Timing of surgical repair of bile duct injuries after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A systematic review
2022-04-02PatrykKambakambaSineadCremenBeatckliMichaelLinecker
Patryk Kambakamba, Sinead Cremen, Beat Möckli, Michael Linecker
Patryk Kambakamba, Sinead Cremen, Department of HPB and Transplant Surgery, St. Vincent’s University Hospital Dublin, Dublin d04 T6F4, Ireland
Patryk Kambakamba, Department of Surgery, Cantonal Hospital Glarus, Glarus 8750,Switzerland
Beat Möckli, Department of Visceral and Transplantation Surgery, University of Geneva Hospitals, Geneva 1205, Switzerland
Michael Linecker, Department of Surgery and Transplantation, University Medical Center Schleswig Holstein, Kiel 24105, Germany
Abstract BACKGROUND The surgical management of bile duct injuries (BDIs) after laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) is challenging and the optimal timing of surgery remains unclear. The primary aim of this study was to systematically evaluate the evidence behind the timing of BDI repair after LC in the literature.AIM To assess timing of surgical repair of BDI and postoperative complications.METHODS The MEDLINE, EMBASE, and The Cochrane Library databases were systematically screened up to August 2021. Risk of bias was assessed via the Newcastle Ottawa scale. The primary outcomes of this review included the timing of BDI repair and postoperative complications.RESULTS A total of 439 abstracts were screened, and 24 studies were included with 15609 patients included in this review. Of the 5229 BDIs reported, 4934 (94%) were classified as major injury. Timing of bile duct repair was immediate (14%, n =705), early (28%, n = 1367), delayed (28%, n = 1367), or late (26%, n = 1286).Standardization of definition for timing of repair was remarkably poor among studies. Definitions for immediate repair ranged from < 24 h to 6 wk after LC while early repair ranged from < 24 h to 12 wk. Likewise, delayed (> 24 h to > 12 wk after LC) and late repair (> 6 wk after LC) showed a broad overlap.CONCLUSION The lack of standardization among studies precludes any conclusive recommendation on optimal timing of BDI repair after LC. This finding indicates an urgent need for a standardized reporting system of BDI repair.
Key Words: Bile duct injury; Major bile duct injury; Laparoscopic cholecystectomy; Surgical repair;Immediate repair; Early repair; Delayed repair; Late repair; Biliary reconstruction; Standardization of bile duct injury repair reporting
INTRODUCTION
Bile duct injury (BDI) remains the most serious and challenging adverse event after laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC)[1-5]. If not recognized and treated properly, BDI may lead to severe morbidity and even death of the patient due to biliary peritonitis and sepsis[6-8].
The management of BDI requires multidisciplinary input, demanding close collaboration of surgeons,gastroenterologists, and interventional radiologists[9-13]. Endoscopic or interventional strategies may suffice in the treatment of minor BDI such as cystic stump leakage or partial laceration[14,15]. However,major BDI often requires surgical repair[10,16]. Due to the anatomical complexity of the biliary tree,surgical BDI repair requires a certain expertise in biliary reconstruction and therefore referral to a tertiary center with a division specialized in hepatobiliary (HPB) surgery is strongly recommended[17-21].
Alongside the extent of injury and surgical experience of those managing BDI, it has been suggested that timing of BDI repair may be a significant prognostic factor for clinical outcomes[10,20-24]. To date,the timing of BDI repair is controversial, with discussions in the literature failing to reach clear recommendations. Whereas several groups claim superiority of early BDI repair[25,26], other publications report beneficial outcome measures if BDI repair was delayed[27-29]. Inconsistent methods of reporting and a plethora of distinct definitions for time intervals create difficulties in comparing study outcomes and draw conclusions on the best timing of BDI repair[29,30].
Therefore, the aim of this systematic review was first to investigate the existing literature on outcome after BDI repair according to timing of repair and second to analyze the standardization concerning definitions of timing of BDI repair among studies.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Search strategy
A systemic electronic search for studies published until August 2021 was preformed, which screened different databases such as Medline, EMBASE, and Cochrane. The search strategy was designed to screen for publications reporting timing of BDI repair and outcome according to timing. Related key phrases and MESH subject headings were combined. The initial search was completed by an objective librarian (Supplementary Table 1).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
All studies reporting BDI repair after LC, including information on timing and postoperative outcome,were included. Abstracts, reviews, case reports, letters to the editor, and articles only available in non-English language were excluded from analysis. Additionally, studies not reporting postoperative outcome according to timing of BDI repair were excluded.
Data extraction and risk of bias assessment
The following data was extracted: Study period, number of patients, age, number of BDI, classification of BDI, presence of concomitant vascular injury, timing and type of BDI repair, and postoperative outcome after BDI repair. The primary outcome of this study was the definition of timing of BDI repair.Postoperative complications were considered as the secondary outcome.
Two independent reviewers (Kambakamba P and Linecker M) screened all articles and checked the extracted data for accuracy. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale was used to assess included papers for risk of bias[31,32].
Statistical analysis
Variables are described as the median and interquartile range (IQR), unless specified differently. The Mann-Whitney U Test or the one-way ANOVA tests was used.
Due to the fact that point estimates from most of the studies (e.g., odds ratios or risk ratios for binary outcomes, or mean difference for quantitative outcomes including 95% confidence interval) were missed, a statistical analysis by pooling the data according to the meta-analysis methods could not be performed. Significance was set atP= 0.05 and statistical trend was defined asP≤ 0.1. Statistical analyses were performed with the software package SPSS 22 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Ill) and Graph Pad Prism Software Version 6.0.
RESULTS
Search results
From all the databases searched, 539 studies were identified through screening of Medline (n= 296),EMBASE (n= 200), and Cochrane (n= 43, Figure 1). After excluding duplicates, a total of 539 studies remained for abstract reviewing. Of these, 275 studies were excluded because of reporting of interventional management of BDI only (i.e., endoscopy), or representing review articles or case series < 10 patients. Finally, after critical reading of 127 articles, 24 studies were considered for the final analysis(Figure 1)[18,20,25-28,33-51].
All 24 studies were assessed for the criteria selection (case definition, representativeness of cases,selection of controls, and definition of controls), comparability (age and sex, and other factors), and exposure (ascertainment of exposure, follow-up, and adequacy of follow-up; Supplementary Figure 1).
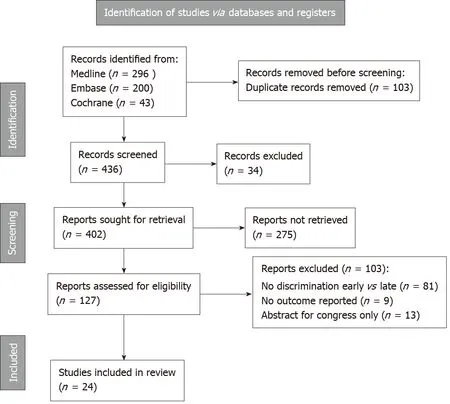
Figure 1 Flowchart of literature research.
Descriptive cohort
A total of 24 studies met the inclusion criteria and reported sufficient information on timing of surgical BDI repair and postoperative outcome after BDI repair. Overall, 15609 patients undergoing cholecystectomy were enrolled. Out of 5229 described injuries of the bile duct, 94% (n= 4934) were classified as major BDI with the need for surgical repair (Table 1).

Table 1 Descriptive cohort, n (%)
Three different classifications were used to characterize the type of major BDI: The Strasberg classification, the Bismuth classification, and the Stewart Way System. Fifteen studies, accounting for 49% (n= 2440)[26,33,34,36-43,45-47,49,50] of BDIs, used the Strasberg classification system, three studies,including 8% (n= 395)[43,47,51] of BDIs, used the Bismuth classification, and one study, reporting 6% (n= 307)[18] of BDIs, used the Stewart Way System (Table 2).Five studies, including 36% (n= 17924)[25,27,28,35,49] of patients, did not identify which classification system was used. Of note, one study including 12 patients used both the Bismuth and the Strasberg classification[39]. Concomitant vascular injury was reported in 4% (n= 222)[28,33,34,36,37,43-45,47] of included patients.
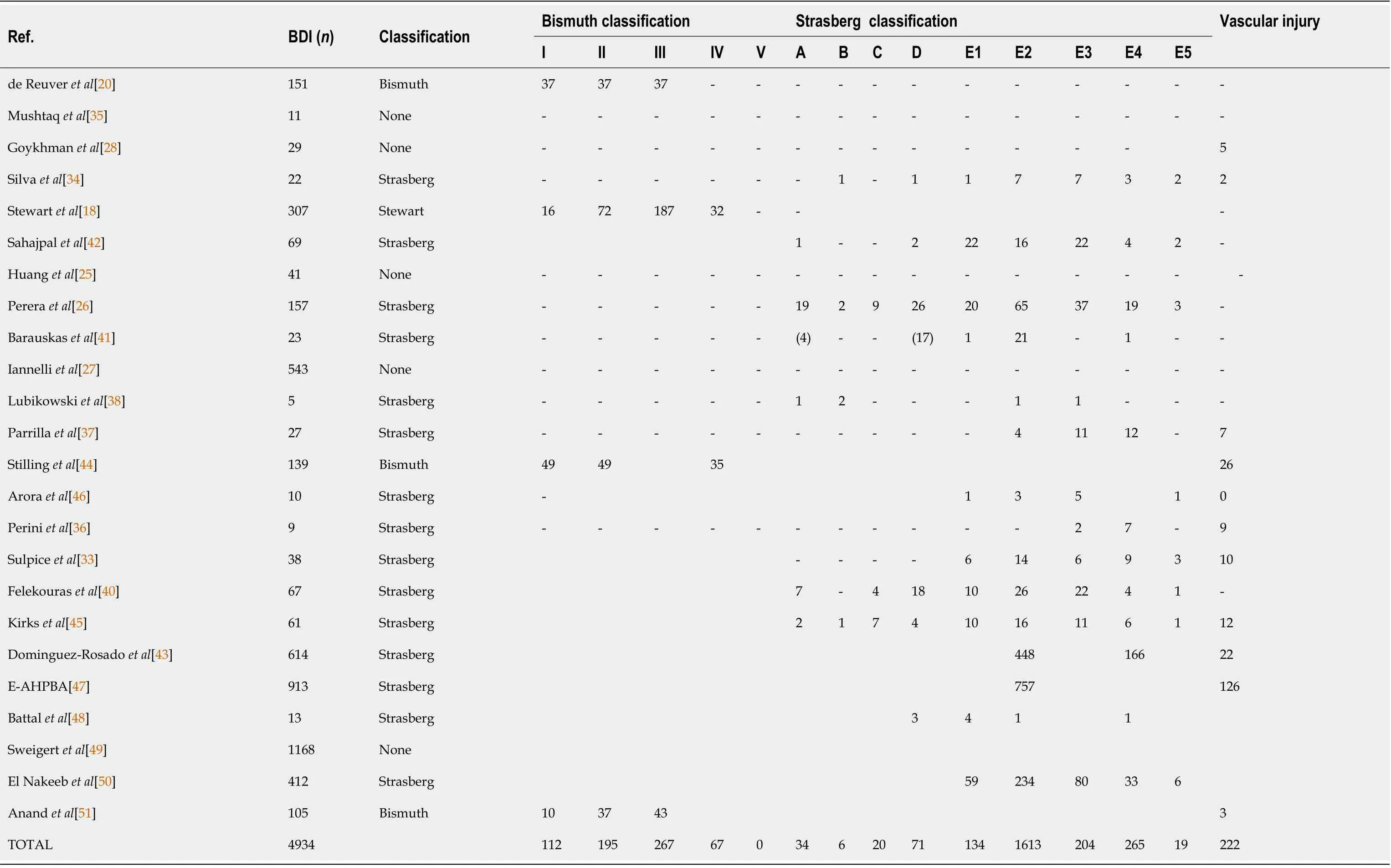
Table 2 Classification systems of bile duct injury
Timing of BDI repair
Details on timing of surgical BDI repair were available in 98% (n= 4879) of analyzed major BDIs.Among all studies, the timing of repair was categorized as “immediate”, “early”, “delayed”, or “late“. In the literature, all four strategies were used in comparable frequencies: 14% (n= 705) of BDI repairs were classified as immediate and 28% (n= 1367) as early, whereas delayed and late repair represented 28% (n= 1364) and 26 % (n= 1286) of BDI repairs, respectively (Table 3).
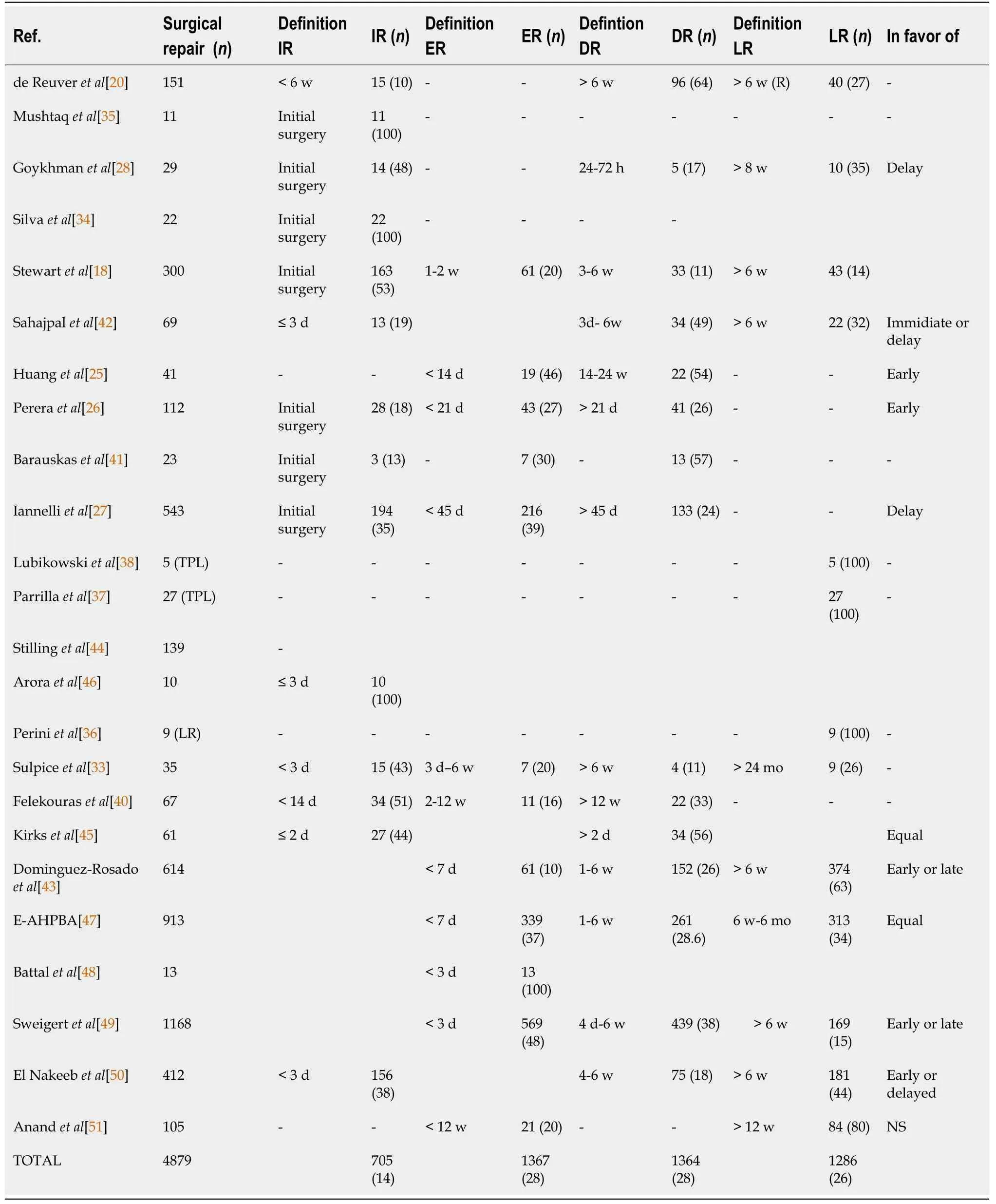
Table 3 Timing of bile duct injury repair, n (%)
The most common type of surgery was biliodigestive reconstruction with a hepaticojejunostomy(median, 95%, IQR: 88%-100%; Table 4).Additionally, the late BDI repair group included nine (0.2%)cases of hepatic resections and 32 (0.6%) patients who were treated by liver transplantation.
Postoperative outcome after BDI repair
Thirteen studies, including 94% (n= 4643) of BDI repairs, defined postoperative outcome according to various timing groups of BDI repair, which included immediatevsearlyvsdelayed in four studies (n=745); immediatevsdelayedvslate in four (n= 661); immediatevsearlyvsdelayedvslate in three (n=335); earlyvsdelayed in three (n= 335); earlyvsdelayvslate in three (n= 2695); and earlyvslate in one (n= 105) (Table 3). Overall, 11 studies (n= 4006) proposed a recommendation for timing of BDI repair.Two manuscripts were in favor of delayed (n= 572, 12%)[27,28], while two other groups (n= 153, 3%)[25,26] recommended early repair of BDI (Figure 2). The other eight studies (n= 3281, 66%) postulating a recommendation for timing found equal results for early or delayed BDI repair[42,43,45].
Median overall morbidity after bile duct repair was 28% (IQR: 19-38) and did not vary significantly between the different timings of BDI repair (P= 0.789; Table 4). Further, mortality was low and was not different among groups (P= 0.832). A detailed list of reported complications can be found in Table 5.
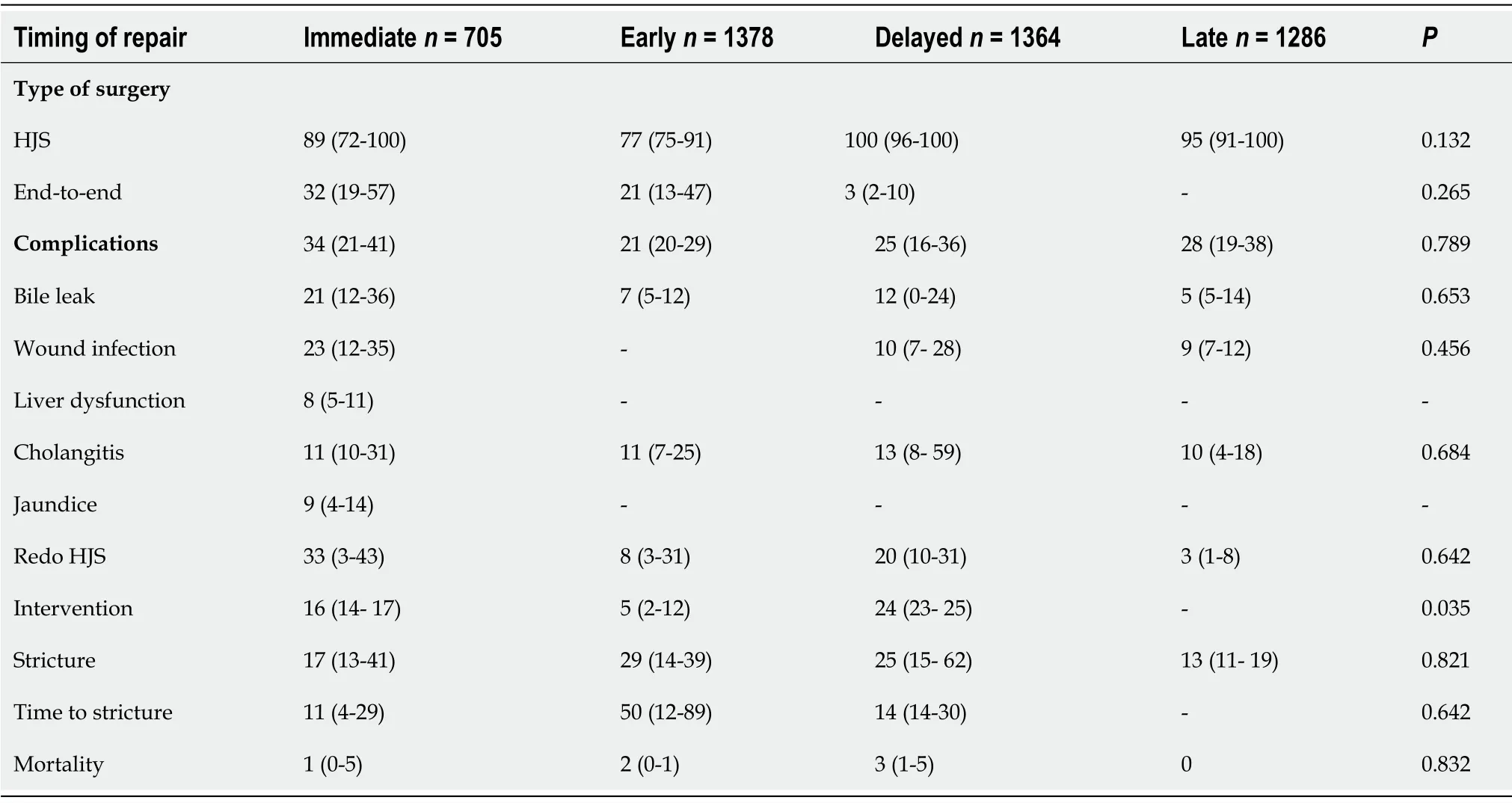
Table 4 Outcome according to timing of bile duct injury repair
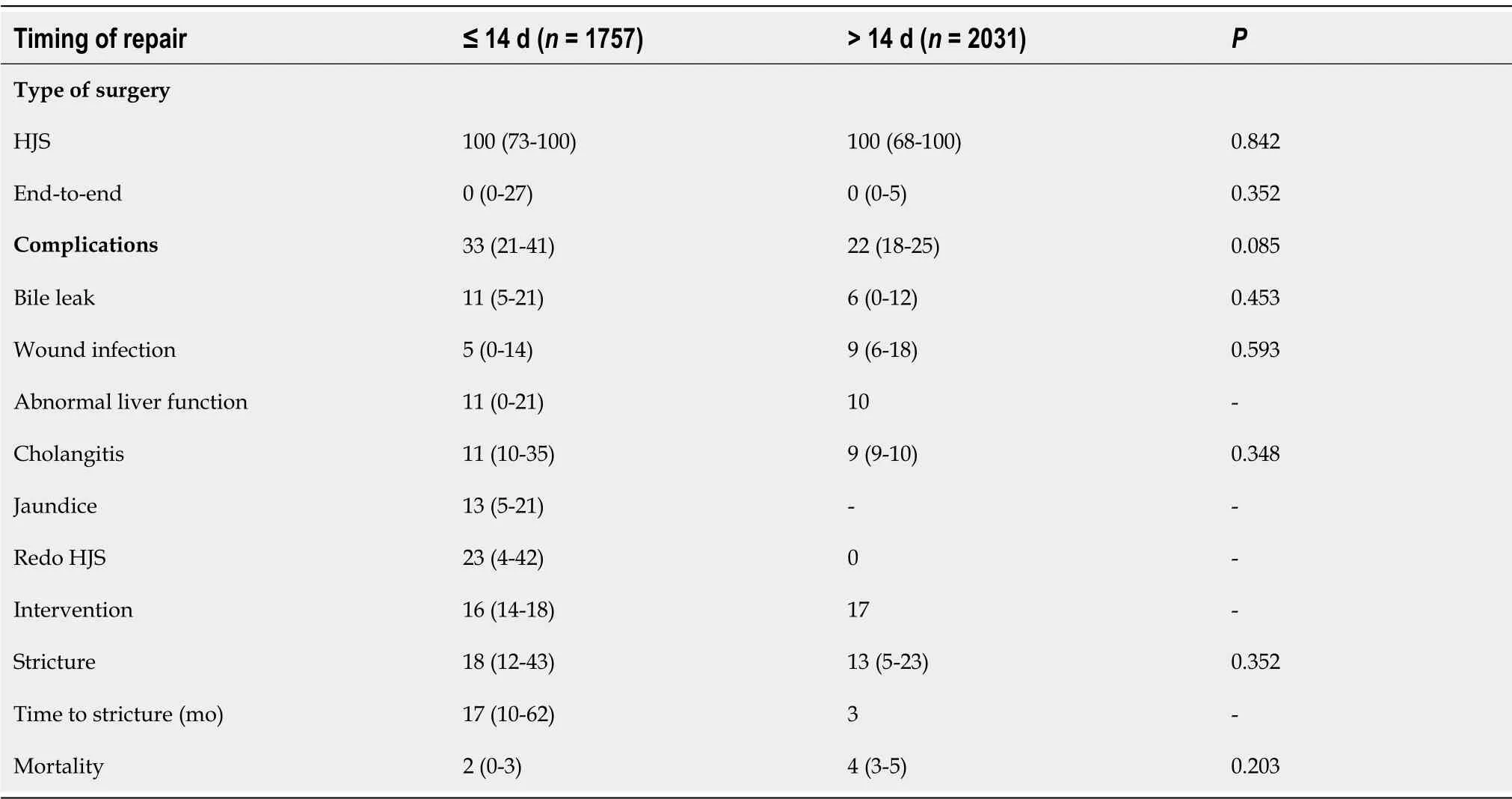
Table 5 Outcome after bile duct injury within 14 d or later
Standardization of reporting of timing of repair
Among 14 studies, we found 14 different definitions of immediate repair (n= 705; Figure 3), ranging from a surgical repair during initial LC (n= 435/705, 62%) to BDI repair within 2 d (n= 27/705, 4%), 3 d(n= 179/705, 7%), 2 wk (n= 34/705, 5%), or within 6 wk (n= 15/705, 2%) after cholecystectomy(Figure 3). Six various definitions for early BDI repair (n= 1367) were provided. Early repair was described as surgery within 1 wk (n= 1053/1367, 67%), 2 wk (n= 80/1367, 5%), 3 wk (n= 43/1367, 3%),4 wk (n= 12/1367, 1%), 6 wk (n= 223/1367, 16%), or 12 wk (n= 32/1367, 2%). Similar, definitions ofdelayed (n = 1364) and late repair (n = 1286) suffered from inconsistent reporting and were described in six and three distinct ways, respectively. The term “delayed” ranged from after 2 d (n = 34/1364, 3%) to within 3 d (n = 5/1364, 0.5%) to within 6 wk (n = 994/1364, 73%), to a minimum delay after cholecystectomy of 2 wk (n = 22/1364, 5%), 6 wk (n = 308/1364, 22%), or 12 wk (n = 22/1364, 3%). Late BDI repairs (n = 1286) were defined as BDI repair 6 wk (n = 1142/1286, 88%), 8 wk (n = 10/1286, 1%), 12 wk (n = 84/1286, 7%), or 2 years (n = 9/1286, 1%) after LC. In 3% (n = 41/1286) of patients undergoing late repair, the time interval was not further specified at all.
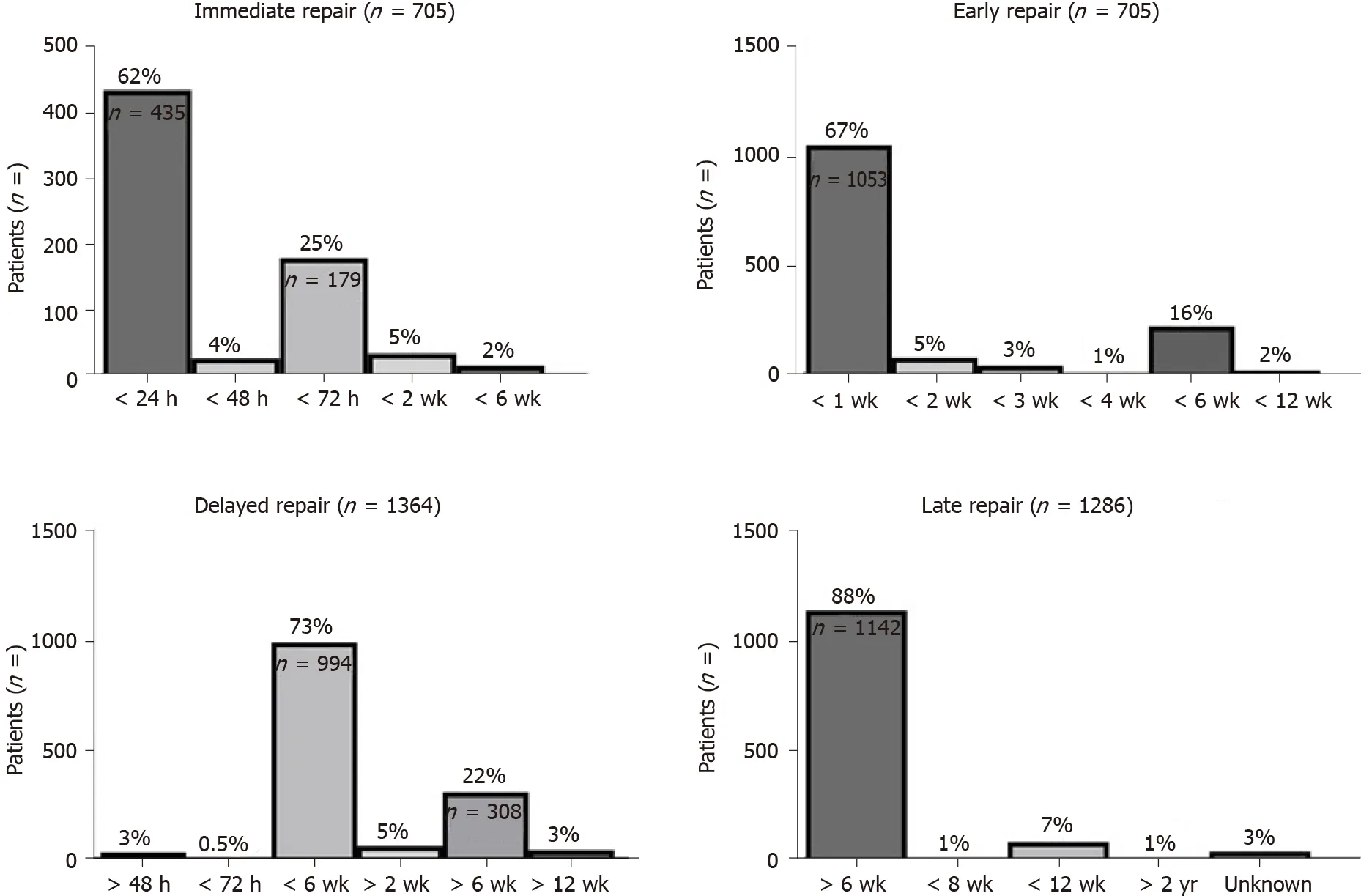
Figure 3 Distribution of definitions of bile duct injury repair timing. Definitions of timing were heterogeneous among publications. Immediate, early,delayed, and late repairs were defined in four, five, six, and five different manners.
As described above, the standardization of timing of repair was remarkably poor among[8,29]studies. Based on the included literature, most commonly used definitions for immediate and early BDI repair were < 24 h and < 1 wk after (Figure 3). Both delayed and late repairs were equally described as BDI repair 6 wk after index surgery in the majority of reported cases (Figure 3). Overall, the lack of standardized reporting leads to a broad overlap of time intervals (Figure 4A), which precludes any conclusive comparison of different studies.
Nonetheless, the provided data allowed the formation of two groups without being confronted by an overlap. In an attempt to standardize the population according to timing of BDI repair, a cut off of 14 d was proposed (Figure 4B). This subgroup analysis revealed increased complications for a BDI repair within 14 d (n = 1757)[2,11,15,16,20,27,29,30,37,38,42,43,45-49] when compared to surgical repair after this interval (n = 2031)[18,20,25-28,33,40,42,43,47,49,51]. Nevertheless, this difference did not reach statistical significance, implicating that outcome is not dependent on timing of repair only. Therefore,based on the present literature, no recommendation can be given on whether early or delayed BDI repair should be preferred. Moreover, there are many inconsistencies in the reporting of timing intervals for BDI repair following LC in the identified literature.
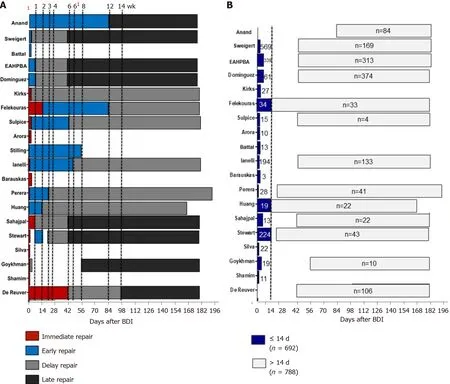
Figure 4 Overlapping definitions of timing of bile duct injury repair. A: Dotted lines indicate different cut offs according to heterogeneous definitions of timing; B: Subgroup analysis after exclusion of overlapping definitions. Dotted lines indicates cut off for BDI repair at 14 d after LC. 1: 24 h and 72 h. 61: 45 d.
DISCUSSION
The analysis of this systematical review revealed that standardization of definitions for timing of repair is remarkably poor among studies. This lack of standardized reporting precludes any conclusive recommendation on optimal timing of BDI repair after LC and claims for a uniform reporting system.
Despite single reports postulating reduced occurrence of BDI, it remains a major concern after LC[8,29]. The repair of major BDI requires exact preoperative characterization of lesions and sufficient expertise in HPB surgery[18,26]. As a result, there are numerous studies that investigate factors influencing outcome following biliary reconstruction for BDI[11,18,29]. Both patient-associated factors,such as septic complications and complexity of BDI, and surgical technique are known prognostic factors for outcome of BDI repair[10,11,18]. Additionally, several authors attach great importance to the optimal timing of surgical BDI repair[23-25,27,29,40]. Whereas immediate repair requires early identification of the injury and potentially shortens patient’s cumulative hospital stay, delayed reconstruction may provide optimal planning and enable the eradication of intra-abdominal infection prior to surgery.Both strategies are equally supported and opposed by various groups and therefore a conclusiverecommendation on timing of BDI repair remains unclear[25-28,42,43,45].
Inconsistent methods of reporting the timing of BDI is a major reason for these continued inconsistencies in recommendations[30]. Substantial variability in presentation of data makes comparison of results difficult and precludes a synoptic statement. In line with our findings, a recent study by the group of Strasberg highlighted the weaknesses of irregular formats of observational studies in the field of BDI repair[30]. Likewise, our systematic review found a multitude of definitions for timing of BDI repair in the literature, resulting in a broad overlap of time intervals among studies. As a result, BDIrepair may be considered as “early” in one study, whereas the same time interval may be classified as“delayed” or even “late” in another paper. This lack of standardized definition for BDI timing repair means that a conclusion on superiority of either one of the strategies cannot be reached. Hence, two studies included in this review proposed the early[25,26], while another two recommended the delayed[27,28] approach as treatment of choice. This goes in line with the findings of two recent meta-analyses that BDI repair should be undertaken either early or in a delayed fashion after 6 wk, whereas the time frame between 2-6 wk seems to be associated with increased morbidity[23,24].
In order to overcome this inconsistency in reporting of timing, the population was divided into two subgroups based on BDI repair within 14 d and after 14 d. Admittedly, the subgroup analysis failed to reveal a significant difference for outcome. This result emphasizes that outcomes after BDI repair are influenced by multiple variables and not just by timing of repair. Likewise, a multivariate analysis including 307 major BDIs concluded that timing of BDI repair plays a subordinate prognostic role for outcome[18]. In contrast, sepsis control, accurate characterization of the BDI, and surgical experience seem to be the major factors influencing the postoperative course.
Many of the studies included in this review were retrospective, which accounts for a major limitation of this systematic review. The retrospective study design does not allow conclusions on patients’condition prior to surgery and the reason for surgeon’s choice for one strategy or the other. Surgeons’decision was likely driven by extent of BDI, concomitant vascular injury, and inflammatory status than by standardized protocols. Subsequently, a retrospective comparison of early and delayed BDI repair group leads to clustering of two fundamentally heterogeneous populations. Nevertheless, the low incidence and the unpredictable course of BDI complicate the design of a prospective randomized control trial.
Likewise, the value of the attempt to standardize the groups according to a BDI repair within 14 d or more than 14 d is diminished by the above-mentioned limitations in data reporting. Still, this allowed a more precise pooling of patients undergoing BDI. In line with other publications, timing alone did not predict outcome in this subgroup analysis. Nevertheless, caution should be taken in interpreting these results based on the quality of provided data and heterogeneity of populations.
In this context, original raw data of the included studies was not available and all analyses were based on provided medians. Therefore, the analysis was limited by data quality, which precluded pooling the data according to the methods of a meta-analysis. However, this study has certain strengths,including the systematical character with providing a comprehensive review of studies declaring outcome according to timing of bile duct repair.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, based on clinical practice, it is assumable that immediate BDI repair is reasonable if detected intraoperatively and sepsis control should be guaranteed before delayed BDI repair.Nevertheless, only standardized reporting can help to answer the ongoing debate of influence of timing on outcome and provide solid fundament for a recommendation. Therefore, based on the findings of this review, a consensus in the field of timing of BDI repair is urgently needed.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Bile duct injuries (BDIs) are an important topic for the practicing hepatobiliary (HPB) surgeon. While it is widely agreed that most major BDIs after laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) should undergo surgical repair, the timing of repair is still controversially discussed in the literature.
Research motivation
Our research motivation was: (1) To bring clarity into the terms "immediate", "early", "delayed", and"late" repair; and (2) to assess postoperative complications.
Research objectives
The objective of this study was to assess timing of bile duct repair after BDI and postoperative complications.
Research methods
A systematic review of the literature was performed using the databases MEDLINE, EMBASE, and The Cochrane Library. These databases were systematically screened up to August 2021. Bias assessment was performed using the Newcastle Ottawa scale.
Research results
A total of 439 abstracts were screened, and 24 studies were included with 15609 patients included in this review. Of the 5229 BDIs reported, 4934 (94%) were classified as major injury. Timing of bile duct repair was immediate (14%, n = 705), early (28%, n = 1367), delayed (28%, n = 1367), or late (26%, n = 1286).Standardization of definition for timing of repair was remarkably poor among studies.
Research conclusions
The lack of standardization among studies precludes any conclusive recommendation on optimal timing of BDI repair after LC. This finding indicates an urgent need for a standardized reporting system of BDI repair.
Research perspectives
Future perspectives include the establishment of a clear definition for the terms "immediate", "early","delayed", and "late" repair. Only such a definition can make comparisons of study outcomes possible.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Kambakamba P, Cremen S, Möckli B, and Linecker M all contributed in creating this manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All the authors declare no conflict of interest for this article.
PRISMA 2009 Checklist statement:The authors have read the PRISMA 2009 Checklist, and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the PRISMA 2009 Checklist.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:Germany
ORCID number:Patryk Kambakamba 0000-0001-8846-9468; Sinead Cremen 0000-0002-6319-0556; Beat Möckli 0000-0002-9020-8416; Michael Linecker 0000-0002-0721-6811.
Corresponding Author's Membership in Professional Societies:IHPBA; E-AHPBA
S-Editor:Liu M
L-Editor:Wang TQ
P-Editor:Liu M
杂志排行
World Journal of Hepatology的其它文章
- COVID-19 and liver disease: Are we missing something?
- Glycogen hepatopathy in type-1 diabetes mellitus: A case report
- Step-up approach in emphysematous hepatitis: A case report
- Learning from a rare phenomenon — spontaneous clearance of chronic hepatitis C virus post-liver transplant: A case report
- β-arrestin-2 predicts the clinical response to β-blockers in cirrhotic portal hypertension patients: A prospective study
- Modified EASL-CLIF criteria that is easier to use and perform better to prognosticate acute-on-chronic liver failure
