Functions of three ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 2 genes in hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis
2022-07-04ChunYeZhangMingYang
Chun-Ye Zhang,Ming Yang
Chun-Ye Zhang,Department of Veterinary Pathobiology,University of Missouri,Columbia,MO 65211,United States
Ming Yang,Department of Surgery,University of Missouri,Columbia,MO 65211,United States
Abstract BACKGROUND Liver cancer ranks the third cause of cancer-related death worldwide.The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC).The survival time for HCC patients is very limited by years due to the lack of efficient treatment,failure of early diagnosis,and poor prognosis.Ubiquitination plays an essential role in the biochemical processes of a variety of cellular functions.AIM To investigate three ubiquitination-associated genes in HCC.METHODS Herein,the expression levels of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes 2(UBE2)including UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S in tumor samples of HCC patients and nontumor controls at the Cancer Genome Atlas(TCGA)database,was comprehensively analyzed.The relationship of UBE2 gene expression level with cancer stage,prognostic outcome,and TP53 mutant status was studied.RESULTS Our results showed that UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S genes were overexpressed in HCC samples compared to non-tumor tissues.Dependent on the cancer progression stage,three UBE2 genes showed higher expression in tumor tissues at all four stages compared to non-tumor control samples.Furthermore,a significantly higher expression of these genes was found in stage 2 and stage 3 cancers compared to stage 1 cancer.Additionally,overexpression of those genes was negatively associated with prognostic outcome and overall survival time.Patients with TP53 mutation showed a higher expression level of three UBE2 genes,indicating an association between UBE2 expression with p53 function.CONCLUSION In summary,this study shed light on the potential roles of UBE2C,UBE2T,UBE2S on diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for HCC.Moreover,based on our findings,it is appealing to further explore the correlation of those genes with TP53 mutation in HCC and the related mechanisms.
Key Words: Hepatocellular carcinoma;Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 2;UBE2C;UBE2T;UBE2S;TP53 mutant;Biomarker;Diagnostic;Prognostics
lNTRODUCTlON
Liver hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC,or LIHC)is the most common type of primary liver cancer,which is the third most common cause of cancer-related death worldwide[1,2].Hepatitis viral infections,abuse of alcohol,liver fibrosis,and cirrhosis are the major factors that cause liver cancer.HCC is closely associated with many metabolic diseases,such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD),diabetes,obesity,cardiovascular diseases[3].Surgical operation is a curative treatment for early-stage of liver cancer[4].However,most HCC cases were found at the late stage due to a lack of effective diagnostic biomarkers,which are not suitable for surgical procedures[5].Therefore,early diagnostic and exploration of novel treatment options are urgently needed.The mechanism-based investigation both on the genetic and molecular levels is necessary to further facilitate the exploration of diagnosis and treatment.
Ubiquitin is a highly conserved regulatory protein in all eukaryotic organisms,and it is covalently tagged to proteins,severing as a signal for further proteasome degradation[6].Ubiquitination is an essential biochemical process,which contributes to a variety of cellular functions,such as cell signaling pathway regulation,cell death,protein degradation,innate and adaptive immune response.Due to the significant role of ubiquitination in cell survival and death,it is closely associated with host health and disease[7,8].When exploring the top overexpressed genes of E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes(UBE2)in HCC patient tumor samples from the Cancer Genome Atlas(TCGA)database,UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S were ranked as top 4,top 8,and top 31,respectively.Those highly expressed genes draw our attention in exploring their roles in cancers,specifically for HCC.Therefore,in this study,we focused on the investigation of highly expressed UBE2C,UBE2T,UBE2S as potential biomarkers for HCC diagnosis and prognosis,as well as their expression levels at different cancer stages.
UBE2 is a large enzyme family that plays a fundamental role in the second step of ubiquitination that connects the first step of ubiquitin activation by UBE1 enzyme and together with the third step ubiquitin-protein ligationviaUBE3 enzyme to conduct the complex ubiquitination process[7].UBE2C protein,encoded by geneUBE2C,was reported to exacerbate cell apoptosis[9]and contribute to chromosome mis-segregation during the formation of tumors[10].Overexpression of geneUBE2Chas been found in tumor cells of HCC patients compared to noncancerous liver cells in 62 out of the studied 65 clinical cases[11].Most recently,another study also showed that UBE2C can promote cancer cell growth and migration[12].
UBE2T can bind to Fanconi anemia complementation group L and meditate the monoubiquitinating of Fanconi anemia complementation group D2(FANCD2),a critical process of regulation associated with damaged-DNA repair in the Fanconi anemia pathway[13,14].It was also reported that UBE2T played an important role in the carcinogenesis in different cancer types[15-18],such as human breast cancer cells[17,18],lung cancer[19],gastric cancer[20],etc.
UBE2S serves as the key component on the degradation of anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome substrateviamitosis,in which process UBE2C is also involved[21].In breast cancer cells,UBE2S deficiency can suppress their migration,invasion,and growthviadisruption of actin cytoskeleton and focal adhesion[22].In addition,silencing UBE2S reduced cell proliferation and colony formation of lung cancer cells,resulting in cell apoptosis[23].In HCC,UBE2S was upregulated and showed oncogenic activity by increasing p53 ubiquitination[24].Overall,these three genes play pivotal roles in cancer cell progression and invasion,indicating the potential as biomarkers for HCC.
However,the bioinformatic-based systematic analysis of UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S in liver cancers from clinical patients have not been reported.Herein,this study carried a comprehensive bioinformaticbased analysis of clinical data from the online database to illustrate the significant roles of threeUBE2genes in HCC,by analyzing their gene expression levels between non-tumor and tumor tissues,their association with cancer progression stage,and their prognostic values,and by investigating their expression in different cell types,association with TP53 mutation status,co-expression efficiency,involved signaling pathways,and associated proteins in interaction networks.
MATERlALS AND METHODS
Ethics statement
All the data for this study originated and was generated from the online open resource database and published literature.
TCGA database
The RNA-seq data and LIHC/HCC patient clinic information were originated and generated from TCGA.(TCGA research network: https://www.cancer.gov/tcga).The genomic alterations for UBE2C,UBE2T,UBE2S in different liver cancer types were analyzed using cBioPortal(https://www.cbioportal.org/)[25,26].A survival heatmap was generated using GEPIA[27].
UALCAN
The expression level of the genes of interest on pan-cancer was analyzed using UALCAN web-based tool.The quired gene expression level in pan-cancer was analyzed using Student’st-test to compare the normal and tumor group withP< 0.05 as significant differential expression.Heatmap was generated to display the RNA-seq data using the median value of expression Log2(TPM+1).Analysis of gene expression level on HCC cancer progression stages,expression level on TP53 mutant status and non-TP53 mutant status was performed using online resources UALCAN[28].
Human Protein Atlas Database
The analysis of RNA expression in different cell types and the expression location ofUBE2genes in three different cells including epidermoid carcinoma cell line A-431,human osteosarcoma cell line U-2 OS,and human glioblastoma cell line U-251 MG were explored using the Human Protein Atlas database(Human Protein Atlas,https://www.proteinatlas.org,Protein Atlas version 21.0),an online public resource for the investigation of protein-coding genes of variable cancers in cell and tissue samples[29].
STRING database for PPI network
In this study,the STRING online tool[30]was used to show the interaction of functional enrichment of the generated network with queried input: UBE2C,UBE2T,UBE2S,and TP53.(Default threshold for interaction specificity score > 0.4 was defined as significant).The functional property was generated and summarized based on the online information and literature.
Statistical analysis
The survival curve was generated using Kaplan Meier-plotter that was commonly used for assessment of the gene expression on survival from a large database such as TCGA samples.The significance of survival impact was measured by a log-rank test.A log-rankP< 0.05 was set for statistically significant cut-off.
Expression of genes in tumor samples and normal samples using Student’st-test(considering unequal variance)for comparison between different groups.APvalue less than 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
Overall survival heat map of the patients across multiple cancer types was generated with the input of 95% confidence interval and the calculation of the hazard ratio based on the Cox PH model.Pearson's correlation coefficient(r)was used to plot the co-expression between quired input paired genes.
RESULTS
Expression levels of UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S in pan-cancers
As shown in Figure 1,three UBE2 family members including UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S were highly expressed in most tumor samples compared to the corresponding normal(non-tumor)samples.A formula of log2(TPM+1)was used to calculate theUBE2gene expression level,where TPM is transcripts per million.The case numbers for each cancer were included in the figure.The expression level among normal and tumor tissues are heterogeneous,with relatively high expression in both normal and tumors,such as colon and rectum adenocarcinoma(COAD and READ),skin cutaneous melanoma(SKCM),and thymoma(THYM).For HCC(or LIHC),UBE2C showed a high expression level in tumor samples(n= 371)compared with normal samples(n= 50),with the mean value of the log2(TPM + 1)of 4.2 for tumor samples and 0.7 for normal samples.UBE2T also showed an increased expression level in tumor samples with the mean value of log2(TPM + 1),compared to 0.6 for normal samples.Similarly,a higher expression level was shown for UBE2S,with the value of the log2(TPM + 1)of 4 for tumor samples and the value of log2(TPM + 1)of 2 for normal samples.
Expression level in liver cancer and normal samples
Similarly,the distribution of the expressionUBE2C,UBE2T,andUBE2Sindicated that they were expressed in HCC tumor samples compared to normal samples(Figure 2A-C),indicating the potential as a diagnostic biomarker for HCC.Furthermore,the expression of each gene at different tumor stages was analyzed to investigate the association of gene expression with the tumor progression stage.The results demonstrated that along with the progression of cancer,the expression patterns of genesUBE2C,UBE2T,andUBE2Skept increasing from stage 1 to stage 3(Figure 2D-F).There was a pike level at stage 3,while at stage 4,the expression level significantly decreased forUBE2CandUBE2Scompared to that from stage 2 and stage 3,even though it was increased compared to that in normal tissue(Figure 2D and F).In addition,the expression ofUBE2Twas also decreased at stage 4 of HCC,but without significant change compared to that in stages 2 and 3,which might be impacted by the sample size(Figure 2E).Even though,the significantly increased expression level of those genes in HCC stage 1,2,and 3 when compared to normal samples or compared between stage 1 and stage 2&3,which suggests that it is valuable for further exploring them as potential biomarkers or key genes mediating HCC progression.
Relationship between UBE2 expression and the survival of HCC patients
To explore the prognostic value of these gene expression levels in HCC patients,the survival outcome of patients,the expression ofUBE2genes,and the survival curve were analyzed.Remarkably,high expression levels ofUBE2C,UBE2T,andUBE2Swere associated with a negative prognostic outcome in HCC patients.The patients with overexpression ofUBE2C(n= 91)showed significantly less survival time compared to the patients with low or medium expression levels(n= 274)(Figure 3A,P< 0.0001).ForUBE2T,277 patients with low or medium expression levels showed significantly higher survival days compared to the patients(n= 88)with high expression levels(Figure 3B,P< 0.0001).Similar results were also found forUBE2S,a significantly shorten survival time was associated with the higherUBE2Sexpression level(n= 89)compared with longer survival patients with low or medium expression levels of UBE2S(n= 276)(Figure 3C,P< 0.0001).
In addition,with the analysis of prognostic markers for pan-cancers,the results indicated that a higher expression level ofUBE2C,UBE2T,andUBE2Swas associated with the poor prognostic outcome for most of the cancers,such as adrenocortical carcinoma(ACC),kidney chromophobe(KICH),brain lower grade glioma(LGG)(Figure 3D).
Genetic mutations in UBE2 genes in HCC
We further explored the underlying mechanisms of threeUBE2genes in HCC development and progression.A total of 1238 samples were analyzed using the cBioPortal from the TCGA pan-cancer database for genetic alterations including mutations,structural variants,and copy number alteration of threeUBE2genes.The OncoPrint results analyzed from cBioPortal showed the queried genes genomic alteration frequency from TCGA studied HCC samples is 2.1%(26 out of 1238).Among them,the genetic alteration occurred on genesUBE2TandUBE2S,and no alteration was found forUBE2C(Figure 4A).Then,the genetic alteration based on liver cancer subtypes was further analyzed.Among 1238 samples,369 samples were HCC and 712 samples were hepatobiliary cancer.The genetic alteration was mostly found in HCC and hepatobiliary cancer.For HCC,the overall genetic alteration frequency of genesUBE2TandUBE2Swas 6.23%(23 out of 369 samples)that largely resulted from amplification(5.96%,22 cases,red color)and less from mutation(0.27%,1 case,green color)out of 369 cases.For hepatobiliary cancer,the overall genetic alteration frequency of genesUBE2TandUBE2Swas 0.28% in total 712 cases with 1 case amplification(0.14%)and 1 case mutation(0.14%)(Figure 4B).Specifically,for geneUBE2T,the only genetic alteration type is amplification which was found in 21 out of 369 cases of HCC samples,while no mutation had occurred forUBE2T(Figure 4C).ForUBE2S,genetic alteration occurred in 2 cases out of 369 cases(0.54%)in HCC,including 1 case of mutation(0.27%)and 1 case of amplification(0.27%).Similarly,genetic alteration ofUBE2Soccurred in 2 cases out of 712 cases(0.28%)in hepatobiliary cancer,including 1 case mutation(0.14%)and 1 case amplification(0.14%)(Figure 4D).Overall,the most of genetic alteration occurred in HCC samples with 23 out of 369 samples(6.23%),which was mainly from geneUBE2T.

Figure 1 Gene expression levels of UΒE2C,UΒE2T,and UΒE2S in pan-cancer with normal samples and tumor samples(the Cancer Genome Atlas database).N: Normal samples;C: Cancer samples.Color-coded only based on each cancer type.Red: higher expression level;Blue: lower expression level when compared tumor samples with normal samples in a particular cancer type.The number represents the median value of expression Log2(transcript count per million(TPM)+1).The total sample number for the corresponding cancer type was listed on the right side of the figure(N: total sample number of normal samples.C: total sample number of tumor samples)Abbreviations: BLCA: Bladder urothelial carcinoma;BRCA: Breast invasive carcinoma;CESC: Cervical squamous cell carcinoma;CHOL: Cholangiocarcinoma;COAD: Colon adenocarcinoma;ESCA: Esophageal carcinoma;GBM: Glioblastoma multiforme;HNSC: Head and Neck squamous cell carcinoma;KICH: Kidney Choromophobe;KIRC: Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma;KIRP: Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma;LIHC(HCC): Liver hepatocellular carcinoma;LUAD: Lung adenocarcinoma;LUSC: Lung squamous cell carcinoma;PAAD: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma;PRAD: Prostate adenocarcinoma;PCPG: Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma;READ: Rectum adenocarcinoma;SARC: Sarcoma;SKCM: Skin Cutaneous Melanoma;THCA: Thyroid carcinoma;UCS: Uterine Carcinosarcoma;THYM: Thymoma;STAD: Somach adenocarcinoma;UCEC: Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma)
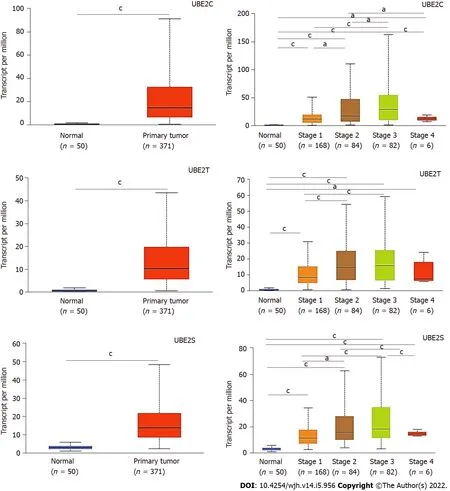
Figure 2 UΒE2C,UΒE2T,and UΒE2S expression levels in hepatocellular carcinoma based on normal and tumor sample types and based on cancer stages(the Cancer Genome Atlas database).A: Expression of UBE2C in hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)based on sample types;B: Expression of UBE2T in HCC based on sample types;C: Expression of UBE2S in HCC based on sample types;D: Expression of UBE2C in HCC based on individual cancer stages;E: Expression of UBE2T in HCC based on individual cancer stages;F: Expression of UBE2S in HCC based on individual cancer stages(aP < 0.05;cP < 0.001).
RNA and protein expression patterns
Single-cell RNA sequencing(scRNA-seq)revealed three clusters c-6(B-cells),c-15(T-cells),and c-16(Erythroid cells)exhibited high mRNA expression of all threeUBE2C,UBE2T,andUBE2S(Figure 5AG).In addition,the protein expression location in three cell lines including A-431,U-2 OS,and U-251 MG(Human Protein Atlas,https://www.proteinatlas.org)indicated that UBE2C was mainly expressed in the cytosol and plasma membrane,UBE2T was mainly expressed in nucleoli or nucleoplasm,and UBE2S was highly expressed in the cytosol and plasma membrane and less expressed in nucleoli(Figure 6).Furthermore,the co-expression relationship of these genes was analyzed,since all three genesUBE2C,UBE2T,andUBE2Swere expressed by the same clusters in HCC.The correlation expression of pair-wise genes was analyzed using Pearson methods(Figure 7A,7B,7C).Results showed there was a co-expression between two paired genes(r= 0.83 UBE2C-UBE2S;r= 0.76 UBE2C-UBE2T;r= 0.76 UBE2S-UBE2T).In addition,the analysis of co-expression of their proteins also showed that there was a correlation among three proteins(Figure 7D),indicating a co-expressing pattern.

Figure 3 Association of expression levels of UΒE2C,UΒE2T,and UΒE2S with prognostic outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients.A: Survival of patients with a high expression level of UBE2C compared with patients with low/medium expression level;B: Survival of patients with a high expression level of UBE2T compared with patients with a low/medium expression level;C: Survival of patients with a high expression level of UBE2S compared with patients with low/medium expression level;D: Overall survival heat map of patients across multiple cancer types.Red color represents higher risk on survival and blue color represents lower risk.The frame indicated the significant unfavorable(red)and favorable(blue)prognostic outcome.(Calculation of the hazards ratio based on Cox PH Model,95% Confidence Interval)(ACC: Adrenocortical carcinoma;LGG: Brain lower grade glioma;DBLC: Lymphoid Neoplasm Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma;MESO: Mesothelioma;OV: Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma;TGCT: Testicular germ cell tumors;UVM: Uveal melanoma).
TP53 mutation impacts the expression of UBE2S,UBE2T,and UBE2S genes
Notably,the expression levels of all three genesUBE2C,UBE2T,andUBE2Swere significantly higher inTP53mutant samples compared with both normal samples and non-TP53mutant samples(Figure 7E-7G).However,the correlation or causation between the higher expression level ofUBE2C,UBE2T,UBE2S,andTP53mutation is unknown.This finding of a comprehensive analysis of clinical patient samples was supported by several studies.For example,overexpression ofUBE2Cin patients with endometrial cancer was associated with cancer progression and recurrence,by increasing endometrial cancer cell proliferation,migration,invasion,as well as the process of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of p53 expression[31].UBE2T can enhance the ubiquitination of p53 in HCC cells[32,33].Similarly,UBE2S also can promote the ubiquitination of p53 and mediate its protein degradation in HCC cells[24].Therefore,recovering or enhancing p53 function can partially attenuate UBE2 genesinduced malignant phenotypes of tumor cells.
Protein-protein interaction network
To further investigate the association among three genesUBE2S,UBE2T,UBE2S,andTP53function,we generated the protein-protein interaction network using their proteins andTP53.The most closely associated proteins related to these protein interactions were analyzed using STRING,shown in Figure 7H.The functional annotation and associated signaling pathways of the queried genes were summarized in Table 1.
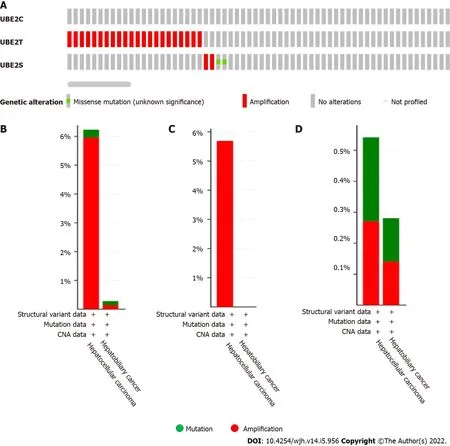
Figure 4 The genetic alteration occurred in UΒE2C,UΒE2T,and UΒE2S in liver cancer(1238 samples from the Cancer Genome Atlas).A: Genetic alteration occurred in UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S in HCC;B: UBE2T and UBE2S,overall alteration frequency 6.23%(23/369 cases)in hepatocellular carcinoma including 22 cases implication and 1 case of mutation.In hepatobiliary cancer type,the alteration frequency is 0.28(2/712)with 1 case of amplification and 1 case of mutation;C: UBE2T genetic alteration frequency 5.69%(21/369 cases)categorized by cancer type;D: UBE2S genetic alteration frequency 0.54%(2/369 cases)in HCC(1 case amplification and 1 case mutation);In hepatobiliary cancer,UBE2S alteration frequency is 0.28%(2/712 cases)(1 case amplification and 1 case mutation).

Figure 5 UΒE2C,UΒE2T,and UΒE2S mRNA expression in different cell types.A: UBE2C expressed genes in each cell cluster of scRNA-seq data;B: Bar plot of the transcript abundance of UBE2C in different cell types based on the scRNA-seq data.The level of UBE2C mRNA was represented by the mean pTPM(Protein-coding transcripts per million);C: UBE2T expressed genes in each cell cluster;D: Bar plot of the transcript abundance of UBE2T in different cell types based on the scRNA-seq data.The level of UBE2T mRNA was represented by the mean pTPM;E: UBE2S expressed genes in each cell cluster;F: Bar plot of the transcript abundance of UBE2S in different cell types based on the scRNA-seq data.The level of UBE2S mRNA was represented by the mean pTPM(Colored according to cell type group);G: Heat map of the expression level of UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S.(Color key from 0-1 represent low-high expression).

Figure 6 UΒE2C,UΒE2T,and UΒE2S protein expression in cell lines.A: UBE2C was mainly expressed in cytosol and plasma membrane;B: UBE2T was mainly expressed in nucleoli or nucleoplasm;C: UBE2S was highly expressed in cytosol and plasma membrane and less expressed in nucleoli.

Figure 7 UΒE2C,UΒE2T,and UΒE2S expression in homo sapiens and protein-protein interaction network.A: Co-expression of UBE2C and UBE2S;B: Co-expression of UBE2C and UBE2T;C: Co-expression of UBE2T and UBE2S;D: Co-expression of UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S predicts functional association.In the triangle matrices above,the intensity of the color indicates the level of confidence that two proteins are functionally associated in Homo sapiens.Figures E-G showed the expression of UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S in HCC based on TP53 mutation status.TCGA samples for analysis;E: UBE2C expression in normal,HCC with TP53 mutation,and HCC non-TP53 mutation samples;F: UBE2T expression in normal,HCC with TP53 mutation,and HCC non-TP53 mutation samples;G: UBE2S expression in normal,HCC with TP53 mutation,and HCC non-TP53 mutation samples.(cPvalue < 0.001 Compared with other two groups);H: Protein-protein interaction of functional enrichment of queried network using query input of UBE2C,UBE2T,UBE2S,and TP53.

Table 1 Functional enrichment in the queried network (query input UΒE2C,UΒE2T,UΒE2S,TP53)
DlSCUSSlON
The early diagnostic of HCC or LIHC is critically important for cancer treatment and selection of therapeutic methods[34-36].In addition,a better understanding of the development and progression of the cancer stage is helpful to choose the therapy that can result in a good outcome.In this study,with clinical data analysis,we found that the expression ofUBE2C,UBE2T,andUBE2Swas increased in tumor tissue compared to normal tissue,and their expression was associated with the procession of cancer stage from stage 1 to stage 3,although there was a decrease at last stage(stage 4).These results suggest there is a potential to use those genes as biomarkers to assist the diagnosis of HCC at the earlystage point.What’s more,the results also showed that there was a significantly increased expression level of those genes at stage 2 and stage 3 compared with stage 1 during HCC progression.This may shed light on the potential usage of those genes as biomarkers to better predict the cancer progression stage.
UBE2 family members play a role in the development and prognosis of cancers[37,38],such as ovarian cancer.It has been shown that the mRNA expression of UBE2A in liver cancer cell lines(e.g.,HepG2 and Huh-7)was significantly higher compared to that in normal liver cancer line HL-7702.Meanwhile,UBE2A mRNA and protein were highly expressed in HCC tumor tissues than those in the adjacent normal tissues[39].In HCC,qPCR data showed that the expression of UBE2S was significantly increased in HCC samples compared to non-tumor liver tissues[40].Another study showed that the expression of UBE2T mRNA and protein was significantly increased in HCC tissues compared to adjacent non-tumor tissues.A molecular mechanism study showed that UBE2T can suppress the G2/M transition of hepatoma cells by regulating cyclin B1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 1 expression[41].A recent study showed that the expression of UBE2T can be regulated by microRNA miR-212-5p,and overexpression of UBE2T can promote HCC cell proliferation and migration[42].In this study,we have demonstrated that overexpression of UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S was associated with poor prognosis and shorter survival time.These results indicate the gene expression levels of three genes might be useful to assist to predict the outcome of HCC.Remarkably,our analysis revealed that HCC tumors withTP53mutant status exhibited significantly higher expression levels of those genes compared withTP53non-mutant status in tumor samples.This finding shows the potential correlation between the overexpression of investigated genes andTP53mutation status,as well as their contribution to HCC progression.A further mechanistic study needs to be investigated in the field.
From the therapeutic and treatment standpoint,considering the significant roles of UBE2C[43,44],UBE2T[33,45],and UBE2S[46,47]in the ubiquitination process,which contributes to the cellular function and their close association with tumor cell’s function,UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S could be used as a diagnostic biomarker to assist the diagnosis and prediction of the progression of HCC as mentioned above.Most importantly,the causation of the higher level of UBE2 expression,as well as the contributing effect of those highly expressedUBE2genes on the disease outcome should be thoroughly investigated for further exploration of the effective therapeutic strategy discovery.
Further studies from following aspects,such as(1)Identification of causing factors of UBE2 overexpression;(2)investigation of the underlying mechanism on overexpression ofUBE2genes causing disease severity and poor survival outcome of patients;(3)exploration of the associated therapeutic targets of UBE2;(4)the roles of co-expressed genes from the analysis of protein-protein network in HCC;and(5)the relationship of p53 mutation with UBE2 expression;will be studied in the future research to better understand the role of threeUBE2genes in liver cancer.
CONCLUSlON
This bioinformatics study sheds light on the important roles of UBE2C,UBE2T,UBE2S for HCC diagnostic and prognostic as potential biomarkers.In addition,it is appealing to further explore the correlation of those genes with TP53 mutation in HCC and the related mechanisms.
ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS
Research background
The expression of three ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes 2(UBE2)including UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S was significantly increased in HCC samples compared to non-tumor tissues.
Research motivation
To explore potential diagnostic and prognostic markers for HCC.
Research objectives
To identify the potential of UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S as potential biomarkers as HCC.
Research methods
Online database was analyzed with different bioinformatic tools.
Research results
Our data showed that UBE2C,UBE2T,and UBE2S genes were overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)samples compared to non-tumor tissues.Dependent on the cancer progression stage,three UBE2 genes showed higher expression in tumor tissues at all four stages compared to non-tumor control samples.Furthermore,a significantly higher expression of these genes was found in stage 2 and stage 3 cancers compared to stage 1 cancer.Additionally,overexpression of those genes was negatively associated with prognostic outcome and overall survival time.Patients with TP53 mutation showed a higher expression level of three UBE2 genes,indicating an association between UBE2 expression with p53 function.
Research conclusions
This bioinformatics study sheds light on the important roles of UBE2C,UBE2T,UBE2S for HCC diagnostic and prognostic as potential biomarkers.In addition,it is appealing to further explore the correlation of those genes with TP53 mutation in HCC and the related mechanisms.
Research perspectives
Further studies from following aspects,such as(1)Identification of causing factors of UBE2 overexpression;(2)investigation of the underlying mechanism on overexpression of UBE2 genes causing disease severity and poor survival outcome of patients;(3)exploration of the associated therapeutic targets of UBE2;(4)the roles of co-expressed genes from the analysis of protein-protein network in HCC;and(5)the relationship of p53 mutation with UBE2 expression;will be studied in the future research to better understand the role of three UBE2 genes in liver cancer.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Zhang CY and Yang M conceived the idea for this study and collected and analyzed the data,wrote,finalized the manuscript letter,and contributed equally;All authors approved the submitted version and published version.
lnstitutional review board statement:This study was performed without animal and human studies.
lnstitutional animal care and use committee statement:This study was performed without animal and human studies.
Conflict-of-interest statement:Both authors declared that there was no conflict of interest with the content of this study.
Data sharing statement:All the data analyzed in this study originated from publicly available The Cancer Genome Atlas database(TCGA Research Network: https://www.cancer.gov/tcga).
ARRlVE guidelines statement:The authors have read the ARRIVE guidelines,and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the ARRIVE guidelines.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial(CC BYNC 4.0)license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:United States
ORClD number:Chun-Ye Zhang 0000-0003-2567-029X;Ming Yang 0000-0002-4895-5864.
S-Editor:Liu JH
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Liu JH
杂志排行
World Journal of Hepatology的其它文章
- Role of hepatitis Β virus in development of hepatocellular carcinoma:Focus on covalently closed circular DNA
- Emerging curative-intent minimally-invasive therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Saving time and effort: Βest practice for adapting existing patientreported outcome measures in hepatology
- Loco-regional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma:Role of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography
- Βenign focal liver lesions:The role of magnetic resonance imaging
- Pediatric acute viral hepatitis with atypical variants:Clinical dilemmas and natural history
