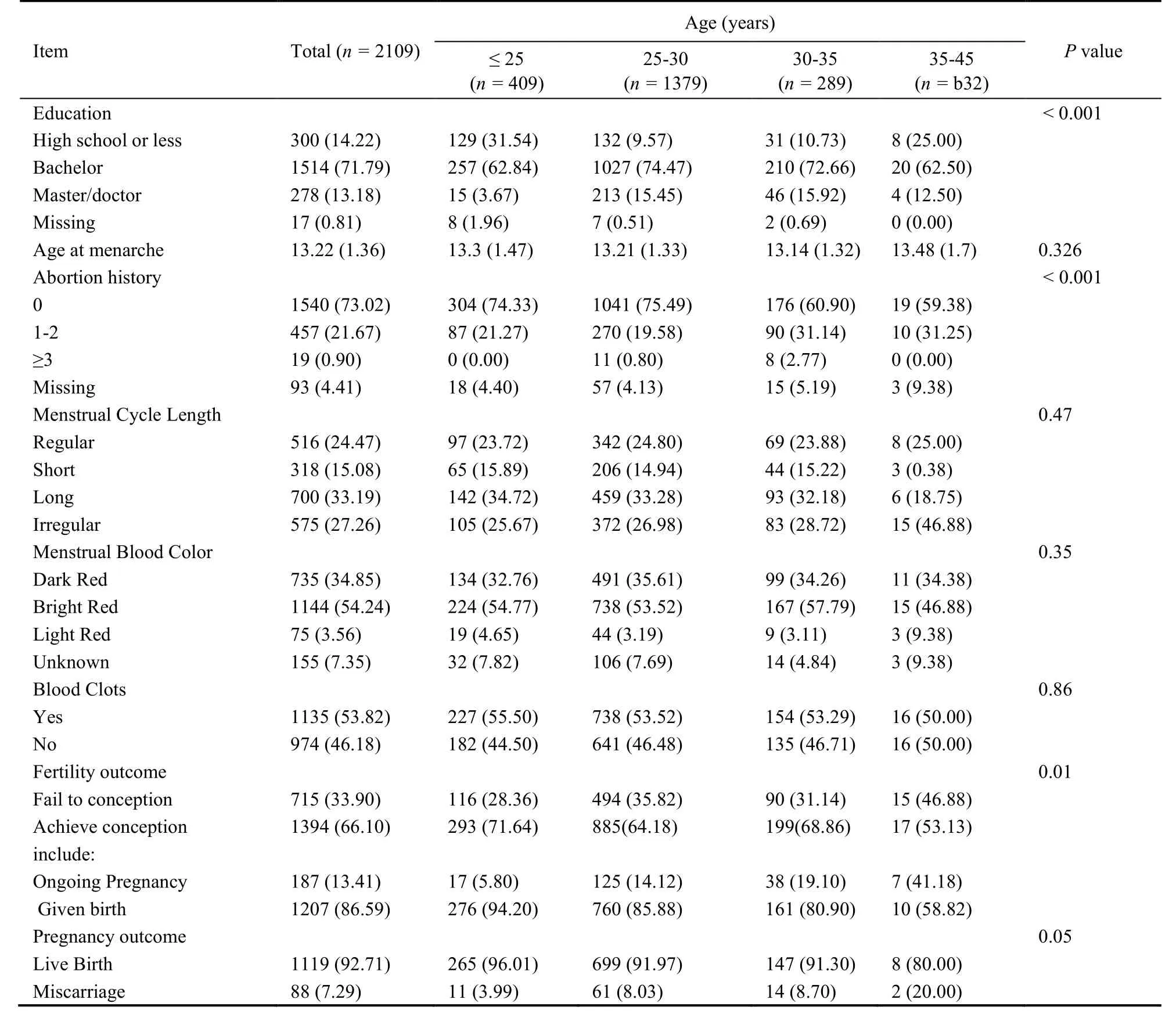
Table 2 Characteristics of Study participants with different age group [n (%)]
We also summarized the baseline characteristics according to age in Table 3.As expected,women with elder age were less likely to achieve pregnancy (P=0.01),and more likely to end in miscarriage (P=0.05).However,no statistical significance of distributions of MC length pattern,blood color or clots was found among different age groups.
The FOR data among different MC characteristics can be found in Table 3.Women with irregular MC length pattern reported the lowest pregnancy rate (59.13%),followed by those with short cycle (66.67%),long cycle(69.00%) and normal cycle (69.57%).The results from multivariable regression model,using normal pattern as reference level,indicated that the irregular MC women were less likely to become pregnant (crudeFORirregular=0.63;95%CI=0.49-0.82).After adjusting for the main confounders,the effect remained similar [adjusted (adj.)FORirregular=0.59;95%CI=0.45-0.77].Short or long cycles were also assoCIated with a potential decline in likelihood of conception,albeit in slight extents,with an adj.FORshortof 0.82 (95%CI=0.6-1.12) andFORlongof 0.92 (95%CI=0.72-1.2),respectively,in the adjust model (Table 3).
Both linear and logistic models suggested that menstrual blood color indeed impact fertility outcome.Women who self-judged menstrual blood in bright red color reported the lowest pregnancy rate (64.25%),and were less likely to become pregnant (adj.FOR=0.79;95%CI=0.63-0.98).Women having menstrual blood in light red color were at higher risk of miscarriage,though not significantly,with an adjustedORof 2.39 (95%CI=0.91,6.28,P=0.08).The menstrual blood clots showed no obvious impacts on the fertility outcomes (Table 4).
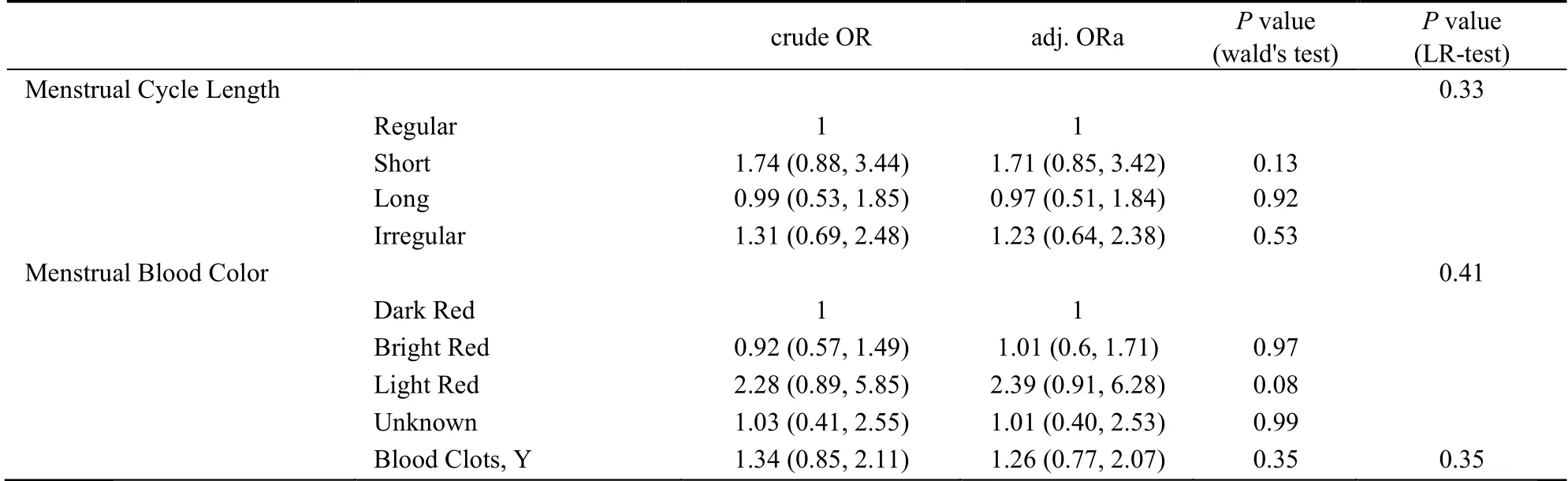
Table 3 Pregnancy outcome (live birth,miscarriage) by MC characteristics (n=1394)

Table 4 Fertility outcome by MC characteristics (n=2109)
4.DISCUSSION
The present study indicated that MC length pattern and menstrual blood color are assoCIated with fertility outcomes among Chinese rural women with statistical significance.Women with irregular MC length pattern or bright red color of menstrual blood had lower PRs and FORs.Short or long cycles were also assoCIated with a slight decline in the possibility of conception.Women with light red blood color had higher risk of miscarriage.Menstrual blood clots have no apparent relationship with fertility outcomes.
Our results of MC length and fertility are consistent with previous studies.Wesselinket al24indicated that menstrual irregularity was associated with a slight reduction of fecundability (FOR=0.93;95%CI=0.81-1.06).Kolstadet al25found that of women with a cycle length that differed by >10 d from the usual cycle length,fecundity was only approximately 25% of women who had no variation (odds ratio=0.25,95%CI=0.09-0.68).Women with irregular cycles may have longer time to pregnancy due to higher risk of anovulation,26and/or anunderlying disorder of the hypothalamic-pituitaryovarian axis or the uterus.27As to longer or shorter MC length,the negative impacts on FOR were also reported in previous studies.Jensen et al.found lower fecundability after cycles of >35 d (FOR=0.74;95%CI=0.70-0.87).28Short menstrual cycles may reflect ovarian aging29or a narrow fertile window and are associated with higher risk of anovulation28and lower fecundability compared with normal length cycles.9
While western physiology describes the menstrual cycle in terms of hormones which influence the ovaries and the uterus,TCM captures it in the aspects ofQiand Blood,YinandYangon the Uterus.If some basic elements (Qi,Blood,Yin,Yang) were in pathology status,reproductive dysfunction may be affected.One may takeQi,a vital form of energy which circulates in meridians (or channels) to nourish the body,as an example.Women withQideficiency may have scanty menstruation,or oligomenorrhea.The transport ofQialong the meridians,in some cases,represents the energy movement in body.In a menstrual cycle,the movement ofQican facilitate the journey of an egg from ovary through fallopian tube to uterus at ovulation time.IfQistagnates,the ovulation process might fail,the menstrual cycle can be in an irregular pattern,which may reduce the ability of conception.
Our results also indicated that the lighter menstrual blood color,the higher risk of low fertility rate and miscarriages.Menstrual blood color is rarely considered by western doctors,but as always,is inquired by TCM doctors.Physiologically,blood color is mainly determined by hemoglobin concentration.30According to this hypothesis,the lighter menstrual blood color,the lower level of hemoglobin.From the TCM perspective,the lighter menstrual blood color may be a typical symptom belongs to the pattern ofQideficiency,Blood deficiency orYangdeficiency,all of which are risk patterns of low fecundability and miscarriage.14Menstrual blood color may also be impacted by estrogen level,and light color may indicate low estrogen.Analogue to the Haemoglobin Color Scale that was developed by WHO to screen for anemia,31it’s reasonably considerable to develop a menstrual blood color scale,as a simple and inexpensive tool to assess reproductive health.
Although no significant association between menstrual blood clots and fertility was found in this study,we believe that more attention should be paid to the menstrual blood clots.In TCM view,blood clots are caused by Blood Stasis in body,which is a common risk pattern of miscarriage.32Pathologically,visible or frequent clots can be a signal of many medical issues,such as uterine polyps or fibroids,endometriosis,adenomyosis,hormonal imbalances.33Therefore,more rigorous investigations on menstrual blood clots and their correlations with healthy status and fertility outcomes are needed in future studies.
While we have unraveled the important impact of MC characteristics on fertility of women,this study remained needed to be advanced in future work.First,the menstrual blood color and clots are highly timedependent.For example,fresh menstrual blood can change its color and clotting status with prolonging time,and it is almost not possible to obtain the data of the very fresh menstrual blood in the daily life of the recruited women.This may explain why we did not observe obvious correlation between menstrual blood clots and FOR.Second,the volume of menstrual blood loss and menstrual bleed length are lacked in this study,which will be took into consideration in our next step.Last but not least,though the whole study,we only collected the MC characteristic data in a relatively short period (three months),which may increase the data variance,and therefore longer observation is required in future study.In conclusion,the present community-based study revealed that irregular,short or long MC length pattern,and bright menstrual blood color were intimately or potentially associated with low FOR,and light red color might be a risk factor for miscarriage in the study population.Menstrual blood clots,however,had no significant correlation with fertility outcomes.Since the self-reported MC characteristics can be easily collected online (viaapp in smart phones),we suggested that MC characteristics,including MC lengths,blood color and clots,can be taken as indicators into consideration in women’s preconception health assessment and clinical deCIsion-making process.34Further elaborate studies are needed to testify our findings before clinical application.From the present results,we propose that regulating women's menstrual cycle may be an effective but cheap and easy routine to improve fertility outcome.Indeed,“regulating menstrual cycle”,which was recommended by TCM masters in thousand years,is one of the core principles to improve fecundability in TCM.13We believe that increasing the knowledge and awareness of MC characteristics for women in productive ages would also bring great benefits to understand their preconception health conditions.
5.ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank Lü Aiping for research protocol,Qi Zhengping and Kou Huixin for data collection,and Betty Chang for giving advice on the whole manuscript.
杂志排行
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Acupoint application therapies for essential hypertension:a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Biosynthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Hypericum perforatum and Origanum vulgare extracts and their main components,hypericin and carvacrol as promising antibacterial agents
- Protective effect of resveratrol on rat cardiomyocyte H9C2 cells injured by hypoxia/reoxygenation by regulating mitochondrial autophagy via PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1/Parkinson disease protein 2 signaling pathway
- Efficacy of aqueous extract of flower of Edgeworthia gardneri (Wall.)Meisn on glucose and lipid metabolism in KK/Upj-Ay/J mice
- Effect of manipulation on cartilage in rats with knee osteoarthritis based on the Rho-associated protein kinase/LIM kinase 1/Cofilin signaling pathways
- Baicalin inhibits inflammation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via toll like receptor-4/myeloid differentiation primary response 88/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway
