Mechanism of Xingnaojing injection intervention in cerebral ischemiareperfusion rat model based on GC-MS metabolomics
2022-06-23HaoQiLiuHanLaiZhangYuanYuanLiKeSongNaAnLiQinWangYiKunSunYongHongGao
Hao-Qi Liu, Han-Lai Zhang,2, Yuan-Yuan Li, Ke Song, Na An, Li-Qin Wang, Yi-Kun Sun, Yong-Hong Gao✉
1. Key Laboratory of Chinese Internal Medicine of Ministry of Education and Beijing, Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
2. Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the protective effect of Xingnaojing injection on cerebral ischemiareperfusion in rats and its metabolic pathway and mechanism. Methods: The cerebral ischemia reperfusion model of rats was established by suture occlusion. After successful model evaluation, he rats were randomly divided into model group and Xingnaojing group with eight rats in each group. In the sham operation group, only blood vessel separation was performed without embolization. Xingnaojing group was given intraperitoneal injection, model group and sham operation group were given the same dose of normal saline, twice a day. Three days later,HE staining and GC-MS metabolomics were used to detect the changes of endogenous metabolites in the rat brain tissue. Principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) were used to screen out differential metabolites and analyze their metabolic pathways. Results: Endogenous metabolites were disturbed after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Seventy-one different metabolites were screened from the model group and the sham group, of which three were down-regulated and sixty-eight were up-regulated. Eighty-eight different metabolites were found between Xingnaojing group and sham operation group, among which eight were down-regulated and eighty up-regulated. After screening of Xingnaojing group and model group, twelve different metabolites were obtained, among which seven were down-regulated and five up-regulated. By analyzing the differences of metabolites, Xingnaojing injection was considered to be involved in the metabolic pathway after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats, including amino acid metabolism (beta alanine metabolism, alanine, glutamic acid and aspartic acid metabolism,histidine metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism), glutathione metabolism, pyrimidine metabolism, ABC transporter, nitrogen metabolism and other metabolic pathways. Conclusion:Xingnaojing injection can restore the levels of metabolites in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats in certain degrees, mainly through amino acid metabolism, ABC transporter, glutathione metabolism and other metabolic pathways to regulate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.
Keywords:Xingnaojing injection Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion Metabolomics GC-MS
1. Introduction
Stroke is a common disease in clinic because of its high morbidity, disability and mortality. Among stroke diseases, acute ischemic stroke accounts for 60% ~ 80% of stroke diseases [1].The occurrence of cerebral ischemia injury is a complex process,including inflammatory response, free radical damage and apoptosis[2]. Metabolomics is a technique that interprets the pathological and physiological processes of a disease and searches for diagnostic markers or prognostic biomarkers associated with the disease.Xingnaojing injection is derived from "Angongniu huang Pill" in"Wenbingtiaobian". It is mainly composed of borneol, gardenia,musk and tumeric, and has important functions of anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation. Studies have shown that Xingnaojing injection can play a protective role on brain tissue after entering the human body [3]. Previous studies of our group have shown that Xingnaojing injection has a certain protective effect on brain tissue in penumbra region in the acute stage of cerebral ischemia, and alleviates the damage to microvessels, glial cells and neurons after cerebral ischemia [4]. However, the effects of cerebral ischemiareperfusion injury on metabolites have not been reported. This study used rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model and metabolomics related technologies to explore the changes and related pathways of endogenous metabolites in brain tissue after the intervention of Xingnaojing injection, providing a new theoretical basis for clinical application.
2. Data and methods
2.1 Animal
There were 24 SPF male SD rats, weighing 260±10g. All the experimental animals were provided by Beijing Vitonglihua Experimental Animal Technology Co., LTD. (License Number:[SCXK (Beijing) 2016-0006]). All experimental animals in this study were kept in barrier Environmental Animal Department,Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (License No. : [SCYK (Beijing) 2015-0001]). All animals eat water freely and keep bedding clean. This experiment has been approved by the Medical And Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Dongzhimen Hospital of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and the regulations on the management of experimental animals have been strictly observed throughout the experiment. The animal experiment ethics number is 19-06.
2.2 Main reagents and equipment
Xingnaojing Injection (Wuxi JiminXinxinShanhePharmaceutical Co., LTD, National Drug approval Z32020563), Suppant Thread(Beijing Xinong Technology Co., LTD, 2636-A4), Medical silk Braiding Thread (Shanghai Pudong Jinhuan Medical Products Co., LTD, XS6-0), Paraffin sectioning machine, Tissue embedding machine, Tissue cooling table, Tissue exhibition machine (Leica/Germany), adhesive slide (Fuzhou Meixin Biotechnology Co.,LTD), Optical microscope (Olympus BX60/ Japan), Thermostatic heater (HARV ARD/ USA), L-2-chlorophenylalanine (Shanghai Heng Chuang Biotechnology Co., LTD), PBS buffer, methanol,water, n-hexane (HPLC grade, CNW Technologies), pyridine,TBSTFA+1%TMCS, 97% O-methyl hydroxylamine hydrochloride,(CNW Technologies), Chloroform (AR grade, Titan), 11 fatty acid methyl esters (Larodan, NC-CheK, DR), Gas bath constant temperature oscillator (Jiangsu Huanyu Science Instrument Factory),frozen concentration centrifugal dryer (Jiangsu Taicang Huamei Biochemical Instrument Factory), vacuum drying oven (Shanghai Huitai Co., LTD), chromatographic column DB-5MS (Model: 30M 0.25mm 0.25μm), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (Agilent/USA).
2.3 Model preparation
The cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model of rats was prepared by suture supposation method. Rats were given 1% pentobarbital(0.5mL /100g) in abdominal anesthesia and placed on a 37℃thermostatic blanket during the operation. After the right common carotid artery was exposed and the external carotid artery and the internal carotid artery were separated to the bifurcation, the external carotid artery was ligated near the bifurcation and fused with an electric coagulation device. An incision was cut at the proximal end of the external carotid artery about 4mm from the bifurcation. The length of the insertion of the cord plug to the internal carotid artery was about 18-22mm away from the branch, and stopped when there was resistance. Gauze soaked with normal saline was used to cover the wound. After 90min of ischemia, the cord plug was pulled out and perfusion was performed for ligation. After the animals woke up, the modified neurological deficit score was used to assess the neurological function of rats, and a score of 7-12 could be regarded as successful modeling [5]. After modeling, the rats were placed in a clean cage and allowed to eat freely.
2.4 Grouping and administration
After successful modeling, 8 rats in each group were randomly divided into model group and Xingnaojing group. The administration time was 2h after successful modeling. After converting the clinical dosage according to the body surface area, xingnaojing group was intraperitoneally injected with xingnaojing injection at 0.18ml/100g.The model group and the sham operation group were injected with the same dose of normal saline. Each group was given 2 times a day.
2.5 HE dyed
After 3 days of administration, 2 rats in each group were anesthetized and fixed on the anatomical board in the back position.The chest cavity was cut open to expose and free the heart. The perfusion needle was inserted into the aortic arch from the left ventricle through the apex of the heart, the abdominal aorta was clipped and the right atrial appendage was cut open, and 150ml sterile normal saline was perfused until the lungs and front PAWS turned white, and 150ml 4% paraformaldehyde was perfused.The brain was dehydrated, transparent and embedded in paraffin 24h after decapitation. Paraffin sectioning machine was used for continuous coronal sectioning (thickness 4μm). After baking for 3h,HE staining was performed. After baking for 30min, the slices were placed in xylene ⅰ, ⅱ and ⅲ tanks for dewaxing for 15min each. It was transferred to the alcohol tank and tap water under hydration for 5min respectively. Hematoxylin dyeing solution was dyed for 8min,the excess dyeing solution was washed out and differentiated with 0.5% hydrochloric acid alcohol for 10s, and then washed for 10min to return blue. The slices were placed in 0.5% eosin dye solution for 5min, and the excess dye solution was washed away. After the gradient dehydration of 70%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 100% ⅰ and 100%ⅱ alcohol tanks for 5min each. Xylene I, II and III were transparent for 10 min, and the tablets were sealed. The morphological changes of the infarct area and surrounding brain tissue were observed and photographed with light microscopy.
2.6 Metabolomics in GC-MS
2.6.1 Sample processing
After anaesthesia, 6 rats in each group were decapitated and cerebral cortex tissue was extracted from the infarct. After rinsing with 0.9% normal saline, the rats were placed in a cryopath tube and frozen with liquid nitrogen for sample processing. 30mg brain tissue was added to the centrifugal tube containing internal label, placed in the refrigerator at -80℃ for 2min, then ground, 120μL chloroform was added and mixed for 2min, and 200μL supernatant was extracted after ice bath ultrasound, standing and centrifugation. The quality control samples were dried in a centrifugal concentrated dryer,followed by adding 80μL pyridine methoxylamine hydrochloride solution to vortex for 2min, then reacted with oxime in an incubator at 37℃ for 90min, adding 80μL BSTFA(containing 1%TMCS) and 20μL n-hexane, adding 10μL 11 internal standards to vortex for 1h,and leaving at room temperature for 30min. Metabolomics analysis was performed.
2.6.2 Chromatographic conditions and mass spectrometry conditions
The carrier gas was high purity helium and db-5MS capillary column. The initial temperature of the column temperature box was 60℃(maintained for 0.5min), and the temperature was respectively 8℃/min to 125℃, 5℃/min to 210℃, 10℃/min to 270℃ and 20℃/min to 305℃(maintained for 5min). Electron bombardment ion source (EI) Ion source temperature is 230℃, quadrupole temperature is 150℃, electron energy is 70eV.
2.7 The data processing
The data were analyzed by principal component analysis (PCA)and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLSDA). According to the variable weight value (VIP) > 1 obtained by OPLS-DA model and the probability value P(P < 0.05) obtained by T test, the difference metabolites between groups were screened out.
3. Result
3.1 Pathological changes
HE staining results were shown in Figure 1. In the sham operation group (A), the brain cells were arranged in A dense and orderly manner, and the basic morphology and structure of the rats were normal without obvious pathological changes. In model group (B),the infarct area of rat brain tissue was necrotic, the cell arrangement was loose and irregular, the cells were edema and degeneration,and the nuclei were wrinkled. Compared with the model group, the brain structure of the rats in the Xingnaojing group (C) was less disordered, the nuclear structure was clearer, the degree of nuclear pyknosis and nuclear lysis was reduced, and the brain injury caused by cerebral ischemia and reperfusion was reduced.

Figure 1 Pathological changes of brain tissue structure in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion 3 days after surgery (HE staining, ×200)
3.2 Superposition of total ion current in rat brain tissue quality control samples
As shown in Figure 2 below, by comparing the overlap of the total ion current diagram of QC samples, it can be concluded that the peaks are well separated, and the reaction degree of each peak is basically the same as the retention of time. On this basis, this study continued to use a variety of analysis methods to analyze the differences in metabolites between the Xingnaojing group, the model group and the sham operation group.

Figure 2 Superposition of total ion current in rat brain tissue quality control samples
3.3 PCA score graph and its system stability analysis
PCA scores (Figures 3 and 4) are shown below. Each symbol point in the score graph represents a brain tissue sample, and the different spatial distribution of each group of samples represents the metabolic status of different groups of samples. The separation trend between the model group and the sham group was very obvious, indicating that there were significant differences in the metabolites of the brain tissue in the model rats with cerebral ischemia and reperfusion.The separation between xingnaojing group and model group was obvious, and the difference between the two groups was large,indicating that the endogenous metabolites of Xingnaojing injection had significant changes after intervention.

Figure 3 PCA score of mode group and sham operation group

Figure 4 PCA score of Xingnaojing group and model group
3.4 Orthogonal Partial least Squares Discriminant Analysis(OPLS-DA)
The differences among groups were further found, and the rats brain tissue samples were analyzed by supervised OPLS-DA analysis. The results showed as shown in Figure 5 and 6 below, the OPLS-DA score of the model group and the sham operation group,and the Xingnaojing group and the model group were significantly separated, and the degree of clustering was good, indicating that there were significant differences in endogenous metabolites between the model group and the sham operation group, and between the Xingnaojing group and the model group. In the OPLSDA displacement diagram, the closer the values of R2X and R2Y are to 1, the better the model fitting data is; and when Q2intercept on the Y-axis is less than 0, the analysis model is reliable. In the OPLS-DA replacement diagram, R2X =0.853 and R2Y=0.997 were compared between the model group and the sham operation group, and R2X=0.788 and R2Y=0.887 were compared between the Xingnaojing group and the model group, indicating that the model fitting effect was good. The intercept of Q2 on the Y-axis was -0.077 in the model group and -0.097 in the Xingnaojing group compared with the model group, indicating that the analytical model was stable and reliable.

Figure 6 OPLS-DA score and OPLS-DA replacement test of Xingnaojing and model group
3.5 Results of differential metabolite analysis
After analysis and screening, twelve differential metabolites were obtained in xingnaojing group and model group. Among these differential metabolites, five were up-regulated and seven were down-regulated. The up-regulated metabolites included L-glutamine,boric acid, spermidine, carbamate, 1, 3-dihydroxy pyridine and other metabolites. The down-regulated differential metabolites include 3-amino-isobutyric acid, aspartic acid, biphenyl, dodecanol,cytosine, gallic acid, myxic acid and other metabolites. The results of differential metabolites are shown in Table 1.
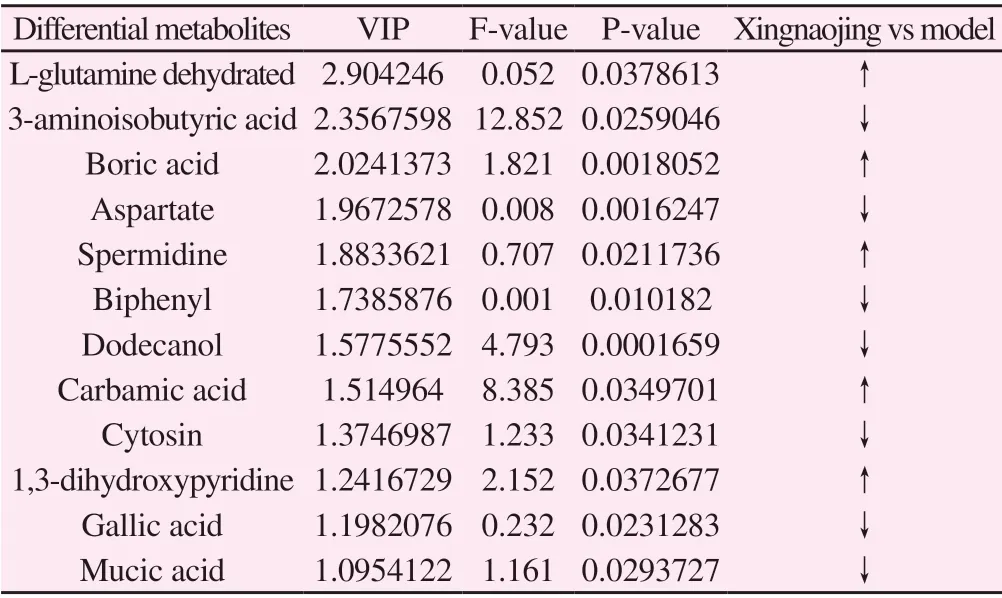
Table1 Results of different metabolites between model group and Xingnaojing group
3.6 Enrichment analysis of metabolic pathways
The metabolic pathway enrichment analysis of twelve differential metabolites was carried out through KEGG metabolite database,and the path analysis results were obtained as shown in Figure 7.In the Figure 7. The ordinate represents metabolic pathways and the abscissa represents enrichment factors. The enrichment factors showed the enrichment degree of metabolites in this pathway. The results showed that amino propionic acid metabolism, alanine,aspartic acid and glutamic acid metabolism, pyridine metabolism,histidine metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism, and glutathione metabolism are important related metabolic pathways.

Figure 7 Bubble diagram of metabolic pathway
4. Discussion
Metabolomics is the observation of biological systems that have been disturbed or stimulated, and the study of changes in the metabolites of an organism over time or changes in metabolites.Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury refers to the condition in which the blood flow of brain tissue and cells is restored after a period of cerebral ischemia, but the degree of injury of the tissue and cells is aggravated. Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury is by no means a result of single link, single factor, and multiple and single pathways[6]. A large number of studies have shown that Xingnaojing injection can inhibit inflammation and autophagy, reduce oxidative stress and nerve injury, and inhibit neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion [7-8]. In this paper, HE staining method was used to observe the pathological and physiological changes of brain tissue,and the regulation metabolites of Xingnaojing injection were further discussed based on GC-MS metabolomics technology. HE staining results showed that the brain tissues of the model group showed certain degree of necrosis, uneven arrangement of histiocytes and nuclear shrinkage. However, in the xingnaojing group, the disorder of brain tissue was significantly reduced, the nuclear structure was clearer, and the degree of nuclear pyknosis was also decreased,suggesting that Xingnaojing injection could protect and improve cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats.
The metabolic results showed that endogenous metabolites were disordered after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. A total of 71 metabolites were found to be associated with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion after comparison between the model group and the sham operation group. Mainly involved in the biosynthesis of ammonia acyl, cancer center of carbon metabolism, starch and sucrose metabolism, ABC transporters, GSH metabolism, galactose metabolism, valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis, arginine and proline metabolism, beta alanine metabolism, phenylalanine,tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, and fructose Mannose metabolism, etc. A total of 12 different metabolites were found between the Xingnaojing group and the model group. Involved in beta alanine metabolism, pyrimidine metabolism, ABC transporters, nitrogen metabolism, alanine,glutamic acid and aspartic acid metabolism, GSH metabolism,histidine metabolism, ascorbic acid and uric acid metabolism of al,glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, cysteine and methionine metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism, and many other metabolic pathways.
Amino acid is not only the basic constituent unit of protein, but also a particularly important energy source for human metabolism.Its abnormal situation will directly affect the synthesis of protein and human metabolism [9]. In the pathophy and syological process of cerebral ischemia and reperfusion, amino acid metabolism runs through the whole process, which is the most significant metabolic feature [10]. As one of the most abundant amino acids in muscle and liver, L-glutamine plays an important role in growth and immunity,anti-oxidative stress, anti-infection and fatigue, maintenance of acidbase balance and other aspects [11]. In addition, l-glutamine, as a precursor of the antioxidant glutathione (GSH), has an important role in antioxidant stress [12]. Studies have shown that L-glutamine can reduce the volume of cerebral infarction in ischemic injury mice and has the effect of restoring neurobehavior [13]. The results of this study showed that l-glutamine was significantly increased in the Xingnaojing group compared with the model group, indicating that Xingnaojing injection may regulate amino acid metabolism through the up-regulation of L-glutamine, so as to promote the improvement of cerebral ischemia.
Some metabolic differences, such as β-alanine, glutamate and arginine, also improve cerebral ischemia reperfusion through amino acid metabolism pathway. β-alanine is a non-proteinogen β-amino acid that is a known rate-limiting precursor to the histidine containing dipeptide carnosine [14]. Studies have shown that β-alanine, a major energy dietary supplement, can improve athletic performance by effectively increasing muscle carnosin levels [15]. As an excitatory amino acid, glutamate maintains the normal operation of the body. Some studies have shown that [16] high concentration of glutamate can overactivate glutamate receptors, leading to the destruction of the blood-brain barrier. Arginine is a conditional amino acid. The level of arginine decreases after the body is damaged and pathological changes occur. Studies have shown that ischemic brain injury leads to decreased arginine content in blood and cerebrospinal fluid, and arginine content is negatively correlated with cerebral infarction and neurological function impairment [17-18]. Spermidine is a key arginine metabolite in mammalian tissues, and it has been found that spermidine plays a key role in regulating vascular tone[19]. Metabolomics results showed that the pathological process of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion was accompanied by changes in the levels of amino acids and their derivatives. For example, in the differential metabolites comparison between the Xingnaojing group and the model group, the levels of spermidine metabolites were upregulated after xingnaojing injection intervention. These results indicated that Xingnaojing injection could normalize the level of metabolites.
In addition, ABC transporter and glutathione metabolism also play an important role. ABC transporters is the largest living species, type one of the most abundant protein superfamily, and steady state in the cell, signal transduction, drug metabolism and nutrition absorption plays a very important role in many biological processes, they limit or reduce nerve toxin accumulated in the brain to play a protective function [20]. Glutathione is the most abundant antioxidant in human body and plays a crucial role in the antioxidant defense system and the maintenance of neuronal REDOX homeostasis [21]. In the enrichment pathway in this study, it was found that the different metabolites in Xingnaojing group could regulate the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rat model through ABC transporter, glutathione metabolism and other pathways.
These studies indicate that Xingnaojing injection has a good therapeutic effect on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats, reduces nerve cell damage, and plays a regulatory role through amino acid metabolism, ABC transporter, glutathione metabolism and other pathways. There are still some deficiencies in this study, which requires further verification and analysis of differential metabolites.In the future, the discovered metabolites and pathways as well as related biological processes need to be studied in vivo and in vitro.
Author’s contribution
The experimental design was the corresponding author Gao Yonghong, the animal modeling experiment was the first author Liu Haoqi and Zhang Hanlai, the pathological staining experiment was the third author Li Yuanyuan and the fourth author Song Ke, the statistics were the fifth author Anna and the sixth author Wang Liqin,the seventh author Sun Yikun and the corresponding author Gao Yonghong were reviewed. The article was co-written by Liu Haoqi and Zhang Hanlai, with equal contributions.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress on the role of gut microbiota dysregulation in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy
- Research on the effect of Bletilla striata and the mechanism of the treatment of bronchoplumonary inflammation based on network pharmacology
- Efficacy and safety of Nephritis rehabilitation tablet combined with Valsartan for chronic glomerulonephritis: A system review and metaanalysis
- Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Endostar combined with vinorelbine and cisplatin in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
- Clinical significance of the detection of Rh blood group antigens and irregular antibodies in pregnant women with a second pregnancy
- Randomized controlled trial of Qing Gan Huo Xue Prescription in the treatment of alcoholic liver cirrhosis
