Observation of the efficacy and safety of the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation for patients with prediabetes
2022-02-24LIMin李敏PENGNa彭娜ZENGJiaofei曾姣飞ZHOUYing周英DENGYihui邓奕辉HEQinghu何清湖
LI Min (李敏), PENG Na (彭娜), ZENG Jiaofei (曾姣飞), ZHOU Ying (周英), DENG Yihui (邓奕辉), HE Qinghu (何清湖)
1 Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
2 Hunan Traditional Chinese Medical College, Zhuzhou 412012, China
3 Hunan Want Want Hospital, Changsha 410016, China
Abstract
Keywords: Tuina; Massage; Manual Therapies; Zhen-Vibrating Manipulation; Prediabetic State; Blood Glucose; Lipid Metabolism; Insulin Resistance
In recent years, diabetes has turned into an epidemic,and the prediabetes is at a high prevalence[1-3]. An abnormal glucose metabolic state can cause impairment of several physiological functions. It has been demonstrated that an abnormal glucose metabolic state in prediabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular and neurological disorders[4-6]. Prediabetes can be considered as a sub-healthy stage of diabetes. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) believes that through active intervention, a sub-healthy person can fully regain a healthy state[7]. Therefore, based on the understanding of sub-health in TCM, it is significant if active prevention and treatment can be carried out in prediabetes (i.e., the sub-healthy stage of diabetes) so that it will not progress to diabetes[8]. External therapies of TCM, such as acupuncture, auricular acupressure, acupoint injection,acupoint application, Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage), massage, etc., have significant effects on diabetes and its complications, among which the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation is one of the most prominent external therapies of TCM[9].The Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation is modified based on the Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation, and has been widely used in the treatment of various diseases and become an emerging school of TCM in the field of visceral Tuina[10-13]. In this study, we observed the safety of the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation and its effects on blood glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with prediabetes through a randomized controlled clinical trial, in order to provide clinical evidence for the intervention of the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation for prediabetes.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
The diagnostic criteria for prediabetes, also known as impaired glucose regulation (IGR), referred to theChinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes(2013 Edition)[14], which adopted theDefinition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications: Report of A WHO Consultation. Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus[15]from the World Health Organization in 1999, and IGR is diagnosed by meeting any of the following diagnostic criteria.
Impaired fasting glucose (IFG): Fasting plasma glucose(FPG) 6.1-7.0 mmol/L and 2-hour postload plasma glucose (2hPG) level during an oral glucose tolerance test(OGTT) <7.8 mmol/L.
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT): FPG <7.0 mmol/L,and 2hPG ≥7.8 mmol/L, but <11.1 mmol/L.
The criteria for identifying spleen Qi deficiency in prediabetes were developed with reference to theGuiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines[16]. Primary symptoms are poor food intake,abdominal bloating, loose stools, shortness of breath and reluctance to speak, fatigue, and weak pulse.Secondary symptoms are spontaneous sweating and a pale tongue. The diagnosis can be made by having two of the primary symptoms and one of the secondary symptoms.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Met the above diagnostic criteria for prediabetes and the TCM criteria for spleen Qi deficiency; had not used any previous treatment regimen for IGR; aged 20-70 years old, male or female; had not participated in any other drug or non-drug treatment trials within the last three months; agreed to sign the informed consent form and were able to adhere to the course of treatment.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Stressed or elevated blood glucose secondary to other causes; with serious diseases of the cardiovascular,cerebrovascular, liver, kidney, or hematopoietic system;psychiatric patients; unable to cooperate with researchers and physicians; with tumors, tuberculosis,infectious diseases, or a history of significant trauma;with skin breakdown at the manipulation site, i.e.,abdomen, lower extremities; pregnant or lactating women, as well as women who planned to get pregnant and had no contraceptive plan; with systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥160 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure(DBP) ≥100 mmHg, and secondary hypertension; total cholesterol (TC) ≥6.22 mmol/L or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) ≥4.14 mmol/L.
1.4 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 22.0 statistical software. Data with non-normal distribution were transformed to normal distribution first by taking its natural logarithmic value. Rates were compared using Chi-square test. Measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s),and the pairedt-test was used for intra-group comparisons before and after the treatment. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for repeated measures was used if the data met the spherical symmetry of covariance matrix; if not, the multivariate ANOVA was used.P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
1.5 General data
Patients were obtained from those diagnosed with prediabetes by FPG and OGTT between September 2016 and September 2018 at the First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan Traditional Chinese Medical College and Hunan Want Want Hospital. The purpose of this study and the intervention method were explained in detail to the patients before enrollment. All patients met the enrollment criteria and signed the informed consent form. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and Chinese norms and regulations regarding drug clinical trial studies. The clinical trial protocol was approved by the study unit in charge.
A total of 102 patients were enrolled in this study and were divided into a manipulation group and a control group according to the random number table method,with 51 cases in each group. During the trial, three patients in the manipulation group were unable to adhere to the treatment due to changes in workplace or working hours, two dropped out due to lost visits, and one was unable to receive manipulation due to abdominal trauma; four patients in the control group dropped out due to poor compliance and not taking medication on time as required, three dropped out due to lost contact, and one dropped out due to unplanned pregnancy. Finally, 88 patients completed the trial,including 45 cases in the manipulation group and 43 cases in the control group. There was no statistically significant difference in the general data between the two groups (P>0.05), (Table 1).
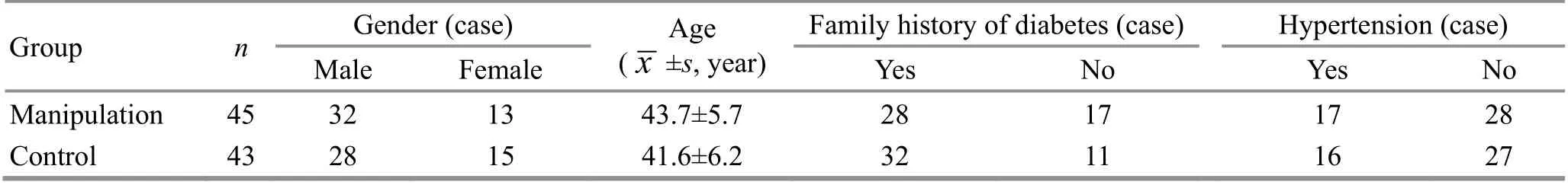
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the two groups
2 Treatment Methods
During the trial, all patients were prohibited from using other medications that affected blood glucose, as well as Chinese herbal medicine and Chinese patent medicine labeled for the treatment of “diabetes” or“Xiao Ke”. Other TCM interventions, such as acupuncture,scraping therapy, cupping, and foot bath, were also prohibited.
General behavioral interventions, including prediabetes diet management and exercise education,were provided in both groups.
2.1 Manipulation group
The patients in the manipulation group were treated with the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation in addition to the general behavioral intervention.
The Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation is modified based on the Zhen-Vibrating manipulation. Before the improvement, it was mainly generated by the static force of the forearm and hand,which made the doctor feel fatigued during the operation and was difficult to operate for a long time,which limited the therapeutic effect. Later, through the joint efforts of BI Yongsheng, DAI Jianguo and Professor ZANG Fuke of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, a unique visceral Tuina therapy with the basic theory of moving Qi, the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating manipulation as the representative technique, and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen as the main manipulation form, was gradually formed. The Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating manipulation uses a single palm to stimulate the abdominal meridians and acupoints with beneficial frequency vibrations, so that both the doctor and the patient can reach a relaxed state and thus resonate with each other. The application of such manipulation to the abdomen is called Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation[17-18]. This manipulation requires“double relaxation and dual intention”, that is, the operator should be relaxed, but the intention should not be relaxed; the patient should be lost, but the intention should be placed on the abdomen.
Acupoints selected: Shenque (CV8), Zhongwan (CV12)and Guanyuan (CV4).
Manipulation details: Each research center arranged two permanent operators and a uniform Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation method was used. All operators were intensively trained twice a week,1 h each time, for three months before starting the study,and were trained and evaluated by Professor WANG Deyu from Hunan Traditional Chinese Medical College.The treatment time, treatment area, and operation procedure were all unified for the patients. The patient was in a supine position, breathing evenly and relaxing the whole body. The operator sat by the patient's side,with Laogong (PC8) in the palm aligned with the patient’s Shenque (CV8), the middle finger on Zhongwan (CV12),the palm root on Guanyuan (CV4), the index finger and ring finger on the Kidney Meridian, and the thumb and little finger on the Stomach Meridian. The operator’s upper limbs were fully relaxed and the forearm was placed naturally on the patient's abdomen. The operator released the wrist spasm with full relaxation, and the manipulation could be performed with the whole palm,palm root, and fingertips generating force alternately.The frequency was 400-600 times/min, and each manipulation lasted 20 min.
Treatment course: One session every other day for the first three months, then two sessions per week, for a total of six months.
2.2 Control group
Patients in the control group were given oral metformin hydrochloride tablets in addition to the general behavioral intervention. The dose started from 250 mg twice daily to 500 mg twice daily one week later,for a total of six months.
3 Observation of Results
3.1 Observation items
Body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, blood pressure, FPG, 2hPG level during an OGTT, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), plasma fasting insulin (FINS)were observed. The blood tests were performed by the Laboratory Department of the corresponding study unit.Patients’ homeostasis model assessment-2 of insulin resistance (HOMA2-IR) was calculated using the HOMA2 calculator, which can be downloaded at http://www.dtu.ox.ac.uk/. Lipid items, including TC,triglycerides (TG), LDL-C and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), were tested.
The above items were tested at three months and six months of treatment to observe the development of each group. The change of IGR was divided into three groups. The first was conversion to diabetes (FPG≥7.0 mmol/L or 2hPG ≥11.1 mmol/L). The second was reversal to normal glucose regulation (NGR) (FPG<6.1 mmol/L and 2hPG ≤7.8 mmol/L). The third was maintenance of IGR. The development was determined based on the test items at 6 months of treatment. If the condition improves and the IGR changes to NGR, the trial will be discontinued; if it stabilizes at the IGR stage, the trial will also be discontinued and the patient will be advised to monitor blood glucose and seek medical consultation when necessary; if the condition progresses to diabetes, treatment will be carried out according to the procedures and protocols of diabetes control in Western medicine.
3.2 Results
After the treatment, indicators except for waist circumference, blood pressure, and LDL-C in both groups were statistically different from those before treatment(P<0.05). The BMI of the manipulation group after six months of treatment was lower than that of the control group at the same time point (P<0.01). Please see Table 2 for details.
HbA1c was lower in the manipulation group than in the control group at the third month and the sixth month(P<0.05,P<0.01), and FPG was also lower than that in the control group (P<0.01,P<0.05). The 2hPG of the manipulation group was lower than that of the control group at the sixth month (P<0.01). These results suggest that the blood glucose in the manipulation group decreased more when compared with the control group.The FINS of the manipulation group at the sixth month was lower than that of the control group (P<0.05).HOMA2-IR was lower in the manipulation group than in the control group at the third month and the sixth month(P<0.05,P<0.01). These results suggest that insulin resistance is more significantly improved in the manipulation group. The TC and TG in the manipulation group were lower than those in the control group at the sixth month, and HDL-C was higher than that in the control group, with significant differences between the two groups (P<0.01); the differences in LDL-C between the two groups were not significant (P>0.05). Please see Table 3 for details.
After the intervention, the prediabetes control rate was 93.3% in the manipulation group and 74.4% in the control group, and there was a significant difference in the glucose metabolic state between the two groups(P<0.05), suggesting that the improvement of the glucose metabolic state in the manipulation group is better than that in the control group. Please see Table 4 for details.
Table 2. Comparisons of the waist circumference, BMI, and blood pressure between the two groups before and after the treatment( ±s)
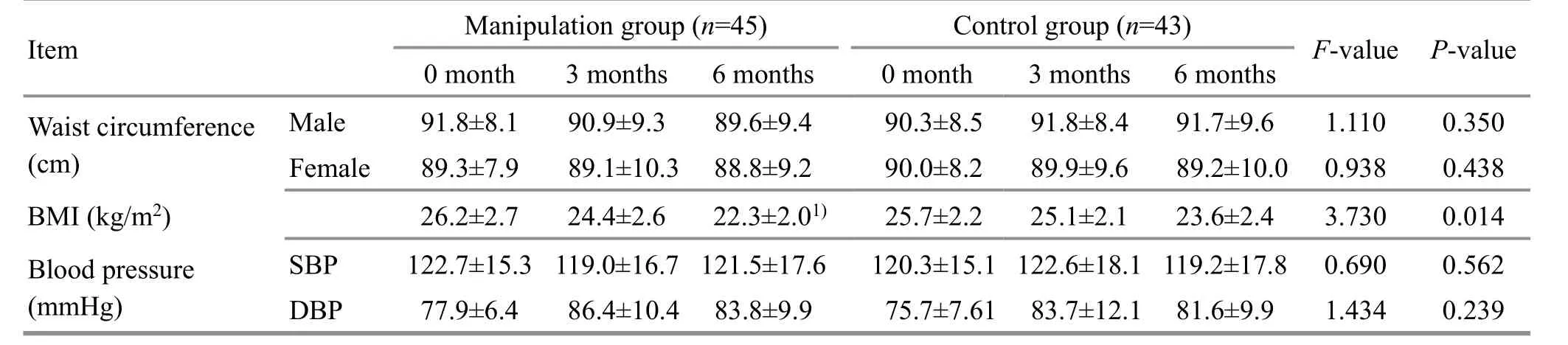
Table 2. Comparisons of the waist circumference, BMI, and blood pressure between the two groups before and after the treatment( ±s)
Note: BMI=Body mass index; SBP=Systolic blood pressure; DBP=Diastolic blood pressure; compared with the control group at the same time point, 1) P<0.01
Item Manipulation group (n=45) Control group (n=43) F-value P-value 0 month 3 months 6 months 0 month 3 months 6 months Waist circumference(cm)Male 91.8±8.1 90.9±9.3 89.6±9.4 90.3±8.5 91.8±8.4 91.7±9.6 1.110 0.350 Female 89.3±7.9 89.1±10.3 88.8±9.2 90.0±8.2 89.9±9.6 89.2±10.0 0.938 0.438 BMI (kg/m2) 26.2±2.7 24.4±2.6 22.3±2.01) 25.7±2.2 25.1±2.1 23.6±2.4 3.730 0.014 Blood pressure(mmHg)SBP 122.7±15.3 119.0±16.7 121.5±17.6 120.3±15.1 122.6±18.1 119.2±17.8 0.690 0.562 DBP 77.9±6.4 86.4±10.4 83.8±9.9 75.7±7.61 83.7±12.1 81.6±9.9 1.434 0.239
Table 3. Comparison of the blood glucose and lipid indicators between the two groups before and after treatment ( ±s)
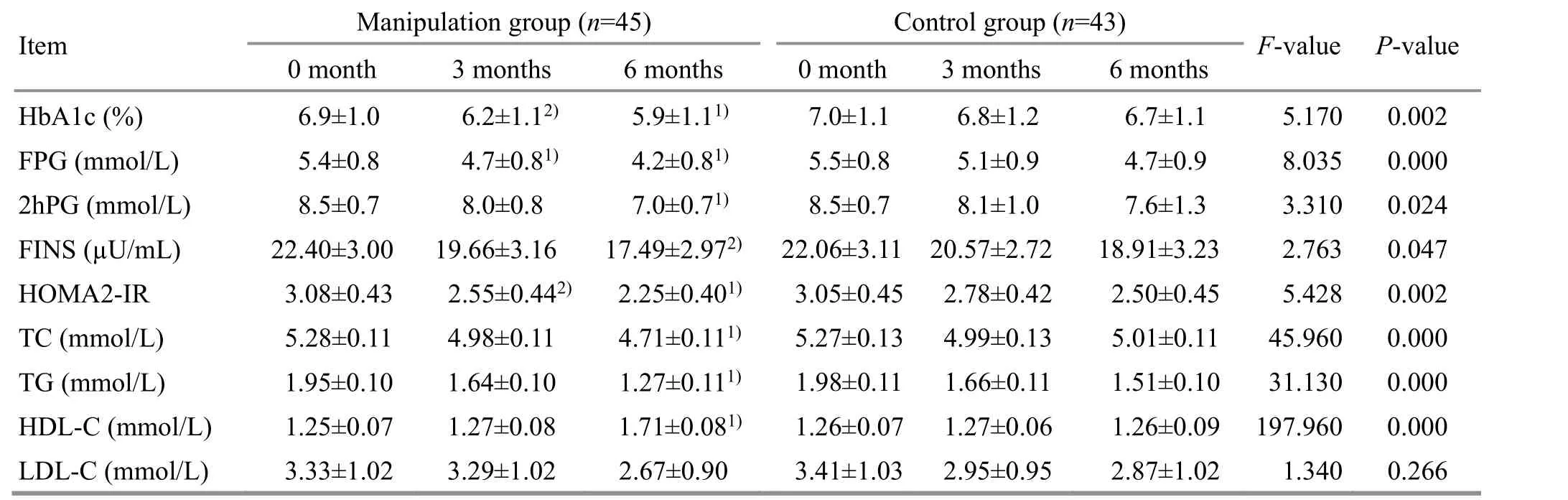
Table 3. Comparison of the blood glucose and lipid indicators between the two groups before and after treatment ( ±s)
Note: HbA1c=Glycosylated hemoglobin A1c; FPG=Fasting plasma glucose; 2hPG=2-hour postload plasma glucose level during an oral glucose tolerance test; FINS=Plasma fasting insulin; HOMA2-IR=Homeostasis model assessment-2 of insulin resistance; TC=Total cholesterol; TG=Triglycerides; HDL-C=High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C=Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; compared with the control group at the same time point, 1) P<0.01, 2) P<0.05
Item Manipulation group (n=45) Control group (n=43) F-value P-value 0 month 3 months 6 months 0 month 3 months 6 months HbA1c (%) 6.9±1.0 6.2±1.12) 5.9±1.11) 7.0±1.1 6.8±1.2 6.7±1.1 5.170 0.002 FPG (mmol/L) 5.4±0.8 4.7±0.81) 4.2±0.81) 5.5±0.8 5.1±0.9 4.7±0.9 8.035 0.000 2hPG (mmol/L) 8.5±0.7 8.0±0.8 7.0±0.71) 8.5±0.7 8.1±1.0 7.6±1.3 3.310 0.024 FINS (µU/mL) 22.40±3.00 19.66±3.16 17.49±2.972) 22.06±3.11 20.57±2.72 18.91±3.23 2.763 0.047 HOMA2-IR 3.08±0.43 2.55±0.442) 2.25±0.401) 3.05±0.45 2.78±0.42 2.50±0.45 5.428 0.002 TC (mmol/L) 5.28±0.11 4.98±0.11 4.71±0.111) 5.27±0.13 4.99±0.13 5.01±0.11 45.960 0.000 TG (mmol/L) 1.95±0.10 1.64±0.10 1.27±0.111) 1.98±0.11 1.66±0.11 1.51±0.10 31.130 0.000 HDL-C (mmol/L) 1.25±0.07 1.27±0.08 1.71±0.081) 1.26±0.07 1.27±0.06 1.26±0.09 197.960 0.000 LDL-C (mmol/L) 3.33±1.02 3.29±1.02 2.67±0.90 3.41±1.03 2.95±0.95 2.87±1.02 1.340 0.266
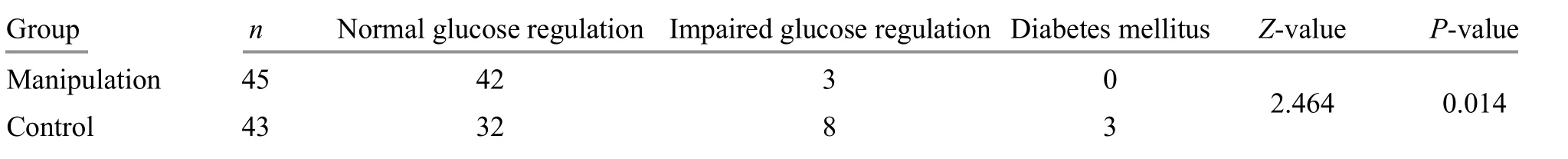
Table 4. Comparison of the blood glucose metabolism state between the two groups after the treatment (case)
3.3 Safety
No adverse reactions were observed in the manipulation group. Three patients in the control group reported mild gastrointestinal reactions at the initial dosing, mainly manifested as increased bowel movement frequency and loose stools, which disappeared after 1-2 d of dose reduction. No other adverse events were observed.
4 Discussion
Blood glucose fluctuates within the physiological range is very important for maintaining normal physiological functions of the body. Blood glucose is a direct source of energy for tissues and organs. Abnormal states of glucose metabolism, including hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, have adverse effects on the organs.A study has shown that a 6-year active lifestyle intervention can reduce cardiovascular mortality by 17.0%, and reduce the incidences of severe diabetic retinopathy and diabetes, and the mortality of cardiocerebrovascular and all-cause[19].
Although lifestyle changes can be of great help to patients with diabetes, they require long-term adherence, and the initial effect is not significant. Some patients with prediabetes are not aware of their later conversion to diabetes or the occurrence of other adverse health events, so the compliance is poor,resulting in most patients not being able to restore normal glucose metabolism through lifestyle improvement alone. Although most current studies suggest that metformin may have a role in regulating the glucose metabolic state of patients with prediabetes and reducing their insulin resistance, it is not yet recommended in existing guidelines and expert consensus opinions, and there are compliance problems over the long run.
TCM plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of diabetes in China, and the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation is one of the unique TCM interventions for prediabetes. The reasons for its positive impact on the metabolism of prediabetic patients are various. From the perspective of TCM, the spleen governs the abdomen, and the abdomen is the pivot of the Qi flow in and out of the body, so conditioning the abdomen can regulate the spleen and restore the clear and turbid flow. Blood glucose is the essence of the human body, which is absorbed by the spleen and stomach and then runs with Qi and blood to the whole body to provide energy for each organ to play its physiological role. Therefore, to a certain extent, the level of blood glucose can reflect the functional state of the spleen and stomach in digesting and absorbing water and food essence in the five Zang organs and six Fu organs. After the body absorbs water and food essence into the blood, it cannot be dispersed and becomes turbid, which will easily lead to high blood glucose. On the one hand, hyperglycemia will cause the loss of nourishment in the five Zang organs, and on the other hand, it will lead to various degenerative diseases[20]. To investigate the causes, spleen deficiency and loss of transportation is important pathogenesis. Many experts believe that the disorder of glucose metabolism is closely related to the deficiency of spleen Qi. For example, SHI Jinmo held that if the spleen transportation is not regulated, the glucose in the blood cannot nourish the organs and reach the whole body, leading to the buildup and rise of blood glucose; the failure of spleen’s transportation and transformation and loss of essence source should be the key. Hence, he proposed that strengthening the spleen and reinforcing Qi are essential for the treatment of prediabetes[21]. The Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation can regulate prediabetes, which may also be related to the fact that the spleen dominates the muscles. Modern medical research has shown that insulin resistance is closely related to muscles. Muscles are the main site of peripheral glucose utilization. In insulin resistance,muscle tissue has reduced glucose uptake and utilization stimulated by postprandial insulin, and the causes of muscle insulin resistance formation are in turn related to obesity and lack of physical activity. According to TCM,the spleen is the master of the muscles. The spleen disperses essence to the muscles through the function of transporting and transforming, so that the muscles consume essence while performing the corresponding function, thus promoting the spleen's function of dispersing essence, and the two promote each other. The loss of muscle activity can lead to a loss of Qi movement,which in turn can lead to spleen deficiency and loss of transportation, further aggravating the metabolic disorder of blood glucose. Therefore, almost all current diabetes guidelines on the prevention of type 2 diabetes emphasize the importance of moderate exercise for diabetes and prediabetes. The China Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study showed that moderate-intensity activity of at least 20 min per day reduced the cumulative incidence of type 2 diabetes by 43.0% over 14 years[19].In this study, the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation, by vibrating the abdomen of prediabetic patients at high frequency, can drive the activities of their abdominal muscles and organs. The abdomen is governed by the spleen, so by vibrating the abdomen, it can, to a certain extent, relax the spleen Qi and restore its healthy movement. The vibration of the abdominal muscles can also promote the smooth flow of Qi, which in turn acts on the spleen and plays a corresponding role in regulating blood glucose metabolism. As a result, not only the blood glucose state is restored, but also the degree of insulin resistance is reduced.
The results of this study show that both the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation and metformin can significantly reduce the FPG and 2hPG in prediabetic patients, and the FPG in the manipulation group decreased more than that in the control group after three months of treatment, and the 2hPG in the manipulation group was lower than that in the control group after six months of treatment. The effect of the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation on the control of blood glucose in patients with prediabetes is superior. Meanwhile, the FINS levels decreased in both groups after the treatment (P<0.01).The HOMA2-IR also decreased in both groups. The HOMA2 homeostasis model is a better formula for calculating the insulin resistance index in clinical patients,and the HOMA2-IR of patients in both groups was significantly higher than that of the normal population,suggesting the existence of a certain degree of insulin resistance. After three months of treatment, the HOMA2-IR decreased in both the manipulation group and the control group, but the decrease was more pronounced in the manipulation group, and further decreased after six months of treatment, and the manipulation group was also better than the control group, which indicates that both metformin and the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation can lower the degree of insulin resistance,but the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation is more beneficial to the reduction of insulin resistance. The effects of the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation and metformin on the lipids of the patients were also different, and the data showed that both had a certain effect on the normalization of lipid metabolism in patients with prediabetes, such as the reduction of TC, TG, and LDL-C,but metformin had less effect on HDL-C, while the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation increased the HDL-C of the patients, and it can be considered that the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation has a more positive effect on the lipid metabolism of prediabetic patients.
In conclusion, the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation has the effect of lowering blood glucose and adjusting lipid metabolism in patients with prediabetes, and it can improve their insulin resistance to a certain extent. Besides, the existence of this effect confirms that the elevation of blood glucose in prediabetic patients is closely related to the failure of spleen’s transportation and transformation according to TCM. The present study suggests that the combination of the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation and lifestyle intervention can be clinically effective, safe, and reliable, and provides research and treatment directions for the prevention and treatment of prediabetes. However, there are several limitations, such as a small sample size, fewer study centers, and no posttreatment follow-up, which need to be improved in future studies.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Key Project of Hunan Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine(湖南省中医药管理局重点科研项目, No. 201526).
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.Received: 14 September 2020/Accepted: 27 April 2021
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Literature review and application experience of needling the Belt Vessel for low back pain
- Investigating the influence of moxibustion on colonic mucosal barrier in rats with dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis
- Clinical study of acupuncture plus Dang Gui Bu Xue Qu Feng Tang for benign essential blepharospasm
- Clinical efficacy of umbilical therapy with herbal cakes of different dosages for damp-heat diarrhea in young children
- Clinical study on Tuina plus Shen Ling Bai Zhu San in treating children with diarrhea due to spleen deficiency
- Effects of acupuncture combined with Brunnstrom staging on upper-limb motor function, cerebral arterial blood flow velocity, and brain function remodeling after stroke
