Clinical significance of the detection of Rh blood group antigens and irregular antibodies in pregnant women with a second pregnancy
2022-06-23XiaoLingFuXingDanZhaoAiHanWengSuJiaoLiXueYuWangKaiNianYang
Xiao-Ling Fu, Xing-Dan Zhao, Ai-Han Weng, Su-Jiao Li, Xue-Yu Wang, Kai-Nian Yang
1. Department of Blood Transfusion, Hainan Women and Children’s Medical Center, Haikou 570311, China
2. Linze County People's Hospital, Zhangye 734200. China
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the phenotype distribution of five antigens of Rh blood group system and the specificity of Rh blood group irregular antibodies in pregnant women with second child.To analyze the relationship between Rh blood group antibody and hemolytic disease of the newborn(HDN) in second-child pregnant women, and to provide laboratory basis for the diagnosis and treatment of hemolytic disease of the newborn(Rh-HDN). Methods: 500 pregnant women with second child were collected as the study group and 500 pregnant women with first pregnancy as the control group(all pregnant women underwent obstetric examination in the integrated obsteric clinic of our hospital from January 2020 to January 2021).To detectethe Rh blood group antigens (D, C, c, E,e) of the two groups of samples,screene the irregular antibodies, identify the specificity of irregular antibodies, determine the titer and record the hemolytic disease of the newborn of pregnant women with positive Rh blood group antibodies. Results: There were 11 Rh phenotypes in the pregnant women with second child in the study group: CCDee(152cases,30.4%),CcDEe(136cases,27.2%)CcDee(84cases,16.8%),ccDEE(30cases,6%),ccDee(31cases,6.2%),CCDEe(14cases,2.8%),ccDEe(9cases,1.8%),cc dee(18cases,3.6%),CCDEE(2cases,0.4%),CcdEe(12cases,2.4%), Ccdee(6cases,1.2%),CCd ee(6cases,1.2%). A total of 42 cases (8.4%) in the pregnant women with second child were negative for RhD. There were 10 Rh phenotypes in the pregnant women with first pregnancy in the control group: CCDee (144cases,28.8%), CcDEe(138cases,27.6%),CcDee(90cases,18%),ccDEE(42cases,8.4%),ccDee(28cases,5.6%),CCDEe(10cases,2%),ccDEe(8cases,1.6%),cc dee(19cases,3.8%),CCDEE(1cases,0.2%),CcdEe(11cases,2.2%),Ccdee (9cases,1.8%).A total of 39 cases (7.8%) in the pregnant women with first pregnancy were negative for RhD.In the pregnant women with second child in the study group, the positive rate of irregular antibody screening was 4.0% (20/500), and the specificity of Rh blood group antibodies was found as follows:anti-E 1.8%(9/500),anti-D 1.4% (7/500),anti-C 0.4%(2/500) and anti-Ec 0.4%(2/500).The positive rate of irregular antibody screening in the pregnant women with first pregnancy in the control group was 0, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P<0.05).Rh-HDN was found in 10 newborns (2%) of the 20 women with positive irregular antibodies in the pregnant women with second child, and the antibody titer during pregnancy was more than 32. No Rh-HDN occurred in newborns in the pregnant women with first pregnancy, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05).Conclusion: Pregnancy stimulation can increase the probability of irregular antibodies in pregnant women, and irregular antibodies in Rh blood group can easily cause Rh-HDN, so attention should be paid to routine detection of five antigens of Rh blood group and irregular antibody screening during prenatal examination. It is helpful for the early detection of Rhblood irregular antibodies and the assessment of fetal or neonatal risk of Rh-HDN.
Keywords:Rh blood group antigen Pregnant woman Irregular antibody detection HDN
1. Introduction
In human erythrocyte blood group system, Rh blood group system is the most complex except ABO blood group system, and in Rh blood group there are mainly 5 antigens that are closely related to clinic, namely D, E, C,c and e antigen. Among them, D antigen has the strongest antigenicity, and there are also weak D and partial D variants. As the two-child policy open, multiple pregnancy pregnant women and always has a history of unexplained abortion of pregnant women, in the process of pregnancy because of the fetus and mother of Rh blood group antigen is different, the red blood cells of the fetus can through the placenta ernter into the mother and stimulate the mother to produce corresponding Rh blood group antibodies,which can cause Rh newborns hemolytic disease(Rh-HDN).Clinical symptoms include neonatal anemia, fetal edema, jaundice, and nuclear jaundice in severe cases. The severity of clinical symptoms is closely related to the number and the titer of blood group antibodies,and the fetal sensitization and the fetal compensatory ability[1],severe cases can result in stillbirth. According to the literature[2,3,4],the blood group antibody that can cause Rh-HDN is not only anti-D,but also anti-E, anti-C, anti-EC antibodies can also cause neonatal hemolytic disease.Therefore,during prenatal prenatal examination,it is of great significance to diagnosis and treatment of RH-HDN by carrying out routine detection of five Rh blood group antigens and irregular antibody screening and dynamic monitoring of the titer of Rh blood group antibodies for the prevention.In this study,we conducted the Rh blood group antigen typing, irregular antibody detection and specificity identification, antibody titer determination and neonatal hemolytic disease detection in second-child pregnant women to explore the relationship between the distribution of Rh blood group antigen phenotype and the antibody and the neonatal hemolytic disease, and to provide experimental basis for clinical early diagnosis and treatment.
2. Materials and method
2.1 Subjects
From January 2020 to January 2021, a total of 500 second-child pregnant women without history of blood transfusion were selected as the study group. Their ages ranged from 25 to 45 years old, with an average age of (33±3.6) years old, gestational age of 28 to 40 weeks, and pregnancy times of 2 to 4 times.A total of 500 firsttrimester pregnant women with no history of blood transfusion were randomly selected as the control group, aged from 20 to 40 years,with an average age of (25±3.6) years and gestational age of 28-40 weeks.
2.2 Reagents and instruments
IgM anti-D antiserum (Shanghai runhai's biotechnology), IgM anti-E antiserum,anti-C, anti-C, anti-e antiserum,anti-human globulin detection reagent, irregular antibody screening cells,2-Me(2-mercaptoethanol) reagent (Shanghai Blood Biomedicine),antibody specific identification cells (Beijing Hantaixu),microcolumn gel card(DiaMed USA).Serum immunology Centrifuge KA-2200 (Kubota,Japan), ID-centrifuge 12S II and ID-incubator 37 SI (DiaMed,USA).
2.3 Experimental methods
The five antigens of Rh blood group were classified by the test tube method , and the irregular antibody detection and specificity identification test and the three tests of neonatal hemolytic disease were all performed by microcolumn gel method. The titer of Rh blood group antibody was determined by the test tube method.All the experimental steps were carried out in strict accordance with the standard operating procedures[5], and the samples were added and the experimental results were recorded in accordance with the kit instructions.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Relevant data were processed by SPSS 20.0 statistical software,and the counting data was expressed by rate (%). Data differences between groups were compared by X2 test, and when P<0.05, the difference is statistic significance.
3. Results
3.1 Distribution of Rh blood group phenotype in the pregnant women with second child and the pregnant women with first pregnancy
There were 11 Rh phenotypes in the pregnant women with second child in the study group: CCDee(152cases,30.4%),CcDEe(136cases,27.2%)CcDee(84cases,16.8%) ,ccDEE(30cases,6%),ccDee(31cases,6.2%),CCDEe(14cases,2.8%),ccDEe(9cases,1.8%),ccdee(18cases,3.6%),CCDEE(2cases,0.4%),CcdEe(12cases,2.4%), Ccdee(6cases,1.2%),CCdee(6cases,1.2%). A total of 42 cases (8.4%) in the pregnant women with second child were negative for RhD. There were 10 Rh phenotypes in the pregnant women with first pregnancy in the control group:CCDee (144cases,28.8%), CcDEe(138cases,27.6%),C cDee(90cases,18%),ccDEE(42cases,8.4%),ccDee(28cases,5.6%),C CDEe(10cases,2%),ccDEe(8cases,1.6%),ccdee(19cases,3.8%),CCD EE(1cases,0.2%),CcdEe(11cases,2.2%),Ccdee (9cases,1.8%).A total of 39 cases(7.8%) in the pregnant women with first pregnancy were negative for RhD.Details were shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Distribution of Rh blood group phenotype in the pregnant women with second child and the pregnant women with first pregnancy
3.2 Positive rate of irregular antibody detection in the pregnant women with second child and the pregnant women with first pregnancy
In the pregnant women with second child in the study group, the positive rate of irregular antibody screening was 4.0% (20/500).The positive rate of irregular antibody screening in the the pregnant women with first pregnancy in the control group was 0, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P<0.05).Details were shown in Table 2.
3.3 Positive rate of irregular antibody test in RhD negative pregnant women
Among 42 RhD negative in the pregnant women with second child in the study group, 7 (16.7%) were positive for irregular antibody detection. There was no positive irregular antibodies of 39 RhD negative in the pregnant women with first pregnancy in the control group, and the positive rate was 0. There was a statistically significant difference (P<0.05) in the positive rate of irregular antibodies between RhD negative in the pregnant women with second child and in the pregnant women with first pregnancy. Details was shown in Table 3.
3.4 Specific distribution of Rh irregular antibody in the pregnant women with second child
Among the 500 pregnant women with second child group in the study group, 20 cases were found to have Rh blood group irregular antibodies. The specific distribution of antibodies was: anti-E 1.8%(9/500), anti-D 1.4%(7/500), anti-C 0.4%(2/500), and anti-EC 0.4%(2/500). No anti-C antibody was found. Details was shown in Table 4.

Table 2 Comparison of positive rate of irregular antibody detection in pregnant women

Table 3 Comparison of positive rate of irregular antibody in RhD negative pregnant women

Table 4 Specific distribution of irregular antibody of Rh blood group in the pregnant women with second child
3.5 The relationship between the irregular antibody specificity and the occurrence of hemolytic disease in their newborns of pregnant women with second child
In the study group, 20 pregnant women with second child were screened positive for irregular antibodies.Rh-HDN was found in 10 neonates delivered of them.There were 3 cases of Ig-G anti-D,6 cases of Ig-G anti-E, and 1 case of Ig-G anti-C.The test results of maternal Rh blood group, pregnancy history, neonatal Rh blood group, antibody specificity and titer, hemolytic disease of the newborn were shown in Table 5.
3.6 Treatment of 10 neonates with hemolytic disease
Follow-up of 10 children with Rh-HDN occurs, they were in anemia of varying degrees and jaundice and other symptoms.Of which five were premature and five were full term.According to the child's hemoglobin value and icteric index,they received the corresponding treatment plan, such as phototherapy, blood transfusion, blood exchange, injection of gamma globulin, etc. 10 children had a good prognosis and were discharged at last.Details was shown in Table 6.

Table 5 The test results of maternal Rh blood group, pregnancy history, neonatal Rh blood group,antibody specificity titer and hemolytic disease of the newborn
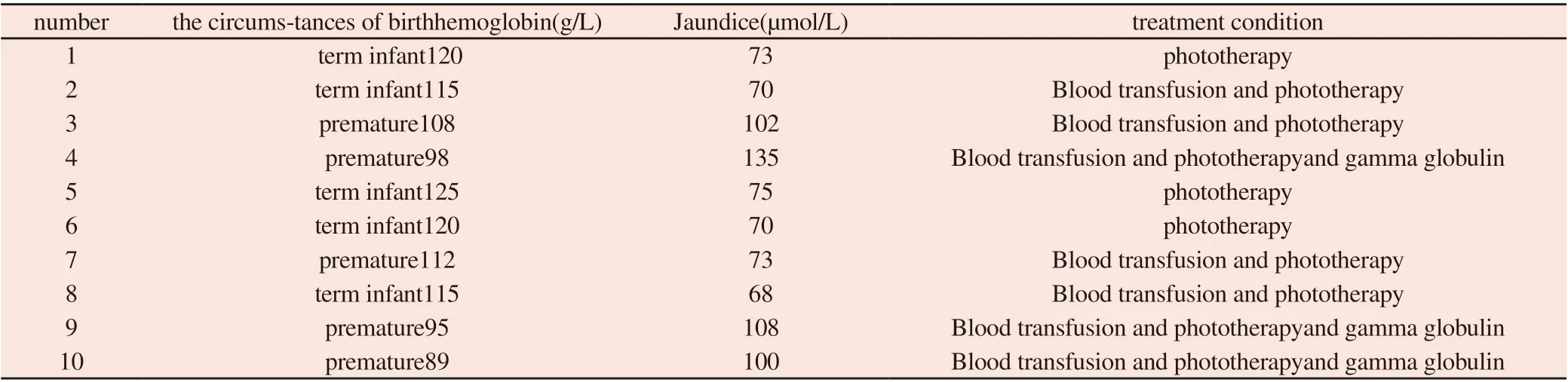
Table 6 The hemoglobin, jaundice and treatment of 10 children with Rh-HDN
4. Discussion
The human red blood cell blood group system has more than 30 types,and the number of antigens has more than 300. In China,ABO and RhD blood group antigens are only routinely detected clinically,but with the development of blood group serological detection technology,other highly immunogenic blood group antigens have been found clinically,for example, the D, E, C, c, e antigens of the Rh blood group system are common antigens with strong immunogenicity.These antigens can produce corresponding immune antibodies due to blood transfusion or pregnancy immune stimulation. According to literature [4,6],anti-e, anti-C, anti-EC and other IgG antibodies of Rh blood group system can combine with corresponding antigens to produce immune reaction, then the clinical symptoms of immune hemolytic reaction and hemolytic disease of newborn appeared, and the severity of Rh-HDN was closely related to the titer of alloantibodies[7,8].Rh-HDN refers to Rh immune antibodies produced by pregnant women during blood transfusion or pregnancy after immune stimulation of Rh blood group antigens they lack, these IgG antibodies enter into the fetus through the placenta and combine with the red blood cells of the fetus to cause the destruction of red blood cells of the fetus or newborn, resulting in hemolysis symptoms. Therefore,it is necessary to pay attention to pregnancy history (including abortion history)and blood transfusion history of pregnant women,and to detect the five antigens of Rh blood group and screen irregular antibodies, and dynamically monitor the titer of Rh blood group antibodies in pregnant women in clinical work. In this study, five antigens of Rh blood group were detected in pregnant women with the second child and with first pregnancy.A total of 500 pregnant women with the second child in the study group had 11 Rh phenotypes, and 42 of them were RhD negative. There were 10 Rh phenotypes and 39 RhD negative phenotypes in 500 pregnant women with first pregnancy in the control group. There was no significant difference in the distribution of Rh antigen phenotypes between the two groups. The positive rate of irregular antibody detection in pregnant women with second child and pregnant women with first pregnancy was 4.0 % and 0,respectively. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05), which was similar to the results reported in literature [9], indicating that the probability and risk of irregular antibody generation would increase with the increase of the number of pregnancy immune stimulation Among the 42 RhD negative pregnant women with second child, 7 were positive for irregular antibodies, with a positive rate of 16.7% (2/12), while 39 RhD negative pregnant women with first pregnancy did not detect irregular antibodies. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05). It suggested that a certain proportion of RhD negative pregnant women with multiple pregnancies produce anti-D antibodies, which is similar to the view reported in literature[10]that multiple pregnancy stimulation can increase the risk of anti-D antibodies. A total of 10 neonates delivered by the pregnant women with second child of irregular positive antibodies developed Rh hemolytic disease, with a incidence rate of 2% (10/500). However,no Rh-HDN was found in neonates delivered by the pregnant women with first pregnancy, suggesting that multiple pregnancy stimulation is the main risk factor for pregnant women to develop Rh blood group alloantibodies.Rh blood group antibody has a greater relationship with Rh-HDN.Clinical attention should be paid to Rh blood group antigen typing and irregular antibody detection in pregnant women with pregnancy history.In this study,20 second-child pregnant women with irregular positive antibodies were followed up, and 10 of them presented symptoms of neonatal hemolytic disease. The results of the neonatal hemolytic disease test showed Rh-HDN, and the sensitized antibodies on the red blood cells of the children were the same as those of their mother,and the titer of Rh antibodies in all of 10 pregnant women was more than 32.However, the titer of Rh isoantibodies in the other 10 second-child pregnant women were all less than 32, and none of the newborns had HDN, suggesting that whether the newborn had hemolytic disease was closely related to the history of pregnancy and delivery, the number and titer of antibodies, the sensitization of the fetus and the compensatory ability. Domestic literature [11-12] also indicates that the titer of Rh blood group antibody is closely related to the severity of Rh-HDN occurrence.It is suggest that clinical attention should be paid to the detection of irregular antibodies during pregnancy and the identification of antibody properties, and the titer of Rh blood group antibody should be determined,which can provided laboratory basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment of Rh-HDN. In this study, 10 cases of Rh-HDN were tracked, including 6 cases of anti-E antibody (60%), 3 cases of anti-D antibody (30%),and 1 case of anti-C antibody (10%). It was found that there were more neonatal hemolytic diseases caused by anti-E antibody than anti-D antibody. The possible reason is that the negative frequency of E antigen is much higher than the negative frequency of D antigen in Chinese Han population. In addition, the immunogenicity of E antigen is second only to D antigen in Rh blood group system,which is similar to the results reported in domestic literature [2,9,13].These results suggest that the same attention should be paid to D, E,C, c and e antigens of Rh blood group system, and routine detection should be carried out. Especially for pregnant women with multiple pregnancy history and abortion history, the stimulation of these antigens is easy to produce corresponding immune antibodies and cause hemolytic reaction. Therefore,during the prenatal examination of pregnant women ,the detection of five antigens of Rh blood group and irregular antibodies is of great significance for prenatal diagnosis and prevention and treatment of hemolytic disease of newborn.
In conclusion, the phenotypic distribution of Rh blood group antigen in pregnant women with second child is closely related to the generation of Rh blood group antibody, and the probability of Rh-HDN occurrence in newborns of pregnant women with irregular antibody of Rh blood group is relatively high.And the antibodies causing Rh-HDN can be single antibody or combined antibody,suah as anti-D antibody, anti-E antibody, anti-C antibody, or anti-EC antibody, and the level of antibody titer is related to the severity of neonatal hemolytic disease.Therefore,with the lifting of the twochild policy and the increasing number of pregnancies,clinical doctors should be fully realized that pregnant women will also increase the risk of produce irregular antibody,and attention should be paid to the detection of the five antigens of Rh blood group and irregular antibodies in pregnant women with second child during pregnancy, and detection of irregular antibody of Rh blood group and monitoring of antibody titer shoud be early,and intrauterine intervention can be carried out when necessary.It is of great significance for the early prevention and treatment of hemolytic disease of newborn, and improving the quality of newborn birth and ensure the safety of blood transfusion.
Author’s contribution
Fu Xiaoling was responsible for the conception and design of the paper, writing the paper, and analyzing and interpreting the results.Zhao Xingdan and Weng Aihan were responsible for experimental operation and feasibility analysis of the experiment. Li Sujiao and Wang Xueyu were responsible for data collection and collation;Yang Kainian was responsible for statistical processing and paper revision.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress on the role of gut microbiota dysregulation in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy
- Research on the effect of Bletilla striata and the mechanism of the treatment of bronchoplumonary inflammation based on network pharmacology
- Efficacy and safety of Nephritis rehabilitation tablet combined with Valsartan for chronic glomerulonephritis: A system review and metaanalysis
- Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Endostar combined with vinorelbine and cisplatin in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
- Randomized controlled trial of Qing Gan Huo Xue Prescription in the treatment of alcoholic liver cirrhosis
- Mechanism of Xingnaojing injection intervention in cerebral ischemiareperfusion rat model based on GC-MS metabolomics
