Development Status and Countermeasures of Passiflora spp. Seedling Industry in Qinzhou, Guangxi
2022-03-07HongliWANGJiuchengZHAOMiaoLAIYingqingZHANGXinfengFU
Hongli WANG Jiucheng ZHAO Miao LAI Yingqing ZHANG Xinfeng FU
Abstract In recent years, the development trend of passion fruit seedling industry in Qinzhou, Guangxi is good, but on the whole, it is still in its infancy and the development of the industry is fragile. This paper briefly described the development status and existing problems of the passion fruit seedling industry in Qinzhou, Guangxi, and put forward reasonable suggestions in order to promote the healthy development of the passion fruit seedling industry, increase farmers’ income and prosper rural economy.
Key words Qinzhou, Guangxi; Passiflora spp. Industry; Investigation and research; Seedling raising; Development status
Received: November 21, 2021 Accepted: January 3, 2022
Supported by Science and Technology Pioneer "Strengthening Farmers and Enriching People" and "Six Ones" Special Action Project (GNKM 202104); Grassroots Agricultural Technology Extension Service Ability Improvement Project of Agriculture and Rural Affairs Department, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region.
Hongli WANG (1992-), male, P. R. China, agronomist, master, devoted to research about vegetable, fruit cultivation and breeding research.
*Corresponding author. E-mail: 307104703@qq.com.
Passiflora spp., also known as passion fruit trees, are perennial evergreen vine fruit trees[1-3]. Passion fruit is a fruit with high economic value. Because of its sweet and sour pulp, rich nutrition and strong aroma, it is deeply loved by consumers around the world. High-quality fresh passion fruit has been in short supply in domestic and foreign markets[4-5]. In recent years, passion fruit trees have become popular fruit trees for the development of countries in Southeast Asia, and the cultivation area continues to increase. Qinzhou City is located in the Beibu Gulf region, with the sea and rivers, and it has a marine subtropical monsoon climate with excellent natural endowments, which is suitable for the growth of passion fruit. At present, passion fruit has always maintained a price advantage and is one of the fruit tree industries with high development potential and sustainable management. Fruit farmers are highly motivated to plant passion fruit trees, and the industry is expanding rapidly. With the vigorous development of the passion fruit planting industry, Qinzhou City has made the passion fruit seedling industry a highlight of the city’s characteristic agriculture by virtue of its early development of the passion fruit industry, complete varieties, and excellent breeding technology. The trend is becoming more and more obvious, attracting a large number of customers such as Yunnan, Guizhou, Fujian and Qiong to come to purchase. In the context of the rapid development of the passion fruit industry, we put forward development suggestions for expanding the passion fruit seedling industry through investigation and analysis of the development status, scale benefits, technology applications, and existing problems of the main passion fruit seedling companies in Qinzhou City, aiming to provide ideas for the development of industrialized seedlings in this region.
Development Status of Passion Fruit Seedling Industry in Qinzhou City
In order to fully understand the basic situation of the development of the passion fruit seedling industry in Qinzhou, we performed in-depth comprehensive research on the industry through various methods such as data review, telephone consultation, enterprise research, production base research, etc.
Main subject of seedling raising
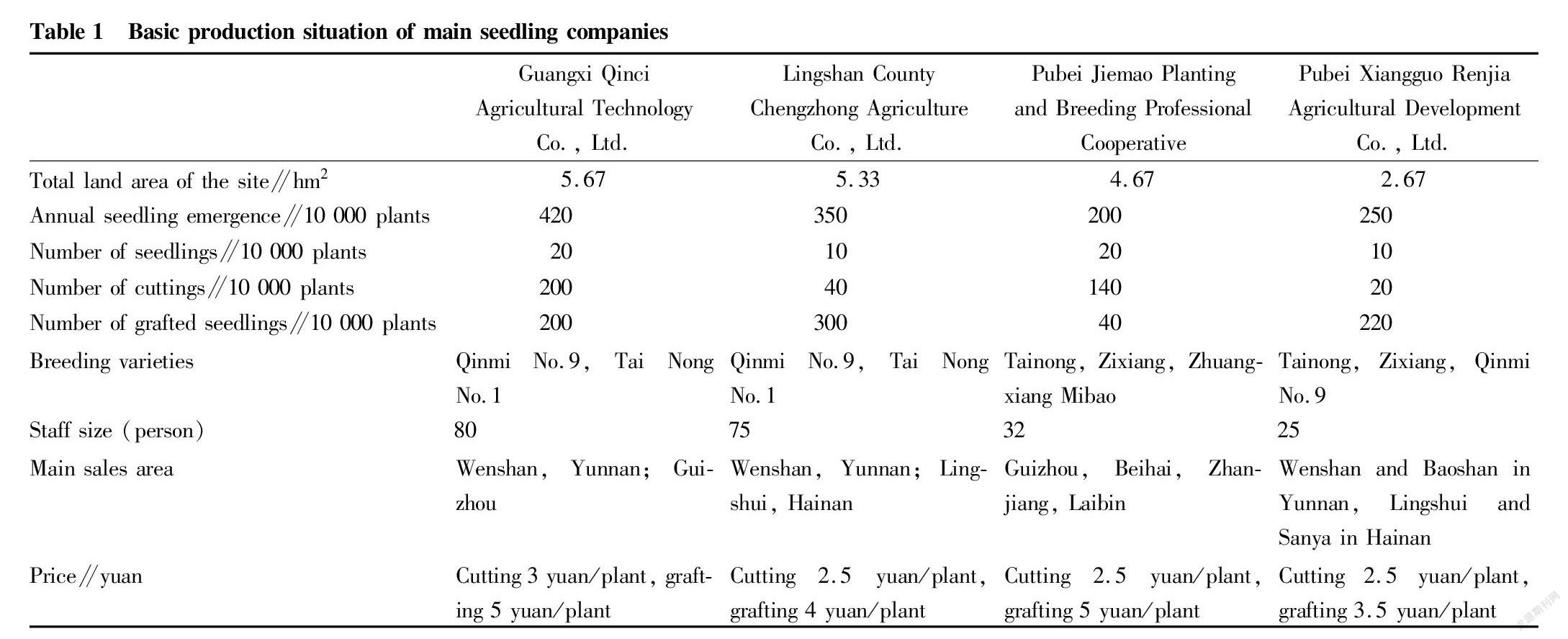
Over the years, due to the low threshold and no industry standards for passion fruit seedling raising, farmers and retail households in some cities and counties in Qinzhou have mostly built small arched sheds in their own backyards and fields to raise seedlings, only to meet their own needs or for sell in a small scale, and there are problems such as small scale of seedling raising, scattered management and uneven quality of seedlings. According to survey statistics, by the end of 2021, there will be more than 50 passion fruit seedling companies in the city, including 4 seedling companies with an annual seedling capacity of more than 2 million, 4 seedling companies with a total land area of 18.33 hm2 and more than 350 seedling plastic greenhouses. There are 3 demonstration sheds, the total annual seedling output is nearly 13 million, and more than 300 jobs are created. It is estimated that 400 seedlings are cultivated per mu of land, which can drive the planting area of passion fruit about 2 166.67 hm2 and help farmers increase their income by 500 million. The basic production situation of major seedling companies is shown in Table 1.
Nursery facilities
The planting facilities of passion fruit seedling enterprises in Qinzhou are simple and extensive in overall. Most of them are plastic greenhouses, and there are no high-standard modern multi-building greenhouses. The passion fruit seedling enterprises are conventionally equipped with simple facilities such as seedbeds, matrix mixers, seedling trays, and nursery rooms, which can basically meet the production of various growth stages from seed sowing to before outplanting.
Seedling management
Seedling management is a crucial link in the production of seedlings. After years of continuous exploration, all seedling enterprises in Qinzhou can basically grasp the technical methods of key links such as temperature, humidity, light, fertilizer and water supply, disease control, and matching of scions and rootstocks in the process of seedling cultivation, and have the ability to grow finished seedlings desired by orders on time according to standards. Production enterprises mostly use matrix plug trays for passion fruit seedling nursing and adopt the spray mode for watering, and Changhuang 511 is mostly used as the rootstock for grafted seedlings. The temperature in sheds is generally controlled at 20-28 ℃, and the humidity is 70%-85%. At night, plant growth lights are used to increase the light. In terms of pest control, 70% thiophanate-methyl wettable powder + 75% chlorothalonil powder 600 times liquid is sprayed once every 8 d, and 2.5% high-efficiency cyfluthrin water emulsion 400 times liquid is added for sterilization and insecticidal management and prevention of cutting rot. The whole process from sowing, germination to seedling emergence, usually takes 60 d for cuttings and 100 d for grafting.
Seedling cost
According to the survey, the wholesale price of passion fruit seedlings in Qinzhou City is generally about 2.5 yuan per cutting seedling, and the gross profit per plant is about 0.75 yuan; and the price of each grafted seedling is about 4.5 yuan, and the gross profit per plant is about 1.35 yuan. After deducting fixed costs such as pesticides and fertilizers, water and electricity costs, labor costs, matrix plug costs, facility depreciation costs, and site costs, the gross profit is about 30%, which is a considerable profit.
Seedling sales
At present, the sales model of various seedling enterprises in Qinzhou is mainly based on order-based production, that is, customers put forward seedling requirements to them, including seedling quantity, variety, quality, delivery time, etc., and seedling enterprises start to arrange production according to customer orders. In addition, seedling enterprises will cultivate a certain number of stock seedlings according to their own judgment of market demand when there is no clear order. In order to reduce the backlog of seedlings, production enterprises generally look for customers through telemarketing, ground promotion, and online release of supply and demand information. Some companies also use agricultural material stores scattered in cities, counties, towns and villages and the heads of agricultural technology promotion stations who have been active in the fields for a long time as sales intermediaries to expand target customers and discover new customers. The sales market of seedling enterprises in Qinzhou City is mainly distributed in the surrounding provinces of Guangxi, of which Wenshan in Yunnan accounts for 70%, Sanya, Lingshui, Chengmai, Meilan and other places in Hainan account for 20%, and Guizhou, Fujian, Guangdong, Jiangxi and Guangxi receive occasional orders in small quantities. Due to the high altitude and low temperature in Yunnan and Guizhou, the cold-resistant variety Tainong No.1 is preferred, and the high temperature in Hainan and Guangdong prefers the cultivation of heat-resistant variety Qinmi No.9.
Major Problems
Lack of excellent germplasm resources and excellent varieties
Excellent variety resources are the basic conditions for the development of passion fruit seedling industry. At present, the main seedling varieties in Qinzhou City are Zixiang, Tainong, Mantianxing, Qinmi No.9 and Zhuangxiang Mibao. There are only a handful of fine varieties. Qinmi No.9 has been applied for variety protection by its owner. If the enterprise is not authorized to produce, there will be legal risks, resulting in the stagnation of production and operation. Therefore, it is of great significance to establish an excellent germplasm resource bank of passion fruit, carry out research on the selection and breeding of new varieties of excellent passion fruit, and cultivate seedlings with complete independent intellectual property rights.
The equipment for raising seedlings is not complete and the degree of mechanization is low
Through this survey, it is found that the seedling enterprises have prominent problems such as insufficient initial capital investment, poor seedling facilities and low degree of mechanization. Most of the larger seedling enterprises still use artificial sowing and raise seedlings based on experience. Mobile seedling bed frame, walking sprinkler and other fertilization spray system, seed germination box, automatic seeding line, plug cleaning and disinfection machine, seedling grafting machine, seedling sorting and transplanting equipment system, high-temperature substrate disinfection equipment and other special machinery for seedling raising, are not equipped by production enterprises.
Low technical content of seedling production and lack of uniform standards
Mature production technology is the foundation for the healthy development of seedling enterprises. Seedling raising involves many links such as seed selection and treatment, substrate ratio, grafting, cutting technology, temperature and humidity control, pest control and so on. Most of the passion fruit seedling enterprises in Qinzhou have primitive and extensive production models, and the technical standards and specifications are not uniform. Relying solely on experience or human judgment can easily lead to large differences in the quality of different batches of seedlings, huge disparities in cost input, different prices, and market conditions. Vicious competition and other issues affect the healthy development of the industry.
Serious diseases and pests
According to the general feedback from nursery production enterprises, passion fruit trees are susceptible to diseases and insects during the nursery period, such as green spot virus disease, stem rot, anthracnose, scale insects, thrips, and aphids. Once infected, there will be problems such as poor plant growth, lignification of fruit or transformation and small fruit, and even failure to harvest in severe cases. The quality of seedlings produced by seedling production enterprises in Qinzhou City is mixed, and the phenomenon of low-quality seedlings and virus-carrying is common.
Serious shortage of professional and technical personnel
The process of raising passion fruit seedlings is cumbersome and requires higher technical level of practitioners, and the requirements for grafting seedlings are specially stricter. Through the investigation, it is found that the current technical personnel and operators in this industry are generally older, mainly between 50 and 55 years old. Most of them have an education level of primary or junior high school, so there is a lack of young backbone technical talents, and the present personnel and operators have poor acceptance of new technologies and skills. Most of the nursery workers are older women from nearby villages. The nursery personnel are not fixed, and have high mobility, and the management is loose. The workers employed by some seedling companies are easily disturbed by external factors and cannot be in place in time. For example, during the busy farming season, farmers need to harvest sugarcane, rice and other crops, and the best time for seedling raising may be missed.
The uneven industrial operation and the single base business
In terms of industrial operation, the production peaks of various seedling enterprises are over-concentrated, and the production and sales in the off-peak season are uneven. The nursery operation time is mainly concentrated from November to May of the following year, with a total of 6 months, of which 2 months are the rest period, and the peak period is from December to March of the next year, totaling 4 months, during which the production and sales account for about 70% of the whole year. The survey found that 80% of the seedling bases only breed passion fruit seedlings. The effective use time of the bases is only 6 months, and half of the time is in an idle state. The seedlings cannot be supplied on an annual basis, and the benefits of the bases are greatly reduced.
Agricultural Biotechnology2022
Suggestions
Set up an improved seed resource garden to reserve a variety of high-quality varieties
Excellent varieties are extremely important means of production in nursery production. In view of the serious shortage of excellent passion fruit germplasm resources in Qinzhou City, narrow genetic background, serious occurrence of diseases and pests and other key problems, it is recommended that the technical personnel of seedling enterprises and relevant agricultural researchers go to the main producing areas and advantageous areas of passion fruit at home and abroad to carry out germplasm resource investigation and collection, introduce high-yield and high-quality passion fruit germplasm resources and advanced breeding technology from areas with developed passion fruit industry, and establish a high-quality passion fruit germplasm resource garden. And research on introduction and cultivation and evaluation of germplasm resources should be carried out. In view of the problem that germplasm cannot be preserved in field germplasm nursery due to virus disease, the research on in-vitro preservation of germplasm should be carried out, so as to lay a foundation for the selection of excellent strains of passion fruit and the cultivation of new varieties.
Innovate facilities and equipment, and actively improve advanced seedling technology
If a worker wants to do a good job, he must first sharpen his tools. It is necessary to introduce and purchase advanced equipment such as precision seeders, seedling grafting machines, seedling sorting and transplanting equipment, heating and cooling equipment, and micro-sprinkler irrigation facilities, and build factory-like intelligent greenhouses, so as to realize the standardization and scale of seedling production. In the seedling cultivation link, it is necessary to cooperate with agricultural scientific research units such as Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Qinzhou Institute of Agricultural Sciences to improve grafting and seedling raising technology, and explore advanced, fast and high-quality seedling raising techniques such as tissue culture, water-growing seedlings, and lake tidal seedlings.
Strengthen the basic research of passion fruit viruses and establish a fast and efficient virus detection technology system
A large-scale production technology system for healthy seedlings of passion fruit, which integrates the selection of high-quality rootstocks of passion fruit, the collection of female parents of excellent varieties, tissue culture detoxification, and standardized grafting and breeding, should be established. We should carry out research on the types of passion fruit pathogenic viruses in Guangxi and their occurrence and epidemic characteristics, and identify the main pathogens that cause virus diseases of passion fruit seedlings through the indicator plant method, electron microscopy, virus genome sequence determination, mass spectrometry analysis and other technical means, and establish a rapid and accurate, sensitive virus detection method. It is also necessary to establish a virus-free seedling breeding supply system suitable for industrial application, including production facilities such as tissue culture workshops, female parent gardens, seed production gardens, and demonstration bases, which form a complete set of virus-free healthy seedling breeding standard production system.
Pay attention to talent training
Seedling enterprises should put talent cultivation in an important position. The first is to adopt the method of bringing in and going out to speed up the training of factory-based nursery managers and technicians. The second is to pay attention to the age and business structure of technical personnel, so as to achieve targeted and planned training. The third is to organize technical personnel in a planned way to participate in technical training and exchange and learning in the advantageous seedling production areas, and to grasp the new trends in the cutting-edge technology of passion fruit seedling cultivation in real time.
Strengthen sales guidance and promotion
Sales are the foundation of a seedling enterprise. Seedling enterprises can use the platform of industry associations to increase the market share and popularity of passion fruit seedlings in Qinzhou City by holding trade fairs, expositions and other activities, and expand their sales market territory. It is also possible to set up a normalized seedling production live broadcast room through WeChat groups, circle of friends, public accounts, e-commerce, TikTok, Kuaishou and other online platforms and live broadcast platforms, and open the seedling production process to the public intuitively and comprehensively, so as to achieve the purposes of popularizing agricultural knowledge, broadening sales channels and improving the comprehensive benefits of the seedling industry.
Create a public brand of local passion fruit seedlings
Agricultural branding is the general trend. It is recommended that the relevant local departments provide more policy support in terms of land transfer, agricultural machinery subsidies, infrastructure investment, etc., so as to support the development of "one product for one county", cultivate a group of public brands of passion fruit seedlings that are famous, strong and influential, and gradually build a passion fruit seedling industry layout based on Qinzhou and radiating to the surrounding areas and even the whole country.
References
[1] LI LP. Research progress on comprehensive development and utilization of passionflower[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science, 2012, 40(28): 13840-13843, 13846. (in Chinese).
[2] HUO DQ, JIANG L, MA LL, et al. Research on the function of passion fruit and its development progress[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2012, 33(19): 391-395. (in Chinese).
[3] ZHENG WW, ZHENG S, LIU YH. Discussion on the production status and development of passionflower in my country[J]. China Tropical Agriculture, 2008(6): 8-9. (in Chinese).
[4] ZENG SX, PENG B, CHEN J, et al. Response surface methodology to optimize the extraction process of anthocyanins from passion fruit peel[J].Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2014, 14(1): 104-113. (in Chinese).
[5] CUI ZJ. The current situation and problems of passion fruit cultivation in Guangxi[J]. Farm Staff, 2018(19): 108, 94. (in Chinese).
Editor: Yingzhi GUANG Proofreader: Xinxiu ZHU
杂志排行
农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Protein 70 Gene in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- Changes in Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Floral Organ
- Research Progress on Lonicera japonica Thunb. Affected by Environmental Stress
- Research Progress on Genetic Diversity of Snap Bean
- Allelopathic Effects of Cedrus deodara Needle Extracts on Seed
- Pathogen Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Sugarcane
