Clinical observation on row needling at the Governor Vessel on the head for poststroke insomnia
2022-02-24XIAJixing夏吉星LIYanhua李延华CHENYunping陈运平
XIA Jixing (夏吉星), LI Yanhua (李延华), CHEN Yunping (陈运平)
1 Department of Neurology, Xianning First People’s Hospital, Hubei Province, Xianning 437100, China
2 Department of Pain Rehabilitation, Xianning First People’s Hospital, Hubei Province, Xianning 437100, China
3 Department of Neurology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022,China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Governor Vessel; Neurotransmitter; Endothelial Cells; Stoke; Insomnia
Stroke, also known as cerebrovascular accident and apoplexy, falls under the category of acute cerebrovascular diseases. It is a brain injury caused by cerebral ischemia due to cerebral vascular obstruction or rupture. Stroke can be classified into ischemic and hemorrhagic types. Patients may present impairments involving motor function, sensory function, and neurologic function, and experience mental symptoms such as sleep disorder, depression, and anxiety[1]. Studies have found that about 56% to 68% of stroke patients may present insomnia symptoms, and the incidence in patients with ischemic stroke is much higher[2]. Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by persistent and frequent difficulty falling asleep, difficulty maintaining sleep, or poor sleep quality[3]. Negative emotions such as depression and anxiety are easily caused by insomnia,which may delay the recovery of stroke and seriously affect the clinical effect as well as the prognosis. Modern medicine usually adopts hypnotic sedative drugs to improve patients’ sleep quality. Long-term adoption,however, is prone to various adverse reactions.Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has shown unique strengths in treating poststroke insomnia. Some studies have pointed out that acupuncture and moxibustion can effectively reduce the neurological deficit and thus improve the sleep quality of patients[4]. In this study, we observed the clinical efficacy of row needling at the Governor Vessel on the head for poststroke insomnia,and analyzed its mechanism.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
1.1.1 Western medicine
The diagnostic criteria referred to theGuidelines on Diagnosis and Treatment of Insomnia in China[5]. The sleep latency is more than 30 min; the actual sleep duration is shortened; the number of waking times increases, and the waking duration is over 30 min; stroke is diagnosed by CT examination.
1.1.2 TCM
The TCM diagnostic criteria were in accordance with Bu Mei (sleeplessness) described in theCriteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine[6]. In mild cases, patients may have trouble falling asleep or wake up frequently with difficulty returning to sleep. In severe cases, patients cannot fall asleep throughout the night,lasting for over three weeks. Associated symptoms may include restlessness, mental fatigue, palpitations, poor memory, dizziness, or headache.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Those who met the above diagnostic criteria and were confirmed by the imaging examination; Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI) score over 7 points; did not receive any other treatments for insomnia one month before the treatment; voluntarily participated in the study and signed informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those who showed poor compliance and inability to cooperate during the study; suffered from severe heart,liver, or kidney diseases.
1.4 Statistical methods
The SPSS version 20.0 statistical software was adopted for data analysis. The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s). The pairedt-test was used for intra-group comparisons, and the independent samplet-test was used for inter-group comparisons. The counting data were expressed as rate and the rank-sum test was employed.P<0.05 indicated statistical significance.
1.5 General data
A total of 33 patients with poststroke insomnia who received routine acupuncture treatment in Xianning First People’s Hospital, Hubei Province, between April 2017 and April 2018 were included in the control group, and 41 patients treated with row needling the Governor Vessel on the head between June 2018 and June 2019 were included in the observation group. There was no statistical difference between the two groups in the general data (P>0.05), (Table 1). This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Xianning First People’s Hospital, Hubei Province (Approval No. 0019284).
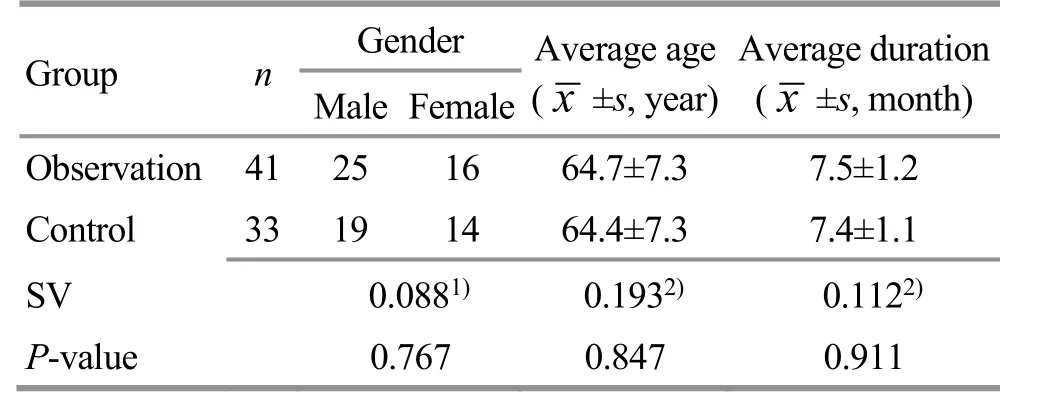
Table 1. Comparison of the general data between the two groups
2 Methods
2.1 Control group
Patients in the control group received routine acupuncture treatment.
Major acupoints: Shenmai (BL62), Zhaohai (KI6),Anmian (Extra), Baihui (GV20), Neiguan (PC6), and Shenmen (HT7).
Adjunct acupoints: Neiting (ST44), Fenglong (ST40)and Zhongwan (CV12) for patients with disturbance of phlegm heat; Fengchi (GB20), Xingjian (LR2) and Taichong (LR3) for those with liver Qi stagnation transforming into fire; Yongquan (KI1), Taixi (KI3) and Taichong (LR3) for syndrome of Yin deficiency leading to fire hyperactivity; Qiuxu (GB40), Danshu (BL19) and Xinshu (BL15) for patients with Qi deficiency of the heart and gallbladder; Sanyinjiao (SP6), Pishu (BL20) and Xinshu (BL15) for deficiency of the heart and spleen syndrome[7].
Methods:Hwato brand acupuncture needles of 0.30 mm in diameter and 25-40 mm in length were used.Acupuncture was performed after routine disinfection with 75% alcohol cotton balls. Even reinforcing-reducing manipulation was adopted after the needling sensation arrived (Deqi). The insertion depth was generally 10-30 mm, specifically depending on the patient's physique and the location of acupoints. The needles were retained for 10 min in the prone position and for 20 min in the supine position. Patients were given this treatment once a day.
2.2 Observation group
Patients in the observation group were additionally needled at the acupoints of the Governor Vessel on the head.
Major acupoints: Besides the major acupoints in the control group, Qianding (GV21), Xinhui (GV22),Shangxing (GV23), and Shenting (GV24) were added.
The adjunct acupoints were the same as those in the control group.
Methods:The patient took a supine position. After routine disinfection, the acupoints of the Governor Vessel were punctured with a 30° angle to the skin.Needled Shenting (GV24) firstly, slowly inserted 0.5 Cun,and then inserted a needle from Shenting (GV24) back along the Governor Vessel at an interval of 0.5-1.0 Cun until Baihui (GV20), a total of five needles. The needles were retained for 20 min after the arrival of needling sensation (Deqi). The acupuncture methods and needle retention time of the other acupoints were the same as those in the control group.
3 Observation of Clinical Efficacy
3.1 Observed items
3.1.1 Sleep structure
Micro-movement sensitive mattress sleep monitoring system (MSMSMS) and sleep structure analysis software were employed to monitor the sleep structure of the patients. MSMSMS records basic physiological parameters such as human activity, respiration, and cardiac cycle during sleep, and identifies the sleeprelated information. The information was collected by the system and checked and corrected by the sleep structure analysis software to obtain the specific situation of the patient's sleep structure.
3.1.2 Serum amino acid neurotransmitters
Before and after the treatment, the patient fasted for 8-10 h, and was collected 5 mL venous blood for centrifugation (3 000 r/min, 10 min). The serum was stored in a refrigerator at -20 ℃. An automatic biochemical analyzer was used to test the levels of glutamic acid (Glu) and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
3.1.3 Vascular endothelial cell function
Five milliliter elbow venous blood was collected on an empty stomach in the morning for centrifugation(2 000 r/min, 5 min). The serum was stored in a refrigerator at -80 ℃. The levels of endothelin-1 (ET-1),bradykinin (BK), and calcitonin gene-related peptide(CGRP) were measured by radioimmunoassay. An atomic fluorescence spectrophotometer was used to test the level of nitric oxide (NO) by the nitrate reductase method.The ET-1 kit (Article No. JK-EA00120), BK kit (Article No.JK-EA00418), CGRP kit (Article No. JKSJ-2051), and NO kit(Article No. JKSJ-2092) were purchased from Shanghai Jing Kang Bioengineering Co., Ltd., China.
3.1.4 Serum cytokine levels
Before and after the treatment, 5 mL elbow venous blood was collected on an empty stomach in the morning and centrifuged at 4 000 r/min for 10 min. Then brain-derived neurological factor (BDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The BDNF kit (Article No.JK-EA00210), NGF kit (Article No. JK-EA00219), TNF-α kit(Article No. JKSJ-1857), and IL-6 kit (Article No. JKSJ-2176)were purchased from Shanghai Jing Kang Bioengineering Co., Ltd., China.
3.1.5 PSQI score
PSQI was used to evaluate the sleep quality of the patients. There are a total of 18 items in 7 dimensions,including subjective sleep quality, sleep latency, sleep duration, habitual sleep efficiency, sleep disturbances,use of sleeping medication, and daytime dysfunction.Each dimension is scored between 0 and 3 points. A total score over 7 points indicates insomnia symptoms. The higher the score, the worse the sleep quality.
3.1.6 Cognitive function
Mini-mental state examination (MMSE) was employed to evaluate the cognitive function of the patients. The full score of MMSE is 30 points. Normal cognitive function: 27-30 points; cognitive impairment:less than 27 points (21-26 points suggest mild cognitive impairment; 10-20 points suggest moderate cognitive impairment; less than 10 points suggest severe cognitive impairment).
3.2 Efficacy evaluation criteria
The efficacy evaluation criteria were in accordance with Bu Mei (sleeplessness) described in theCriteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine[6].
Cured: The patient can sleep deeply with normal actual sleep duration, and feels refreshed after waking up.
Markedly effective: Insomnia symptoms are significantly relieved, and the total sleep duration increases by no less than 3 h.
Effective: Insomnia symptoms are relieved, and the total sleep duration increases by less than 3 h.
Invalid: There is no significant change in the insomnia symptoms and no increase in the total sleep duration.
3.3 Results
3.3.1 Comparison of the clinical efficacy
The cured and markedly effective rate of the observation group was 65.9%, and that of the control group was 39.4%. The rank-sum test showed that there was statistical significance between the two groups(P<0.05), suggesting that the efficacy of the observation group is better than that of the control group (Table 2).
3.3.2 Comparison of the sleep structure
Before the treatment, there was no statistical difference in the sleep structure between the two groups(P>0.05). After the treatment, the indicators of sleep structure in the observation group were improved compared with those before the treatment, and the intra-group differences were statistically significant(P<0.05), while there was only statistical significance in comparing the total waking time in the control group(P<0.05). There was statistical significance in comparing the indicators of sleep structure between the two groups after the treatment (P<0.05). Check Table 3 for details.

Table 2. Comparison of the clinical efficacy between the two groups (case)
Table 3. Comparison of the sleep structure between the two groups ( ±s)
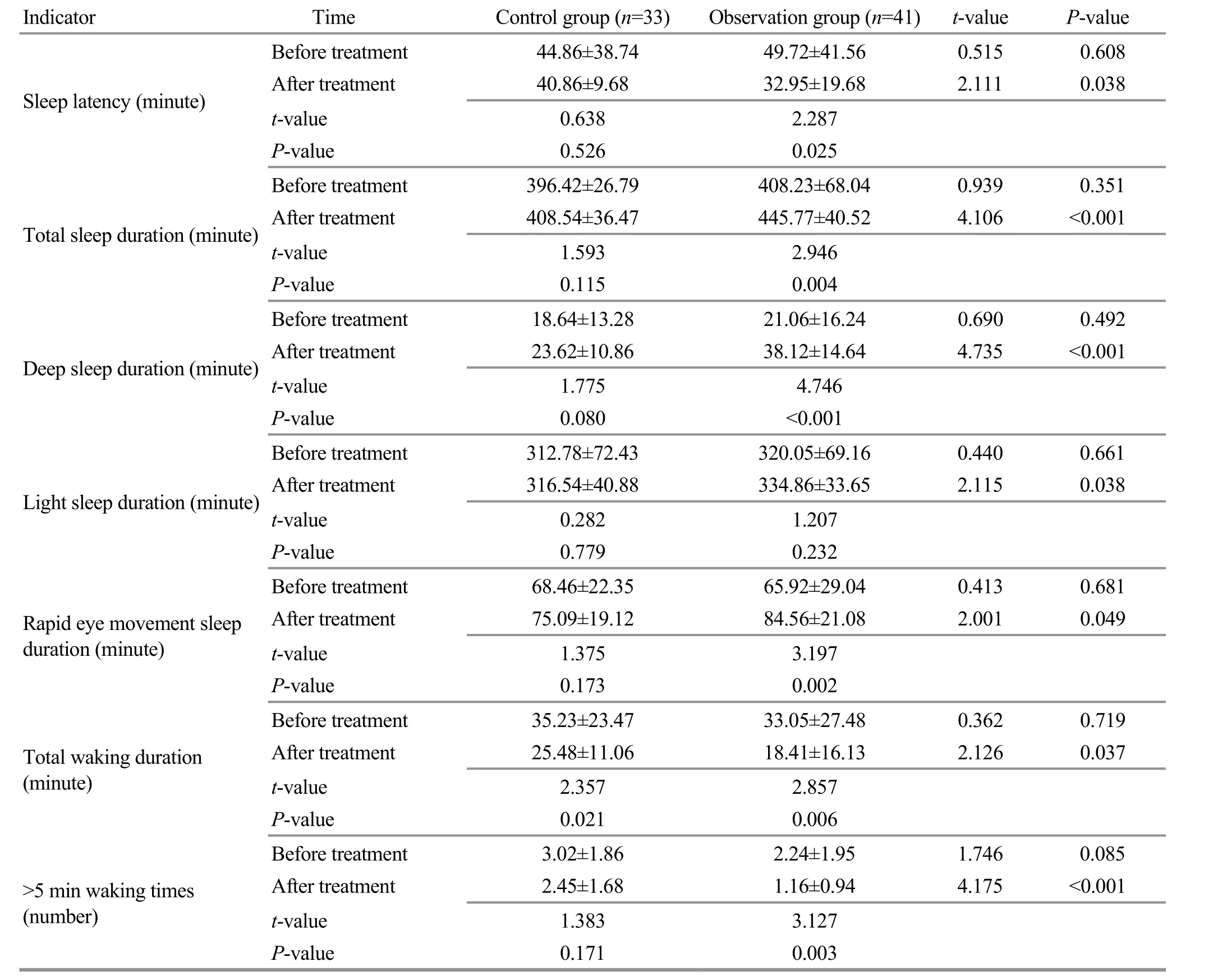
Table 3. Comparison of the sleep structure between the two groups ( ±s)
Indicator Time Control group (n=33) Observation group (n=41) t-value P-value Before treatment 44.86±38.74 49.72±41.56 0.515 0.608 Sleep latency (minute)After treatment 40.86±9.68 32.95±19.68 2.111 0.038 t-value 0.638 2.287 0.526 0.025 396.42±26.79 408.23±68.04 0.939 0.351 408.54±36.47 445.77±40.52 4.106 <0.001 1.593 2.946 0.115 0.004 18.64±13.28 21.06±16.24 0.690 0.492 23.62±10.86 38.12±14.64 4.735 <0.001 1.775 4.746 0.080 <0.001 312.78±72.43 320.05±69.16 0.440 0.661 316.54±40.88 334.86±33.65 2.115 0.038 0.282 1.207 0.779 0.232 68.46±22.35 65.92±29.04 0.413 0.681 75.09±19.12 84.56±21.08 2.001 0.049 1.375 3.197 0.173 0.002 35.23±23.47 33.05±27.48 0.362 0.719 25.48±11.06 18.41±16.13 2.126 0.037 2.357 2.857 0.021 0.006 3.02±1.86 2.24±1.95 1.746 0.085 2.45±1.68 1.16±0.94 4.175 <0.001 P-value Before treatment Total sleep duration (minute)After treatment t-value P-value Before treatment Deep sleep duration (minute)After treatment t-value P-value Before treatment Light sleep duration (minute)After treatment t-value P-value Before treatment Rapid eye movement sleep duration (minute)After treatment t-value P-value Before treatment Total waking duration(minute)After treatment t-value P-value Before treatment>5 min waking times(number)After treatment t-value 1.383 3.127 P-value 0.171 0.003
3.3.3 Comparison of the serum amino acid neurotransmitter levels
Before the treatment, there was no statistical significance in comparing the levels of serum amino acid neurotransmitters between the two groups (P>0.05).After the treatment, the levels of Glu and GABA in the two groups were higher than those before the treatment,showing intra-group statistical significance (P<0.05); the levels of Glu and GABA in the observation group were higher than those in the control group, showing intergroup statistical significance (P<0.05). Check Table 4 for details.
3.3.4 Comparison of the vascular endothelial cell function
Before the treatment, there was no statistical significance in comparing the vascular endothelial cell function between the two groups (P>0.05). After the treatment, the indicators of vascular endothelial cell function in the two groups were significantly different from those before the treatment (P<0.05). The levels of CGRP and NO in the observation group were higher than those in the control group, while the levels of BK and ET-1 were lower than those in the control group, showing inter-group statistical significance (P<0.05). Check Table 5 for details.
3.3.5 Comparison of the cytokine levels
Before the treatment, there was no statistical significance in comparing the levels of related cytokines between the two groups (P>0.05). After the treatment,the levels of related cytokines in the two groups were significantly different from those before the treatment(P<0.05). The levels of BDNF and NGF in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group, while the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 were significantly lower than those in the control group,showing inter-group statistical significance (P<0.05).Check Table 6 for details.
Table 4. Comparison of the serum amino acid neurotransmitter levels between the two groups ( ±s, mmol/L)
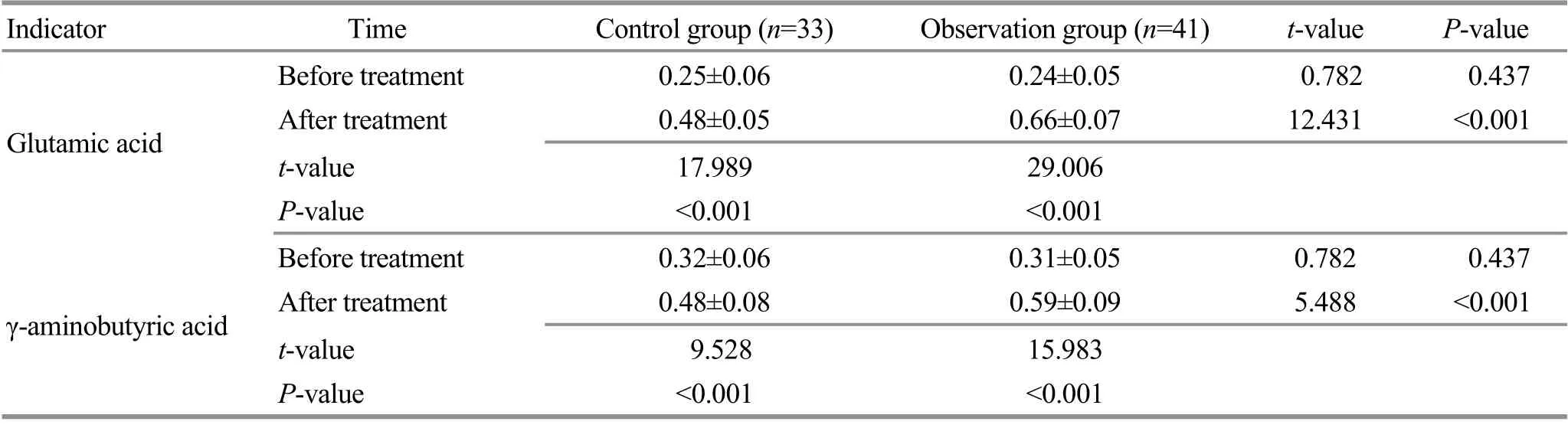
Table 4. Comparison of the serum amino acid neurotransmitter levels between the two groups ( ±s, mmol/L)
Indicator Time Control group (n=33) Observation group (n=41) t-value P-value Before treatment 0.25±0.06 0.24±0.05 0.782 0.437 Glutamic acid After treatment 0.48±0.05 0.66±0.07 12.431 <0.001 t-value 17.989 29.006 P-value <0.001 <0.001 Before treatment 0.32±0.06 0.31±0.05 0.782 0.437 γ-aminobutyric acid After treatment 0.48±0.08 0.59±0.09 5.488 <0.001 t-value 9.528 15.983 P-value <0.001 <0.001
Table 5. Comparison of the vascular endothelial cell function between the two groups ( ±s)
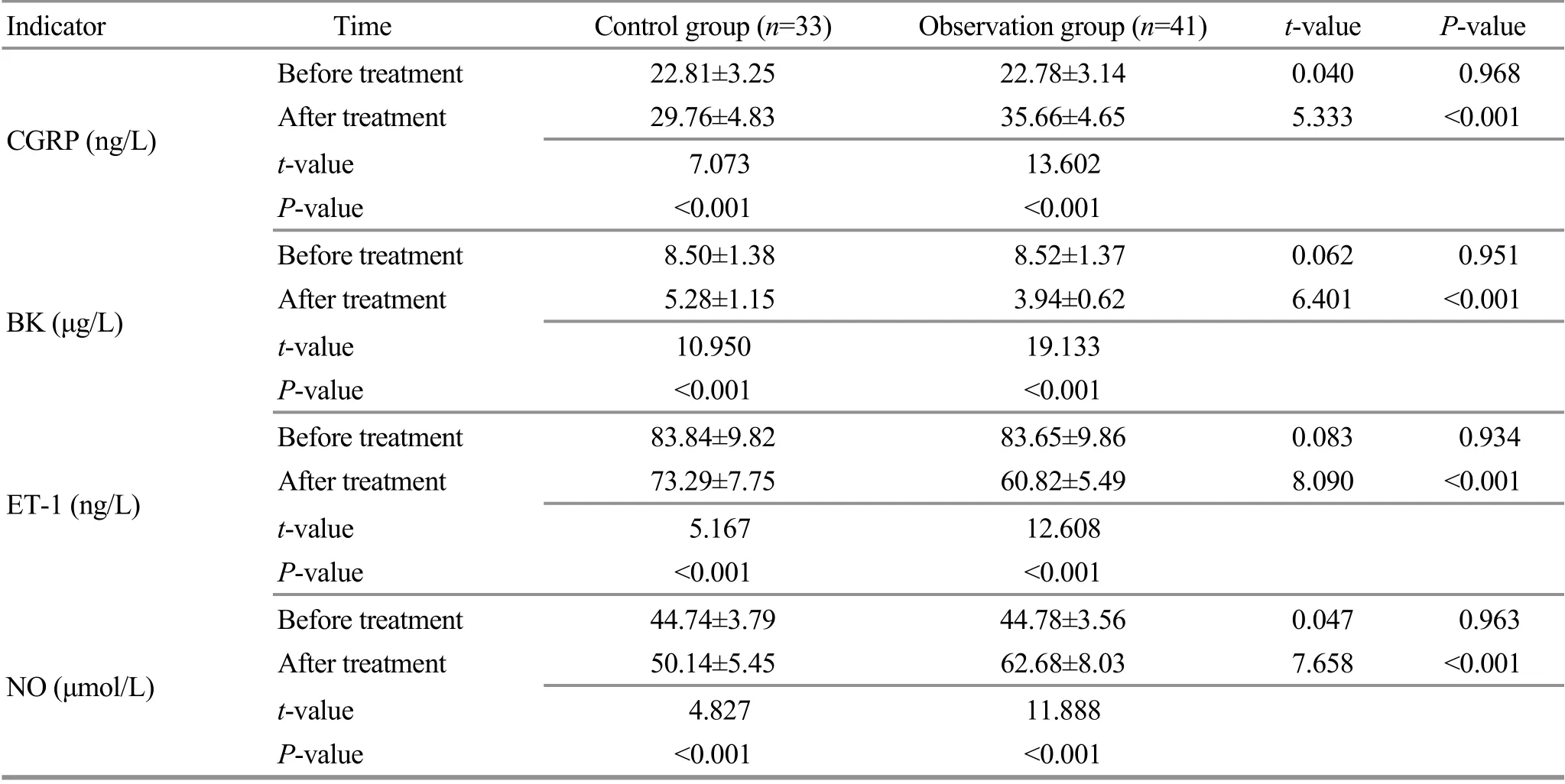
Table 5. Comparison of the vascular endothelial cell function between the two groups ( ±s)
Note: CGRP=Calcitonin gene-related peptide; BK=Bradykinin; ET-1=Endothelin-1; NO=Nitric oxide
Indicator Time Control group (n=33) Observation group (n=41) t-value P-value Before treatment 22.81±3.25 22.78±3.14 0.040 0.968 CGRP (ng/L)After treatment 29.76±4.83 35.66±4.65 5.333 <0.001 t-value 7.073 13.602 P-value <0.001 <0.001 Before treatment 8.50±1.38 8.52±1.37 0.062 0.951 BK (μg/L)After treatment 5.28±1.15 3.94±0.62 6.401 <0.001 t-value 10.950 19.133 P-value <0.001 <0.001 Before treatment 83.84±9.82 83.65±9.86 0.083 0.934 ET-1 (ng/L)After treatment 73.29±7.75 60.82±5.49 8.090 <0.001 t-value 5.167 12.608 P-value <0.001 <0.001 Before treatment 44.74±3.79 44.78±3.56 0.047 0.963 NO (μmol/L)After treatment 50.14±5.45 62.68±8.03 7.658 <0.001 t-value 4.827 11.888 P-value <0.001 <0.001
Table 6. Comparison of the cytokine levels between the two groups ( ±s)
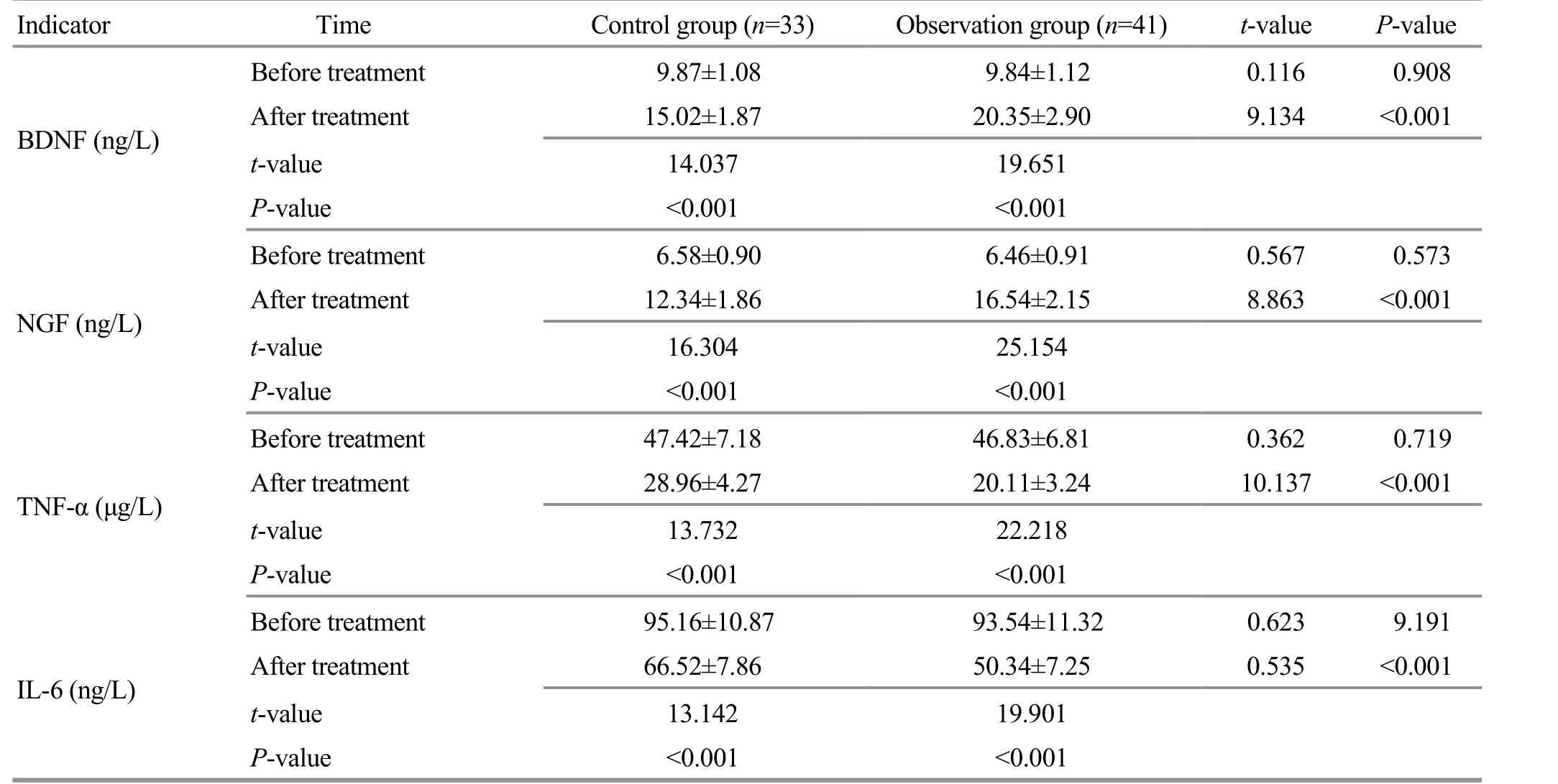
Table 6. Comparison of the cytokine levels between the two groups ( ±s)
Note: BDNF=Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; NGF=Nerve growth factor; TNF-α=Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6=Interleukin-6
Indicator Time Control group (n=33) Observation group (n=41) t-value P-value Before treatment 9.87±1.08 9.84±1.12 0.116 0.908 BDNF (ng/L)After treatment 15.02±1.87 20.35±2.90 9.134 <0.001 t-value 14.037<0.001 6.58±0.90 12.34±1.86 16.304<0.001 47.42±7.18 28.96±4.27 13.732<0.001 95.16±10.87 66.52±7.86 19.651 P-value <0.001 Before treatment 6.46±0.91 0.567 0.573 NGF (ng/L)After treatment 16.54±2.15 8.863 <0.001 t-value 25.154 P-value <0.001 Before treatment 46.83±6.81 0.362 0.719 TNF-α (μg/L)After treatment 20.11±3.24 10.137 <0.001 t-value 22.218 P-value <0.001 Before treatment 93.54±11.32 0.623 9.191 IL-6 (ng/L)After treatment 50.34±7.25 0.535 <0.001 t-value 13.142 19.901 P-value <0.001 <0.001
3.3.6 Comparison of the sleep quality and cognitive function
Before the treatment, there was no statistical significance in comparing the PSQI and MMSE scores between the two groups (P>0.05). After the treatment,the PSQI and MMSE scores of the two groups were significantly different from those before the treatment(P<0.05). The MMSE score of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group, and the PSQI score was significantly lower than that of the control group, showing statistical significance (P<0.05).Check Table 7 for details.
Table 7. Comparison of the sleep quality and cognitive function between the two groups ( ±s, point)
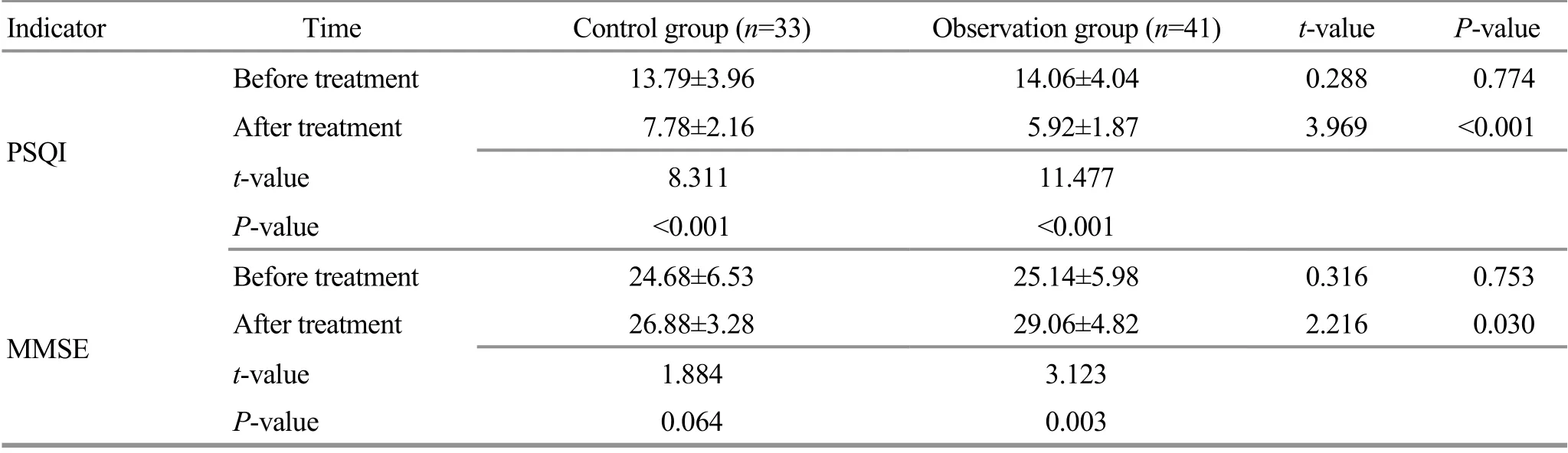
Table 7. Comparison of the sleep quality and cognitive function between the two groups ( ±s, point)
Note: PSQI=Pittsburgh sleep quality index; MMSE=Mini-mental state examination
Indicator Time Control group (n=33) Observation group (n=41) t-value P-value Before treatment 13.79±3.96 14.06±4.04 0.288 0.774 PSQI After treatment 7.78±2.16 5.92±1.87 3.969 <0.001 t-value 8.311 11.477 P-value <0.001 <0.001 Before treatment 24.68±6.53 25.14±5.98 0.316 0.753 MMSE After treatment 26.88±3.28 29.06±4.82 2.216 0.030 t-value 1.884 3.123 P-value 0.064 0.003
4 Discussion
Insomnia falls under the category of Bu Mei(sleeplessness) in TCM, and the main pathogenesis is disharmony between Yin and Yang and Yang failing to enter Yin[8].
The Governor Vessel is the sea of Yang meridians, and the head is the convergence of all Yang meridians.Needling the Governor Vessel on the head can harmonize Yin-Yang and lead Yang into Yin. Modern medical research suggests that both the source and metabolism of oxygen and nutrients depend on the vascular network of the head[9]. Abnormal hemodynamics may cause insufficient cerebral blood perfusion, resulting in cerebral ischemia and hypoxia.Patients may experience symptoms such as dizziness,headache, insomnia, and dream-disturbed sleep.Needling the Governor Vessel on the head can stimulate local nerve endings, thus to relax capillaries, improve local blood circulation, restore cerebral blood perfusion,and subsequently relieve insomnia[10]. Row needling method is a technique that punctures a certain part with relatively dense and arranged needles, which can strengthen the stimulation effect and consolidate the clinical efficacy of acupuncture[11]. This method is effective for various diseases of muscle regions and internal medicine.
In this study, the patients in the observation group were given routine acupuncture plus row needling at the Governor Vessel on the head. Shenting (GV24),Shangxing (GV23), Xinhui (GV22), Qianding (GV21), and Baihui (GV20) with a promising effect of calming the mind were selected to regulate the Governor Vessel and consolidate the efficacy. Shenting (GV24) is a major point to regulate the mind, and Baihui (GV20) can calm the mind as well as the five Zang organs[12]. Needling Shenting (GV24) and Baihui (GV20) can treat mental disorders and regulate Yang and the mind. Shangxing(GV23), Xinhui (GV22), and Qianding (GV21), located between Shenting (GV24) and Baihui (GV20), can promote Qi and blood circulation, and calm the mind.The combination of these five acupoints can lead Yang into Yin and calm the mind.
The results of this study showed that the total sleep duration of patients in the observation group was significantly longer than that in the control group, and the total waking duration and waking times over 5 min were significantly less than those in the control group,indicating that the sleep quality of patients in the observation group is significantly improved. The efficacy difference may be due to the insufficient cerebral blood perfusion resulting in the changes of neurotransmitters secretion and vascular function. Needling the Governor Vessel can regulate Yin and Yang, and row needling method has a promising effect of calming the mind. By comparing the levels of amino acid neurotransmitters,vascular endothelial cell function and cytokines between the two groups before and after the treatment, we found that the levels of Glu, GABA, CGRP, NO, BDNF, and NGF in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group, while the BK, ET-1, TNF-α and IL-6 levels were significantly lower than those in the control group. Glu and GABA, as amino acid neurotransmitters, can inhibit the transmission process of central nervous excitation signals, and thus calm the mind and promote sleep[13]. CGRP is an active peptide in the central nervous system that can promote blood reflux and improve vascular function[14]. The vasoactive substance NO can regulate the relaxation and contraction of blood vessels[15]. BDNF and NGF are cytokines that can promote neuronal regeneration and rebuild neural function[16]. The increases of the above indicators are conducive to the recovery of vascular function and the improvement of local blood circulation of brain tissue, which improves the symptoms of nerve defect and the cognitive function of patients. This will not only improve the sleep quality of patients but also relieve insomnia symptoms. BK is a sensitizer of sensory neurons, and its increase will expand the body's inflammatory response[17]. ET-1 is a vasoactive substance,while TNF-α and IL-6 are cytokines with proinflammatory effects. The increase of these four indicators will activate the inflammatory response of stroke lesions, affect the release process of neurotransmitters, and thus lead to sleep disorders. The decreases of these four indicators indicate that the inflammatory response of patients has been effectively controlled, and the symptoms of insomnia have been effectively relieved[18]. Combined with the PSQI and MMSE scores, we found that row needling at the Governor Vessel on the head can significantly improve the sleep quality and cognitive function of patients.
To sum up, the efficacy of routine acupuncture plus row needling at the Governor Vessel on the head for poststroke insomnia is clear. This method can effectively improve the sleep quality and cognitive function of patients, which may be related to the regulation of serum amino acid neurotransmitters, vascular endothelial cell function, and inflammatory response.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project in Hubei Province (湖北省重大科技创新计划项目, No. 2018SY10235).
Statement of Informed Consent
This trial had been approved by the Ethics Committee of Xianning First People’s Hospital, Hubei Province (Approval No. 0019284). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Received: 14 December 2020/Accepted: 27 April 2021
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effects of electroacupuncture with different frequencies on hippocampal neuronal apoptosis and JNK signaling pathway in rats with vascular dementia
- Effects of electroacupuncture pretreatment on M1 polarization of alveolar macrophages in rats with acute lung injury
- Effects of Tuina combined with graded motor imagery on the upper-limb motor function and quality of life of patients with hemiplegia after stroke
- Effects of acupuncture combined with Brunnstrom staging on upper-limb motor function, cerebral arterial blood flow velocity, and brain function remodeling after stroke
- Observation of the efficacy and safety of the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation for patients with prediabetes
- Clinical study on Tuina plus Shen Ling Bai Zhu San in treating children with diarrhea due to spleen deficiency
