Three-dimensional echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular volume in different heart diseases using a fully automated quantification software
2022-06-23ChenKePanBoWenZhaoXuanXuanZhangMeiPanYanKaiMaoYuanYang
lNTRODUCTlON
Accurate quantification of the left heart volume and left ventricular ejection fraction(LVEF)is important for patients with heart diseases[1,2].Dilated cardiomyopathy(DCM),coronary heart disease,and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy(HCM)are some of the most common heart diseases that cause changes in left heart volume and function in clinical studies.Two-dimensional(2D)transthoracic echocardiography is currently the first-line imaging method for the diagnosis of cardiovascular patients and plays an indispensable role in the assessment of hemodynamics,cardiovascular structure size,and cardiac function.The functional evaluation method relies on geometric assumptions;however,there are certain limitations in clinical application.Traditional three-dimensional echocardiography(3DE)does not rely on geometric assumptions and provides true volume data to accurately assess left heart volume and function.Nevertheless,obtaining high-quality 3D volume data depends on the experience and analysis of the operating doctor;furthermore,the process is cumbersome and time-consuming,limiting its routine clinical application[3].
MATERlALS AND METHODS
Patient characteristics
A total of 197 consecutive clinical patients from July 2020 to October 2020 were selected.Forty-seven were excluded for the following reasons: 3 of 17 consecutive myocardial segments were unclear(
= 20);difficulty with holding one’s breath(
= 7);and generation of an incorrect left ventricular mold by automatic quantification software that could not be manually edited and corrected(
= 20).A total of 150 patients were finally enrolled in this study and divided into the following four groups.Group A was the control group(
= 42,18 males,24 females),with an average age of 39 ± 12 years and an average body surface area(BSA)of 1.68 ± 0.13 m².Patients were included after ruling out organic heart diseases by evaluating the patient’s medical history and family history and obtaining an electrocardiogram or conventional echocardiogram.Group B was the dilated cardiomyopathy(DCM)group(
= 35,21 males and 14 females),with an average age of 53 ± 15 years and an average BSA of 1.69 ± 0.16 m²;4 patients also had atrial fibrillation,and 15 had an implanted pacemaker.Patients were those without significant epicardial coronary artery obstructions but with an enlarged left ventricle and diminished left ventricular wall motion on ultrasound.Group C consisted of patients with ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction(AMI)(
= 41,28 males and 13 females),with an average age of 63 ± 11 years and an average BSA of 1.67 ± 0.12 m²;11 patients had a ventricular aneurysm,9 had atrial fibrillation,11 were implanted with a pacemaker,and 4 had a history of mitral valve replacement.All patients had a history of AMI and coronary angiography and ultrasound confirmed segmental or diffuse wall motion abnormalities.Group D was the HCM group(
= 32 cases,22 males and 10 females),with an average age of 55 ± 14 years and an average BSA of 1.73 ± 0.17 m².Five patients had atrial fibrillation.The diagnostic standard for HCM,thickness of at least one myocardial segment ≥ 15 mm that cannot be explained by load alone,was in accordance with the adult standard in the 2014 European Cardiology Association HCM Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines.The study was approved by the ethics committee of Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital,Zhejiang University College of Medicine,with a wavier for individual consent by the committee owing to the retrospective study design.
Then a gust of wind came and blew Curdken s hat away, so that he had to fly over hill and dale after it, and the girl in the meantime quietly combed and plaited her hair: all this the old King observed, and returned to the palace without anyone having noticed him
Instruments
All patients underwent 2D and 3D transthoracic echocardiographic examination using a Philips EPIQ 7C echocardiography diagnosis instrument with an X5-1 probe(1-5 MHz).The instrument was equipped with the HeartModel(HM)3D image acquisition mode and the QLab10.5 software package,including a 3D quantification(3DQ)Advance plug-in image analyzer.A senior doctor with more than 10 years of experience in echocardiography was responsible for the image collection;another 2 sonographers who had been engaged in echocardiography for more than 5 years were responsible for processing the data.
M-Mode and 2D echocardiographic study
After placing the subject in the left lateral position,the electrocardiogram leads were connected,and the instrument parameters were adjusted to obtain the best imaging.M-mode echocardiography was used to measure the left ventricular end-diastolic and end-systolic diameters,and the machine calculated the left ventricular volumes and LVEF automatically by the Teichholzholz method.Images from at least 4 cardiac cycles in dynamic apical two-chamber,three-chamber,and four-chamber views were obtained.Using the biplane Simpson method in the instrument,the endocardium was automatically tracked and then manually adjusted if necessary.The measurement results were recorded as the average of the 3 cardiac cycles with the best image quality(IQ).
3D echocardiographic study
Among all volumetric data collected,93 patients required manual editing,including 20 patients in group A(47%),15 in group B(42%),26 in group C(63%),and 32 patients in group D(100%).Of the cases with a
-Index > 50%,45% of the images still needed to be edited again.
The number and/or pattern of three often appears in fairy tales to provide rhythm and suspense35. The pattern adds drama and suspense while making the story easy to remember and follow. The third event often signals a change and/or ending for the listener/reader. A third time also disallows36 coincidence such as two repetitive events would suggest.

3 DQ method: Offline analysis of the 3D images collected in full volume mode was performed using QLab 10.5 software and the 3DQ Advance plug-in to analyze the images acquired in the apical fourchamber and two-chamber views and the left ventricular short axis view,and the plane on the 2D images was manually corrected.The average of the 3 best-quality cardiac cycles was taken as the measurement result,while in the software,the IQ index was calculated;a value above 50% was defined as good IQ,while that below 40% was defined as poor IQ.
No, said the little one, you must remain at your post, but I shall give you a piece of good advice; you shall go up into the pulpit, and remain standing there
Problems are there to be faced and overcome. We cannot achieve anything with an easy life. Helen Keller was the first deaf and blind person to gain a University degree. Her activism and writing proved inspirational. She wrote, Character cannot be developed in ease and quiet. Only through experiences of trial and suffering can the soul be strengthened, vision cleared, ambition inspired and success achieved.
The left ventricular volume and LVEF obtained by HM through different methods were different among patients with different cardiovascular diseases.For example,in the DCM group,the difference in the quantitatively measured LAESV by the HM-RE and 3DQA methods was greater than that in the other groups,but the correlation for LVEDV,LVESV and LVEF between the two groups was lower.In the SWMA group,the differences in the values of LVEDV,LVESV and LVEF measured by HM were greater than those of the other groups.Therefore,the morphological changes of the heart cavity and the contour of the endocardial surface directly affect the measurement results of HM.In patients with enlarged hearts,in the process of obtaining 3D images,the increase in scanning angle leads to a decrease in frame rate,which affects IQ.For patients with significantly enlarged hearts,HM is even unable to obtain a complete 3D image for analysis.
Advanced cardiac 3DQ(3DQA)method: The QLab 10.5 software 3DQ plug-in was used to analyze the 3D images collected in full volume mode using the images obtained in three cross-sectional views used for the 3DQA method.After determining the end-diastolic frame,the region of interest was drawn on the four-chamber and two-chamber views of the apical long axis to obtain the left ventricular area model;the steps were repeated for the end-systolic frame.The above steps were repeated,and the average of the 3 best-quality cardiac cycles was taken as the measurement result.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 23.0 software and GraphPad Prism 8 software were used to analyze the data.The mean ± SD is used to represent the measurement data,and depending on the distribution of the data,parameter comparisons between the groups were performed using one-way ANOVA or the matched samples rank-sum test.The correlation and agreement between two sets of measurements were tested by Spearman’s correlation coefficient.Bland-Altman analysis was performed by calculating the bias and the limits of agreement;if more than 90% of the points fell within the 95% confidence interval,the consistency was considered high.Statistical significance was defined as
< 0.05.The intragroup and intergroup repeatability of the different quantitative methods are expressed by the coefficient of variation.
RESULTS
Study population and feasibility
After the above steps,the xPlane mode was started,the angle and instrument settings were adjusted,and the frame rate was kept > 18 frames/s.The patient was instructed to maintain a breathhold,at the end of expiration,after which the “HM ACQ” button was clicked to collect 6 consecutive cardiac cycles.Clicking the “HM” button,the system automatically calculated the LV end-diastolic volume(LVEDV),LV end-systolic volume(LVESV),LVEF and left atrial end-systolic volume(LAESV).Using the boundary setting HM80-40,the average of the 3 cardiac cycles with the best IQ was obtained to record the HM data without endocardial boundary editing(HM-NE).Then,the endocardial boundary was manually fine-tuned as needed,and the average of the 3 best-quality cardiac cycles was again obtained to record the HM data with endocardial boundary editing(HM-RE).One week later,the same observer analyzed all the images again,while a second observer analyzed them for the first time(Figure 1).
Comparison of LV volumes,LVEF,and LAV measured by different methods
The differences in the LVEDV,LVESV,LVEF and LAESV values measured by the different methods in the four groups were statistically significant(
< 0.05 for all),as shown in Table 1.Among them,the LVEDV and LVESV of group B were higher than those of the other groups(
< 0.05 for all),the LVEF of group B was lower than that of the other groups(
< 0.05 for all),and the LVEF of group D was higher than that of the other groups(
< 0.05 for all).In all groups,the measured values of LVEDV,LVESV,LVEF and LAESV obtained by HM-NE and HM-RE were greater than those of the 3DQA and Simpson methods(
< 0.05 for all).
They embraced and kissed each other, and the Queen went to the King, who was standing16 by in great astonishment17, and began to speak to him, saying, Dearest husband, now I can speak and tell you openly that I am innocent and have been falsely accused
Comparison between HM-NE and HM-RE
When Muriel and I reached our little garden and sat down, his words came back to me. God had spoken through an inebriated18 old derelict. It is you who is whispering to my spirit, I likes it, tha s good, I said aloud. I may be on the bench, but if you like it and say it s good, that s all that counts.
Correlation and consistency between M-Mode and two- and three-dimensional echocardiography
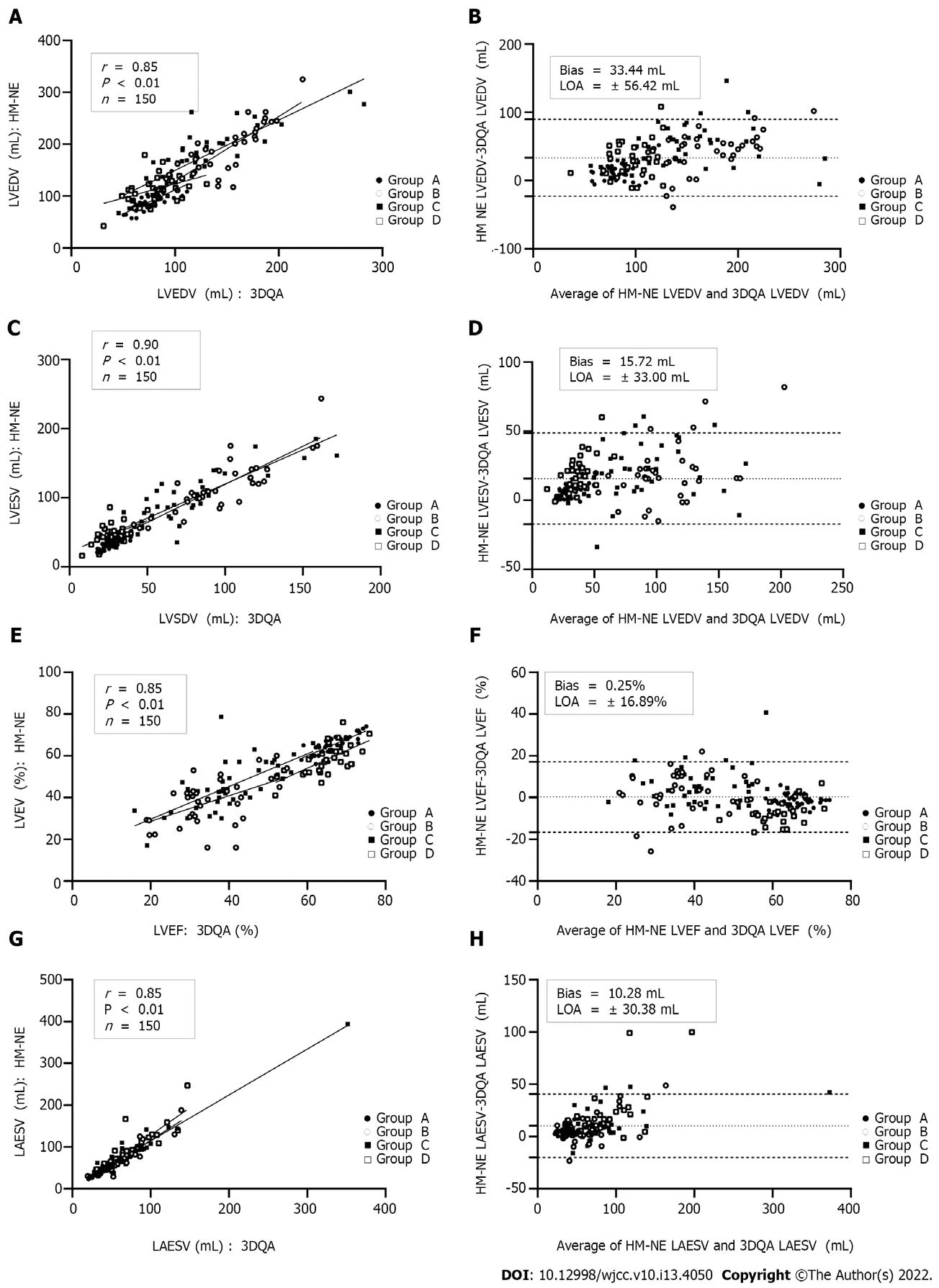
Compared with those measured by 3DQA,the volume values measured by HM-NE and HM-RE in eachgroup were higher.Among all the methods,the 3DQ measurements had the highest correlation with 3DQA(
r
= 0.96-0.98,
< 0.01 for all),and the consistency was good(LVEDV bias = 2.4 mL,LVESV bias= 1.3 mL,LVEF bias = 0.1%).The correlation between the LVEDV,LVESV,LVEF values measured by HM-NE and 3DQA(
r
= 0.85-0.90,
< 0.01 for all)was similar to that of the Teichholz method,but the deviation bias(LVEDV,33.4 mL,LVESV,15.7 mL,LVEF,0.2%)was smaller than that of the Teichholz method.After fine-tuning,the correlation(
r
= 0.91-0.95,
< 0.01 for all)and consistency(bias: LVEDV,28.1 mL;LVESV,14.9 mL;LVEF,0.0%;LAESV,8.1 mL)were all increased;the Teichholz method had the lowest correlation with 3DQA(
r
= 0.82-0.89,
< 0.01 for all)(Table 3,Figures 2 and 3).



A considerable number of heart patients are shown to have atrial fibrillation in routine clinical practice.Therefore,some studies recommend measuring several consecutive cardiac cycles to obtain the average value of the quantitative parameters[20].Guidelines from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Cardiovascular Imaging Association indicate that the assessment of patients with atrial fibrillation must include at least 5 cardiac cycles[1].However,the guidelines also indicate that it is feasible to use representative cardiac cycles to obtain quantitative parameters in clinical practice.Otani
[21]used HM to automatically quantify and manually track the left ventricular volume and LVEF of 88 patients with atrial fibrillation.The results showed that the measurements from HM were highly correlated with those from 3DQA(
= 0.88-0.98),and left ventricular function in particular had high repeatability[coefficient of variability(CV)< 5%],indicating that HM could be used to assess atrial fibrillation.The study also used HM to evaluate the left heart parameters of all patients for 10 consecutive cardiac cycles and found that the LVEF of all patients had the highest variability(36%),indicating that random selection of a cardiac cycle may underestimate or overestimate this parameter.However,there was a good linear correlation between the average quantitative left ventricular parameters obtained through multiple cardiac cycles and the measured values(
= 0.94-0.99)obtained from a single cardiac cycle when a regular normal heart rhythm was used,and the coefficient of variation of the left ventricular quantitative parameters remained low(3.5%-4.8%).This study shows that the repeatability of HM-RE is better than that of traditional 2DE and 3DE,but the coefficient of variation of the retest was lower than that of Otani
[21].
The deviation bias of each HM-NE measurement in groups A and D was the largest among all methods and was significantly reduced after fine-tuning.The LVEF measurement bias of HM-NE in group B had the largest deviation and was reduced after fine-tuning,but the deviation bias of LVEDV,LVESV and LAESV was not significantly reduced after fine-tuning.In group C,the deviation bias of LVEDV and LVESV was the largest with the Teichholz method,and the deviation bias of LVEF and LAESV was the largest with HM-NE.After manual fine-tuning,the deviation bias of the two methods was significantly reduced,with the reduction in the bias of LVEF being the most significant(Table 4,Figure 4).

Repeatability analysis of the results for the different quantitative methods
Because HM-NE is a fully automatic method,the intraobserver and interobserver coefficients of variation were both zero.Among the other methods,except for the repeatability between the observersfor group D,the intraobserver and interobserver repeatability of the HM-RE measurements in the other groups was better than those of the other methods.The intra- and interobserver repeatability of the measured values for the different methods in group D was lower than those of the other groups.The intraobserver repeatability of the HM-RE method was slightly higher than the interobserver repeatability,but the difference was small,and its interobserver repeatability was slightly higher than that of the other methods(Table 5).



DlSCUSSlON
The accuracy and repeatability of the assessment of left ventricular volume and LVEF are critical in the diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases[1-2],and changes in these parameters can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of drugs or treatments[4].At present,many methods are employed for assessing left heart volume and function,such as cavitation,radionuclide imaging,magnetic resonance imaging(MRI),computed tomography,and echocardiography[5-9].Compared with the previous methods,cardiac ultrasound does not involve additional radiation and contrast agents.Although the accuracy of MRI results is higher,its use is limited in certain patients with a history of metal foreign body implantation[10,11].Although European and American guidelines have recommended the use of 3DEultrasound to quantify heart volume[12],due to its cumbersomeness and time-consuming nature,currently,left heart volume and ejection fraction are still assessed using the two-dimensional echocardiography(2DE)biplane modified Simpson method[13].HM is a fully automatic,quantitative cardiac cavity analysis method developed based on 3D ultrasound.Compared with traditional 3DE,HM is easier to operate and boasts better measurement accuracy and repeatability.At present,few studies have compared HM with traditional 2DE and 3DE methods in evaluating the accuracy of left heart volume and function in common clinical heart diseases.
In this study,3DQA was used as a reference method in assessing patients with atrial fibrillation,pacemaker implantation history and valve replacement history.The HM method was applied to evaluate the accuracy and repeatability in left ventricular volume and function quantification among patients with different common clinical heart diseases and compared with traditional 2DE and 3DE methods.The results showed that the HM method can accurately assess the left atrial volume of common clinical heart disease patients with a high correlation.In the DCM and segmental wall motion abnormality(SWMA)groups,HM quantified left ventricular volume parameters,obtaining values that were highly correlated and larger than those obtained with 3DQA,consistent with the results of Spitzer
[14]and Tsang
[15].A meta-analysis by Kitano
[16]also showed that although compared with MRI,the 3DE method underestimates the left ventricular volume,the LVEF value obtained was similar[confidence interval(CI)-0.6% and -1.1%,respectively],and using HM can further improve the accuracy and repeatability of the measurement.The results of this study and those of Feng Cheng
[17],conducted on 156 subjects,showed that HM is highly correlated with the measured value of 3DQA(
= 0.90-0.97).The accuracy and repeatability of the quantitative measurement of left ventricular volume with HM in the HCM group were lower than those in the other groups,and the correlation could not be improved with manual fine-tuning.These errors arise from the insufficient spatial resolution of 3DE,the further reduced left ventricular systolic volume of HCM patients,and the inability of the software to correctly distinguish the borders of the endocardium,resulting in insufficient reconstruction[18].Although the accuracy of the quantitative HM-NE and HM-RE measurements of the patients in the DCM group were both high,the LVEF needed to be manually fine-tuned,and the measured values of the left heart obtained by HM-NE and HM-RE were not significantly different(
=0.05-0.86).In this study,the results obtained in the SWMA group were different from the results of Cai
[19].They used HM to quantify the heart parameters of 72 patients with left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction and concluded that the LVEF obtained by the three types of HM(HM-NE,HM-GE,HM-RE)were not significantly different from that of the 3DQA method(
= 0.39 and 1.00).The left ventricular parameters obtained by HM-RE had the highest correlation with those obtained by the 3DQA method(
= 0.88-0.93).
When the youth entered the room where she was, the Golden Blackbird broke forth into a joyful14 song, and the Porcelain Maiden sang too, and jumped for joy
Let me have a bag, I ll go see. Mike made his way across the heather to the dense11, low-lying bushes and started to move the leaves aside to seek out the hidden fruit.
The correlation of left ventricular volume and LVEF between 3DQA and HM-NE in group A(
r
=0.73-0.81,
< 0.01 for all)was slightly lower than that between the Simpson method(
r
= 0.83-0.85,
<0.01 for all),which was manually fine-tuned,and HM-NE.The correlations of these values between the traditional methods and HM-RE were relatively increased(
r
= 0.82-0.96,
< 0.01 for all).In group B,the LVEF value of HM-NE had a low correlation with that of 3DQA(
r
= 0.46,
< 0.01).After manual finetuning,the correlation for LVEDV and LVESV increased slightly,and the correlation for LVEF increased significantly(
r
= 0.71,
< 0.01).In group C,the correlation for left ventricular volume and LVEF between HM-NE and 3DQA was higher than that between HM-NE and both the Teichholz method and Simpson method.After manual fine-tuning,the correlation was further improved(
r
= 0.80-0.90,
< 0.01 for all).The values measured with HM-NE in group D had a low correlation with those measured with 3DQA(LVESV
r
= 0.35,LVEDV
r
= 0.46,LVEF
r
= 0.63,
< 0.01 for all).After manual fine-tuning,the correlation was slightly improved,but the correlation for LVESV was still low(
r
= 0.48,
< 0.01 for all).The measured LAESV values of the two HM methods were highly correlated with those of the 3DQA method(
r
= 0.93-0.95,
< 0.01 for all).In group D,the LAESV measured by HM-RE had the highest correlation with the 3DQA LAESV(
r
= 0.98,
< 0.01),which was slightly higher than that of group A(
r
= 0.97,
< 0.01).
Limitations
First,the study excluded patients with a poor acoustic window who were unable to perform a breathhold;therefore,the feasibility and accuracy of the study results cannot be extended to all patients.Second,only the traditional 3DQA measurement was used as the standard,and MRI measurements were not used;however,previous studies confirmed that the two measurement methods demonstrate a good correlation.Third,previous studies[22]showed that when the default HM value was 80-40,the intraobserver and interobserver coefficients of variation were low(3%-9%),and the correlation with MRI was above 0.91.However,in patients with severe ventricular dilatation and an LVEF ≤ 50%,the consistency with MRI was higher when the boundary was set to HM90-50,but in this study,we used a preset value of HM80-40 and did not make any comparisons with HM90-50.Further study is required to determine the effect of the two preset values.Finally,the sample size of this study was small and should be further increased in the future to evaluate the application value of HM in all patients with common clinical cardiovascular diseases.
CONCLUSlON
HM without regional endocardial border editing(HM-NE)quantified left ventricular volume parameters,obtaining values that were highly correlated and larger than those obtained with advanced cardiac 3D quantification(3DQA)(bias: LVEDV,28.17 mL;LVESV,14.92 mL;LAESV,8.18 mL;LVEF,-0.04%).The correlations between HM without regional endocardial border editing(HM-RE)and 3DQA(
r
= 0.91-0.95,
< 0.05 for all)were higher than those between HM-NE(
r
= 0.85-0.93,
< 0.05 for all).The correlations of LVEDV and LVESV between HM-RE and 3DQA were good for the control group,dilated cardiomyopathy group and segmental wall motion abnormality group,but remained weak for the HCM group(
r
= 0.48-0.54,
< 0.05 for all).The intraobserver and interobserver variability for the HM-RE measurements were low.
Research background
This study used HeartModel(HM),a new software to quickly quantify the left heart volume and left ventricular function in patients with common heart diseases to determine whether there are differences in the feasibility,accuracy,and repeatability of measuring the left ventricular end-diastolic(LVEDV),LV ejection fraction(LVEF)and left atrial end-systolic volume(LAESV)and to compare these measurements with those obtained with traditional methods.
After all, six hundred years is an eternity14! Ah, dear king, replied the young man, your offer is very tempting15! But at the end of six hundred years we should have to die, so we should be no better off! No, I must go on till I find the country where there is no death at all
Research motivation
Compared with traditional three-dimensional echocardiography(3DE),HM is easier to operate and boasts better measurement accuracy and repeatability.At present,the application value of HM in quantifying left heart volume and left ventricular function in patients with common heart diseases remains unclear.
Research objectives
The study aimed to assess the value of HM in quantifying the left heart volume and left ventricular function of patients with common heart diseases.
Research methods
This study retrospectively assessed patients with common heart diseases who were divided into 4 groups:(1)Patients with normal heart shape and function(control group,Group A);(2)patients with dilated cardiomyopathy(DCM)(Group B);(3)patients with LV remodeling after acute myocardial infarction(Group C);and(4)patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy(HCM)(Group D).The measurements obtained were assessed.
Research results
HM can conveniently and accurately quantify the left ventricular volume and ejection fraction of patients with common heart diseases.Manual adjustment is highly repeatable and will further improve accuracy;thus,HM with manual adjustment should be popularized and applied in clinical practice.ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS
Research conclusions
HM can accurately assess the left atrial volume of common clinical heart disease and fibrillation patients with a high correlation.
Research perspectives
Future studies should increase the sample size and are confirm that these findings can be extended to more patients.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We immensely thank all the patients for their willingness to share clinical data for research.
Compared with HM-NE,manual adjustment yielded reduced LVEDV,LVESV,and LAESV values in group A,LVEDV,LVEF,and LAESV values in group C,and LVEDV and LVESV values in group D,but the LVEF value of group D was increased.The remaining parameters were not significantly different before and after manual adjustment(
> 0.05)(Table 2).When contour adjustment was performed,group D showed a wide bias,while the bias in group A was the smallest among the four groups.Compared with the measured value of LV volume,the deviation bias of the measured LAESV value of the four groups was smaller(Figure 2).
With these and like words the wolf comforted the Prince, and warned him specially17 not to touch the wall or let the horse touch it as he led it out, or he would fail in the same way as he had done with the bird
The portraits of the old citizens became alive, steppeddown from the walls against which they had hung for centuries, andtook seats near the church door
FOOTNOTES
Pan CK collected and analyzed the data,wrote the paper;Zhao BW designed and oversight the study;Zhang XX assisted with data analysis;Pan M,Mao YK and Yang Y was involved with data collection;all authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
The study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Boards of Sir Run Run Shaw Institute of Clinical Medicine of Zhejiang University Ethics Committee in China(No.KY20200210-78).
Patients were not required to give informed consent to the study because the analysis used anonymous clinical data.
There are no conflicts of interest to report.
No additional data are available.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial(CC BYNC 4.0)license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
China
Chen-Ke Pan 0000-0001-6144-0737;Bo-Wen Zhao 0000-0003-4911-9371;Xuan-Xuan Zhang 0000-0001-6797-3489;Mei Pan 0000-0002-5423-0771;Yan-Kai Mao 0000-0001-7771-8916;Yuan Yang 0000-0001-5023-4065.
Chen YL
A
Chen YL
1 Lang RM,Badano LP,Mor-Avi V,Afilalo J,Armstrong A,Ernande L,Flachskampf FA,Foster E,Goldstein SA,Kuznetsova T,Lancellotti P,Muraru D,Picard MH,Rietzschel ER,Rudski L,Spencer KT,Tsang W,Voigt JU.Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging.
2015;16:233-270[PMID: 25712077 DOI: 10.1093/ehjci/jev014]
2 White HD,Norris RM,Brown MA,Brandt PW,Whitlock RM,Wild CJ.Left ventricular end-systolic volume as the major determinant of survival after recovery from myocardial infarction.
1987;76: 44-51[PMID: 3594774 DOI:10.1161/01.cir.76.1.44]
3 Muraru D,Badano LP,Ermacora D,Piccoli G,Iliceto S.Sources of variation and bias in assessing left ventricular volumes and dyssynchrony using three-dimensional echocardiography.
2012;28: 1357-1368[PMID: 22120046 DOI: 10.1007/s10554-011-9985-0]
4 Kalogeropoulos AP,Georgiopoulou VV,Gheorghiade M,Butler J.Echocardiographic evaluation of left ventricular structure and function: new modalities and potential applications in clinical trials.
2012;18: 159-172[PMID:22300785 DOI: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2011.10.019]
5 Geiser EJ.Three-dimensional echocardiographic reconstruction: how does it stack up?
1985;7: 77-81[PMID: 4055140 DOI: 10.1016/0167-5273(85)90180-9]
6 Dorosz JL,Lezotte DC,Weitzenkamp DA,Allen LA,Salcedo EE.Performance of 3-dimensional echocardiography in measuring left ventricular volumes and ejection fraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
2012;59: 1799-1808[PMID: 22575319 DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.01.037]
7 Acar P,Maunoury C,Antonietti T,Bonnet D,Sidi D,Kachaner J.Left ventricular ejection fraction in children measured by three-dimensional echocardiography using a new transthoracic integrated 3D-probe.A comparison with equilibrium radionuclide angiography.
1998;19: 1583-1588[PMID: 9820998 DOI: 10.1053/euhj.1998.1091]
8 Buck T,Hunold P,Wentz KU,Tkalec W,Nesser HJ,Erbel R.Tomographic three-dimensional echocardiographic determination of chamber size and systolic function in patients with left ventricular aneurysm: comparison to magnetic resonance imaging,cineventriculography,and two-dimensional echocardiography.
1997;96: 4286-4297[PMID: 9416895 DOI: 10.1161/01.cir.96.12.4286]
9 Vieira ML,Oliveira WA,Cordovil A,Rodrigues AC,Mônaco CG,Afonso T,Lira Filho EB,Perin M,Fischer CH,Morhy SS.3D Echo pilot study of geometric left ventricular changes after acute myocardial infarction.
2013;101: 43-51[PMID: 23740401 DOI: 10.5935/abc.20130112]
10 Vieira ML,Nomura CH,Tranchesi B Jr,de Oliveira WA,Naccarato G,Serpa BS,Passos RB,Funari MB,Fischer CH,Morhy SS.Real-time three-dimensional echocardiographic left ventricular systolic assessment: side-by-side comparison with 64-slice multi-detector cardiac computed tomography.
2010;11: 257-263[PMID: 19969534 DOI: 10.1093/ejechocard/jep199]
11 Müller H,Frangos C,Fleury E,Righetti A,Lerch R,Burri H.Measurement of left ventricular ejection fraction by real time 3D echocardiography in patients with severe systolic dysfunction: comparison with radionuclide angiography.
2010;27: 58-63[PMID: 19765068 DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2009.00976.x]
12 Lang RM,Badano LP,Tsang W,Adams DH,Agricola E,Buck T,Faletra FF,Franke A,Hung J,de Isla LP,Kamp O,Kasprzak JD,Lancellotti P,Marwick TH,McCulloch ML,Monaghan MJ,Nihoyannopoulos P,Pandian NG,Pellikka PA,Pepi M,Roberson DA,Shernan SK,Shirali GS,Sugeng L,Ten Cate FJ,Vannan MA,Zamorano JL,Zoghbi WA;American Society of Echocardiography;European Association of Echocardiography.EAE/ASE recommendations for image acquisition and display using three-dimensional echocardiography.
2012;13: 1-46[PMID: 22275509 DOI: 10.1093/ehjci/jer316]
13 Ruddox V,Mathisen M,Bækkevar M,Aune E,Edvardsen T,Otterstad JE.Is 3D echocardiography superior to 2D echocardiography in general practice?
2013;168: 1306-1315[PMID: 23295040 DOI:10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.12.002]
14 Spitzer E,Ren B,Soliman OI,Zijlstra F,Van Mieghem NM,Geleijnse ML.Accuracy of an automated transthoracic echocardiographic tool for 3D assessment of left heart chamber volumes.
2017;34: 199-209[PMID:28240430 DOI: 10.1111/echo.13436]
15 Tsang W,Salgo IS,Medvedofsky D,Takeuchi M,Prater D,Weinert L,Yamat M,Mor-Avi V,Patel AR,Lang RM.Transthoracic 3D Echocardiographic Left Heart Chamber Quantification Using an Automated Adaptive Analytics Algorithm.
2016;9: 769-782[PMID: 27318718 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.12.020]
16 Kitano T,Nabeshima Y,Otsuji Y,Negishi K,Takeuchi M.Accuracy of Left Ventricular Volumes and Ejection Fraction Measurements by Contemporary Three-Dimensional Echocardiography with Semi- and Fully Automated Software:Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 1,881 Subjects.
2019;32: 1105-1115.e5[PMID:31230780 DOI: 10.1016/j.echo.2019.04.417]
17 Feng C,Chen L,Li J,Wang J,Dong F,Xu J.Three-dimensional echocardiographic measurements using automated quantification software for big data processing.
2017;25: 313-321[PMID: 28269820 DOI:10.3233/XST-17262]
18 Mor-Avi V,Jenkins C,Kühl HP,Nesser HJ,Marwick T,Franke A,Ebner C,Freed BH,Steringer-Mascherbauer R,Pollard H,Weinert L,Niel J,Sugeng L,Lang RM.Real-time 3-dimensional echocardiographic quantification of left ventricular volumes: multicenter study for validation with magnetic resonance imaging and investigation of sources of error.
2008;1: 413-423[PMID: 19356461 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2008.02.009]
19 Cai Q,Wang J,Li H,Li C,Wu X,Lu X.Measurement of Left Ventricular Volumes and Ejection Fraction in Patients with Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities Using an Automated 3D Quantification Algorithm.
2018;44:2274-2282[PMID: 30122311 DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.07.015]
20 Peltier M,Leborgne L,Zoubidi M,Slama M,Tribouilloy CM.Prognostic value of short-deceleration time of mitral inflow E velocity: implications in patients with atrial fibrillation and left-ventricular systolic dysfunction.
2008;101: 317-325[PMID: 18656090 DOI: 10.1016/j.acvd.2008.04.006]
21 Otani K,Nakazono A,Salgo IS,Lang RM,Takeuchi M.Three-Dimensional Echocardiographic Assessment of Left Heart Chamber Size and Function with Fully Automated Quantification Software in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation.
2016;29: 955-965[PMID: 27477865 DOI: 10.1016/j.echo.2016.06.010]
22 Levy F,Dan Schouver E,Iacuzio L,Civaia F,Rusek S,Dommerc C,Marechaux S,Dor V,Tribouilloy C,Dreyfus G.Performance of new automated transthoracic three-dimensional echocardiographic software for left ventricular volumes and function assessment in routine clinical practice: Comparison with 3 Tesla cardiac magnetic resonance.
2017;110: 580-589[PMID: 28566200 DOI: 10.1016/j.acvd.2016.12.015]
杂志排行
World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Capillary leak syndrome:A rare cause of acute respiratory distress syndrome
- lmproving outcomes in geriatric surgery:ls there more to the equation?
- Mass brain tissue lost after decompressive craniectomy:A case report
- Primary intracranial extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma:A case report and review of literature
- Spinal canal decompression for hypertrophic neuropathy of the cauda equina with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy:A case report
- Enigmatic rapid organization of subdural hematoma in a patient with epilepsy:A case report
