Application of homogenization techniques for inflow transport approximation on light water reactor analysis
2022-02-23XiangXiaoKanWangTongRuiYangYiXueChen
Xiang Xiao • Kan Wang • Tong-Rui Yang • Yi-Xue Chen
Abstract The transport cross-section based on inflow transport approximation can significantly improve the accuracy of light water reactor (LWR) analysis,especially for the treatment of the anisotropic scattering effect.The previous inflow transport approximation is based on the moderator cross-section and normalized fission source,which is approximated using transport theory.Although the accuracy of reactivity is increased,the P0 flux moment has a large error in the Monte Carlo code.In this study,an improved inflow transport approximation was introduced with homogenization techniques,applying the homogenized cross-section and accurate fission source.The numerical results indicated that the improved inflow transport approximation can increase the P0 flux moment accuracy and maintain the reactivity calculation precision with the previous inflow transport approximation in typical LWR cases.In addition to this investigation,the improved inflow transport approximation is related to the temperature factors.The improved inflow transport approximation is flexible and accurate in the treatment of the anisotropic scattering effect,which can be directly used in the temperature-dependent nuclear data library.
Keywords Inflow transport approximation · Anisotropic scattering effect·Homogenization techniques·Light water reactor
1 Introduction
In light water reactor (LWR) analysis,the anisotropic scattering effect is generally treated by a simplified approximation,such as the transport cross-section (XS)with isotropic scattering approximation from the computational efficiency viewpoint.This approximation has been used in general LWR problems and has reached operational experiences,regardless of its simplicity.However,recent studies suggest that the conventional approximation is inaccurate due to several problems,such as high-leakage,small cores,and fuel assemblies with control rods [1,2].Therefore,the treatment of the anisotropic scattering effect is important for the recent lattice physics code.
There are three major issues in the treatment of the anisotropic scattering effect.The first is a higher-order scattering matrix.TheP2or higher-order scattering matrix is sufficient to maintain calculation accuracy[3].However,a large amount of memory and a long computing time are required to incorporate the higher-order scattering matrix.The high-order scattering matrix is implemented for the whole-core calculation in the Michigan Parallel Characteristics Transport (MPACT) code [4],and whole-core problems are calculated using theP2scattering approximation.The second is the application of the angular-dependent total cross-section.Multi-group total XS is obtained from angular flux condensation [5-7].Conversely,it employs the time-consuming Monte Carlo code,and it is also very difficult to attain the accurate angular flux.A previous study showed that 160 batches with 1 billion neutrons per tally can reach the converged results[8],which is also an impractical method.The third is the transport approximation for transport XS[9].It can be used in theP0scattering matrix and is efficient for large-core calculations.Nevertheless,the key point in the inflow transport approximation is the accurate higher-order flux moment from the neutron transport calculation.Yamamoto[2] adopted the typical neutron spectrum for theP0flux moment,and the higher order flux moment was inversely proportional to the total XS but did not improve the accuracy of reactivity compared to that using the outflow transport approximation.Choi [10] developed an inflow transport approximation from a one-dimensionalPNtransport equation,improving the accuracy in cases of high anisotropic scattering.However,Choi’s one-dimensionalPNtransport equation is based on the moderator region and the normalization of the fission source.Although the accuracy of the reactivity calculation in the high anisotropic scattering cases improved,it was approximated with the theoretical model.Nevertheless,there are many other studies related to the neutron transport problem and crosssection [11-13].
In this study,the improved inflow transport approximation was investigated,and its application in different LWR cases was tested.The transport XS was computed by solving the one-dimensionalPNtransport equation with the homogenized cross-section and accurate fission source,verified through typical LWR cases.The accuracy and application of these transport approximation methods can be determined by comparing thek-infinity,k-effective,andP0flux moments to the reference results.In addition to the inflow transport approximation investigation,the application of the improved inflow transport approximation was tested using different typical LWR cases.Moreover,the results of inflow transport approximations were performed in the lattice code DRAGON5.0.5[14]and compared to the results of experimental values and Monte Carlo code cosRMC [15].The numerical results showed that the improved inflow transport approximation can reach a higher accuracy than the previous method for theP0flux moment,and can retain the same accuracy as the previous inflow transport approximation for the reactivity calculation.In addition,the improved inflow transport approximation is only related to the temperature factor through the verification of typical LWR cases.As a result,the improved inflow transport approximation is precise and flexible in the LWR analysis when applied to a temperature-dependent nuclear data library.
The remainder of this manuscript is organized as follows.Section 2 describes the theory and methodology of the different inflow transport approximations.Section 3 explains the discrepancy analysis between these two methods.Section 4 presents the numerical results for the different LWR cases.The conclusions are expressed in Sect.5.
2 Theory and methodology
2.1 Previous inflow transport approximation
The previous inflow transport approximation was developed by Choi,which is based on the moderator region and normalized fission source.In this method,the multigroup form of the one-dimensionalPNtransport equation is derived as follows:

whereψgis the angular flux in groupg,μis the cosine angle in thez-direction,Pl(μ)is the Legendre polynomial,lis the order of the Legendre polynomial,is thel-th moment macroscopic XS ofxreaction(f:fission,t:total,s:scattering),andis thel-th flux moment.It should be noted that the distinction betweenand(n=1,2…) disappears in the absence of self-shielding(i.e.,infinity dilution) [16].
The multigroup transport equation in Eq.(1) can be extended using Eqs.(2)-(5),as follows:

Multiplying Eq.(6) by the Legendre polynomial(2n+1)Pn(μ)and integratingμfrom-1 to+1,and using the following Bonnet’s recursion formula and the orthogonality of the Legendre polynomials:
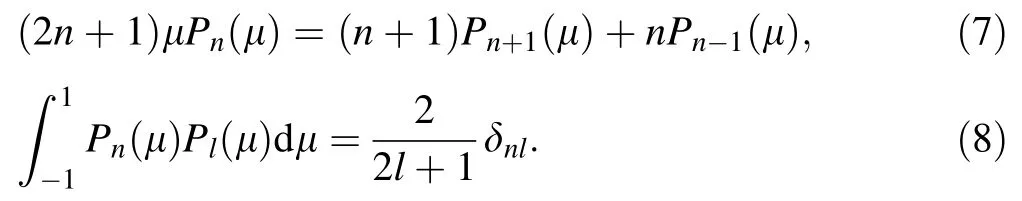
Inserting Eqs.(7) and (8) into Eq.(6) will lead to the following equation:

Approximating the spatial shape using bucklingB:

Inserting Eq.(10) into Eq.(9) will produce the following equation:

Additionally,another approximation was introduced for Choi’s method.The fission source is forced to normalize,and the value ofkis set to 1,leading to:

In Choi’s method,Eq.(11) is then converted to the following equation:

Whennis an even number andn-1 andn+1 are odd numbers.

Inserting Eqs.(16) and (17) into Eq.(14) leads to the following:

If the order ofnis the maximum value,becomes 0.For the oddn,Eq.(14) becomes the following:

The high-order flux moments andP0transport XS are then generated.Furthermore,theP0scattering matrix is calculated using the transport XS,and can be used in the transport computation.Only the corrected diagonal elements are as follows:

The transport equation is related to the geometric valuez.It was calculated for a dominated moderator material in each problem case,and showed a problem-dependent result.
2.2 Improved inflow transport approximation
From the above derivation,a key point in the inflow transport approximation is applying the accurate flux moment from a one-dimensionalPNtransport equation,considering the leakage effect and anisotropic scattering effect.This is the same as the assembly homogenization techniques[17].However,there are two terms(multi-group data and fission source) that are inconsistent with the theoretical model through the derivation of the previous inflow transport approximation.
When applying the flux shape with bucklingB,the multigroup XS and scattering matrix in Eqs.(3) and (4)become the following:
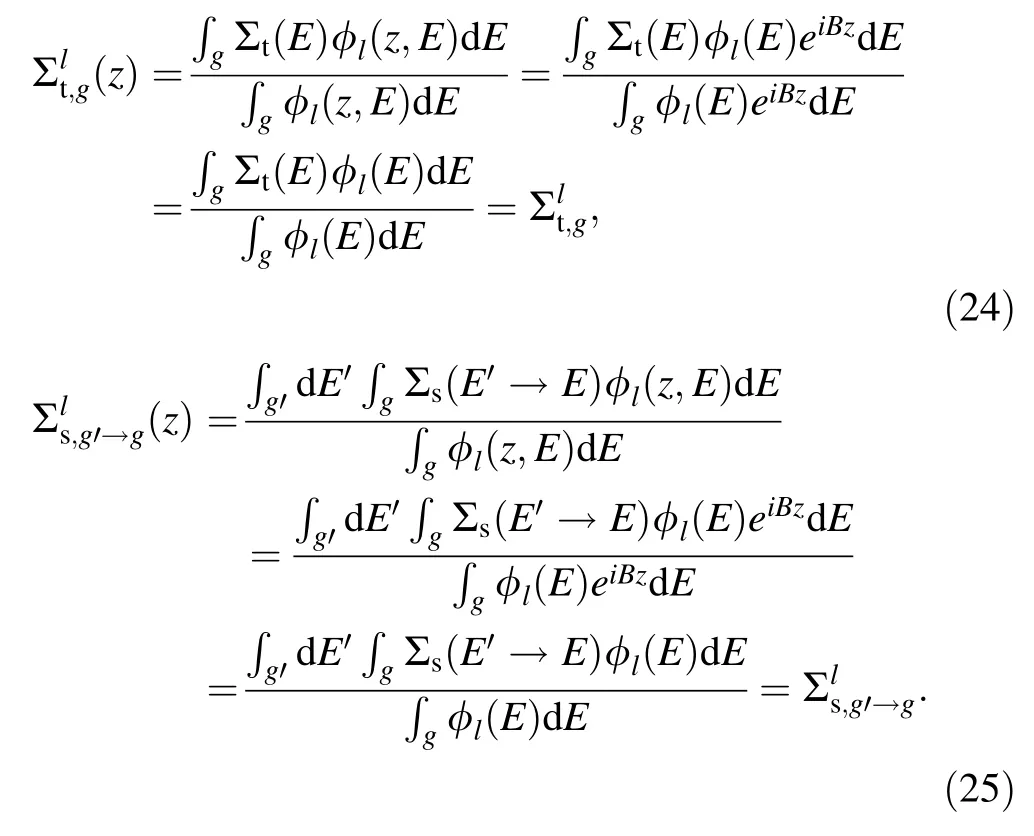
This shows that applying the flux shape with bucklingBeliminates the geometrical valuezin the derivation.Therefore,the previous one-dimensionalPNtransport equation becomes a homogenized system.The cross-section and scattering matrix data are homogenized in the entire region,such as fuel,cladding,and moderator regions.
Excluding the homogenized system,the accurate fission source is also treated using homogenization techniques.Therefore,the transport equation in Eq.(11)is replaced by the following:

The solution of flux moment then leads to the following:

Whennis an even number andn-1 andn+1 are odd numbers.

Inserting Eqs.(30) and (31) into Eq.(27) leads to the following:
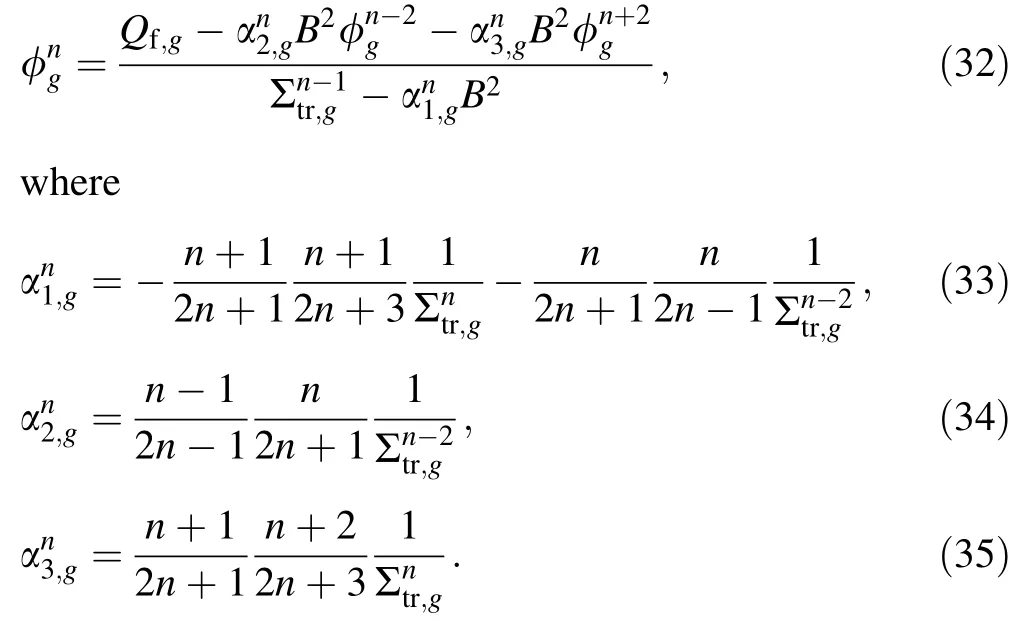
If the order ofnis the maximum value,becomes 0.For the oddn,Eq.(27) becomes the following:
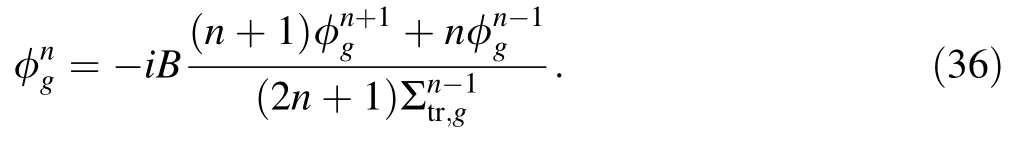
Therefore,the flux moment and transport XS were obtained using the improved inflow transport approximation.Compared with the form of the previous inflow transport equation,the improved inflow transport equation was based on the homogenization XS and accurate fission source,which is consistent with the homogenization techniques.
2.3 Implementation of improved inflow transport approximation
In Choi’s parametric study,the inflow transport approximation is insensitive to the buckling and order of the Legendre polynomial.For the value of buckling,even with a ten-fold difference in buckling,the influence ofkeffective is less than 2 pcm error.Therefore,the typical buckling value(B2=0.0001) was used for the calculation.For the order of the Legendre polynomial,theP1transport equation is sufficient to calculate the convergedP0transport XS,which has the same impact as theP5transport equation [9].
In the improved inflow transport approximation,the typical buckling value andP1transport equation were used.The detailed iteration process is as follows.
(a)Obtain the homogenization data based on the outflow transport approximation in an actual problem.The DRAGON code produces the following homogenization data:

whereiis used for every region,mod is the moderator region,xis represented as the reaction(f:fission,t:total,s:scattering),andnis the order of the Legendre polynomial(the anisotropic scattering effect for non-light nuclides is ignored).
(b) Initial flux moments and transport XS.

(c) Update theP0andP2flux moments using Eq.(32),and the flux moments converge.

(d) Update theP1flux moments.

(e) Update theP0transport XS.

(f) Repeat steps (b)-(e) until the flux moments and transport XS converge.
In the above procedure,the flux moments and transport XS may be negative.The iterative equation is as follows:

wherekis the iterative number.
In this study,the investigation focused only on the dominant moderator material (H2O).Therefore,the transport XS for H2O was selected for the improved transport approximation.A detailed discrepancy analysis between these transport approximations is presented in the next section.
3 Discrepancy analysis
The typical LWR benchmark was selected in this study to determine the accuracy of these transport approximations.This is the same as the problem Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory (BAPL-1) in the WIMS-D Library Update Project (WLUP) [18].The geometry is shown in Fig.1,and the material composition is listed in Table 1.The temperature was set to 300 K for all regions,and the intergap was omitted.

Table 1 The material composition of BAPL-1
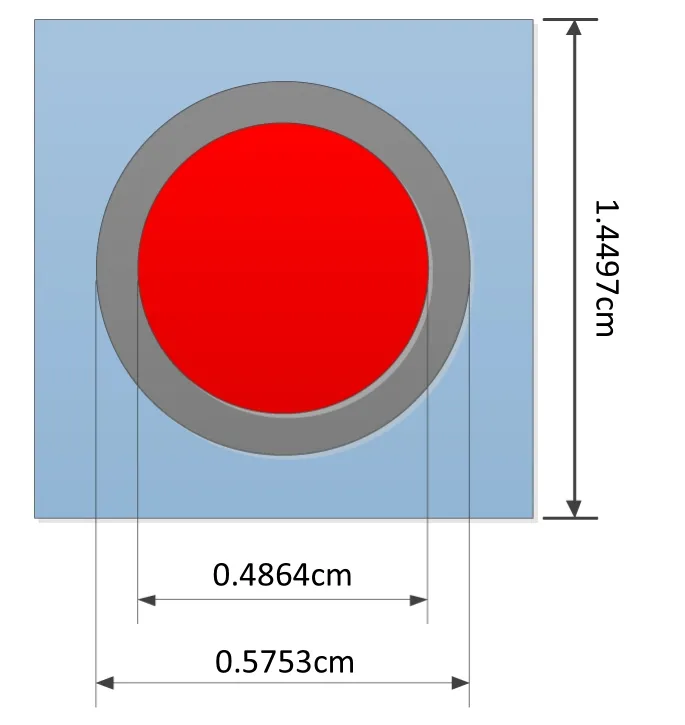
Fig.1 The geometry of BAPL-1
Figure 2a shows the transport XS for H2O in three transport approximations:outflow,previous inflow,and improved inflow transport approximation.The outflow transport approximation had a large discrepancy in the thermal and fast energy ranges to the inflow transport approximation.The transport XS for H2O showed a similar tendency between these two inflow transport approximation methods.
Furthermore,to determine the difference between these inflow transport approximations,a comparison of theP0flux moment is shown in Fig.2b and c.The treatment of the fission source and XS were the main differences between these inflow transport approximations.The reference result was obtained using the Monte Carlo code cosRMC,which was developed by Tsinghua University and the State Power Investment Corporation Research Institute (SPIC).Therefore,there are two types ofP0flux moment comparisons in this study.
(1) The comparison in the moderator region.
(a) Normalized fission source+moderator XS (previous method).
(b) Accurate fission source+moderator XS.
(Reference results:cosRMC’sP0flux moment in the moderator region).
(2) The comparison in the homogenized region.
(a) Normalized fission source+homogenized XS.
(b) Accurate fission source+homogenized XS (improved method).
(Reference results:cosRMCP0flux moment in the homogenized region).
In Fig.2b,the normalizedP0flux moment in the previous inflow transport approximation is significantly different from the cosRMC code.For the moderator system,theP0flux moment changed with different fission sources.When adopting the normalized fission source,theP0fluxmoment became more difficult than the accurate fission source.In Fig.2c,the normalizedP0flux moment in the improved inflow transport approximation agrees well with the cosRMC code.For the homogenized system,theP0flux moment also changed with different fission sources,which had the same tendency as the moderator system.Moreover,for the same fission source with different XS cases,the homogenized XS lead to a 1 MeV decrease in theP0flux moment and was closer to the LWR system[19],but theP0flux moment in the moderator XS was different.Therefore,the inflow transport approximation,with an accurate fission source and homogenized XS,can improve the accuracy of theP0flux moment compared with that using the previous method.

Fig.2 (Color online)Comparison of transport XS and normalized P0 flux moment in the BAPL-1 case. a Transport XS for H2O; b Comparison of normalized P0 flux moments in moderator region;c Comparison of normalized P0 flux moments in the homogenization region
4 Numerical results
4.1 General description of verification
The lattice code DRAGON5.0.5 was used for verification.It was developed bycole Polytechnique de Montre´al for lattice calculations,solving the neutron transport equation with a deterministic approach,and can read different types of multi-group libraries,such as the versions of WIMS-D and MATXS.In this study,the WIMS-D 70 library [20] based on ENDF/B-VII.0 [21] was selected to study the influence of the anisotropic scattering effect.Different transport approximations are implemented in the WIMS-D 70 library through the transport XS and scattering matrix.Resonance self-shielding is an equivalence theory(SHI+LJ+LEVEL2) with the generalized Stamm’ler method [22],Livolant and Jeanpierre normalization factor,and Riemann integration [23].The neutron transport calculation method was the interface current method(SYBILT).cosRMC was used as the reference code.The results of thek-infinity,k-effective,andP0flux moments are compared for various verification problems.
4.2 Typical LWR fuel cell and fuel assembly cases
A typical LWR fuel cell and fuel assembly were used to verify the application of different transport approximations.The factors of the fuel cell,fuel assembly,boron concentration,fuel enrichment,control rod material,and temperature in the fuel assembly with a control rod were selected as verification cases.
The single fuel cell and 17×17 fuel assembly benchmark were extracted from problem-1A and 2A in VERA[24],which contained 3.1 wt% UO2fuel,0.743 g/cc moderators with a 1300 ppm boron concentration,and Zr-4 for cladding.The temperature was 300 K for all regions.The geometric shapes for 1A and 2A are shown in Fig.3,and a detailed description of each case is given in Table 2.

Fig.3 (Color online) Geometry shape of 1A(left) and 2A(right)
Table 3 shows thekinfresults for each case with different transport approximations.Compared with thekinfin cosRMC,thekinferror in DRAGON for inflow transport approximations was less than 100 pcm.Contrarily,the error ofkinfin DRAGON for outflow transport approximation was less than 100 pcm in the fuel cell and fuel assembly,but could cause approximately 150 to 250 pcm in fuel assembly with the control rod.This discrepancy is consistent with that of previous research [9].

Table 2 Detailed description of each case
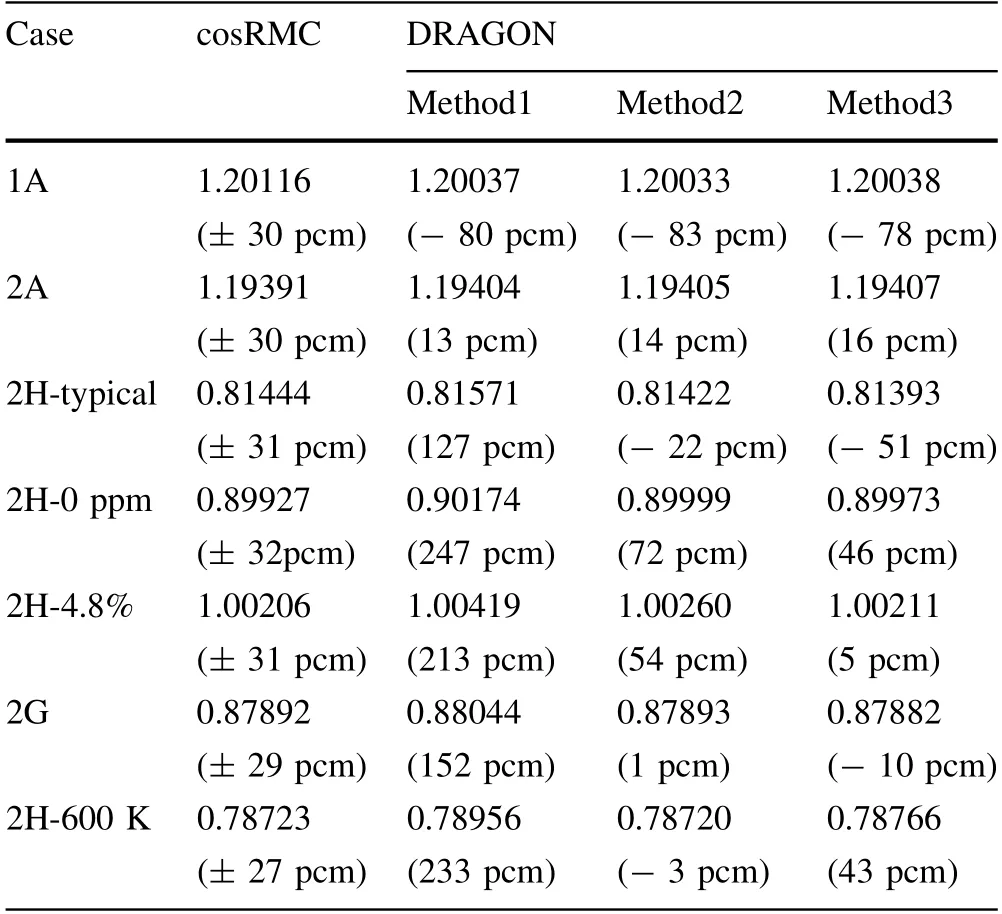
Table 3 Results of kinf in different cases

Table 4 Results of kinf in improved inflow transport approximation
Compared with thekinfin the previous inflow transport approximation,the results of the improved transport approximation were less than 10 pcm in cases 1A and 2A.Moreover,the results of the improved transport approximation were underestimated by 11 to 49 pcm for 2H-typical,2H-0 ppm,2H-4.8%,and 2G,and was also overestimated by 46 pcm for 2H-600 K.This tendency indicates that the transport approximations have less influence on the fuel cell and fuel assembly,but they have some effect on the fuel assembly with control rod cases.For the 300 K cases,the application of homogenization techniques in the improved transport approximation is based on the homogenous XS and accurate fission source,considering the influence of the resonance self-shielding effect in fuel materials.Compared with the previous inflow transport approximation,the improved transport approximation can absorb neutrons in different cases,which finally decreases thekinfresults.During the 600 K case,the impact of the resonance self-shielding effect was weakened in the improved inflow transport approximation with an increase in temperature [25],leading to an increase inkinfcompared to that in the previous transport approximation.
As a result,the different inflow transport approximations reached a higher accuracy than the outflow transport approximation in reactivity calculations,and the error ofkinfwas less than 50 pcm for different inflow transport approximations.
Figures 4 and 5 show the comparison of the normalizedP0flux moment with different inflow transportapproximations for these cases.Specifically,compared with the results of cosRMC,theP0flux moment in the improved inflow transport approximation had a better agreement than the previous method.Furthermore,theP0flux moment of the previous inflow transport approximation was slightly overestimated by approximately 1 MeV and underestimated in the thermal energy range.Particularly,the previous inflow transport approximation made theP0flux moment more difficult than the improved method.
In addition to the above investigation,the results of the improved inflow transport approximation in different LWR cases were in good agreement with the cosRMC,which is more versatile than the previous method.It can achieve higher accuracy for the cases of the fuel cell,fuel assembly,different boron concentrations,fuel enrichment,control rod material,and temperature in fuel assembly with the control rod.Therefore,the improved inflow transport approximation is accurate,universal,and suitable for LWR analysis.
4.3 Analysis of influence factors
In a previous investigation,the inflow transport approximation was problem-dependent.However,transport approximations are problem-independent data in most nuclear data libraries.Hence,we need to study the influence of the transport approximation and produce a nuclear data library with a general transport approximation.
Figure 6 shows the macroscopic transport XS and relative error of 2A for H2O in the different inflow transport approximations.The macroscopic transport XS for H2O was similar in most LWR cases,but the biggest difference existed in the thermal energy group in the 600 K case.The relative error of transport XS in the 600 K case was approximately 30 to 40% in the 2A case in the different inflow transport methods,but was less than 20% in other cases.Therefore,the most significant factor influencing inflow transport approximations is temperature through the comparison of transport XS.
Moreover,for the previous inflow transport approximation,the transport XS was based on the moderator region,and its relative error to 2A was less than 1% with the same moderator XS.Therefore,the previous inflow transport approximation was only related to the moderator region.For the improved inflow transport approximation,the transport XS was based on the homogeneous system,and its relative error to 2A was over 5%in 0.28 to 27.7 eV.Specifically,in a homogeneous system,the resonance selfshielding effect for fuel and absorber nuclides was considered in the derivation of transport XS.Then,the neutron spectrum was changed according to the different nuclide density ratios in the fuel and absorber nuclides.Thus,the transport XS in the improved inflow transport approximation was different from the previous inflow method,which is consistent with the actual LWR model.
The transport XS had a strong correlation with temperature and had less difference in the different LWR operation factors,such as fuel assembly,boron concentration,fuel enrichment,and control rod materials in the fuel assembly with the control rod.There are two different WIMS-D 70-group libraries,based on the improved inflow transport approximation,to test the influencing factors of transport approximations.The first is a problem-dependent library.The transport XS and scattering matrix data for1H and16O are problem-dependent,which are developed by the improved inflow method in actual cases.The second is a problem-independent library.The transport XS and scattering matrix data for H-1 and O-16 are problem independent,developed by the improved inflow method,from the typical 2H case (B4C,300 K,1300 ppm,and 3.1 wt%).

Fig.4 (Color online)Comparison of normalized P0 flux moment with the previous method. a 1A fuel cell; b 2A fuel assembly; c 2H-typical fuel assembly with B4C; d 2H-0 ppm fuel assembly with B4C at 0 ppm; e 2H-4.8% fuel assembly with B4C in 4.8%fuel enrichment; f 2G fuel assembly with AIC; g 2H-600 K fuel assembly with B4C in 600 K
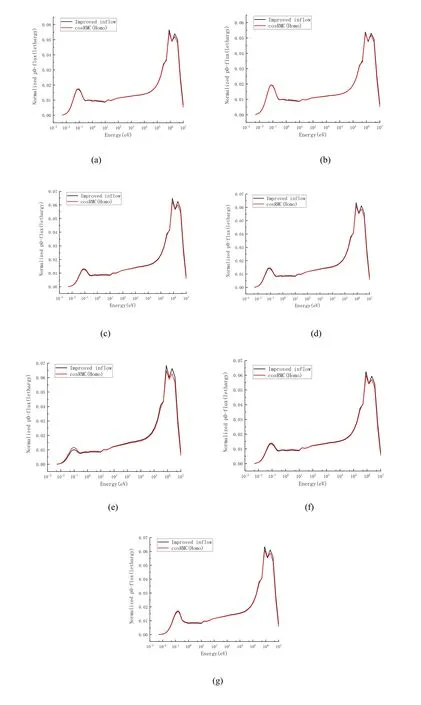
Fig.5 (Color online)Comparison of normalized P0 flux moment in the improved method. a 1A fuel cell; b 2A fuel assembly; c 2H-typical fuel assembly with B4C; d 2H-0 ppm fuel assembly with B4C at 0 ppm; e 2H-4.8% fuel assembly with B4C in 4.8%fuel enrichment; f 2G fuel assembly with AIC; g 2H-600 K fuel assembly with B4C in 600 K
Table 4 shows the results of thekinfin the improved transport approximation.Compared to thekinfresults between the problem-dependent and problem-independent libraries,thekinferror was less than 20 pcm for most cases.However,thekinferror was 37 pcm for the 2H case at 600 K.This indicates that the inflow transport approximation considering fuel and absorber nuclides has less influence onkinfcalculations,but the factor of temperature can influence thekinfresults.This is consistent with the difference in the transport XS in Fig.6.Although the largest difference of transport XS was in the resonance energy range,the magnitude of transport XS in the resonance energy range was comparatively smaller than the thermal energy range,and its influence on thekinferror was less than 20 pcm in each case.Therefore,the improved inflow transport approximation is only related to the temperature factor,and it can be easily implemented in a temperaturedependent nuclear data library.

Fig.6 (Color online)Macroscopic transport XS (left)and relative error (right) of 2A for H2O. a Results of previous inflow transport approximation;b Results of the improved inflow transport approximation
4.4 Application of inflow transport approximation to core cases
The Babcock &Wilcox (B&W) critical experiment benchmarks [26] selected to verify the application of different transport approximations in core cases.The B&W 1484 core 1 and core 3 cases are selected in this section,and the geometry shape is given in Fig.7.The B&W 1484 core 1 is the 48×48 case,and the B&W 1484 core 3 is the 68×68 case.

Fig.7 (Color online)Geometry shape of B&W 1484 Core 1(left) and Core 3 (right)
Table 5 shows the results of the B&W 1484 core 1 and core 3 cases (2D and 3D).The results indicated that the outflow transport approximation can introduce an error of over 1000 pcm in these cases,and both inflow transport methods were close to the reference values.For the B&W 1484 core 1 (2D and 3D) cases,the results ofkinfin the improved inflow transport approximation were overestimated by approximately 364 pcm and 291 pcm,respectively.For the B&W 1484 core 3 (2D and 3D) case,the results ofkinfin the improved inflow transport approximation were overestimated by approximately 115 pcm and 121 pcm,respectively.Thekinferror in the B&W 1484 core 1 and core 3 cases was inversely proportional to the cases of the LWR assembly.In addition,the different transport approximations were sensitive to the small core cases,which can cause over 1,000 pcm for thekinfcalculations in core 1 and approximately 600 pcm in core 3.
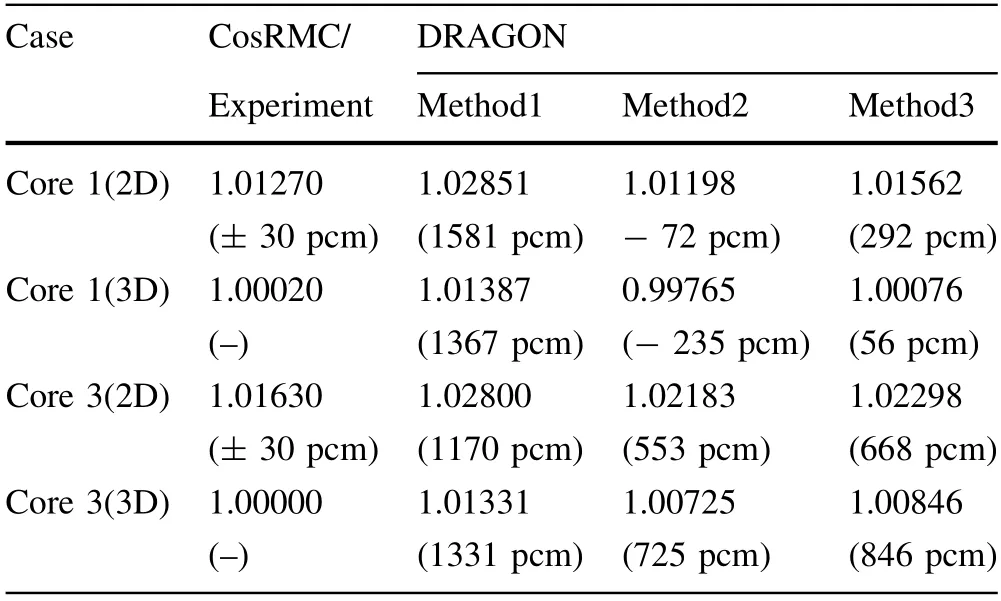
Table 5 Results of kinf/keff in B&W 1484 Core 1 and Core 3
Although the previous inflow method is close to the reference results,the improved inflow method is close to the actual system,which is consistent with the theoretical model.The reason for this tendency may come from thelimitation of the WIMS-D library,such as ignorance of scattering resonance integral,lumped fission spectrum,etc.
In summary,the outflow transport approximation can introduce an error of over 1000 pcm in the B&W 1484 core 1 and core 3 cases,but the inflow transport methods are relatively accurate in the core cases.
5 Conclusion
In this study,the improvement and application of inflow transport approximation in LWR analysis were performed by comparing the results of theP0flux moment,keff,andkinfwith the reference results.The improved inflow transport approximation was based on the homogenized crosssection and accurate fission source,which was different from the previous method.
For the LWR assembly cases,the results of three transport approximations (outflow,previous inflow,and improved inflow) were compared for the cases of the fuel cell,fuel assembly,boron concentration,fuel enrichment,control rod materials,and temperature in the fuel assembly with a control rod.Thekinferror in the inflow transport approximation was less than 100 pcm compared to that in the Monte Carlo code cosRMC,which was more accurate than the outflow transport approximation in the treatment of the anisotropic scattering effect.Compared to theP0flux moment,the results of the improved inflow transport approximation were closer to the cosRMC code in each case.The homogenized cross-section and accurate fission source were the main factors influencing theP0flux moment.In addition to the above investigation,the improved inflow transport approximation is only related to the temperature factor for typical LWR cases.Excluding the temperature case,thekinferror was less than 20 pcm between the problem-dependent and problem-independent transport approximations.For the B&W 1484 core cases,the outflow transport approximation introduced an error of over 1000 pcm.The inflow transport approximation significantly improved thekinfaccuracy,and the results were closer to the reference value.
In summary,the improved inflow transport approximation is more flexible and accurate in the treatment of the anisotropic scattering effect,and it can be easily implemented in the temperature-dependent nuclear data library for LWR analysis.
Author contributionsAll authors contributed to the study conception and design.Material preparation,data collection and analysis were performed by Xiang Xiao,Kan Wang,Tong-Rui Yang,and Yi-Xue Chen.The first draft of the manuscript was written by Xiang Xiao and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript.All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
杂志排行
Nuclear Science and Techniques的其它文章
- Calibrating the linearity between grayscale and element content for X-ray KES imaging of alloys
- High RF power tests of the first 1.3 GHz fundamental power coupler prototypes for the SHINE project
- Studies of the radiation environment on the Mars surface using the Geant4 toolkit
- Evaluation of neutron beam characteristics for D-BNCT01 facility
- Modular next generation fast-neutron detector for portal monitoring
- A novel 4D resolution imaging method for low and medium atomic number objects at the centimeter scale by coincidence detection technique of cosmic-ray muon and its secondary particles
